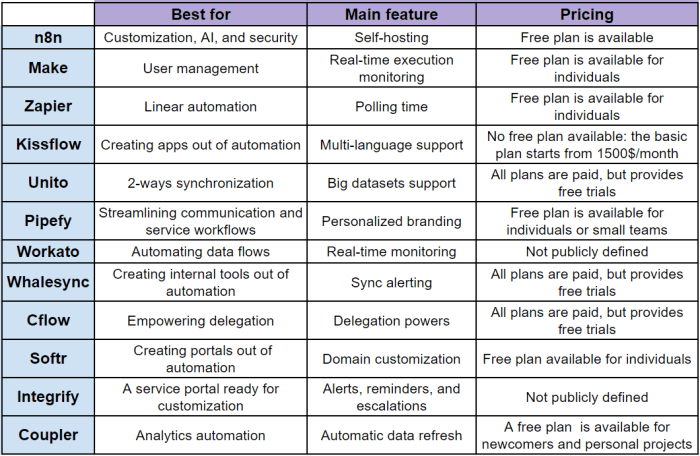
Workflow rules vs process builder vs flows – deciphering these automation tools is key for any business looking to streamline operations. This in-depth comparison will explore the nuances of each, highlighting their strengths, weaknesses, and ideal use cases. We’ll cover everything from basic triggers to complex integrations, offering a clear understanding of when to use each tool for optimal efficiency.
From simple data updates to intricate approval workflows, these tools empower businesses to automate tasks, improve productivity, and free up valuable time. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the knowledge to choose the right tool for your specific needs and optimize your automation strategy.
Introduction to Automation Tools
Salesforce automation tools are essential for streamlining business processes and boosting efficiency. Workflow rules, Process Builder, and Flows are powerful tools that automate various tasks, from simple data updates to complex business processes. Understanding their differences and appropriate use cases is crucial for maximizing their impact within an organization.These tools allow businesses to reduce manual effort, minimize errors, and improve overall productivity.
They are especially beneficial for repetitive tasks and those requiring significant data manipulation. By automating these tasks, employees can focus on higher-value activities, leading to improved customer service, faster turnaround times, and increased revenue.
Overview of Automation Tools
Workflow rules, Process Builder, and Flows are three distinct Salesforce automation tools. Workflow rules are best suited for simple, predefined actions based on specific criteria. Process Builder excels in orchestrating more complex business processes with branching logic and multiple steps. Flows offer the most comprehensive automation capabilities, handling sophisticated logic, complex data transformations, and external integrations.
Fundamental Differences
Workflow rules are triggered by changes in specific fields within records. They are limited in their ability to handle complex logic and branching. Process Builder allows for more intricate steps and conditions, enabling branching logic and multiple actions based on defined criteria. Flows, on the other hand, offer the most robust capabilities, allowing for sophisticated branching, complex data transformations, and integrations with external systems.Workflow rules are typically used for simple actions such as updating fields, sending emails, or creating tasks.
Process Builder is suitable for automating more complex processes involving multiple steps and decisions. Flows are used for sophisticated automation needs, such as integrating with other applications, performing calculations, and creating custom data transformations.
Use Cases for Each Tool
Workflow rules are well-suited for straightforward automation tasks. A common example is automatically updating a “Status” field to “Closed” when a “Close Date” is entered. Process Builder is ideal for more intricate processes like approval workflows, where multiple steps and decisions are involved. For instance, a process to automatically route an order to the appropriate department based on customer location and order type.
Flows are used for complex automation, such as integrating with third-party applications, calculating values based on multiple fields, or performing data transformations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Workflow Rules | Process Builder | Flows |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Low | Medium | High |
| Use Cases | Simple updates, email notifications, basic validations | Approval workflows, order routing, task assignments | Complex integrations, data transformations, sophisticated logic |
| Learning Curve | Easy | Moderate | Steep |
Workflow Rules: Workflow Rules Vs Process Builder Vs Flows
Workflow rules are a fundamental automation tool in Salesforce, enabling automatic actions based on specific criteria within your data. They are particularly useful for simple to moderately complex data updates and processes. They excel at ensuring data integrity and consistency, automatically triggering actions when certain conditions are met. However, their limitations need to be considered, as they might not be the optimal solution for highly intricate or multi-step processes.Workflow rules are essentially sets of rules that, when triggered by a specific event, execute predefined actions.
