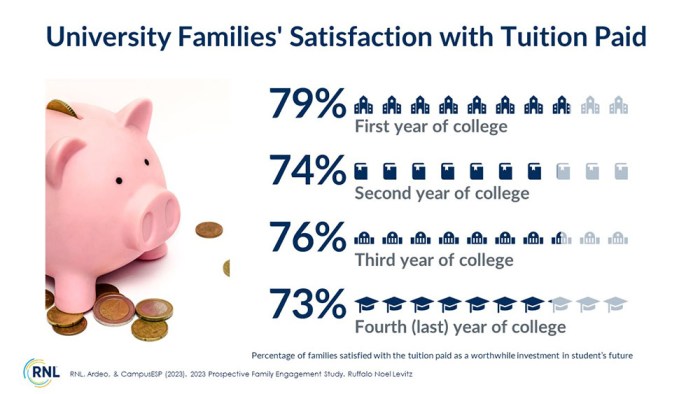
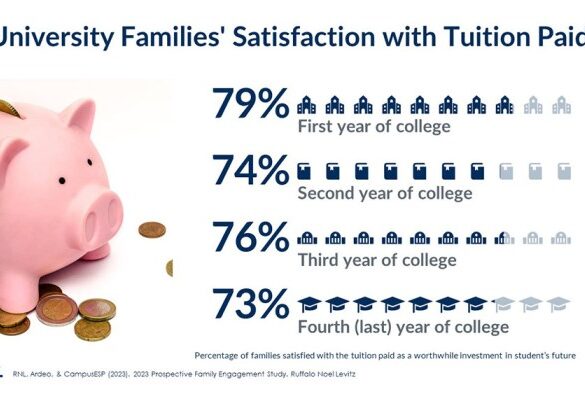
Tuition incentives to keep costs low for on the fence parents are crucial for families navigating the rising costs of higher education. This exploration delves into the anxieties and concerns of parents contemplating college for their children, examining various financial pressures and the diverse financial situations of families. We’ll explore the different types of tuition incentives offered by institutions, and how they impact enrollment decisions, ultimately aiming to shed light on designing effective incentive programs and creating strategies to communicate effectively with parents.
Understanding the diverse needs of families, from public to private institutions, is key to tailoring effective tuition incentive programs. This article explores the financial implications of different educational paths, common misconceptions about incentives, and the crucial role of transparency and accessibility in encouraging enrollment.
Understanding Parent Concerns

Parents considering higher education for their children often face a complex web of anxieties and financial pressures. Tuition costs are a significant factor, and this often leads to uncertainty and a need for comprehensive information. The decision to invest in a child’s future education is deeply personal, influenced by individual financial situations, family values, and the perceived value of different educational paths.
Tuition incentives are a great way to ease the financial burden on parents considering a school, especially when costs are a major factor. To attract prospective students and their families, schools could explore creative digital marketing strategies like the ones detailed in this helpful article on 5 easy digital marketing ideas holidays. These tactics, tailored to the holiday season, could effectively highlight the value proposition of the school and further solidify the school’s position as an excellent choice, ultimately encouraging those on the fence to enroll.
Parental Anxieties Regarding Tuition Costs
The escalating cost of higher education is a significant source of anxiety for many parents. Tuition fees, coupled with other expenses like room and board, textbooks, and potential living costs, can quickly become overwhelming. This financial burden often leads to hesitation and questioning of the long-term financial viability of pursuing higher education. The fear of accumulating substantial debt and its potential impact on future financial security is a common concern.
Financial Pressures Influencing Parental Decisions
Financial pressures significantly impact parental decisions regarding higher education. Factors like fluctuating incomes, existing debts, and the need to support other family members contribute to the financial strain. The perceived return on investment (ROI) for higher education is often carefully assessed. Parents may consider the potential career opportunities and earning potential associated with different degree programs and institutions.
