UX and UI design is the art and science of creating digital experiences that are both aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly. This exploration delves into the intricate world of user-centered design, exploring the core principles and methodologies that drive successful digital products. From the historical context of UX and UI design to emerging trends, this blog post will take you on a journey through the exciting world of creating effective digital interactions.
We’ll examine the fundamental differences between UX and UI, exploring the unique roles each plays in shaping the overall user experience. We’ll also explore the crucial role of user research in informing design decisions, and examine various design methodologies and tools to create seamless and intuitive user interfaces.
Introduction to UX and UI Design

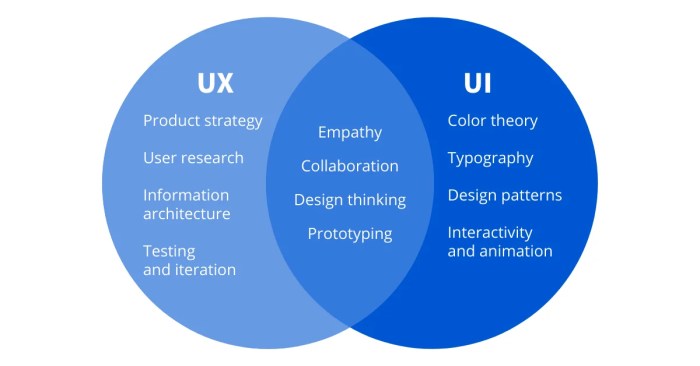
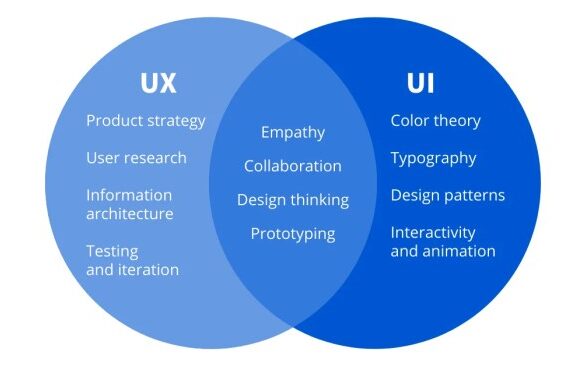
User experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design are crucial aspects of creating digital products that are both functional and engaging. They focus on understanding and meeting user needs, shaping how users interact with and perceive products. This introduction explores the fundamentals of UX and UI design, delving into their definitions, key differences, historical evolution, and the importance of user-centered design.UX and UI design are often used interchangeably, but they are distinct disciplines.
UX design emphasizes the overall experience a user has with a product, while UI design focuses on the visual elements and interactive components that make up the product’s interface. Understanding these nuances is key to creating a product that satisfies user needs and meets business objectives.
Defining UX and UI Design
UX design, at its core, is the process of designing products that meet user needs and expectations. It encompasses all aspects of a user’s interaction with a product, from initial discovery to ongoing use. UI design, on the other hand, focuses on the visual and interactive elements of a product. It is concerned with the aesthetics, layout, and functionality of the interface.
Key Differences Between UX and UI Design
UX design centers on user needs and satisfaction, while UI design focuses on visual appeal and intuitive interactions. A strong UX design considers the user’s journey through a product, optimizing for ease of use and efficiency. UI design, conversely, aims to make the interface aesthetically pleasing and consistent with brand guidelines. A good UI is crucial for enhancing user engagement and satisfaction.
A poor UI, on the other hand, can lead to frustration and abandonment.
Historical Context of UX and UI Design
The concept of user-centered design has existed in some form for decades. Early examples of UX design principles can be seen in the development of early computer interfaces and the understanding of human-computer interaction. The formalization of UX and UI as distinct disciplines emerged with the rise of the internet and the proliferation of digital products. The increasing complexity of software applications and websites demanded a more structured approach to user interaction and design.
The development of early graphical user interfaces (GUIs) also laid the groundwork for modern UI design.
