What is a content hub? It’s more than just a collection of articles; it’s a strategic approach to creating valuable, interconnected content. Imagine a central hub where all your information converges, attracting visitors and providing a rich resource for your audience. This guide will explore the core principles of building a compelling content hub, from defining its purpose to measuring its success.
This comprehensive look at content hubs covers everything from defining their structure and types to developing a robust content strategy and promoting your hub effectively. We’ll delve into practical examples and essential steps to make your content hub a powerhouse for your business or brand.
Defining a Content Hub: What Is A Content Hub
A content hub is a central repository of interconnected content designed to address a specific audience’s needs and interests. It’s more than just a collection of articles; it’s a curated ecosystem where information is organized and presented in a way that fosters engagement and deep learning. Unlike individual blog posts or articles, a content hub aims to provide a comprehensive overview of a particular topic, often with multiple entry points and various content formats.Content hubs distinguish themselves from other content formats through their interconnected nature, their comprehensive approach to a topic, and their focus on a specific audience.
They provide a valuable resource by offering multiple perspectives, in-depth explorations, and various supplementary materials, all within a structured environment. This interconnectedness fosters a more immersive learning experience, unlike simply scattering content across different pages.
Key Characteristics of a Content Hub
Content hubs are characterized by several key attributes that set them apart from other content formats. These characteristics contribute to their effectiveness as a comprehensive resource.
- Interconnectedness: Content hubs are not a simple collection of articles; they are a network of related pieces. Each piece links to other related content, forming a web of information that allows users to explore the topic in various ways. For example, a hub on sustainable agriculture might have articles on specific farming techniques, connected to infographics explaining the environmental impact of different practices, and further linked to interviews with farmers applying these techniques.
- Comprehensive Coverage: A content hub aims to provide a complete picture of a subject. It goes beyond surface-level information to delve deeper, addressing various aspects, perspectives, and nuances. This comprehensive coverage is crucial for users seeking a thorough understanding.
- Targeted Audience: Content hubs are specifically designed to meet the needs of a particular audience. By understanding the audience’s interests and knowledge levels, content creators can tailor the information to resonate effectively.
- Variety of Content Formats: Content hubs utilize various content formats beyond text, including infographics, videos, podcasts, and downloadable resources. This diversity caters to different learning styles and preferences, ensuring that the content is accessible to a broader audience. A hub on personal finance, for example, might include articles on budgeting, videos demonstrating investment strategies, and downloadable templates for financial planning.
Purpose and Objectives of Creating a Content Hub
Creating a content hub has specific purposes and objectives that drive its design and development. These goals contribute to its overall effectiveness and impact.
- Establish Authority: A well-structured content hub demonstrates expertise and authority on a specific topic, building trust and credibility with the target audience. For example, a hub on data analysis showcasing advanced techniques and real-world case studies would establish authority in the field.
- Drive Engagement: Content hubs foster deeper engagement with the audience by providing a comprehensive and interconnected resource. This engagement can manifest in various ways, such as increased time spent on the site, higher readership numbers, and greater interaction with the content.
- Enhance User Experience: The interconnected structure of a content hub facilitates a seamless user experience. This seamless navigation and access to related information make learning and discovery more enjoyable.
- Generate Leads and Conversions: Content hubs can be strategically designed to generate leads and conversions. By offering valuable information and resources, a hub can attract potential customers and encourage them to take desired actions, such as making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter. For example, a content hub on digital marketing might offer free downloadable guides and webinars to capture leads and eventually promote paid services.