Diverse Family Financial Situations, Tuition incentives to keep costs low for on the fence parents
Families come from diverse financial backgrounds. Some families have substantial savings and readily available resources to support their children’s education, while others face significant financial constraints. Single-parent families, families with multiple children, and those experiencing economic hardship face unique challenges. The ability to afford higher education varies widely depending on the individual family’s financial situation.
Common Misconceptions Surrounding Tuition Incentives
Several misconceptions surround tuition incentives. Some parents may believe that incentives are limited or only available to specific demographics. Others may misunderstand the eligibility criteria or the terms and conditions associated with the incentives. It is crucial to dispel these misconceptions and provide accurate information to empower parents in making informed decisions.
Comparing Educational Paths
| Factor | Public Institution | Private Institution |
|---|---|---|
| Tuition Costs | Generally lower, varying by state and program. | Generally higher, often with more specialized programs and facilities. |
| Financial Aid Availability | Often more extensive financial aid packages available. | May have specific financial aid programs, but the availability and amount might differ. |
| Faculty Qualifications | Highly variable; some may be less experienced or have fewer research opportunities than at private institutions. | Often professors with substantial research experience and prestigious academic affiliations. |
| Student Support Services | Generally available but may vary by institution and program. | Often extensive and tailored support services for students, like career counseling, tutoring, and academic advising. |
The table above presents a general comparison of the costs and benefits associated with public and private institutions. Specific figures and details will vary significantly based on the individual institution, program, and location. The decision should be tailored to the individual needs and financial resources of the family.
Types of Tuition Incentives
Tuition incentives are crucial for attracting and retaining students, especially in competitive educational markets. They offer a valuable means of bridging the financial gap for families, thereby making higher education more accessible and affordable. These incentives can take various forms, catering to diverse financial needs and circumstances. Understanding these different models is essential for both institutions and prospective students alike.
Tuition Waivers and Scholarships
Tuition waivers and scholarships are direct financial aid aimed at reducing or eliminating tuition costs. These are frequently awarded based on academic merit, financial need, or specific program areas. A robust scholarship program can significantly impact the institution’s ability to attract high-achieving students and cultivate a diverse student body.
- Academic Merit-Based Scholarships: These scholarships recognize exceptional academic performance, demonstrated through high grades, standardized test scores, or participation in extracurricular activities. Eligibility criteria typically involve meeting specific academic thresholds, such as GPA requirements or test score benchmarks. The financial benefits vary widely depending on the scholarship amount, ranging from partial to full tuition coverage. Limitations may include the scholarship’s duration or a requirement to maintain a specific GPA.
- Need-Based Scholarships: These scholarships are awarded to students demonstrating financial need, typically assessed through financial aid applications. Eligibility criteria often include demonstrating a specific level of financial hardship and fulfilling application requirements. Financial benefits can range from a small amount to a full tuition waiver, often dependent on the student’s demonstrated need. Limitations might include annual renewal or the availability of funding based on the scholarship’s budget.
- Program-Specific Scholarships: These scholarships are often tailored to students pursuing particular majors or programs. Eligibility often focuses on demonstrated interest in a specific field, or a commitment to a particular area of study. The financial benefits vary depending on the scholarship’s value, which could be a small amount or a significant reduction in tuition fees. Limitations may include specific course requirements or participation in related activities.
Financial Aid Packages
Financial aid packages are comprehensive approaches to financial support that combine multiple forms of assistance. They consider a student’s financial need and academic merit. A well-structured package can offer significant financial relief and encourage students to pursue their chosen field of study.
- Grants: Grants are awarded based on financial need and may not require repayment. Eligibility criteria typically involve demonstrating financial need through a standardized application process. Financial benefits can range from small amounts to substantial support, reducing the overall cost of tuition and associated fees. Limitations might involve the availability of funding, eligibility requirements, or the need to maintain a minimum GPA.
- Loans: Loans provide financial assistance, but require repayment. Eligibility criteria often involve creditworthiness and meeting specific requirements Artikeld by the lender. Financial benefits can range from partial to full tuition coverage, potentially covering additional living expenses. Limitations include interest rates and repayment schedules, potentially leading to significant long-term financial obligations.