Evolution of UX and UI Design Principles
Early design principles were often intuitive and based on trial and error. Over time, principles became more structured, with a greater emphasis on user research and testing. The iterative design process, now a standard practice, was further refined to allow for continuous improvement and user feedback. With advancements in technology, there’s been a corresponding increase in sophisticated design tools and methodologies.
Importance of User-Centered Design in UX and UI Design
User-centered design is paramount to the success of any digital product. It prioritizes understanding user needs, behaviors, and motivations to create products that truly meet their requirements. By incorporating user feedback throughout the design process, products can be adapted and refined to optimize the user experience. This iterative approach, emphasizing user needs and feedback, leads to products that are more usable, enjoyable, and successful.
Comparing UX and UI Design Methodologies
| Feature | UX Design | UI Design |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | User experience | User interface |
| Goal | User satisfaction | Aesthetic appeal |
| Methods | User research, usability testing | Visual design, prototyping |
Core Principles of UX Design
UX design is more than just making things look pretty; it’s about creating seamless and enjoyable user experiences. At its core, UX design prioritizes the user, aiming to understand their needs and motivations to craft intuitive and effective interfaces. This involves a deep understanding of the core principles that underpin user-centered design.Understanding these principles allows designers to create products that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also highly usable, accessible, and enjoyable to interact with.
This, in turn, leads to higher user satisfaction, increased engagement, and ultimately, more successful products.
UX and UI design is all about creating intuitive and user-friendly interfaces. But, when you consider how much personal data is collected by voice assistants like “Ok Google,” it raises questions about privacy. Are we truly in control of our information? That’s something to consider when designing interfaces for voice-activated services, especially in the context of the ongoing debate about user privacy, like the one presented in this article about Ok Google are you spying on me.
Ultimately, good UX/UI design needs to acknowledge and address these privacy concerns.
Usability, Ux and ui design
Usability is a critical aspect of UX design, focusing on how easily users can interact with a product or service. It encompasses several key elements, including efficiency, learnability, memorability, and error prevention. A highly usable design allows users to accomplish their tasks quickly and effectively with minimal effort.Real-world examples of good usability include well-structured websites like Google or Amazon, where users can easily find information and complete transactions.
Conversely, poorly designed interfaces can frustrate users and lead to abandonment.
Accessibility
Accessibility is paramount in UX design, ensuring that products and services are usable by people with diverse abilities. This includes considerations for users with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments. By adhering to accessibility guidelines, designers can create inclusive experiences that cater to a wider audience.Examples of accessibility in action include websites that use alt text for images, allowing screen readers to convey the image’s content to visually impaired users, and keyboard navigation options that allow users to interact with websites without a mouse.
Learnability
Learnability refers to how quickly users can master the use of a product. A design that is easily learned allows users to start interacting with it effectively without extensive training. Effective design guides users through the product, reducing the learning curve and increasing user satisfaction.A great example of learnability is the consistent design language and intuitive navigation of popular social media platforms.
Users quickly grasp the core functionalities and interactions, allowing for smooth and engaging use.
User Research
User research is fundamental to UX design, forming the basis of all design decisions. It involves gathering insights into user needs, behaviors, and preferences. Research methods can include user interviews, surveys, usability testing, and more. This deep understanding of the target audience allows designers to create products that truly meet their needs.By understanding the users’ needs, pain points, and desires, designers can make informed decisions about how to design interfaces that are effective, efficient, and enjoyable to use.
User Personas and User Journeys
User personas are detailed representations of the target user, including demographics, motivations, and goals. They provide a clear picture of the user and their needs. Understanding user journeys maps the steps a user takes when interacting with a product, identifying potential pain points and opportunities for improvement.A well-defined user persona helps designers to anticipate user needs and tailor the design accordingly.
For example, a persona for a mobile banking app might highlight the need for fast transactions, secure access, and clear instructions. Similarly, a user journey map for the same app might reveal a friction point in the account verification process, leading to potential design improvements.