This automation streamlines repetitive tasks and helps maintain data accuracy. They are powerful tools but should be implemented strategically to avoid creating overly complex or difficult-to-maintain automation solutions.
Workflow Rule Triggers
Workflow rules are triggered by specific events, such as record creation, record update, or a change in a specific field. Understanding these triggers is crucial for determining when a rule should be activated. This allows users to automate actions based on the exact moment data changes.
- Record creation:
- Record update:
- Field updates:
- Specific criteria on the record:
Workflow rules offer a powerful way to automatically update records or trigger actions based on various triggers, ensuring that data is always accurate and consistent.
Workflow Rule Actions
Workflow rules can perform various actions once a trigger is met. These actions can range from updating fields to sending emails or creating new records.
- Updating fields:
- Creating new records:
- Sending emails:
- Running Apex code:
Understanding the available actions within workflow rules is critical to selecting the appropriate automation solution. Properly configuring actions within workflow rules can drastically improve efficiency and reduce manual intervention.
Workflow Rule Limitations
While workflow rules are powerful, they do have limitations. They are best suited for straightforward tasks, not complex ones.
- Limited complexity:
- Limited branching logic:
- Limited ability to handle complex business logic:
Workflow rules are excellent for simple to moderate automation, but more advanced processes might require more robust tools like Process Builder or Flows.
Workflow Rule Advantages
Workflow rules offer significant advantages, particularly for simple to moderately complex tasks. Their ease of use and immediate impact make them a valuable tool for automation.
- Ease of use and implementation:
- Data integrity and consistency:
- Automated updates and tasks:
- Reduced manual effort:
Role in Data Management
Workflow rules play a crucial role in maintaining data accuracy and consistency by automatically updating records based on pre-defined rules. This ensures that the data within your Salesforce org is reliable and up-to-date. By applying workflow rules to data management processes, you can enhance the overall quality of your data.
Workflow Rule Scenarios
Workflow rules are ideal for automating various tasks in Salesforce, including:
- Account creation: Automating the creation of a contact when a new account is created.
- Opportunity updates: Updating opportunity stages automatically based on specific criteria.
- Lead qualification: Automatically classifying leads based on criteria, such as lead source and industry.
- Contract renewals: Sending automated reminders to clients about upcoming contract renewals.
These examples illustrate how workflow rules can be tailored to specific business processes and used to create efficient, automated workflows.
Figuring out workflow rules, process builder, and flows can be tricky, right? Choosing the right tool depends on your specific needs. To really nail down your tech firm’s identity, consider these top 5 tips for developing your tech firm’s brand strategy, which will help you decide what tools are best for your business top 5 tips for developing your tech firms brand strategy.
Ultimately, understanding your target audience and goals will help you determine the best way to automate tasks within your Salesforce environment using the most appropriate tool, whether it’s workflow rules, process builder, or flows.
Creating a Workflow Rule – Step-by-Step
The following steps Artikel the process for creating a workflow rule in Salesforce.
- Identify the object and criteria:
- Define the workflow rule’s criteria:
- Specify the actions to be performed:
- Save and activate the workflow rule:
Following these steps will ensure your workflow rule is correctly configured and effectively automates the desired tasks.
Process Builder
Process Builder is a powerful tool within Salesforce that allows you to automate complex business processes. Unlike workflow rules, which are primarily focused on simple, single-step actions, Process Builder enables the creation of more intricate, multi-step workflows. It provides a visual drag-and-drop interface, making it easier for users to design and manage complex automation flows. This approach facilitates greater control and visibility into the process execution.Process Builder excels at automating a wide array of tasks, from simple data updates to multi-stage approval workflows.
It is particularly well-suited for processes that require branching logic, decision points, and multiple actions in response to specific conditions. By automating these tasks, organizations can reduce manual effort, improve accuracy, and increase efficiency in their daily operations.
Types of Actions and Decisions
Process Builder supports a variety of actions and decisions. Actions can include updating fields, sending emails, creating records, and even invoking Apex code. These actions can be chained together in a sequence, creating a series of steps within the process. Decisions allow for branching logic, enabling the process to take different paths based on specific criteria. For example, a process might update a record if a certain field is populated, or send an email if a deadline is missed.
Automation vs. Approval Processes
Automation processes in Process Builder are designed to execute a sequence of actions automatically, based on pre-defined criteria. Approval processes, on the other hand, incorporate a step for human intervention. In an approval process, the process waits for an approver to complete an action before proceeding to the next step. This distinction is crucial; automation handles tasks without human input, while approval processes involve a human review.