- Work-Study Programs: These programs provide part-time employment opportunities for students, enabling them to earn money to contribute towards their education. Eligibility criteria usually include financial need and the willingness to work a specified number of hours per week. Financial benefits involve earned income, reducing the overall tuition burden. Limitations may include limited work hours, the availability of positions, and the necessity to balance work and studies.
Tuition Discounts and Payment Plans
Tuition discounts and payment plans are designed to offer flexibility and affordability. They are often beneficial for students, offering a means of reducing tuition costs or allowing for more manageable payment schedules.
- Early Bird Discounts: These discounts incentivize early enrollment, potentially offering significant savings. Eligibility criteria usually involve registering for classes before a specific deadline. Financial benefits often involve a percentage reduction in tuition fees. Limitations might include the discount’s duration or the necessity to meet specific registration requirements.
- Family Discounts: These discounts provide financial incentives for families enrolling multiple students. Eligibility criteria may include enrollment of multiple family members at the same institution or program. Financial benefits can range from a percentage reduction in tuition to a fixed amount off per student. Limitations might involve a maximum discount amount or the requirement to be a direct family member.
- Payment Plans: These options allow students to pay their tuition fees in installments. Eligibility criteria are typically related to the student’s financial standing and meeting the payment plan’s terms. Financial benefits involve spreading the cost of tuition, reducing the burden of a large lump-sum payment. Limitations might include interest charges, penalties for late payments, or a maximum installment period.
Table of Tuition Assistance Programs
| Program Type | Eligibility Criteria | Financial Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Academic Merit Scholarships | High GPA, standardized test scores | Partial or full tuition coverage | Scholarship duration, GPA maintenance |
| Need-Based Scholarships | Financial need assessment | Partial or full tuition coverage | Annual renewal, funding availability |
| Financial Aid Packages | Financial need, academic merit | Combination of grants, loans, and work-study | Loan repayment, grant eligibility |
| Tuition Discounts | Early enrollment, multiple family members | Percentage reduction in tuition | Discount duration, registration requirements |
| Payment Plans | Financial standing, meeting payment terms | Installment payments | Interest charges, late payment penalties |
Impact of Incentives on Enrollment Decisions: Tuition Incentives To Keep Costs Low For On The Fence Parents
Tuition incentives, designed to make higher education more accessible, play a crucial role in shaping parental decisions. Parents often weigh various factors, including financial constraints, educational opportunities, and perceived value, when choosing institutions for their children. Incentives, therefore, serve as a significant catalyst in this decision-making process, potentially shifting enrollment preferences towards institutions offering these benefits.Incentives act as a powerful tool for attracting prospective students and their families.
By directly addressing the financial burden associated with higher education, they can sway parents toward institutions that provide these attractive options. These incentives often encourage families to consider institutions they might have previously overlooked due to cost concerns.
Influence on Parental Decisions
Parental decisions regarding educational choices are often driven by a combination of factors, including financial considerations, academic reputation, and perceived value. Tuition incentives directly impact the financial aspect, making certain institutions more attractive than others. Families will often prioritize institutions that offer substantial financial relief, and this prioritization is often directly correlated with the incentive value offered. The potential for savings, in turn, can influence parents to consider institutions they may not have otherwise considered.
Examples of Successful Implementations
Several institutions have successfully leveraged tuition incentives to attract students and bolster enrollment. For example, community colleges frequently offer reduced tuition rates or specialized scholarships for local residents, demonstrating a clear correlation between incentive and enrollment. Similarly, some universities have implemented merit-based scholarships and need-based aid programs, which can also serve as significant incentives. These programs are particularly effective in attracting students from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds.
Correlation Between Incentive Value and Enrollment Rates
A clear correlation often exists between the value of tuition incentives and enrollment rates. Institutions that offer substantial financial aid packages tend to see higher enrollment rates compared to those offering minimal or no incentives. However, the precise relationship is complex and depends on several factors, including the overall cost of attendance, the perceived value of the institution, and the marketing strategy employed by the institution.
