Url canonicalisation seo guide – URL canonicalization guide is your key to optimizing WordPress for search engines. This guide dives deep into understanding and implementing proper canonicalization strategies. We’ll explore everything from basic definitions and best practices to advanced techniques and troubleshooting, ensuring your website ranks higher and drives more traffic. We’ll cover everything from common errors to fixing them, and even look at specific scenarios for different websites.
This guide will be your comprehensive resource for optimizing your WordPress site for search engines, from the basics to advanced implementation strategies. You’ll learn how to avoid common pitfalls and ensure your site is easily crawled and indexed by search engines.
Introduction to URL Canonicalization
URL canonicalization is a crucial technique that helps search engines understand which version of a webpage is the definitive one. It’s essentially a way to tell search engines that multiple URLs are pointing to the same content, ensuring that only one version is indexed and ranked. This prevents duplicate content issues and improves search engine visibility.Proper implementation of URL canonicalization is vital for maintaining a clean and efficient website structure.
It allows search engines to focus their indexing efforts on the designated canonical URL, leading to improved website traffic and rankings. A well-structured canonicalization strategy significantly impacts search engine results, directly influencing the amount of organic traffic a website receives.
Defining URL Canonicalization
URL canonicalization is the process of specifying the preferred URL for a web page. This designated URL, known as the canonical URL, acts as the primary representation for that specific content. Search engines use this information to index and rank the correct version of the page, avoiding issues of duplicate content and improving performance.
Importance of URL Canonicalization for
URL canonicalization is critical for because it avoids duplicate content issues. Multiple URLs pointing to the same content can confuse search engines, potentially diluting the website’s search engine rankings. By establishing a canonical URL, webmasters clearly indicate the preferred version of the page, ensuring that search engines index and rank the intended page, ultimately improving the site’s visibility in search results.
This, in turn, leads to higher organic search traffic and a better user experience.
Benefits of Proper URL Canonicalization
Implementing proper URL canonicalization provides several advantages:
- Improved Search Engine Rankings: Search engines can effectively index the desired page, leading to better visibility and higher rankings in search results. This increased visibility is directly proportional to the amount of organic traffic a website receives.
- Reduced Duplicate Content Issues: Canonicalization prevents search engines from treating multiple URLs with identical or near-identical content as separate pages, avoiding the negative impact of duplicate content penalties.
- Enhanced Website Traffic: By ensuring search engines index the intended page, canonicalization leads to a significant boost in organic search traffic, resulting in a higher volume of visitors.
- Improved User Experience: A well-structured website with clear canonical URLs ensures that users are directed to the intended page, improving their overall experience and navigation within the site.
Best Practices for Establishing a Canonical URL Structure
Implementing a proper canonical URL structure involves several key best practices:
- Use the rel=”canonical” tag: This HTML tag is the standard way to specify the canonical URL for a webpage. It’s crucial for signaling the preferred version to search engines.
- Maintain Consistent URLs: Use consistent URLs across different platforms and content formats. Avoid variations in URLs for the same page.
- Employ 301 Redirects: Redirect older, non-canonical URLs to the preferred version using 301 redirects. This ensures that search engines understand the page’s new location and retain the value.
- Regularly Audit URLs: Periodically review and update canonical URLs to maintain accuracy and consistency as your website evolves.
Common Issues in URL Canonicalization
| Issue | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Canonical Tag Placement | The rel=”canonical” tag is incorrectly implemented in the HTML source code. | Search engines might not recognize the preferred URL, leading to duplicate content issues and poor rankings. |
| Missing Canonical Tag | The rel=”canonical” tag is absent, resulting in a lack of clear preference for a particular URL. | Search engines might index multiple versions of the same content, leading to diluted search engine rankings and potential duplicate content penalties. |
| Inconsistent Canonical URLs | Different URLs on the site point to the same content without a clear canonical designation. | Search engines struggle to understand which version of the page to index and rank, potentially resulting in lower rankings and decreased organic traffic. |
| Canonical URLs with Errors | Canonical URLs contain errors, like broken links or redirects, or they point to pages that no longer exist. | Search engines may not be able to access the designated page, causing indexing issues and potentially damaging the site’s . |
Understanding Canonicalization Issues
Canonicalization is crucial for , ensuring search engines understand which version of a page is the authoritative one. Incorrect or missing canonical tags can lead to duplicate content penalties, hindering your website’s ranking. Understanding the common pitfalls and how to fix them is vital for maintaining a healthy online presence.Identifying and resolving canonicalization issues requires a deep dive into your website’s structure.