Usability Heuristics
Usability heuristics are guidelines for evaluating the usability of a product or service. They provide a framework for assessing the effectiveness of the design. By applying these heuristics, designers can identify areas for improvement and refine their design accordingly.Some key usability heuristics include visibility of system status, match between system and the real world, user control and freedom, consistency and standards, error prevention, recognition rather than recall, flexibility and efficiency of use, aesthetic and minimalist design, help users recognize, diagnose, and recover from errors, help and documentation.A good example of using heuristics in practice is evaluating a website’s navigation.
Does the navigation clearly reflect the site’s structure (match between system and the real world)? Are there clear feedback mechanisms (visibility of system status)? Applying these heuristics allows for a comprehensive evaluation of the usability of the design.
Core Principles of UI Design
UI design, the art of crafting the visual interface of a product, is crucial for user experience. A well-designed UI not only looks aesthetically pleasing but also guides users intuitively through the product, making their interactions seamless and enjoyable. This involves a careful consideration of several core principles, which we’ll explore in detail.Visual hierarchy is fundamental in UI design.
It refers to the arrangement of elements to guide the user’s eye and attention. By strategically placing elements with varying sizes, colors, and spacing, designers can direct users to critical information first. This ensures users are able to quickly and easily scan a screen and locate important features or calls to action.
Visual Hierarchy
Visual hierarchy is achieved through a combination of factors including size, color, contrast, and whitespace. Larger elements and bolder colors naturally attract more attention, while carefully placed whitespace separates content and creates visual breathing room. This creates a clear pathway for the user to interact with the interface. For instance, a prominent call-to-action button will typically be larger and more visible than other elements on the page.
Typography
Typography plays a significant role in conveying the brand identity and readability of the interface. Choosing the right font family, size, and style can significantly impact the user experience. A legible font, appropriate size, and consistent application are essential for creating a user-friendly interface. A bold headline font might be used for titles, while a more subtle font is used for body text.
Color Palettes
Color palettes are crucial for creating a cohesive and memorable visual identity. A well-chosen palette can evoke specific emotions and create a consistent brand experience. Color psychology plays a significant role in UI design, with different colors eliciting different responses. For example, blue is often associated with trust and reliability, while red can be used to signal urgency or excitement.
Visual Consistency
Maintaining a consistent visual style across the entire interface is critical. This includes consistent use of fonts, colors, and button styles. Visual consistency helps users understand the interface quickly and intuitively, as they are able to easily identify and interact with elements. Consistency also fosters a strong brand identity and reinforces user expectations.
Effective Navigation
Navigation design guides users through the interface. Clear and intuitive navigation paths are essential for a positive user experience. This includes using menus, breadcrumbs, and other navigation elements to help users find their way around the interface. Effective navigation minimizes the effort needed for users to achieve their goals. For instance, a website should have a prominent menu bar that clearly indicates the different sections.
UI Design Patterns
Many UI design patterns have proven effective for achieving specific design goals. For instance, the use of tabs for grouping related content or tooltips for explaining functionality. Understanding and utilizing these patterns can lead to more efficient and user-friendly interfaces.
Feedback Mechanisms
Feedback mechanisms are vital for keeping users informed about their actions. When a user interacts with an element, the interface should provide immediate and appropriate feedback. This feedback can take many forms, from visual cues like loading indicators to auditory alerts. A button that changes color or emits a subtle sound when clicked provides valuable feedback.
Comparison of UI Design Styles
| Design Style | Key Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Material Design | Emphasis on tactile interactions, realistic shadows, and depth. Focuses on creating a sense of realism and physicality within the digital space. | Google apps, such as Gmail and Google Maps. |
| Flat Design | Simple shapes, bright colors, and minimal design elements. Focuses on clean lines, uncluttered layouts, and a streamlined look. | Microsoft apps, such as Office and Windows. |
User Research Methods in UX Design
Uncovering user needs and preferences is paramount in creating effective and user-friendly designs. User research methods provide invaluable insights into how users interact with products and services, helping designers make informed decisions throughout the design process. This understanding directly translates to better products and a more positive user experience.User research is not a one-size-fits-all approach. The most effective strategy often involves a combination of different methods, tailored to the specific project and its goals.