Further research is often needed to establish precise metrics, and different institutions may see different results based on their specific circumstances.
Impact on Student Body Demographics
Tuition incentives can have a profound impact on the overall student body demographics. By making higher education more affordable, these incentives can attract students from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. This can lead to a more inclusive and representative student body, which benefits both the students and the institution. Incentives can also attract students from areas where educational opportunities are traditionally limited, potentially broadening the range of perspectives and experiences within the institution.
Tuition Costs and Enrollment Rates
The following graph illustrates the relationship between tuition costs and enrollment rates. The horizontal axis represents the tuition cost per year, and the vertical axis represents the enrollment rate. A negative correlation is often observed, indicating that as tuition costs increase, enrollment rates tend to decrease.
(Graph placeholder: A hypothetical graph showing a negative correlation between tuition cost and enrollment rate. The graph would be visually clear and show a downward trend.)
While this is a general trend, it is important to note that other factors such as reputation, location, and program offerings also influence enrollment decisions.
Designing Effective Incentive Programs
Tuition incentives can be powerful tools to attract and retain students, especially when prospective families are on the fence. Crafting programs that are transparent, accessible, and appealing to a diverse range of parents is crucial for maximizing their impact. These programs should not only be well-designed but also evaluated regularly to ensure they remain effective over time.Designing effective tuition incentive programs goes beyond simply offering discounts.
It requires a deep understanding of parent concerns and a strategic approach to program design. Transparency in communication, clarity in program structure, and ease of application are all vital components. A robust evaluation process allows the institution to adapt and refine the program based on real-world data. Furthermore, diverse financial aid models should be considered to cater to a broader range of financial situations.
Transparency and Clarity in Incentive Programs
Transparency in tuition incentive programs is paramount. Parents need to understand the specific terms and conditions, eligibility criteria, and the program’s overall structure. Clearly outlining the incentive’s value, the duration it’s available, and any associated limitations builds trust and fosters a clear understanding. Vague or complex terms can lead to confusion and mistrust, which can ultimately reduce the program’s effectiveness.
Tuition incentives are a fantastic way to lower costs for parents considering higher education options. Understanding how these incentives work is key, and knowing how to use them effectively is crucial. This often involves digging into the details of technical SEO, which is a vital part of marketing for educational institutions. What is technical SEO and how it can help institutions reach prospective students is a complex subject, but ultimately helps in attracting more students, which can lead to more tuition incentives.
Ultimately, the goal is to make higher education more accessible, and tuition incentives are a big part of that.
Providing easily accessible information, such as a dedicated webpage or FAQ section, can significantly improve transparency.
Structuring Incentives for Broad Appeal
Tuition incentive programs should be designed with a broad range of parent demographics in mind. This might involve offering various levels of discounts or incentives based on factors like family size, income, or length of enrollment. For instance, a tiered discount system based on enrollment years could incentivize long-term commitment. Consider offering different payment plans, such as flexible installment options, to address financial constraints.
Additionally, offering incentives for specific program areas (e.g., scholarships for students in high-demand fields) can create a more targeted approach.
Accessibility and Ease of Application
The application process for tuition incentives must be straightforward and accessible. Complex paperwork, stringent requirements, or lengthy wait times can deter potential applicants. The application process should be designed to be user-friendly, using clear language and concise instructions. Digital platforms can be leveraged to make the application process easier, faster, and more accessible to a wider audience.
Tuition incentives are a great way to lower the financial barrier for parents considering higher education. Understanding the true cost of educational investments, like the often hidden costs of salesforce consulting services, real cost of salesforce consulting services , is crucial for making informed decisions. Ultimately, these incentives help make post-secondary education more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Providing multiple application methods (online, by phone, in person) also caters to diverse preferences and circumstances.
Incorporating Diverse Financial Aid Models
Tuition incentive programs should consider incorporating various financial aid models to better address the financial needs of prospective students. This could involve partnerships with existing financial aid organizations or the development of novel programs. Scholarships, grants, and loans should be explored as components of the overall financial aid package, alongside tuition incentives. Offering a combination of aid types can significantly increase the program’s reach and support a wider range of families.
