Visual search and Google Lens are revolutionizing how we interact with information online. Imagine searching for a specific item just by taking a picture of it – that’s the power of visual search. Google Lens, a powerful tool, leverages image recognition to unlock a world of possibilities beyond traditional text-based searches. This exploration delves into the technology behind visual search, examining its evolution, Google Lens’s functionalities, and the impact it has on various sectors.
From finding similar products in retail to identifying plants in nature, visual search is rapidly becoming an indispensable tool. Understanding how image recognition works is key to grasping the potential of this technology, and Google Lens acts as a gateway to this exciting new realm of digital exploration.
Introduction to Visual Search
Visual search technology is rapidly evolving, enabling users to search for information by uploading images instead of relying solely on text queries. This innovative approach allows for a more intuitive and comprehensive search experience, particularly for complex or ambiguous concepts. It is transforming how we find and interact with information online.Visual search is no longer a futuristic concept but a tangible reality impacting various sectors.
From simple image identification to complex object recognition, this technology bridges the gap between human perception and digital information retrieval.
Evolution of Visual Search
Visual search technology has progressed significantly since its inception. Early iterations primarily focused on image recognition, aiming to identify objects within an image. The evolution has been marked by advancements in machine learning algorithms, particularly deep learning models. These models have enabled the system to understand complex relationships between objects, leading to more accurate and nuanced results. Key milestones include the development of sophisticated algorithms for object detection, image classification, and semantic understanding.
These advancements have made it possible to search for images based not just on visual similarity but also on contextual information.
Visual Search vs. Text-Based Search
Visual search fundamentally differs from traditional text-based search in several aspects. Text-based searches rely on s and structured data, whereas visual search leverages the visual characteristics of images. For example, if you want to find similar products to a specific item, a text search would require knowing the product’s name or specific attributes. A visual search, on the other hand, would use the image of the product to find similar items, even if the user does not know the exact name or description.
This ability to search based on visual characteristics allows users to discover products or information that might be difficult or impossible to locate using text-based methods.
Comparison of Visual and Text-Based Search Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Search | Intuitive, effective for complex queries, finds similar items, identifies objects in images, understands context, easier for users who are not familiar with the item’s name or description | Limited accuracy for highly complex images, requires high-quality images, may not be suitable for all types of searches, sometimes slower than text-based search, reliance on image quality | Product identification, finding similar images, identifying objects in a scene, locating places, finding clothing items, identifying plants and animals, searching for products based on image |
| Text-Based Search | Widely available, fast, highly structured, easy to implement, relatively inexpensive | Reliance on s, limited context understanding, misses subtle information in images, requires precise knowledge of the item’s name or characteristics, can be less intuitive for visual tasks | Finding specific information, retrieving documents, searching for data based on s, retrieving information from structured databases, accessing large volumes of text-based data |
Google Lens Functionality
Google Lens, a powerful visual search tool integrated into Google’s suite of applications, transcends the limitations of traditional text-based searches. It leverages advanced image recognition technology to understand and interpret the visual world, enabling users to interact with the surrounding environment in novel and insightful ways. It’s not just about finding similar images; it’s about extracting meaningful information from any image.Google Lens’s core functionality revolves around image recognition and understanding.
By analyzing the visual content of an image, it can identify objects, translate languages, extract information from documents, and perform numerous other tasks. This ability to “see” and “understand” empowers users with a whole new level of interaction with information.
Core Functionalities of Google Lens
Google Lens’s core capabilities are built upon a robust image recognition system. This system enables the application to identify objects, translate text, find similar images, and perform various other actions based on the visual input. The accuracy and efficiency of this system are critical for the diverse range of tasks Google Lens can perform. The core functions include recognizing objects, extracting information, and understanding context.
Tasks Google Lens Can Perform
Google Lens can perform a wide array of tasks, ranging from simple object identification to complex document analysis. It’s not just about finding information; it’s about using that information in practical ways. Examples include translating foreign languages in real-time, identifying plants and animals, and even extracting information from product packaging.
- Object Recognition: Google Lens can identify a vast array of objects, from everyday items to more complex ones. It can recognize plants, animals, landmarks, and even artworks. This identification goes beyond simple matching; it often provides additional information, such as the species of a flower or the artist of a painting.
- Text Recognition and Translation: One of the most practical applications of Google Lens is its ability to recognize and translate text in various languages. This capability is particularly useful for travelers, students, and anyone encountering foreign language materials. The translation process is often seamless, providing instant interpretations.