Structure of a Content Hub
A content hub’s structure is crucial for its effectiveness. It ensures that the information is easily accessible and organized for the user.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Central Topic | The core subject area that the entire hub focuses on. |
| Interconnected Articles | Articles that delve deeper into various aspects of the central topic, linked to each other to form a comprehensive understanding. |
| Supplementary Resources | Supporting materials like infographics, videos, podcasts, or downloadable guides to enrich the learning experience. |
| Search Functionality | Provides users with an easy way to find specific information within the hub. |
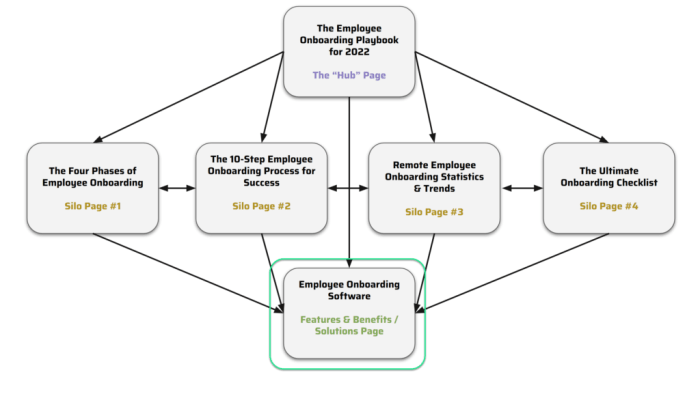
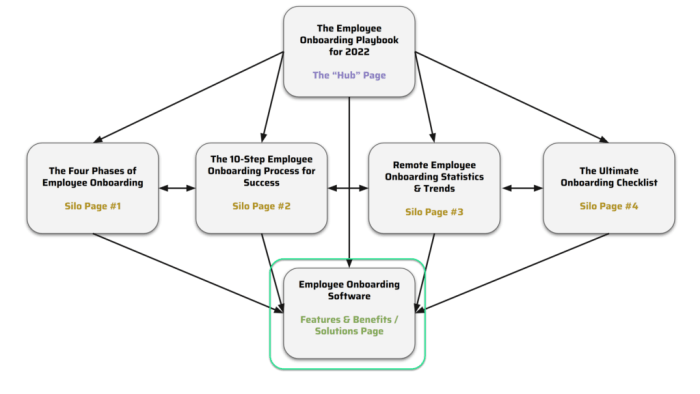
A simple diagram illustrating the structure could show a central topic with radiating lines representing interconnected articles and supplementary resources.
A content hub is essentially a central point for all your content, making it easier for audiences to find everything you offer. Understanding how the YouTube algorithm works, particularly organic reach, is crucial for a successful content hub. For example, optimizing your videos to maximize visibility on YouTube, as outlined in this resource on youtube algorithm organic reach , directly impacts how your content hub performs.
Ultimately, a strong content hub relies on strategic content planning and execution across various platforms.
Types of Content Hubs
Content hubs aren’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Their effectiveness hinges on tailoring the content strategy to the specific goals and target audience. Different types of hubs cater to various needs, from educating customers to driving sales. Understanding these variations is key to creating a successful hub.Content hubs come in various shapes and sizes, each with its own unique characteristics and purposes.
This variety allows businesses to select a content hub model that aligns perfectly with their strategic objectives and target market. This section delves into the diverse types of content hubs, highlighting their strengths and suitable applications.
Industry-Specific Content Hubs
These hubs focus on a particular industry or niche. They provide in-depth information and resources specifically for professionals and enthusiasts within that industry. This approach allows for a deeper engagement with a specialized audience, establishing authority and trust within the niche. By providing valuable content that is tailored to the needs and challenges of the specific industry, these hubs can effectively position themselves as a go-to resource.
Product-Focused Content Hubs
These hubs concentrate on a particular product or product line. They provide comprehensive information, reviews, and resources related to the product. This approach is excellent for showcasing the product’s capabilities and benefits, building brand awareness, and fostering customer engagement. They serve as a centralized location for everything related to a product or product line, making it easier for customers to find the information they need.
Blog-Based Content Hubs
These hubs primarily consist of blog posts, articles, and other written content. The strength of this approach lies in its ability to attract organic traffic and establish a community around the brand. Regularly updated content keeps the hub fresh and engaging, drawing in readers seeking relevant information. This model works well for businesses looking to build an online presence and establish themselves as thought leaders.
Resource-Based Content Hubs
These hubs offer a compilation of valuable resources, such as white papers, case studies, templates, checklists, and other downloadable materials. They focus on providing practical solutions and actionable advice. This type of hub can be particularly effective for businesses that want to provide value and build trust with their audience. By offering downloadable resources, resource-based hubs offer a tangible benefit for visitors, which can foster loyalty and encourage repeat visits.