Approval processes are often used for sensitive decisions or those requiring a second set of eyes.
While workflow rules, process builder, and flows are all powerful tools for automating tasks in Salesforce, choosing the right one can be tricky. Knowing how to effectively manage 404 errors in WordPress is crucial for a smooth user experience. For example, this helpful guide shows you how to easily track and redirect those lost pages, which ultimately translates to a more optimized website.
Ultimately, understanding the nuances of each automation tool will help you decide which best fits your specific needs.
Flexibility for Complex Processes
Process Builder demonstrates significant flexibility in handling complex business processes. It allows for conditional logic, loops, and complex decision trees. This enables the automation of sophisticated workflows that require multiple steps, choices, and actions based on various conditions. For instance, a process might handle a customer’s request for a new product, involving steps like data validation, approval by multiple managers, and finally, order fulfillment.
This versatility makes Process Builder a powerful tool for organizations with intricate processes.
Best Practices for Effective Process Builder Flows
Designing effective Process Builder flows involves several best practices. First, clearly define the desired outcome and break the process into smaller, manageable steps. Second, utilize the visual interface to create a clear and intuitive flow. Third, meticulously test the process with various scenarios to ensure accuracy and reliability. Finally, maintain and update the process as business needs evolve.
These practices lead to a more efficient and effective automation process.
Comparison Table: Workflow Rules vs. Process Builder
| Feature | Workflow Rules | Process Builder |
|---|---|---|
| Conditions | Simple, primarily based on field values | Complex, supporting multiple criteria, including formulas and Apex |
| Actions | Limited to updating fields, sending emails, and creating/updating records | Broader range of actions, including sending emails, creating records, updating fields, invoking Apex code, and more. |
| Decision Logic | Basic, primarily if/then statements | Sophisticated, including loops, decision trees, and branching logic |
| Concurrency | Limited, one rule operates at a time | More robust, enabling concurrent execution of process instances. |
| Complexity | Simple automations | Complex business processes |
Flows
Flows in Salesforce are powerful automation tools that extend beyond the limitations of workflow rules and process builders. They offer a more flexible and robust approach to handling complex automations, especially when dealing with custom integrations and API calls. They provide a visual interface for designing complex automation logic, enabling greater control and customization.Flows are essentially a series of steps that automate actions within Salesforce.
These actions can range from simple data updates to intricate integrations with external systems. Their visual representation makes them highly intuitive for both beginners and experienced users.
Different Types of Flows
Flows in Salesforce come in various types, each designed for specific functionalities. Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the right tool for your automation needs. These types are tailored for different use cases, from simple data manipulation to intricate integrations.
- Auto-launched Flows: These flows automatically run based on specified events, such as record creation, update, or deletion. They are ideal for tasks that need to happen immediately after a particular event, ensuring data integrity and accuracy.
- Scheduled Flows: Scheduled flows are triggered at predefined intervals, such as daily, weekly, or monthly. They are excellent for tasks requiring periodic execution, like data cleansing or reporting.
- Record-Triggered Flows: These flows respond to specific events related to a record, such as a new lead or an opportunity closed. This allows for dynamic responses based on record-specific data.
- Screen Flows: Screen flows offer a more interactive user experience. They allow for user input, validation, and branching logic, making them suitable for complex data entry or decision-making processes.
- Apex Flows: These flows incorporate Apex code, giving developers greater control over the flow’s logic. This type allows for intricate custom integrations with external systems or complex business rules that require Apex code.
Benefits of Flows for Complex Automation
Flows excel in handling complex automations that workflow rules and process builders struggle with. Their ability to handle multiple steps, conditional logic, and intricate integrations makes them a superior choice for multifaceted processes. The visual nature of flows simplifies the understanding and management of complex automation sequences.
- Multiple Steps: Flows can encompass multiple steps, allowing for complex workflows with branching logic, conditional checks, and loops. This is a significant advantage over workflow rules, which are limited in their ability to handle intricate processes.
- Conditional Logic: Flows support various conditional logic options, allowing for automation based on specific criteria or conditions. This adaptability is key for managing diverse scenarios and tailoring actions to specific circumstances.
- Custom Integrations: Flows seamlessly integrate with external APIs and systems, facilitating custom integrations that are crucial for modern business needs. This makes flows an essential tool for modern automation demands.