By employing a variety of techniques, designers can gather comprehensive data and build a deeper understanding of the target user base.
Common User Research Methods
User research methods are diverse and encompass various approaches. Each method provides unique insights and should be selected based on the specific research objectives. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each method allows designers to effectively integrate them into their design process.
- Surveys: Surveys are a common method for gathering quantitative data from a large number of users. They are efficient for collecting opinions and preferences on a broad scale. Surveys often employ multiple-choice questions, rating scales, and open-ended questions to gauge user attitudes and behaviors. Surveys can be used to understand user demographics, identify pain points, and gather feedback on existing products or services.
They are especially valuable for assessing user satisfaction and measuring the impact of design changes.
- Interviews: Interviews provide in-depth qualitative data about user experiences. They allow for a more nuanced understanding of user motivations, needs, and behaviors. Structured, semi-structured, or unstructured interview formats can be employed, depending on the research objectives. Interviews are valuable for understanding complex user needs and gaining insights into the context of use. They can reveal the ‘why’ behind user behavior and preferences.
Examples include one-on-one discussions, focus groups, and contextual inquiries.
- Usability Testing: Usability testing observes how users interact with a product or prototype in a real-world setting. This method focuses on evaluating the ease of use, efficiency, and effectiveness of a design. Participants are typically asked to complete specific tasks while their behavior is observed and documented. This provides valuable data on areas needing improvement in terms of navigation, layout, and overall interaction.
UX and UI design is all about creating user-friendly interfaces, and understanding how people interact with products. Recently, Moz released their annual local search rank factor survey, which highlights the crucial factors impacting online visibility for local businesses. This survey, moz releases annual local search rank factor survey , offers valuable insights for designers, helping them create websites that rank higher in local search results, thus improving the user experience.
Ultimately, this directly ties back to the importance of crafting intuitive and engaging user interfaces.
Usability testing often reveals critical usability issues that might otherwise be overlooked.
Importance of User Feedback
User feedback is integral to the design process. It serves as a crucial source of information to inform design decisions, ensuring that the final product meets user needs and expectations. Constructive criticism from users can lead to significant improvements in usability and overall user experience.
- Informing Design Decisions: User feedback provides critical data for making informed design choices. By analyzing user feedback, designers can identify areas where the design falls short of user expectations and make necessary adjustments. This feedback can be used to refine the design, prioritize features, and ensure that the product meets the needs of its target users. Analyzing feedback on a product’s functionality can inform decisions about the product’s development.
- Improving Usability: User feedback can pinpoint specific usability issues that might not be apparent to the design team. By addressing these issues, designers can improve the overall usability of the product, making it easier and more enjoyable for users to interact with. This iterative process of gathering feedback, analyzing it, and incorporating it into the design is key to creating user-friendly products.
Examples of User Research Data
User research data can be used to guide design decisions in various ways. It helps designers understand user needs and preferences, leading to the creation of products that are intuitive and user-friendly.
UX and UI design is all about creating intuitive and visually appealing interfaces. It’s a fascinating field, and seeing how these principles translate into real-world success stories, like those of Ted DeBasik, a San Francisco CPA, is truly inspiring. Success stories ted debasik san francisco cpa demonstrate how well-designed interfaces can boost efficiency and user satisfaction.
Ultimately, strong UX/UI design is crucial for any successful product or service.
- Task Completion Rates: In usability testing, the rate at which users successfully complete tasks provides insights into the design’s effectiveness. Lower completion rates often indicate areas where the design is confusing or difficult to use. Data from usability testing helps to refine the design to improve task completion rates.
- User Comments and Suggestions: Qualitative data from interviews and surveys reveals valuable insights into user preferences and expectations. Direct feedback from users can identify pain points, highlight areas needing improvement, and offer creative suggestions for enhancing the product. User comments often lead to a better understanding of user behaviors and the reasons behind their actions.
Tools and Techniques for User Research
Various tools and techniques are used to conduct effective user research. Choosing the right tools and techniques depends on the specific research objectives and the nature of the project.