- Information Extraction: Google Lens can extract information from various sources, including images of documents, receipts, and business cards. This function can save time and effort by automatically extracting key details from the image, such as contact information, addresses, or dates.
- Shopping and Product Information: Users can identify products in images, find similar products on the internet, and access product details. This functionality connects users with online retailers and product information, making shopping more efficient.
Image Recognition in Google Lens
Google Lens utilizes a sophisticated image recognition system to interpret and understand the visual content of images. This system involves complex algorithms and a vast database of images and associated data. The accuracy of this recognition is constantly improving, and it underpins the numerous tasks Google Lens can perform. The process involves analyzing the image, identifying patterns and features, and comparing them to the database to reach a conclusion.
Applications of Google Lens
The diverse applications of Google Lens make it a valuable tool in various aspects of daily life. This table Artikels some of the key use cases, showcasing the versatility of the technology.
| Task | Input Type | Output | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identify a plant | Image of a plant | Name of the plant, species, and related information | Gardening, botany research |
| Translate a sign | Image of a foreign language sign | Translation of the text in the user’s preferred language | Travel, language learning |
| Find similar products | Image of a product | List of similar products available online | Shopping, product research |
| Extract information from a document | Image of a document | Extracted text and data from the document | Research, business tasks |
Image Recognition Techniques
Visual search engines, like Google Lens, rely heavily on sophisticated image recognition techniques to understand and categorize the content within images. These techniques enable the engine to identify objects, scenes, and even text within an image, allowing users to perform searches based on visual cues rather than s. This process involves a complex interplay of algorithms and models that transform raw pixel data into meaningful information.
Fundamental Techniques
Image recognition relies on a series of steps to process and interpret images. These steps involve transforming the image into a format suitable for analysis, extracting features that represent the image’s content, and using machine learning algorithms to classify and categorize these features. A crucial component is the extraction of relevant features that differentiate one object from another, such as edges, corners, textures, and shapes.
Image Recognition Models
Various models are employed in image recognition, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. These models are trained on massive datasets of images, learning to identify patterns and relationships between visual features and corresponding object classes. The models then use this learned knowledge to classify new, unseen images. The complexity of the model directly impacts its accuracy and efficiency.
Different model types are designed for different tasks and image types.
Different Types of Image Recognition Models
Different models cater to various image recognition tasks. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are a prominent example, excelling in image classification tasks. These networks employ a layered structure that progressively extracts hierarchical features from the input image, enabling the network to identify increasingly complex patterns and objects. Another important class of models is based on deep learning techniques, which excel in complex scenarios like object detection and image segmentation.
Comparative Analysis of Image Recognition Models
| Model | Strengths | Weaknesses | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) | Excellent at image classification, relatively efficient, and good generalization capabilities. | Can be computationally intensive for very large images, may struggle with complex scenes or subtle variations of objects. | Identifying objects in images, image categorization, and image tagging. |
| Region-based Convolutional Neural Networks (R-CNNs) | Good at object detection, precisely localizing objects within images. | Can be slow and computationally demanding for real-time applications. | Object detection in images, identifying and locating specific objects within scenes. |
| You Only Look Once (YOLO) | Real-time object detection, fast processing speed. | May have lower accuracy compared to R-CNNs for some complex object detection tasks. | Object detection in real-time applications, such as self-driving cars and surveillance systems. |
| Deep Learning Models (e.g., ResNet, Inception) | State-of-the-art performance on various image recognition tasks, particularly in image classification and object detection. | Can be very complex to train and require significant computational resources. | Advanced image analysis tasks like image segmentation, scene understanding, and medical image analysis. |
Applications and Use Cases
Visual search technology is rapidly transforming various industries and aspects of daily life. From finding the perfect product online to identifying plants in your garden, visual search is proving to be a powerful tool for quick and efficient information retrieval. This versatility extends far beyond simple image recognition, enabling a more intuitive and user-friendly interaction with the digital world.
Visual search, powered by Google Lens, is changing how we interact with the digital world. Understanding how these systems function is key to leveraging their potential. To track user interactions with these visual search features effectively, you need to be familiar with events in Google Tag Manager, such as image clicks or object recognition events. This deeper understanding of events in google tag manager ultimately helps refine visual search strategies and improve user experience, allowing for more targeted marketing and better insights into how people use Google Lens.
The applications are vast and continue to evolve, promising significant advancements in fields like retail, education, and healthcare.
Visual Search in Retail
Visual search is revolutionizing the retail landscape, offering customers unprecedented ways to discover and purchase products. Users can simply take a picture of an item they see in a store or online and use visual search to find similar products, alternative styles, or detailed information about the item. This streamlines the shopping experience, allowing for faster and more targeted product searches.