Examples of Successful Content Hubs
Several successful content hubs demonstrate the effectiveness of various approaches. For example, HubSpot’s blog-based hub offers a wealth of marketing and sales resources, positioning them as a leading authority. Likewise, a well-known example in the software industry provides comprehensive documentation and tutorials related to their products.
| Type of Content Hub | Characteristics | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Industry-Specific | Focuses on a particular industry, providing in-depth information and resources. | Professionals and enthusiasts within the industry. |
| Product-Focused | Concentrates on a specific product or product line, offering comprehensive information and reviews. | Potential customers interested in the product. |
| Blog-Based | Primarily consists of blog posts, articles, and other written content. | Individuals seeking relevant information and industry insights. |
| Resource-Based | Offers a compilation of valuable resources, such as white papers and templates. | Professionals seeking practical solutions and actionable advice. |
Content Strategy for a Hub
A well-defined content strategy is the bedrock of a successful content hub. It acts as a roadmap, guiding the creation, distribution, and optimization of content to attract and engage the target audience, ultimately driving desired outcomes. Without a clear strategy, content efforts risk becoming scattered and ineffective, failing to capitalize on the potential of a content hub. A robust strategy ensures that every piece of content contributes meaningfully to the overall goals of the hub.A content strategy for a content hub is more than just a collection of blog posts or articles.
It’s a comprehensive plan encompassing target audience identification, content pillars, a content calendar, and a method for measuring success. This holistic approach ensures that the content hub consistently delivers valuable information and maintains relevance in the competitive landscape.
Defining the Target Audience
Understanding the target audience is paramount for a content hub. This involves more than just demographics; it necessitates a deep dive into their needs, pain points, interests, and online behavior. Identifying the target audience and their needs is a crucial first step in creating a successful content hub. This deep understanding allows for content creation that resonates with their specific interests and effectively addresses their needs.
- Identifying needs: Utilize surveys, focus groups, and market research to pinpoint the specific challenges and aspirations of your target audience. Analyzing existing data from your website, social media, and other channels can reveal patterns in user behavior and preferences. This analysis reveals what topics are most engaging for your audience and can be a great source of information about their specific needs and desires.
- Analyzing online behavior: Investigate how your target audience interacts with online content. Look at their search queries, social media activity, and engagement patterns on similar platforms. Understanding their online behavior helps tailor the content to their preferred consumption methods and ensure the hub’s content reaches the intended audience effectively.
- Creating detailed profiles: Develop detailed profiles of your ideal audience members, including their demographics, interests, pain points, and preferred content formats. This step is critical for tailoring content to resonate with the specific needs of different segments within your target audience. This will help you to understand your audience and what kind of content they’re looking for.
Establishing Content Pillars
Content pillars are the foundation upon which the entire content hub is built. They represent broad, overarching themes that guide the creation of all content. Identifying and establishing these pillars ensures that the hub remains focused and delivers consistent value.
- Identifying core topics: Carefully analyze your target audience’s needs and interests to determine the key topics that resonate most with them. Look for topics that are relevant, in-demand, and align with the overall mission of your content hub. These topics form the basis for developing compelling content that resonates with your audience and keeps them coming back for more.
- Developing supporting topics: From the core topics, branch out into supporting topics. These are related concepts that further expand on the core themes. Consider related s and variations of the core ideas to build a comprehensive and in-depth resource for your audience. Think about the specific questions your audience is likely to ask, and provide the answers in a comprehensive way.
- Defining content format: Determine the ideal format for your content. Will it be blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, or a combination? Each format serves a specific purpose and should be tailored to the needs of the target audience. Consider what format your audience is most likely to engage with and use that as a guide.
Creating a Content Calendar
A content calendar is an essential tool for organizing and scheduling content creation. It ensures consistent posting and prevents gaps in content delivery.
- Planning content schedule: Create a detailed schedule outlining the content to be published, the date of publication, and the responsible team member. This helps to maintain a consistent posting schedule, ensuring that the content hub stays active and relevant.
- Assigning tasks: Assign specific tasks to team members to ensure that content is created, edited, and published on schedule. This ensures accountability and efficiency in the production process.