Advantages of Flows for Custom Integrations and APIs
Flows provide a streamlined approach to custom integrations with external systems and APIs. They simplify the process of sending data, receiving data, and managing interactions with external applications. This integration capability is essential for organizations that need to connect their Salesforce data with other systems.
- Direct API Calls: Flows can directly interact with external APIs, enabling the retrieval or transmission of data between Salesforce and other systems. This is a crucial advantage over other automation tools.
- Custom Logic: The ability to incorporate custom logic, especially using Apex, empowers developers to tailor the integration to meet specific business requirements.
- Error Handling: Flows offer robust error handling mechanisms, preventing failures from impacting other steps in the automation process. This is vital for ensuring reliable integrations and data integrity.
Steps Involved in Building a Simple Flow
Building a simple flow typically involves defining the trigger, creating steps, and configuring the desired actions. This structured approach ensures that the flow functions as intended.
- Define the Trigger: Specify the event that will initiate the flow, such as a new record creation or an update to an existing record.
- Create Steps: Design the actions the flow will perform, such as data updates, record creations, or API calls.
- Configure Actions: Customize the actions to match the specific requirements, ensuring that data is correctly processed.
- Test and Deploy: Thoroughly test the flow to validate its functionality and deploy it to production once verified.
Use Cases Where Flows Excel
Flows excel in scenarios where workflow rules and process builders fall short. Their versatility and adaptability make them ideal for complex automations.
- Complex Data Transformations: Flows can handle complex transformations of data, enabling seamless integration with external systems and manipulation of data to meet specific needs.
- Custom Integrations with APIs: When integrating with external APIs, flows provide a robust and flexible approach, ensuring reliable data exchange and custom logic implementation.
- Decision-based Actions: Flows support intricate decision-making processes, making them suitable for complex business rules and branching logic, which workflow rules and process builders often struggle with.
Comparing and Contrasting
Choosing the right automation tool for your Salesforce needs can be tricky. Workflow Rules, Process Builder, and Flows each have unique strengths and weaknesses, making understanding their differences crucial for optimal efficiency. This section dives deep into their capabilities, limitations, and ideal use cases, empowering you to make informed decisions.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Tool
Workflow Rules are simple, declarative automation tools primarily focused on basic actions like updating fields and sending emails based on criteria. They are quick to set up and straightforward to manage, especially for simple rules. However, their functionality is limited, making them unsuitable for complex processes or advanced logic. Process Builder, a more powerful tool, provides visual workflow design, enabling complex branching logic, sequential actions, and multiple record interactions.
It offers a visual interface that facilitates easy understanding and modification, but it has limitations in handling large-scale data manipulation and sophisticated logic compared to Flows. Flows are the most versatile and powerful option, capable of handling complex logic, sophisticated data manipulation, and large-scale data operations. However, their setup can be more intricate than Process Builder or Workflow Rules.
Scenarios Where One Tool Might Be Superior
Workflow Rules excel in simple, trigger-based actions. For example, automatically updating a field when another field meets a specific criteria is a prime use case for Workflow Rules. Process Builder shines when you need more complex branching logic and multiple record interactions, such as routing cases based on specific conditions or updating related records in a multi-step process.
Flows are ideal for complex, multi-step processes involving large volumes of data, integrations with external systems, and intricate custom logic. For example, a flow might be necessary to integrate with a third-party application to automate data migration or perform sophisticated calculations.
Use Cases for Each Tool
- Workflow Rules: Updating a field on a contact record based on the value of another field, sending a notification email when a lead is converted, or automatically creating a task when a specific record type is created. These examples demonstrate the simple, direct actions Workflow Rules are suited for.
- Process Builder: Automating a case routing process with conditional branching based on case details, updating multiple related records in a sequential manner, or triggering actions based on custom objects. These more complex scenarios highlight Process Builder’s advantage.
- Flows: Migrating data from one object to another, performing complex calculations on data, integrating with external APIs, and handling large-scale data manipulation. These tasks require the advanced capabilities of Flows.
Practical Tips for Selecting the Right Tool
Consider the complexity of the automation task when choosing the appropriate tool. For simple, trigger-based actions, Workflow Rules are sufficient. Process Builder is a better choice for more complex, visual workflows. For large-scale data manipulation, sophisticated logic, or integrations, Flows are the preferred option.