For instance, a shopper could snap a picture of a pair of shoes they like and instantly see similar styles available online or in other stores. This eliminates the need to manually search through extensive catalogs or websites, saving time and effort. Furthermore, retailers can use visual search to enhance their inventory management, optimize product displays, and provide more accurate product information to their customers.
Visual Search in Education
Visual search has the potential to significantly enhance the educational experience by providing a more engaging and interactive learning environment. Students can use visual search to identify objects, plants, or historical artifacts, quickly accessing detailed information and supporting materials. For example, a student studying botany could take a picture of a plant and instantly access information about its species, characteristics, and habitat.
This capability extends beyond simple identification, enabling a deeper understanding of the subject matter through visual exploration and readily available information. Teachers can also leverage visual search to create more dynamic lessons, incorporate real-world examples, and present information in a more engaging manner.
Visual search, like Google Lens, is becoming increasingly powerful. It’s not just about finding images; it’s about understanding the context and the potential for deeper insights. This directly ties into how analytics is transforming customer loyalty, allowing businesses to better understand consumer preferences and tailor their offerings accordingly. Analytics is transforming customer loyalty by providing valuable data on everything from product popularity to browsing habits.
Ultimately, visual search tools like Google Lens will become even more sophisticated, utilizing these insights to enhance the user experience and drive sales.
Visual Search in Healthcare
Visual search technology is demonstrating promise in the healthcare sector, potentially aiding in diagnosis, drug identification, and patient care. Visual search tools can be used to quickly identify medical conditions or injuries based on images, potentially providing faster and more accurate diagnoses. For example, a doctor could take a picture of a skin lesion and use visual search to receive potential diagnoses and necessary treatment options.
Moreover, visual search could help identify unknown or counterfeit medications, improving patient safety and reducing the risk of harmful interactions.
Visual Search in Daily Life
Visual search is increasingly integrated into our daily lives, streamlining tasks and providing quick access to information. We can use visual search to identify plants, animals, landmarks, and everyday objects. For example, identifying a rare bird species or a particular flower in a garden is made easier through visual search tools. This capability also extends to identifying products or services from a photograph, leading to more convenient shopping experiences.
Use Cases Across Sectors
| Sector | Use Case | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Finding similar products, checking product availability, verifying product authenticity | Improved shopping experience, faster product discovery, enhanced inventory management | Potential for counterfeiting detection, accurate product representation in images |
| Education | Identifying plants, animals, historical artifacts, locating relevant information | Enhanced learning experience, interactive lessons, easier access to information | Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the identified information, potential for misidentification |
| Healthcare | Identifying medical conditions, verifying medication authenticity, accessing treatment options | Potentially faster diagnoses, improved patient safety, convenient access to information | Ensuring the accuracy of medical diagnoses, potential for misinterpretation of images |
| General | Identifying plants, animals, landmarks, everyday objects, checking product details | Convenience, efficiency, easy access to information | Ensuring the accuracy of identified information, potential for misidentification, privacy concerns |
Visual Search and User Experience
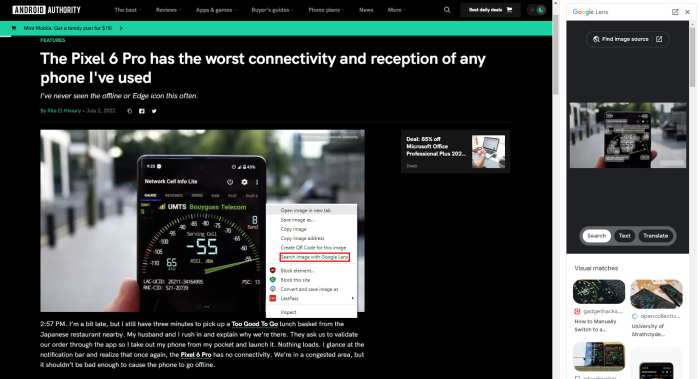
Visual search, while powerful, is only as effective as its user experience. A seamless and intuitive interface is crucial for widespread adoption and positive user engagement. A well-designed visual search system should anticipate user needs, minimize friction points, and make the entire process enjoyable and efficient. This section delves into the key aspects of user experience in visual search, focusing on interface design and interaction considerations.
User Interface and Interaction Design
The user interface (UI) of a visual search engine plays a critical role in shaping the user experience. A clean, uncluttered design with clear visual cues is essential for guiding users through the process. The interaction design (ID) must be intuitive and responsive to user actions. Visual search interfaces should allow for easy image uploads, enabling users to quickly and effortlessly share the image they want to search.