- Measuring results: Track the performance of each piece of content to identify what resonates best with the audience. Analyzing these results helps optimize future content creation efforts and tailor them to the interests of your audience.
Content Creation for a Hub
A content hub thrives on a diverse and engaging collection of content. This requires careful planning and execution to ensure the pieces effectively support the overall hub’s purpose and attract the target audience. A well-structured approach to content creation is key to a successful content hub.Creating valuable content that resonates with your target audience is crucial for a content hub’s success.
A content hub is essentially a central online space for all your valuable information. It’s like a digital library, organized and optimized for visitors. To make sure your hub is accessible, understanding how to host a website how to host a website is key. Having a robust hosting solution ensures your content hub is always up and running, attracting and retaining your audience.
This involves understanding not just what to create, but how to create it in a way that maximizes its impact and encourages engagement.
Content Formats for a Hub
A diverse range of content formats is essential for a robust content hub. Using various formats caters to different learning styles and preferences, boosting audience engagement and driving traffic.
- Articles: In-depth articles provide comprehensive information on specific topics, establishing your hub as a trusted source of knowledge. These are valuable for detailed explanations and exploring complex subjects.
- Guides: Step-by-step guides offer practical advice and actionable steps, helping users solve problems and achieve their goals. They are particularly useful for tutorials and problem-solving.
- Infographics: Visual representations of data, statistics, or concepts make complex information easily digestible. Infographics are perfect for presenting data in a visually appealing and easily understandable manner.
- Videos: Videos offer a dynamic and engaging way to communicate information, presenting complex ideas through storytelling and visuals. They are especially effective for tutorials, interviews, and demonstrations.
- Case Studies: Real-world examples of how your content has helped others provide tangible evidence of its value. These are effective in showcasing the practical application of your insights.
- Podcasts: Audio-based content offers a flexible listening experience. They can be valuable for discussing trends, providing updates, or featuring interviews with experts.
Actionable Steps for High-Quality Content
Creating high-quality content requires a methodical approach. The following steps Artikel a process for crafting content that is both informative and engaging.
- Define Your Content Pillars: Identify the core themes and topics your content hub will focus on. This helps maintain a consistent message and attracts a specific audience.
- Research: Understand the search terms your target audience uses to find information related to your content pillars. This ensures your content is discoverable.
- Content Planning: Create a content calendar outlining the topics, formats, and publication schedule for your content. This ensures consistency and helps maintain momentum.
- Content Creation: Craft compelling and informative content that aligns with your pillars and targets your audience’s needs. This should incorporate research, analysis, and engaging writing.
- Content Optimization: Optimize your content for search engines and user experience. This involves incorporating relevant s, structuring the content logically, and ensuring it’s accessible.
- Promotion and Engagement: Promote your content across various channels and encourage engagement through comments, shares, and interactions. This will increase visibility and establish a community around your hub.
Examples of Content Pieces
Here are some examples of different content pieces that could be included in a content hub:
- A comprehensive article about the benefits of a healthy diet for weight loss.
- A step-by-step guide on how to create a successful social media marketing strategy.
- An infographic showcasing the latest trends in sustainable fashion.
- A video tutorial demonstrating how to use a new software application.
- A case study analyzing the success of a specific marketing campaign.
- A podcast interview with a leading expert in the field of artificial intelligence.
Content Format Comparison
| Content Format | Benefits | Use Cases in a Content Hub |
|---|---|---|
| Articles | In-depth information, establishes authority | Explaining complex topics, providing comprehensive guides |
| Guides | Actionable steps, problem-solving | Tutorials, how-to’s, troubleshooting |
| Infographics | Visual representation of data, easily digestible | Presenting statistics, comparing data, highlighting key trends |
| Videos | Dynamic engagement, visual storytelling | Tutorials, demonstrations, interviews, explaining complex processes |
| Case Studies | Tangible results, credibility | Showcasing success stories, highlighting practical applications |
| Podcasts | Flexible listening experience, interviews | Expert insights, discussing industry trends, updates |
Content Promotion and Distribution
Promoting a content hub effectively is crucial for maximizing its reach and impact. A well-structured promotion strategy ensures that the valuable content within the hub is discovered by the target audience, leading to increased engagement and brand visibility. This section delves into various methods for promoting content, optimizing for search engines and social media, and integrating promotion into broader marketing strategies.Effective promotion goes beyond simply creating great content; it involves actively spreading that content to reach the intended audience.
This involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing diverse channels and strategic optimizations. This section details the core components of a robust content promotion and distribution plan.
Methods for Promoting Content within a Content Hub
Promoting content within a content hub requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing various channels and strategies. Different methods cater to different audiences and objectives.
- Social Media Marketing: Leveraging social media platforms like Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, and Instagram is a potent strategy. This involves creating engaging posts, utilizing relevant hashtags, and running targeted ads to reach specific demographics. For example, a content hub focused on sustainable living could share articles on eco-friendly products on Instagram, alongside visually appealing images.
- Search Engine Optimization (): Optimizing content for search engines like Google is essential for organic visibility. This involves using relevant s in titles, meta descriptions, and body text. Properly structuring the content with headers, subheadings, and internal links improves user experience and rankings.
- Email Marketing: Building an email list allows for direct communication with potential and existing readers. Email newsletters featuring curated content from the hub can effectively engage subscribers and keep them informed.
- Paid Advertising: Targeted advertising campaigns on search engines, social media, and other platforms can quickly expand reach and exposure. A tailored ad campaign can direct specific demographics towards the content hub, increasing traffic and engagement.
- Influencer Marketing: Partnering with relevant influencers in the niche can significantly amplify the reach of the content hub. Influencers can promote the hub’s content to their engaged audiences.
Strategies for Optimizing Content for Search Engines and Social Media
Optimizing content for search engines and social media enhances visibility and engagement. A well-structured approach yields better results.
- Research: Identifying relevant s for the content hub is crucial for . Tools like Google Planner can help identify high-volume, low-competition s.
- Content Formatting: Employing headings, subheadings, bullet points, and visuals enhances readability and engagement on social media. Clear formatting improves the overall user experience and encourages social sharing.
- Social Media Post Optimization: Crafting compelling social media posts with eye-catching visuals and concise descriptions is crucial for engagement. Use relevant hashtags and call-to-actions (CTAs) to encourage interaction and clicks.
Integrating Content Promotion with Overall Marketing Strategies
A well-coordinated promotion strategy aligns seamlessly with the broader marketing goals. This integration ensures consistency and a unified message.
- Brand Consistency: Maintaining a consistent brand voice and tone across all promotion channels reinforces brand identity. Visual elements and language used in all promotions should reflect the hub’s brand image.
- Customer Journey Mapping: Understanding the customer journey allows for tailored content promotion at each stage. Different promotional strategies can be employed at various touchpoints, from initial awareness to conversion.
- Performance Tracking and Analysis: Regular monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) like website traffic, social media engagement, and lead generation provides insights into the effectiveness of promotional efforts. Adjusting strategies based on performance data ensures continuous improvement.
A Plan to Distribute Content from a Content Hub Across Various Platforms, What is a content hub
A strategic plan for distributing content across multiple platforms ensures maximum visibility and engagement.
- Content Calendar: Develop a content calendar outlining the schedule for publishing new content and promotional activities across all platforms. This ensures consistent posting and targeted campaigns.
- Platform-Specific Strategies: Tailor content formats and messaging to each platform. Visuals might be more important on Instagram, while longer-form articles are better suited for a blog.
- Cross-Platform Promotion: Promote content across various platforms to reach a wider audience. Sharing articles on social media, embedding them in email newsletters, and linking them from other relevant pages can boost visibility.
Measuring Success of a Content Hub
A successful content hub isn’t just about creating great content; it’s about understanding how that content performs and adapting strategies accordingly. Measuring the success of your hub allows you to refine your approach, optimize your content strategy, and ultimately achieve your business goals. Tracking key metrics provides insights into audience engagement and identifies areas needing improvement.Understanding audience interaction and adapting to changing preferences is crucial for long-term success.
A content hub is essentially a central repository of valuable information, designed to attract and retain a specific audience. Understanding how your content performs is key, and that often involves analyzing data, like data sampling in Google Analytics. A well-structured content hub, using insights from data sampling google analytics , can significantly boost your SEO efforts and user engagement, ultimately strengthening your online presence.