Errors in implementation, conflicting canonical tags, and consequences of missing or incorrectly implemented canonical tags are all crucial elements in maintaining good practices. This section will delve into these critical areas, helping you understand and troubleshoot potential problems.
Common Errors in Implementing Canonical Tags
Incorrect implementation of canonical tags is a frequent cause of issues. Common errors include using the wrong format, incorrect URL structure, or mismatching the canonical URL with the actual content. Inaccurate or inconsistent implementation can lead to search engines indexing different versions of the same content, potentially diluting your efforts.
Multiple Canonical Tags Affecting Indexing
Search engines encounter difficulties when multiple canonical tags point to different pages. This confusion leads to inconsistencies in indexing, potentially affecting the visibility of the intended page. A single, accurate canonical tag is essential for clear indexing by search engines.
Consequences of Incorrect or Missing Canonical Tags
Missing or incorrectly implemented canonical tags can have significant repercussions. Search engines might index duplicate content, leading to decreased rankings or even penalties. This can negatively impact organic traffic and overall website visibility. In severe cases, a website might be penalized, hindering its performance in search results.
Comparing and Contrasting Canonicalization Issues
Different canonicalization issues arise from various factors. One major category involves implementing the canonical tag incorrectly or in a way that is inconsistent with other best practices. Another category relates to technical errors on the website, such as incorrect URL structures or redirects. These issues, while distinct, share a common consequence: potentially misleading search engines about the authoritative version of a page.
Locating and Resolving Canonicalization Problems
Identifying canonicalization issues involves a methodical approach. Start by analyzing your website’s structure, looking for inconsistencies in URLs and canonical tags. Tools and techniques, like using sitemaps and crawling tools, help pinpoint problematic areas. A comprehensive audit is essential to identify and fix these issues.
Methods for Fixing Canonicalization Issues
Addressing canonicalization problems involves fixing the source of the issue. This includes reviewing and updating canonical tags, ensuring correct URL structures, and implementing redirects where necessary. By systematically identifying and correcting the problem areas, you can improve your website’s performance.
Common URL Structures Requiring Canonicalization
Different URL structures often require canonicalization to avoid duplicate content issues. This includes variations in query parameters, different pagination structures, and URL parameters for language versions of a page. Canonicalization is vital to guide search engines towards the intended, authoritative version of the page. A list of common examples follows:
- Different query parameters: Example: `www.example.com?param1=value1` vs. `www.example.com?param1=value2`. Both URLs could point to the same page but with different parameters.
- Different pagination structures: Example: `www.example.com/page-1` vs. `www.example.com/page-2`. Canonicalization ensures that the search engine indexes only the main page, not each individual page.
- URL parameters for language versions: Example: `www.example.com/en-us/page` vs. `www.example.com/fr-ca/page`. Canonicalization helps direct search engines to the appropriate language version.
Implementation Strategies: Url Canonicalisation Seo Guide
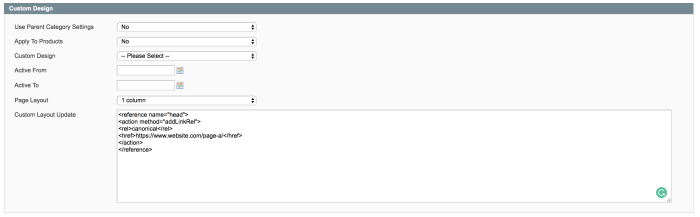
Mastering URL canonicalization is crucial for success. Implementing canonical tags correctly ensures search engines understand the primary version of your content, preventing duplicate content penalties and improving your website’s overall ranking. This section dives deep into practical strategies for implementing canonicalization across various website architectures.Proper implementation is essential to maintain a clean and consistent representation of your content to search engines.