The system should also provide clear feedback mechanisms, indicating the search progress and displaying results in a visually appealing and organized manner. Furthermore, the UI should adapt to different screen sizes and devices, ensuring a consistent experience across various platforms.
Design Considerations for a Seamless Visual Search Experience
Several design considerations contribute to a seamless visual search experience. Prioritizing a simple and intuitive interface is paramount. Users should be able to easily locate the upload area for images, the search button, and results display. Clear visual cues, like highlighting interactive elements or using subtle animations, can significantly improve user understanding and navigation. Additionally, incorporating visual feedback mechanisms, like loading indicators or progress bars, enhances the user’s perception of responsiveness.
Finally, enabling users to refine their searches with filters, advanced options, and alternative search methods enhances the depth and precision of the results.
Key User Experience Factors for Visual Search
Effective visual search depends on several key user experience factors. These factors are interconnected and influence each other, creating a holistic experience for the user.
Visual search, like Google Lens, is revolutionizing how we interact with the digital world. It’s fascinating how these tools use images to find information online, but optimizing your online presence for visual search is a whole other ballgame. A crucial aspect of that optimization is understanding how SEO consultants, like the ones described in this article about what is an seo consultant , can help you reach the top of search results.
They can help you leverage the power of images to boost your online visibility. In short, visual search and Google Lens rely heavily on well-structured data and careful optimization for a strong online presence, which SEO consultants can expertly manage.
| Factor | Description | Importance | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intuitive Interface | The interface should be easy to understand and use, minimizing the learning curve for users. Clear labeling, consistent design elements, and intuitive navigation are essential. | Crucial for user adoption and satisfaction. | Clear upload buttons, well-organized search results, easy-to-use filters. |
| Fast Response Time | Users expect quick results. The system should respond rapidly to user actions, reducing wait times and improving perceived efficiency. | Impacts user satisfaction and engagement. A slow system can frustrate users. | Immediate image loading, rapid search processing, and fast display of results. |
| Comprehensive Results | The search results should accurately reflect the user’s query and offer diverse options. A wide range of relevant results, including different formats and sources, will enhance the user experience. | Ensures users find what they need and are satisfied with the search outcome. | Displaying results in various formats (images, videos, articles), providing options for further exploration. |
| Effective Feedback Mechanisms | Providing clear and informative feedback during the search process enhances the user experience. Progress indicators, error messages, and confirmation messages are important. | Reduces user uncertainty and improves understanding of the system’s actions. | Loading indicators, error messages for invalid image uploads, confirmation messages for successful searches. |
Challenges and Limitations: Visual Search And Google Lens
Visual search, while rapidly advancing, still faces significant hurdles. The inherent complexity of interpreting visual information, coupled with the vastness and diversity of the visual world, presents substantial technical challenges. Current systems often struggle with nuanced details, context, and the ability to generalize across variations in image styles, lighting conditions, and object orientations. This inherent complexity makes accurate and reliable visual search a continuous area of research and development.
Technical Challenges in Visual Search
Visual search technology faces several technical challenges. One key hurdle is the need for robust and accurate image understanding. This requires sophisticated algorithms capable of identifying and classifying objects, scenes, and actions within images, often amidst significant variations in lighting, pose, and background clutter. Another critical challenge involves dealing with the vast amount of data required to train these algorithms.
Training models to recognize and understand diverse visual concepts requires substantial labelled image datasets. Furthermore, the ability to handle complex scenes and multi-object interactions is a significant hurdle, requiring sophisticated models that can separate and interpret different elements in a visual context. Developing algorithms that can capture and leverage the context of an image—such as identifying the relationship between objects or the scene’s overall meaning—is also a key technical challenge.
Limitations of Current Visual Search Systems
Current visual search systems exhibit limitations in several areas. A frequent issue is the difficulty in accurately interpreting complex images, especially those containing multiple objects, intricate details, or ambiguous visual relationships. Furthermore, these systems often struggle with identifying subtle variations in objects, colors, or styles. This limitation can lead to missed or inaccurate results. The lack of context understanding, particularly in identifying the relationship between objects or the overall scene’s meaning, is another significant limitation.
Challenges in Interpreting Complex Images
Interpreting complex images remains a significant challenge for visual search. For example, recognizing a specific type of bird within a dense forest scene requires sophisticated image understanding. Similarly, accurately identifying a particular item within a cluttered room, or understanding the relationship between multiple objects in an image, presents significant challenges. The presence of occlusions, variations in lighting, and different viewpoints further complicate the task.