Evaluating Incentive Program Effectiveness
Evaluating the effectiveness of tuition incentive programs over time is essential for continuous improvement. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be established and tracked regularly. This might include metrics such as enrollment increases, retention rates, and parent satisfaction. Regular surveys and feedback mechanisms from parents can provide valuable insights into the program’s strengths and weaknesses. Data analysis should be used to identify areas for improvement and to refine the program based on real-world results.
Collecting feedback directly from parents and students is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of the incentive.
Key Elements of a Successful Tuition Incentive Program
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Transparency | Clear communication of terms, conditions, and eligibility criteria. |
| Clarity | Concise and user-friendly program structure with easy-to-understand language. |
| Accessibility | Multiple application methods, digital platforms, and simplified processes. |
| Broad Appeal | Different levels of incentives tailored to diverse family situations. |
| Financial Aid Integration | Partnership with financial aid organizations and diverse aid models. |
| Evaluation | Regular tracking of KPIs, parent feedback, and data analysis. |
Communication Strategies for Parents
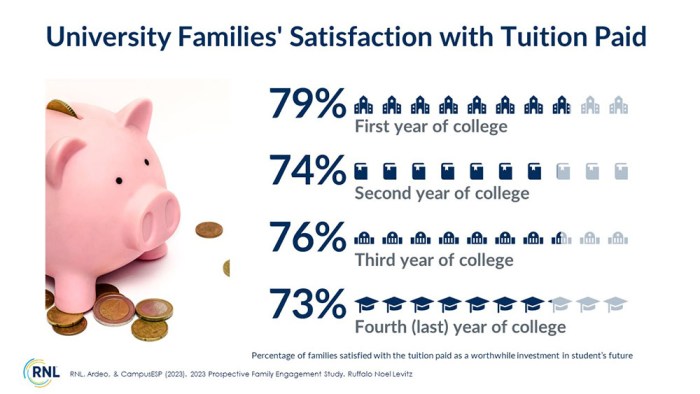
Reaching out to prospective parents is crucial in highlighting the value of tuition incentives. Effective communication fosters trust and understanding, ultimately influencing enrollment decisions. A well-structured approach, incorporating various channels and tailored messages, can significantly impact parent perceptions and make the institution stand out.
Effective Communication Channels
Clear and consistent communication across multiple platforms is essential. This includes not only direct mail and email campaigns but also leveraging social media platforms and engaging with parents through virtual events. Targeted advertisements on platforms frequented by parents of prospective students can significantly enhance visibility and generate interest.
Tailoring Messages to Parent Demographics
Different parent demographics respond to various communication styles. Understanding these nuances is vital for crafting effective messaging. For example, parents actively involved in their children’s education might respond better to detailed information on academic outcomes and the long-term benefits of the program. Parents seeking financial assistance might be more receptive to concise summaries of the incentive programs and eligibility requirements.
Tailoring the message ensures a more personal touch, increasing the likelihood of resonating with each demographic.
Highlighting Benefits with Marketing Materials
Using compelling marketing materials is crucial. Brochures and flyers should clearly explain the tuition incentives, highlighting the financial relief they offer. Include testimonials from satisfied families to build trust and credibility. Consider interactive online resources, such as websites and landing pages dedicated to the incentive programs, with clear calls to action. For example, a dedicated landing page could showcase various incentive packages with detailed descriptions, estimated savings, and application instructions.
A well-designed infographic could also visually present the financial benefits of choosing the institution.
Clear and Concise Information on Eligibility and Application
Providing clear and concise information about incentive eligibility and application is paramount. Create a dedicated FAQ section on the website to address common questions. A table summarizing the requirements for each incentive program, outlining eligibility criteria and application procedures, can simplify the process for parents. Use easily digestible language, avoiding jargon and technical terms. Use bullet points and short paragraphs to present information in a clear and straightforward manner.