It prevents the confusion caused by duplicate content, thus allowing search engines to prioritize the intended version of a page.
Canonical Tag Implementation Methods
Implementing canonical tags involves using the ` ` element within the `
` section of your HTML. This tells search engines which version of a page is the preferred one.- Using the `rel=”canonical”` attribute: This is the most straightforward method. Within the ` ` section of your HTML, add a `` tag with the `rel=”canonical”` attribute pointing to the preferred URL. For example, if your page is `https://www.example.com/product-a` and the canonical version is `https://www.example.com/product-a/`, the `` tag would be:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/product-a/" />This tells search engines that `https://www.example.com/product-a/` is the primary version. Crucially, this tag should point to the
-exact* canonical URL, including the correct structure and any necessary query parameters.
Effective Use of the Canonical Tag Attribute
The `rel=”canonical”` attribute’s effectiveness hinges on accuracy and consistency. Carefully crafted tags prevent search engines from indexing duplicate content.
- Correct URL Structure: Ensure the canonical URL accurately reflects the intended version of the page. This includes any query parameters or fragment identifiers.
- Consistent Application: Apply canonical tags to all pages that need them. Inconsistent use can confuse search engines and hinder optimization efforts.
- Avoiding Redundancy: Don’t use canonical tags for pages that are genuinely different or have distinct content. This practice can actually hurt your .
Examples of Properly Structured Canonical Tags
These examples illustrate the correct application of canonical tags in different scenarios.
- Scenario 1: A page with a slightly different URL structure.
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/category/product-a/" />This correctly points to the intended canonical URL for the page.
- Scenario 2: A page with a query parameter.
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/product-a/?color=red" />The canonical URL includes the query parameter for the preferred version.
Using Rel=”Canonical” Links Within HTML
The `rel=”canonical”` attribute is a fundamental part of the HTML structure. Its implementation ensures proper indexing and avoids duplication issues.
- Strategic Placement: Include the `rel=”canonical”` tag within the ` ` section of your HTML document. This ensures that the tag is visible to search engines during crawling.
- Error Prevention: Avoid any syntax errors or incorrect attributes when adding the `rel=”canonical”` tag to prevent unexpected outcomes.
Implementing Canonicalization in Different Website Architectures
The method for implementing canonicalization remains consistent across various website architectures.
- E-commerce Sites: Apply canonical tags to product pages with different variations (e.g., color, size). This prevents search engines from treating each variation as a unique page.
- Dynamic Websites: For pages generated dynamically, implement canonical tags to specify the correct version for search engines. This prevents indexing issues with similar content.
Practical Steps for Implementing Canonicalization for a Multi-Page Website
A systematic approach is essential for implementing canonicalization on large websites.
- Identify Duplicate Content: Use tools to find and analyze pages with similar content.
- Choose the Canonical URL: Decide which version of the content is the preferred one for each page.
- Add Canonical Tags: Implement the ` ` tags with the `rel=”canonical”` attribute to the preferred URLs.
Using 301 Redirects for Canonicalization
301 redirects are an alternative method for directing search engines to the canonical version of a page.
- Permanent Redirect: A 301 redirect permanently redirects users and search engines from one URL to another. This signals to search engines that the original page has been moved to a new location.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Setting Up a 301 Redirect
A well-defined procedure is critical for setting up 301 redirects.
- Identify the source URL: Determine the URL that needs to be redirected.
- Identify the destination URL: Specify the URL to which the source URL should be redirected.
- Configure the redirect: Use your web server’s configuration to set up the redirect.
Technical Considerations
URL canonicalization isn’t just about choosing the right URL; it’s a multifaceted process that deeply integrates with your website’s technical infrastructure. Proper implementation ensures search engines understand your content’s intended representation, minimizing confusion and maximizing your website’s visibility. Server-side configurations, robots.txt directives, and HTTP headers all play critical roles in effective canonicalization.