- Survey platforms: Tools like SurveyMonkey, Google Forms, and Typeform are commonly used to collect and analyze data from a large number of users. These platforms offer templates, question types, and data analysis tools to streamline the survey process. Using survey platforms can help collect data from a wide range of users.
- Prototyping software: Tools like Figma, Adobe XD, and Sketch allow designers to create interactive prototypes of their designs. This allows for usability testing and gathering user feedback early in the design process. Interactive prototypes help to identify issues and gather user feedback early on in the design process, making changes before the design is finalized.
Tools and Technologies for UX/UI Design
The world of UX/UI design relies heavily on a diverse array of tools and technologies to bring designs to life. From initial sketches to final interactive prototypes, these tools streamline the design process, enabling designers to effectively communicate their ideas and ensure a seamless user experience. A strong understanding of these tools is crucial for any aspiring UX/UI designer.These tools not only help designers create visually appealing interfaces but also facilitate testing and iteration, ultimately leading to more user-centered and successful products.
The choice of tools often depends on the specific project, the desired level of interactivity, and the designer’s personal preference.
Popular Design Tools for UX/UI
A wide range of software and applications are commonly used in UX/UI design. These tools cater to different stages of the design process, from initial ideation to final development. Proficiency in these tools empowers designers to effectively convey their vision and create functional and aesthetically pleasing user interfaces.
- Figma is a popular vector graphics editor known for its collaborative features, making it ideal for team projects. Its real-time collaboration tools facilitate seamless communication and design iterations amongst team members. The intuitive interface and wide range of plugins further enhance its usability.
- Adobe XD, a user experience design tool, allows for the creation of interactive prototypes and user flows. Its integration with other Adobe Creative Cloud applications makes it a versatile choice for comprehensive design workflows. It is especially helpful for designers who are already familiar with the Adobe Creative Suite.
- Sketch is a popular vector graphics editor, frequently used by UI designers. Its focus on UI design allows for quick and efficient creation of high-fidelity mockups and interfaces. It boasts a powerful set of tools for vector manipulation, making it a robust choice for UI design projects.
The Role of Prototyping in UX/UI Design
Prototyping is a critical component of the UX/UI design process. It allows designers to test and refine their designs before committing to a final product, thus reducing the risk of creating a solution that doesn’t meet user needs. Early prototyping also enables early feedback and adjustments.
Prototypes, whether low-fidelity or high-fidelity, serve as tangible representations of the user interface. They allow stakeholders to visualize the application’s functionality and provide feedback, leading to a more refined and user-friendly product.
Wireframing and Mockups in the Design Process
Wireframing and mockups are integral stages in the UX/UI design process. Wireframes provide a skeletal structure of the interface, focusing on the layout and information architecture. Mockups, on the other hand, present a more detailed visual representation of the design, incorporating visual elements like color palettes, typography, and imagery.
Wireframes help establish the flow and structure of the application, while mockups bring the design to life. The iterative refinement of wireframes and mockups throughout the design process ensures a user-centered approach and allows for continuous improvement.
Design Systems in Large-Scale Projects
Design systems play a vital role in maintaining consistency and efficiency in large-scale projects. They define and standardize the visual language, components, and interaction patterns of a product or brand. This ensures that the final product has a unified aesthetic and user experience.
By defining a consistent set of components and guidelines, design systems minimize inconsistencies, improve efficiency, and enhance the overall user experience. They also reduce the time and resources needed for design iterations and revisions.
Accessibility Tools in UI Design
Accessibility is a crucial consideration in UI design. Accessibility tools help designers create user interfaces that can be used by people with disabilities. These tools can assist in identifying potential accessibility issues and ensuring that the design adheres to accessibility guidelines.
Tools like screen readers and keyboard navigation simulators are crucial for assessing accessibility. Using these tools allows designers to identify potential usability problems for users with various disabilities.
Prototyping Tools for UX/UI Design
A variety of prototyping tools are available to UX/UI designers, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The choice of tool depends on the specific needs of the project and the designer’s preferences.