Figuring out Workflow Rules, Process Builder, and Flows can be tricky, but understanding their differences is key. They all automate tasks in Salesforce, but their use cases vary. For example, if you’re looking to add more visual appeal to your Salesforce org, installing a custom sidebar plugin like the one from install custom sidebars plugin could significantly enhance your user experience.
Ultimately, the best choice between Workflow Rules, Process Builder, and Flows depends on the specific automation needs. This ultimately impacts how you manage your Salesforce data and processes.
Table Contrasting the Tools
| Tool | Workflow Rules | Process Builder | Flows |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Manipulation | Limited; basic updates | Moderate; complex updates within a process | Extensive; complex data manipulation, large-scale operations, custom logic |
| Triggers | Record-based triggers | Record-based triggers, but more control over triggers | Record-based triggers, custom triggers, and Apex triggers |
Advanced Considerations

Optimizing automated processes in Salesforce goes beyond simply setting up the tools. Understanding performance implications, troubleshooting strategies, and maintaining these processes are crucial for long-term success. This section dives into advanced considerations for workflow rules, process builder, and flows, addressing security, error handling, and monitoring best practices.
Performance Implications
Salesforce automation tools can impact system performance if not implemented effectively. Workflow rules, being relatively lightweight, typically have a lower impact on performance. However, large, complex rules or rules involving multiple stages can slow down record processing. Process Builder, with its ability to trigger actions based on various criteria, can also influence performance. The performance of flows, particularly those involving complex logic and external integrations, is dependent on the specific implementation and the volume of data being processed.
Careful consideration of the triggers, conditions, and actions within each automation tool is vital to ensure smooth and efficient operation. For example, a workflow rule that triggers on every record update in a large object could quickly overwhelm the system. Conversely, a well-structured flow with optimized data access could maintain system speed.
Troubleshooting Automation Tools
Troubleshooting issues with Salesforce automation tools requires a systematic approach. Detailed logging within the tools is essential for diagnosing problems. Reviewing the audit trails for workflow rules, process builder, and flows helps identify the specific point of failure. Understanding the error messages and their context is critical. For example, a “record not found” error in a flow might indicate a data mismatch in a lookup or a change in the data model.
Checking the data in the system and the setup of the automation tool is necessary to identify any inconsistencies.
Maintaining and Updating Automated Processes
Regular maintenance and updates are essential for ensuring the reliability and efficiency of automated processes. Keeping automation tools up to date with the latest Salesforce releases is crucial. Keeping documentation accurate and well-maintained is also key to troubleshooting and updating. Documentation should include the purpose of the automation, the triggers, conditions, and actions, as well as any known issues or limitations.
Version control for changes is essential, allowing for easy rollback if necessary. Consider creating a checklist for regular review and update of the automated processes.
Error Handling and Monitoring
Robust error handling is critical for preventing automated processes from causing data inconsistencies or impacting user experience. Implementing error handling within flows, particularly in external integrations, is essential. This involves catching exceptions and logging them appropriately, preventing data loss or system errors. Regular monitoring is essential to detect and address issues proactively. Utilizing Salesforce’s built-in monitoring tools can provide valuable insights into the performance and health of the automation tools.
Consider creating dashboards to track key metrics such as error rates, execution times, and successful completions.
Security Implications
Security considerations are paramount when using automation tools. Ensure that the data accessed and modified by the automation tools adheres to security best practices. Permissions should be carefully assigned to prevent unauthorized access and modification of data. Consider using appropriate security measures like data encryption when dealing with sensitive information. Regular security audits are crucial to identify and address any potential vulnerabilities.
This includes reviewing access controls, checking for any unauthorized changes in the automated processes, and assessing potential risks for sensitive data. For instance, ensuring that only authorized users can access and update the data processed by the automation tools is vital.
Best Practices and Examples
Automating Salesforce processes is crucial for efficiency and scalability. Understanding best practices for Workflow Rules, Process Builder, and Flows is key to successful implementation. Proper use of these tools can significantly reduce manual effort, improve data accuracy, and boost overall productivity.Implementing automation tools effectively requires a strategic approach, considering the specific needs and complexity of each process. By adhering to best practices and leveraging real-world examples, organizations can maximize the benefits of automation while minimizing potential pitfalls.
Workflow Rules Best Practices
Workflow rules are ideal for simple, declarative automation tasks. They’re generally best suited for triggers based on record creation, updates, or deletions. To ensure efficient workflow rules, keep them focused on a single task or a limited set of related tasks. Avoid overly complex logic within a single rule. Instead, break down complex operations into smaller, more manageable rules.