Understanding these technical aspects is vital for avoiding common issues and maintaining a clean, consistent representation of your website’s content to search engines. These techniques ensure your efforts in optimizing content are reflected accurately, and avoid conflicting signals that could hinder your performance.
Server-Side Configurations
Server-side configurations are crucial for managing how your website responds to requests for different URLs. These configurations directly impact how search engines interpret your content. The server, as the gatekeeper, determines which URLs are canonical and which are redirects.
Understanding URL canonicalization is key in SEO, but it’s just one piece of the puzzle. To truly optimize your website, you need to ensure your on-page SEO is on point. For a comprehensive guide on if your website is optimized, check out this great resource: on page seo is your website optimized. Ultimately, mastering URL canonicalization will help search engines understand your site structure, which is a crucial part of a successful SEO strategy.
- Choosing a canonical URL on the server. The server can be configured to automatically return a canonical URL in its responses. This is done via the server-side code that generates the HTML for the page, ensuring a consistent and clear message to search engines.
- Using a web server or application framework. Many web servers and frameworks offer built-in support for canonicalization, simplifying the process and reducing manual intervention. For example, Apache and Nginx have modules that can handle canonical redirects automatically, based on configuration settings.
Robots.txt
The robots.txt file acts as a guide for search engine crawlers, instructing them on which parts of your website they should or shouldn’t crawl. Its role in canonicalization is indirect but important. By preventing crawlers from indexing non-canonical versions, you can reduce the chances of duplicate content issues.
- Disallowing crawling of non-canonical URLs. A robots.txt file can be used to instruct search engine crawlers to ignore specific URLs that are not the canonical version of a page. This is important because if a crawler indexes non-canonical URLs, it may result in confusion about which URL is the main one.
- Prioritizing canonical URLs. By making sure your robots.txt file directs crawlers to the canonical version of a page, you ensure search engines understand your preferred URL.
HTTP Headers
HTTP headers provide crucial metadata about a web page to the browser and search engines. These headers can be used to explicitly declare the canonical URL.
- `Link` header. The `Link` header is a powerful tool for indicating related resources, including canonical URLs. It allows for explicit declaration of the canonical URL, giving clear instructions to search engines.
- `Content-Location` header. While less frequently used for canonicalization, the `Content-Location` header can indicate the canonical URL, especially when the resource’s location differs from the requested URL.
- `Location` header for redirects. The `Location` header is essential for 301 redirects. A 301 redirect from a non-canonical URL to the canonical URL ensures that search engines follow the redirection and update their indexes accordingly.
Comparison of HTTP Header Options
The `Link` header is generally preferred for canonicalization because it’s specifically designed for linking to related resources, including canonical URLs. The `Location` header, while effective for redirects, is primarily intended for redirecting the user, not for directly declaring a canonical URL.
Identifying and Resolving URL Conflicts
Conflicting URLs can lead to duplicate content issues, negatively impacting . Regularly checking for duplicate content and canonical tags is crucial.
Understanding URL canonicalization is crucial for SEO, especially when managing multiple websites. If you’re running multiple WordPress sites, proper canonicalization becomes even more important to avoid duplicate content issues. For example, using a platform like manage multiple websites on wordpress can make it easier to implement the right canonical URLs across your sites. This helps search engines correctly index and rank your content, ultimately improving your site’s overall visibility.
A well-structured canonicalization strategy remains a key part of a successful SEO approach for multiple websites.
- Using sitemaps and crawler tools. Tools that crawl your site can identify potential conflicts between URLs and identify possible canonicalization errors.
- Analyzing search engine results pages (SERPs). Monitoring SERPs for your website can reveal issues related to conflicting URLs and help to identify any inaccuracies.
Tools and Resources
Several tools and resources can assist in checking URL canonicalization. These tools help you identify errors and optimize your site’s structure for search engines.
- Google Search Console. This free tool provides insights into how Googlebot sees your website, including potential issues with canonicalization.
- Third-party auditing tools. Various tools offer comprehensive audits, including checks for canonicalization errors.