- Adobe XD
- Figma
- InVision
- Marvel
- Axure RP
- Proto.io
Case Studies of Successful UX/UI Design
Diving deep into successful UX/UI design projects provides valuable insights into the strategies, challenges, and ultimately, the impact of effective design. These case studies illustrate how careful consideration of user needs, coupled with innovative solutions, can lead to exceptional user experiences. Learning from past successes empowers designers to create more user-centric and impactful products.Understanding the design process behind successful projects is crucial for aspiring designers.
Analyzing the design decisions, user feedback, and the impact on the final product reveals patterns and principles that can be applied to future projects. By examining these case studies, we can gain a deeper understanding of the iterative nature of design and the importance of continuous improvement.
Airbnb’s Website Redesign
Airbnb’s website redesign, a prime example of a successful UX/UI overhaul, prioritized user experience. The previous design was complex and cluttered, making it difficult for users to navigate and find the information they needed. The redesign focused on simplifying the user flow and improving clarity. By reducing unnecessary elements and creating a more intuitive layout, Airbnb significantly improved the user experience.
This resulted in increased bookings and a stronger brand image. A key element in the redesign was the integration of user feedback into the design process. Surveys and user interviews provided invaluable insights that directly shaped the final product.
Spotify’s Music App
Spotify’s music app stands out for its intuitive design and personalized user experience. The app’s ability to cater to diverse user needs and preferences is a testament to thorough user research and thoughtful design. Key elements contributing to its success include the use of visual cues, consistent branding, and clear call-to-actions. Users are quickly guided through the interface, allowing them to easily discover new music and manage their playlists.
The continuous improvement strategy, incorporating user feedback and data analysis, is a vital component in maintaining the app’s popularity.
Design Process of Airbnb’s Website Redesign (Example)
| Phase | Description | Tools Used |
|---|---|---|
| User Research | Understanding user needs, pain points, and expectations through surveys, user interviews, and competitor analysis. Identifying key user flows and tasks within the platform. | User testing platforms, survey tools, user interview recordings |
| Information Architecture | Structuring and organizing content on the website to make it easily navigable and searchable. | Mind mapping tools, sitemaps |
| Wireframing and Prototyping | Creating low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes to visualize the user flow and identify potential issues before development. | Figma, Adobe XD, Balsamiq |
| Usability Testing | Testing the prototype with real users to gather feedback and identify areas for improvement in the design. Identifying usability issues and refining the design based on user feedback. | User testing platforms, usability testing tools |
| Design and Development | Implementing the final design and ensuring consistency with brand guidelines. | Design software, front-end development tools |
Future Trends in UX/UI Design: Ux And Ui Design
The field of UX/UI design is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing user expectations. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for designers to create intuitive, engaging, and future-proof experiences. This exploration dives into the key areas shaping the future of user interaction, from the impact of AI to the evolution of interfaces themselves.The future of UX/UI design is deeply intertwined with the rapid advancement of technology.
AI, machine learning, and the proliferation of new devices are reshaping how we interact with digital products and services. This section explores the significant impact of these trends on design principles and methodologies.
Emerging Trends in UX/UI Design
Understanding the emerging trends allows designers to anticipate user needs and create interfaces that are not only functional but also anticipatory and intuitive. Key trends include a focus on personalization, accessibility, and a seamless blend of physical and digital experiences.
- Personalization: AI-powered systems are increasingly enabling personalized user experiences. This involves tailoring content, features, and recommendations based on individual user preferences and behaviors. Examples include personalized news feeds, customized product recommendations, and dynamic content delivery in educational platforms.
- Accessibility: Designers are prioritizing inclusive design principles to create interfaces accessible to users with diverse abilities and needs. This includes incorporating features like screen readers, keyboard navigation, and alternative text for images. Examples of this include websites and applications designed with WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) compliance in mind.
- Immersive Experiences: VR (Virtual Reality) and AR (Augmented Reality) are becoming more prevalent, offering immersive and interactive experiences. UX/UI designers are adapting their approaches to create intuitive interfaces for these technologies. Examples include interactive training simulations, virtual product demonstrations, and augmented reality overlays for shopping experiences.