The need to understand context and relationships between objects, beyond simple object recognition, is a critical area for improvement.
Common Limitations of Visual Search Systems
| Limitation | Explanation | Impact | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inaccurate Recognition | Visual search systems sometimes misidentify objects or fail to recognize them altogether, particularly in complex scenes or when dealing with subtle variations. | Results may be irrelevant or incorrect, leading to wasted user time and frustration. | Improving training data quality and the sophistication of image understanding algorithms. |
| Limited Contextual Understanding | Current systems often struggle to grasp the context of an image, such as the relationship between objects or the overall meaning of the scene. | This limits the ability to find images based on the relationships between objects, leading to irrelevant or insufficient results. | Developing algorithms that can better understand and represent context in images. |
| Inability to Handle Complex Scenes | Visual search struggles with images containing multiple objects, intricate details, or ambiguous visual relationships. | Users may not find the desired images when the search query involves complex or multi-object scenarios. | Creating more robust and sophisticated models capable of interpreting complex images. |
| Sensitivity to Variations in Lighting and Viewpoint | Visual search systems can be sensitive to variations in lighting conditions and object viewpoints, making it difficult to retrieve relevant images when the visual input differs from the training data. | This can result in missed relevant images, as the search query may not match the variations in the visual input. | Developing algorithms that are more robust to variations in lighting and viewpoint, potentially using more diverse training data. |
Visual Search and Content Creation
Visual search is rapidly transforming how we create content, offering a wealth of inspiration and resources beyond traditional searches. From finding similar images to discovering fresh design concepts, visual search unlocks creative avenues previously unimaginable. This approach allows for a more intuitive and engaging content creation process, significantly enhancing the quality and originality of outputs.
Using Visual Search for Content Inspiration
Visual search engines excel at providing inspiration for a variety of content types. Instead of relying solely on text-based s, users can leverage visual cues to uncover novel ideas. For example, a graphic designer looking for a specific aesthetic might upload an image representing the desired style, prompting the search engine to return visually similar examples. This process often sparks new concepts and helps avoid creative blocks.
Exploring diverse visual styles, colors, and compositions via visual search can significantly boost creativity.
Finding Similar Images and Objects
Visual search is invaluable for finding similar images or objects. This capability is particularly useful for content creators needing specific visual elements. For instance, an article about ancient Roman architecture might benefit from finding images resembling specific buildings or structures. Users can upload an image of an element, and the search engine returns visually similar examples, allowing for more comprehensive and detailed content.
This process aids in researching historical references and ensuring accuracy in visual representations.
Visual Search for Research Purposes, Visual search and google lens
Visual search has a valuable role in research, particularly in fields requiring visual data. Researchers can use visual search to identify images, illustrations, and photographs related to their area of study. For example, a historian researching a particular historical event can upload an image of a relevant object, finding similar images and context from various sources. Visual search can provide a broad overview of the subject matter, aiding in research accuracy and understanding.
Comparing Visual Search Methods for Content Creation
| Method | Description | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image Upload | Uploading an image to a visual search engine to find similar images or objects. | Easy to use, quick results, broad range of results, useful for inspiration. | Accuracy depends on the quality of the uploaded image, potential for irrelevant results, limited to images already present in the database. |
| Sketching/Drawing | Using a sketching or drawing tool to create a visual representation of the desired element and then searching for similar images. | Allows for more precise searches, can be helpful for complex ideas or concepts that are difficult to capture with a single image. | Requires some level of drawing skill, might not return many results for complex or unique sketches, can be time-consuming. |
| Description-Based Search | Combining text and visual elements, using s and image upload for a more refined search. | Combines the strength of text and image searches, potentially finding a wider variety of results, more accurate in certain situations. | Requires a detailed description, the search may not be as precise as with image upload alone, potential for ambiguity in text descriptions. |
| AI-Powered Visual Search | Using advanced AI algorithms to identify patterns and similarities in images and then return relevant results. | High accuracy in recognizing and classifying images, capable of identifying subtle differences, provides a comprehensive understanding of similar images. | Potentially high computational cost, depends on the accuracy and training data of the AI algorithm, may be limited by the availability of sufficient training data. |
Closing Notes
Visual search, powered by tools like Google Lens, is rapidly changing how we access and process information. The ability to search by image, rather than just text, opens up new avenues for research, discovery, and creativity. While challenges remain in accuracy and interpretation, the future of visual search looks promising, with AI and machine learning poised to enhance its capabilities and expand its applications.
This technology promises to seamlessly integrate into our daily lives, making information more accessible and intuitive than ever before.