Furthermore, always test your rules thoroughly using various scenarios and data sets before deploying them. Consider implementing appropriate error handling and logging to identify and address issues promptly.
Process Builder Best Practices
Process Builder excels at handling more complex automation sequences involving multiple steps and conditional logic. It’s a robust choice for tasks requiring branching logic, custom validations, and multiple actions based on specific criteria. Keep processes focused on a specific business process. Avoid making processes overly complex. Use the visual interface to design the process flow, which helps in clear visualization and easier debugging.
This visual approach makes it easy to identify bottlenecks and modify the process flow.
Flows Best Practices
Flows are the most flexible and powerful tool for advanced automation. They’re suitable for complex scenarios that require extensive data manipulation, custom logic, and integrations with external systems. When using flows, prioritize modularity and reusable components. This will help maintain a clear structure and simplify future updates. Employ best coding practices for data handling and error management.
Detailed logging and error handling within your flows are essential for troubleshooting.
Real-World Examples, Workflow rules vs process builder vs flows
- Customer Onboarding: A Workflow Rule could automatically create a new case record when a new lead is converted into a contact. A Process Builder could send automated emails with onboarding materials and welcome messages, and a Flow could assign the contact to a specific sales representative based on their location.
- Order Fulfillment: A Workflow Rule could automatically update the order status when payment is received. A Process Builder could trigger sending an email to the customer with the tracking number once the order is shipped. A Flow could generate reports on order fulfillment metrics and automatically update inventory levels.
- Account Management: Workflow rules could automatically flag accounts that haven’t logged in for a certain period, prompting a follow-up. Process Builder could trigger a sequence of actions to renew contracts for accounts approaching renewal dates. Flows could analyze historical data to predict customer churn and trigger proactive outreach.
Successful Automation Projects
A significant increase in customer satisfaction was observed in a company that automated their customer support ticket resolution process using a combination of Workflow Rules, Process Builder, and Flows. By streamlining the process, they reduced response times and ensured consistent handling of customer requests, which directly improved the customer experience.
Importance of Documentation
Maintaining comprehensive documentation is critical for maintaining and updating automation solutions. Documenting the logic, triggers, and actions within each automation tool is essential for future troubleshooting and modifications. Clearly define the input and output of each process. This documentation helps new team members understand the automation quickly and efficiently.
Comprehensive Example: Complex Automation Process
Imagine a scenario where a company wants to automate the process of processing new loan applications.
| Step | Tool | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Workflow Rule | Automatically creates a new loan application record when a new lead is converted. |
| 2 | Process Builder | Validates the applicant’s information, checks creditworthiness (using an external API call), and routes the application to the appropriate loan officer based on the loan type. |
| 3 | Flow | Calculates the interest rate based on creditworthiness, generates a loan agreement document, and sends it to the applicant via email. It also updates the loan application status in the system. |
This example showcases how Workflow Rules, Process Builder, and Flows can be used in conjunction to handle a complex process effectively.
Final Conclusion
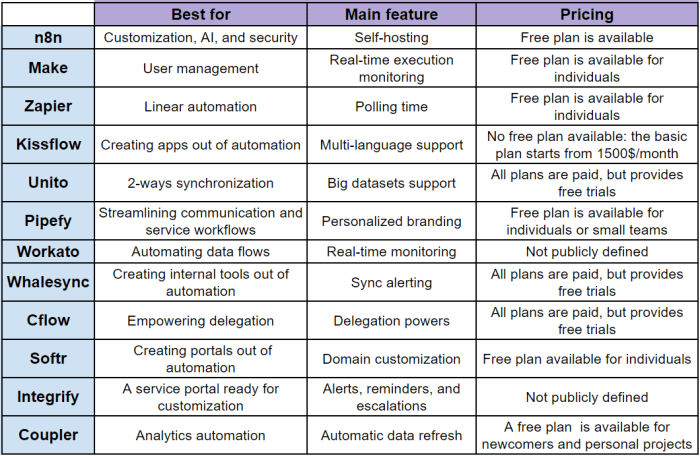
In conclusion, workflow rules, process builder, and flows each offer unique strengths in automating business processes. Workflow rules excel in simple data updates, process builder shines in complex scenarios, and flows dominate custom integrations. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each tool is crucial for choosing the best approach for specific tasks. This guide has hopefully provided a comprehensive overview to make your automation decisions more informed and effective.