- Voice User Interfaces (VUIs): The rise of voice assistants is driving the development of voice-based interfaces. Designers must focus on creating conversational and intuitive voice interactions. Examples include smart home controls, voice-activated search engines, and voice-activated mobile applications.
Impact of New Technologies on UX and UI Design
The advancements in technology, especially in the realm of artificial intelligence, are fundamentally changing the way we design user experiences. This transformation requires designers to adapt and incorporate these advancements to create innovative and impactful products.
- AI-Powered Design Tools: AI-powered tools are becoming increasingly sophisticated, assisting designers in tasks such as prototyping, user research, and interaction design. Examples include tools that automatically generate wireframes, suggest design elements, and analyze user behavior.
- Dynamic Content and Adaptability: New technologies enable interfaces to dynamically adjust based on user context and behavior. This adaptability is critical for creating personalized and efficient experiences. Examples include responsive design, adaptive interfaces that adjust to different screen sizes, and interfaces that learn user preferences over time.
- Integration of Physical and Digital Worlds: The lines between the physical and digital worlds are blurring. UX/UI designers must create seamless experiences that integrate both. Examples include smart home devices that integrate with mobile apps, augmented reality experiences that overlay digital information on the physical world, and wearable technology that connects to mobile applications.
Role of AI and Machine Learning in UX Design
AI and machine learning are playing an increasingly important role in understanding and anticipating user needs, enabling more personalized and intuitive experiences. The data analysis capabilities of these technologies are critical in identifying patterns and trends that inform design decisions.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze user data to predict future behavior and anticipate needs. This enables designers to create interfaces that proactively address user requirements. Examples include personalized recommendations, proactive support, and adaptive content delivery.
- Automated User Research: AI can automate tasks in user research, such as analyzing user feedback and identifying common pain points. This allows for faster and more efficient research processes. Examples include AI-powered tools that analyze user interactions with a product to identify areas for improvement.
- Personalized User Interfaces: AI can tailor user interfaces based on individual user preferences and behaviors. This creates a more customized and efficient user experience. Examples include dynamic website layouts, personalized app features, and adaptive navigation menus.
Future of User Interfaces
The evolution of user interfaces is moving towards more intuitive, context-aware, and seamless interactions. This section details the future of interfaces with examples.
- Contextual Awareness: Interfaces will be more context-aware, anticipating user needs based on the environment and situation. Examples include automatically adjusting interface elements based on location or time of day, and proactively offering relevant information based on user context.
- Natural Language Interaction: Interfaces will increasingly use natural language processing (NLP) to allow for more intuitive and conversational interactions. Examples include voice-activated interfaces, chatbots, and interfaces that understand and respond to user queries in natural language.
- Haptic Feedback: Interfaces will incorporate haptic feedback to provide a more tangible and immersive experience. Examples include interactive surfaces that provide tactile responses to user input, and wearables that provide haptic feedback to enhance user engagement.
Examples of Emerging Design Trends
The evolution of design trends reflects the increasing integration of technology and user needs. Examples of these trends are evident in the ongoing development of user interfaces.
- Minimalist Design: Simplicity and clarity are key. This involves a focus on essential elements and intuitive navigation. Examples include clean, uncluttered interfaces that prioritize functionality and reduce visual noise.
- Dark Mode: Dark mode is becoming increasingly popular for its aesthetic appeal and its potential to reduce eye strain, especially in low-light conditions. Examples include websites and applications that offer dark mode options to users.
- Micro-interactions: Micro-interactions are subtle animations and feedback mechanisms that enhance user experience and provide visual cues. Examples include subtle animations when users interact with buttons, progress indicators, and interactive elements.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding UX and UI design is vital for creating successful digital products. This post highlighted the core principles, methodologies, and tools involved. By applying these concepts, designers can create interfaces that are not only visually appealing but also highly functional and user-centered. The future of UX and UI design is bright, with continuous evolution driven by emerging technologies and user expectations.