Common Server-Side Configurations
| Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
| Apache mod_rewrite | Used for URL rewriting, enabling redirects and canonicalization rules. |
| Nginx rewrite module | Similar to Apache, it handles URL rewriting and redirects. |
| Custom server-side scripts | Employing scripting languages like PHP, Python, or Ruby to handle canonicalization logic. |
Practical Applications and Examples
URL canonicalization is crucial for search engine optimization (). It helps search engines understand which version of a webpage represents the definitive, authoritative version. This prevents duplicate content issues, improves indexing efficiency, and ultimately boosts your website’s ranking in search results. By correctly implementing canonicalization, you ensure search engines don’t waste resources crawling and indexing redundant content, allowing them to focus on the valuable, unique content you want them to highlight.
Properly implemented canonicalization ensures search engines understand the hierarchy and relevance of your content, contributing to a better user experience. Without canonicalization, search engines might index multiple versions of the same page, potentially diluting your website’s ranking signals and making it harder for users to find your content.
Common Scenarios Requiring Canonicalization
Canonicalization is essential in various situations, particularly when multiple URLs point to the same or nearly identical content. Duplicate content issues are a primary concern, as search engines aim to display unique and valuable content to users.
Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can arise from various sources, including content scraping, pagination issues, or different versions of a page accessible via various URLs. Canonicalization addresses this by designating a single, preferred URL as the authoritative version. Search engines then prioritize this URL, preventing the dilution of ranking signals caused by duplicate content. For example, a blog post might be accessible via different URLs, such as with or without a trailing slash or with various query parameters.
A strong URL canonicalization SEO guide is crucial for search engine optimization. It ensures your website’s pages are correctly identified and ranked, which is vital in today’s competitive online landscape. However, keeping up with the latest SEO keyword strategy updates, like those discussed in the seo keyword strategy update or stagnate article, is equally important for maximizing visibility.
Without a robust URL canonicalization strategy, your efforts could be wasted, making it essential to maintain a strong foundation for successful SEO.
Using a canonical tag directs search engines to the correct, preferred URL, avoiding the indexing of duplicate content.
Handling Different Content Formats
Canonicalization is not limited to textual content. It’s equally important for handling diverse content formats, including images, videos, and products. For instance, an e-commerce website might have different image variations for a product (e.g., different resolutions or orientations). Using a canonical tag for the preferred image URL prevents indexing multiple versions of the same image. This helps maintain the integrity of the website’s data and ensures that search engines focus on the high-quality, optimized versions of the content.
Website Scenarios Requiring Canonicalization
Various website scenarios necessitate canonicalization. Consider a blog with multiple authors; authors may unintentionally create similar articles. Canonicalization helps maintain a consistent view of content, avoiding confusion for search engines and users. Likewise, e-commerce sites frequently face duplicate content challenges, particularly with multiple product listings. Canonicalization helps identify the preferred product page, preventing ranking issues from redundant information.
Similarly, a site with multiple language versions of content can use canonicalization to designate the primary language version.
Canonicalization in E-commerce Sites
E-commerce sites are particularly susceptible to duplicate content issues, arising from variations in product listings, filtering options, and pagination. A canonical tag for the main product page is crucial. It ensures search engines index the correct product page, optimizing visibility and preventing ranking problems from similar listings. Consider a product page with various filter options; each filtered page should link back to the canonical main product page.
Implementation Process for Different Website Types
| Website Type | Implementation Strategy |
|—|—|
| Blog | Use a canonical tag on each blog post page, linking to the preferred URL. |
| E-commerce | Use a canonical tag on each product page, linking to the preferred product page. |
| News Site | Implement canonicalization for each article, linking to the primary version. |
| Multi-lingual Site | Designate a canonical URL for each language version, linking to the preferred language version.
|
Canonical Tag Implementations
The canonical tag is an HTML element that specifies the preferred URL for a given page. It’s typically placed in the `
` section of the HTML document. For example:“`html “`
This tag informs search engines that the URL specified by `href` is the definitive version of the page.