Visual Aid for Application Process
A visual aid, such as a flowchart, can significantly simplify the application process for parents. This flowchart should clearly guide parents through each step, from initial inquiry to submitting the application. Each step should be clearly labeled, with specific instructions and deadlines. For example, the flowchart could illustrate the application process, outlining required documents, deadlines, and contact information for support.
This visual approach simplifies complex information, enhancing comprehension and reducing confusion.
| Step | Description | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Inquiry | Contact the admissions office to learn more about incentives. | Immediately |
| 2. Application | Complete the application form, including all required documents. | Within 10 business days |
| 3. Review | The admissions office will review the application and provide feedback. | Within 2 weeks |
| 4. Approval | If eligible, the incentive will be applied to the tuition bill. | Within 2 weeks |
Long-Term Effects and Sustainability
Tuition incentive programs, when implemented thoughtfully, can have a profound and lasting impact on both institutions and the students they serve. Beyond the immediate enrollment boost, these programs can contribute to long-term financial stability for students, reshape the educational landscape, and foster a more equitable and accessible system. Understanding the potential long-term effects is crucial for designing programs that are not only successful in the short term but also sustainable for years to come.Incentive programs can foster a cycle of student success by lowering the financial barriers to higher education.
This, in turn, can lead to improved graduation rates and increased earning potential for graduates, potentially benefiting the overall economy. Successful programs demonstrate a commitment to making higher education more accessible and affordable, which often translates into increased student satisfaction and retention.
Long-Term Financial Stability for Students
Tuition incentive programs can significantly reduce the financial burden of higher education for students, especially those from lower-income backgrounds. This can translate into reduced student loan debt, allowing students to enter the workforce with less financial strain and potentially more disposable income. Examples include successful programs at community colleges that have seen a significant increase in the number of students from disadvantaged backgrounds completing degrees.
These programs have demonstrably assisted students in achieving their academic goals without crippling debt. This is a key factor in creating a more equitable educational system.
Impact on Institutional Financial Stability
Tuition incentives, while potentially decreasing revenue from tuition in the short term, can lead to increased enrollment and, ultimately, long-term financial stability for institutions. This increase in enrollment often leads to a larger pool of students to draw from for other revenue streams, such as campus-based businesses and services, and can also foster a more diverse student body, enriching the overall campus experience.
Increased retention and graduation rates, in turn, further solidify the financial viability of the institution in the long run.
Reshaping the Educational Landscape
Incentive programs can be a catalyst for change within the broader educational landscape. By encouraging more students to pursue higher education, these programs can contribute to a more skilled workforce and a more competitive economy. The programs can lead to a more diverse and inclusive student body, which can benefit both the student and the institution through a broader range of perspectives and experiences.
Strategies for Sustainability
Ensuring the long-term sustainability of tuition incentive programs requires careful planning and evaluation. One key strategy is to explore alternative funding sources to offset the potential reduction in tuition revenue. This could involve partnerships with state or local governments, corporate sponsorships, or philanthropic donations. Regular program evaluation is also essential to assess the program’s effectiveness and make adjustments as needed.
This continuous monitoring allows for the adaptation of the program to meet evolving needs and circumstances.
Table: Long-Term Impacts of Tuition Incentives
| Aspect | Impact on Students | Impact on Institutions |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Stability | Reduced student loan debt, increased earning potential | Potential for increased enrollment, diversified student body, and long-term financial viability |
| Educational Attainment | Increased graduation rates, enhanced student success | Stronger reputation, improved community engagement |
| Equity and Access | Greater access to higher education for disadvantaged students | More diverse student body, broader community impact |
| Overall Impact | Improved overall economic outlook for graduates | Enhanced long-term financial stability, sustainable growth |
Final Summary
In conclusion, tuition incentives are vital for attracting students to higher education while addressing the financial anxieties of parents. Successful programs must be transparent, accessible, and tailored to the diverse needs of prospective students and families. Ultimately, effective communication, a well-structured incentive program, and a clear understanding of long-term impacts will be key to supporting students and institutions alike.