By regularly evaluating your hub’s performance, you can ensure that it continues to attract, engage, and convert your target audience. A well-defined framework for measuring success allows for a data-driven approach to content creation and promotion.
Key Metrics for Tracking Performance
Tracking key metrics is essential for understanding the effectiveness of a content hub. Various metrics can provide valuable insights into different aspects of performance. Website traffic, engagement, and lead generation are all crucial indicators of success. Tracking these metrics helps determine what content resonates most with your audience and what adjustments might be necessary.
- Website Traffic: Website traffic metrics, including unique visitors, page views, and bounce rate, offer insights into the overall reach and appeal of your content hub. Higher unique visitors and page views usually indicate greater interest in your content, while a lower bounce rate suggests users are finding the content valuable.
- Engagement Metrics: Engagement metrics, including time spent on site, social media shares, comments, and click-through rates, are critical indicators of audience interaction. A high time spent on site and substantial social media shares suggest the content is valuable and engaging. More comments and higher click-through rates point to an audience actively interacting with your content.
- Lead Generation Metrics: Lead generation metrics, including form submissions, email sign-ups, and demo requests, provide a clear picture of how your content is driving conversions. Increased form submissions, email sign-ups, and demo requests indicate the content is effectively capturing leads and moving them further down the sales funnel.
Analyzing Data to Understand Audience Interaction
Analyzing data provides crucial insights into audience interaction. Tools like Google Analytics and social media analytics platforms offer comprehensive data sets that help identify trends and patterns. Analyzing these insights can uncover valuable information about audience preferences, behavior, and interests.
- Segmentation: Divide your audience into segments based on demographics, interests, and behaviors. This allows you to tailor content to specific groups and understand what resonates with each. For example, if you notice a particular segment engaging more with blog posts related to specific product features, you can create more content focused on those areas.
- Identifying Patterns: Analyze data to identify recurring patterns in audience interaction. Do certain types of content perform better than others? Are there specific times of day or days of the week when engagement is higher? Understanding these patterns helps you optimize your content strategy and schedule.
- A/B Testing: Implement A/B testing to compare different versions of content to see which performs better. This can involve changing headlines, images, or calls to action. By analyzing the results of A/B tests, you can refine your content to maximize its impact.
Performance Checklist for a Content Hub
Regularly evaluating performance is vital to maintain a successful content hub. This checklist provides a framework for evaluating the success of your content hub.
- Track key metrics: Monitor website traffic, engagement metrics, and lead generation metrics on a regular basis.
- Analyze audience interaction: Use data analytics tools to segment your audience and identify patterns in their behavior.
- Conduct A/B testing: Experiment with different content variations to optimize engagement and conversions.
- Review and adapt: Regularly review your content strategy and make adjustments based on the data you collect.
- Establish clear goals and KPIs: Define specific goals for your content hub and establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress toward those goals.
Content Hub Examples
Content hubs are powerful tools for businesses seeking to establish thought leadership, drive organic traffic, and nurture leads. They serve as central repositories of valuable content, attracting and retaining audiences by providing comprehensive resources on a specific niche or topic. Understanding successful examples of content hubs across various industries offers valuable insights into effective strategies and approaches.
Real-World Examples
Content hubs are not limited to large corporations. Small businesses and even individual bloggers can effectively implement content hubs. For example, a gardening blog could create a hub focused on “container gardening,” providing articles, videos, and downloadable guides on the topic. This approach helps build an authoritative voice in the gardening community. A software company could create a content hub dedicated to “agile project management,” offering templates, case studies, and tutorials to attract users interested in that method.
Categorized List of Successful Content Hubs
- E-commerce Hubs: Companies like Shopify and WooCommerce have extensive content hubs focused on e-commerce best practices. These hubs provide tutorials, guides, and case studies on topics such as store setup, marketing strategies, and payment processing. Their success stems from the extensive nature of their topics, serving as a one-stop shop for aspiring e-commerce entrepreneurs.