Mobile-First Indexing and Canonicalization
With mobile-first indexing, search engines prioritize the mobile version of a website. Canonicalization plays a critical role in this context. The canonical URL should point to the mobile-friendly version of the page. This ensures that search engines index the correct version, leading to improved mobile search rankings.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Maintaining proper URL canonicalization is crucial for search engine optimization and a seamless user experience. Ignoring canonicalization issues can lead to duplicate content penalties, reduced rankings, and ultimately, lost traffic. This section focuses on proactive strategies for identifying, addressing, and preventing problems.
Common Issues in Maintaining Canonicalization
Maintaining consistent canonicalization is an ongoing process. Common issues arise from website updates, server migrations, changes in content structure, and even simple coding errors. These issues can manifest as conflicting canonical tags, missing or incorrect canonical links, or canonicalization rules that don’t reflect current content organization. This necessitates regular monitoring and review.
Monitoring and Tracking Canonicalization Effectiveness
Regular monitoring of canonicalization effectiveness is vital. This involves checking for proper implementation of canonical tags and tracking the impact on search engine results. Tools such as Google Search Console can provide valuable insights into crawl errors, indexation issues, and duplicate content warnings. By monitoring these metrics, you can identify and rectify problems early on, preventing significant drops in rankings.
Identifying and Fixing Issues with Canonicalization Over Time
Regular website audits are essential for identifying canonicalization issues. The process involves a thorough review of the site’s structure, content, and server configurations. By scrutinizing the implementation of canonical tags, and checking for discrepancies between links and tags, potential problems can be detected and resolved. This systematic approach helps maintain a clean and accurate canonicalization strategy.
Verifying Correct Implementation of Canonical Tags
A critical aspect of canonicalization maintenance is verifying the correct implementation of canonical tags. This involves checking for proper syntax, attribute values, and proper use of the ` ` tag within the HTML source code of each page. Thorough code inspection is crucial to ensure the correct implementation of canonicalization across all pages and that there are no discrepancies.
Automated tools and manual checks can be used for this purpose.
Checklist for Regular Canonicalization Maintenance
A regular checklist for canonicalization maintenance is crucial. This checklist should include reviewing and updating canonical tags whenever content or website structure changes, ensuring the tags accurately reflect the intended canonical URLs. It should also involve periodically checking for any new errors or inconsistencies that might arise due to the changing site environment. This approach allows for consistent and proactive management of canonicalization issues.
- Review canonical tags on all important pages.
- Ensure tags accurately reflect the current content organization.
- Check for missing or incorrect canonical tags.
- Verify the canonical URL resolves correctly.
- Monitor for changes in the sitemap and other critical elements.
Common Troubleshooting Steps for URL Canonicalization Issues, Url canonicalisation seo guide
Troubleshooting URL canonicalization issues involves a systematic approach. This includes reviewing server logs, checking for redirects, and inspecting the website’s robots.txt file to identify potential conflicts. Understanding the cause of the issue is essential to develop a targeted solution. This can involve investigating the source code, comparing the canonical tag with the actual URL, and using developer tools to analyze the website’s structure.
- Check for any conflicting redirects or other server-side issues.
- Verify the canonical URL resolves correctly and does not return errors.
- Inspect the website’s robots.txt file for any blocking or conflicting directives.
- Review the server logs for any unusual errors or warnings related to canonicalization.
- Utilize browser developer tools to inspect the HTML structure and canonical tags.
Importance of Periodic Checks for Updated Information and New Issues
Periodic checks for updated information and new issues are vital for maintaining a healthy canonicalization strategy. Websites constantly evolve, with new content, changes in structure, and potential errors arising. Regular checks ensure that the canonicalization rules remain accurate and relevant to the site’s current state. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of the website’s performance and user experience.
Final Review

In conclusion, mastering URL canonicalization is essential for any website aiming for top search engine rankings. This guide has provided a detailed roadmap to help you implement the best practices for your WordPress site. By understanding the intricacies of canonicalization, you can confidently optimize your site for optimal performance and achieve your desired search engine visibility. Remember to consistently monitor and maintain your canonicalization strategy for long-term success.