- Marketing Hubs: HubSpot, a marketing software company, is a prime example. Their content hub covers various aspects of inbound marketing, from and social media to content marketing and sales strategies. Their extensive and consistent content creation has established them as a leading resource in the marketing industry.
- Financial Literacy Hubs: Sites like NerdWallet and Bankrate create content hubs focused on financial literacy. They offer detailed articles, calculators, and interactive tools to help consumers make informed financial decisions. This strategy positions them as trusted sources for financial information.
- Health and Wellness Hubs: Many health and wellness websites and blogs utilize content hubs to address specific health concerns. These hubs may focus on topics such as nutrition, fitness, mental health, or specific diseases. For instance, a nutrition blog could feature recipes, meal plans, and articles on healthy eating habits, building a valuable resource for readers interested in a healthy lifestyle.
Case Studies
A prominent case study involves a company specializing in sustainable living products. They created a content hub dedicated to “eco-friendly home solutions.” The hub included articles on sustainable building materials, energy-efficient appliances, and zero-waste living practices. This comprehensive resource attracted a large following of environmentally conscious consumers, driving significant sales and brand loyalty. Another example involves a SaaS company focused on project management software.
Their content hub covered various aspects of agile project management, from methodologies to tools and techniques. The detailed and practical information significantly improved user adoption and retention, showcasing the effectiveness of a well-structured content hub.
Challenges and Solutions
Creating and maintaining a successful content hub is not without challenges. One common issue is maintaining a consistent flow of high-quality content. To overcome this, companies can implement editorial calendars, Artikel specific content pillars, and delegate tasks to different writers or editors. Another hurdle is ensuring the content remains relevant and up-to-date. Strategies like regular content audits, research, and feedback mechanisms can help in this regard.
Content Hub Architecture
A well-structured content hub is crucial for maximizing its impact. A thoughtful architecture ensures easy navigation, promotes internal linking, and fosters a user-friendly experience. This organization allows users to discover related content, enhancing engagement and driving conversions. Effective architecture also allows for seamless content updates and future expansion.Content hubs can take on various shapes, each optimized for specific goals and target audiences.
By understanding the best structural approaches, you can create a robust content ecosystem that benefits both your audience and your business.
Different Content Hub Structures
Content organization within a hub can follow various patterns. A hierarchical structure, mirroring a website’s navigation, places broad topics at the top level, with subcategories and individual articles beneath. This is effective for comprehensive topics, allowing users to explore specific areas of interest within a broader context. A thematic structure groups content around particular themes or ideas.
This approach is useful for highlighting related information across different formats, promoting a cohesive message. A modular structure allows for independent units of content to be easily rearranged and reused. This flexibility can accommodate seasonal content or changing priorities. Choosing the appropriate structure depends on the content’s scope and the desired user experience.
Importance of Internal Linking
Internal linking is vital for a content hub. Linking related articles helps search engines understand the connections between pieces of content, improving search engine optimization (). It also enhances user experience, allowing visitors to discover relevant information more easily. This fosters deeper engagement with the hub and encourages exploration of additional resources. The strategic placement of internal links is critical for directing users to relevant content, preventing them from getting lost or leaving the hub prematurely.
Benefits of a Clear Navigation System
A well-defined navigation system is paramount for a content hub. It guides users through the hub’s various sections, making it easy to locate desired information. This user-friendly experience promotes engagement and encourages exploration. Clear categorization and intuitive labeling of sections and topics help users find what they need quickly. This results in higher user satisfaction and a lower bounce rate.
Furthermore, a clear navigation system allows for future expansion and modification of the hub without disrupting the user experience.
Flowchart of Content Through a Content Hub
[Insert flowchart image here]A flowchart illustrating the content flow would show the initial entry point into the hub. From there, users would be directed to various topics or categories, based on their interests. Internal links would guide them further to related articles, videos, or other resources within the hub. This process encourages exploration and deep engagement with the content, ultimately driving user interaction and value.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, a content hub isn’t just a website; it’s a dynamic ecosystem of information designed to attract, engage, and retain your audience. By understanding the key components of content strategy, creation, and promotion, you can build a powerful content hub that drives traffic, generates leads, and establishes your authority in your niche. This guide equips you with the knowledge and tools to build your own successful content hub.