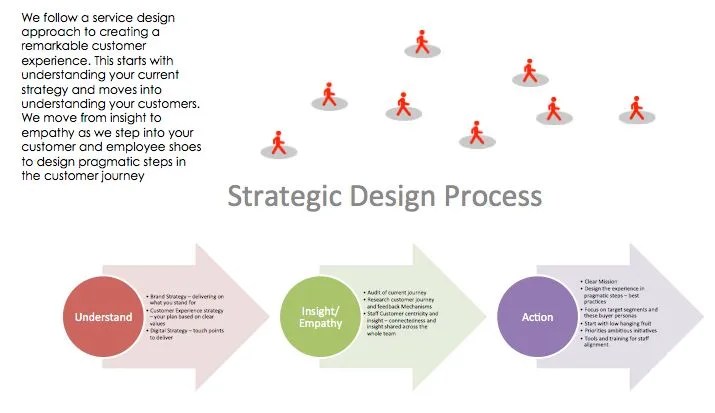
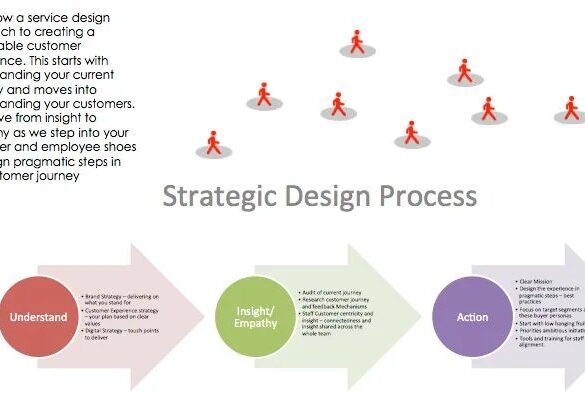
Strategic design in the professional services is transforming how firms approach client needs and market positioning. This guide delves into the core principles, processes, and tools used to craft impactful design solutions tailored to the complexities of professional service sectors like law, consulting, and finance. We’ll explore how aligning design with overall business strategy can drive growth and enhance client experiences.
The document covers everything from defining strategic design within professional services to outlining a typical design process. It also explores the tools and techniques utilized, the methods for measuring impact, and the challenges involved in implementation, all with examples from various professional service sectors. We’ll conclude with an outlook on future trends in this dynamic field.
Defining Strategic Design in Professional Services
Strategic design in professional services is more than just aesthetics; it’s a powerful tool for driving business outcomes. It’s a holistic approach that integrates design thinking principles with a firm’s core strategy to enhance client experience, improve internal processes, and ultimately, boost profitability. This goes beyond simply making things look good; it’s about creating solutions that are effective, efficient, and aligned with the specific needs of the client and the firm’s strategic objectives.This approach is critical for professional service firms, which often operate in complex, specialized environments.
Strategic design helps to deconstruct these complexities, translating them into actionable, user-centered solutions that increase efficiency and improve client satisfaction. It’s about designing not just for the product or service, but for the entire experience.
Defining Strategic Design
Strategic design in professional services is a discipline that utilizes design thinking methodologies to develop solutions that directly address strategic business objectives. It emphasizes a deep understanding of the client’s needs and the firm’s strategic goals to create solutions that are both effective and efficient. It’s a process that combines creativity with analytical rigor, focusing on tangible outcomes that contribute to the overall business success.
Key Characteristics of Strategic Design
Strategic design in professional services differs from other design approaches due to its strong emphasis on alignment with business strategy. It’s not merely about aesthetics; it’s about achieving specific business goals. Key distinguishing characteristics include:
- Focus on Measurable Outcomes: Strategic design initiatives are carefully structured to yield quantifiable results. For example, improved client retention rates, increased efficiency in internal processes, or higher profitability. This contrasts with traditional design, which might prioritize aesthetic appeal over tangible impact.
- Alignment with Business Strategy: Strategic design projects are always tied to the firm’s overall business strategy. This means the design solutions must contribute to the firm’s long-term objectives, whether that’s expanding into new markets, developing a new service line, or improving existing offerings.
- Emphasis on User-Centricity: Understanding and meeting client needs is paramount. Strategic design goes beyond superficial understanding to delve into the motivations, behaviors, and expectations of clients. This ensures the design is tailored to the client’s needs and context.
- Process-Oriented Approach: Strategic design is a structured process, incorporating research, prototyping, testing, and iteration. This iterative approach allows for continuous improvement and ensures the final solution effectively meets the needs identified in the research.
Importance of Alignment with Business Strategy
Aligning design with business strategy is critical for the success of any professional services firm. By creating solutions that directly address strategic objectives, the firm can increase efficiency, enhance client experience, and drive profitability. Aligning design with the firm’s overall strategy avoids the pitfall of creating solutions that are aesthetically pleasing but fail to contribute to the core business goals.
Role of Design Thinking
Design thinking plays a vital role in shaping strategic design initiatives. It provides a framework for understanding complex problems, identifying unmet needs, and generating innovative solutions. The iterative process within design thinking allows for constant refinement and adaptation to ensure the final product or service effectively addresses the identified needs.
Examples of Application in Various Sectors
Strategic design principles are applied across various professional service sectors. In the legal field, strategic design might be used to streamline case management systems, improve client communication channels, or create a more user-friendly website. In consulting, it could involve developing visually appealing presentations, creating interactive dashboards for data analysis, or designing client onboarding processes. Finance firms can use strategic design to improve investment portfolio visualization, create intuitive financial planning tools, or design customer onboarding workflows that are both user-friendly and secure.
Strategic Design Process in Professional Services: Strategic Design In The Professional Services
Strategic design in professional services isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s about crafting a solution that aligns perfectly with a client’s business objectives. This involves a structured process that considers the unique challenges and opportunities within the professional services landscape. The process, from initial assessment to final implementation, demands a deep understanding of the client’s needs and a flexible approach to adapt to evolving requirements.
A well-defined strategic design process for professional services firms ensures that projects are not only successful but also exceed client expectations. It provides a roadmap for navigating the complexities of client needs, ensuring a strong return on investment (ROI) and long-term value for both the client and the firm.
Typical Strategic Design Process
A typical strategic design process for professional services firms often comprises four key phases. Each phase is crucial and builds upon the preceding one, ensuring a cohesive and effective solution. These phases allow for adjustments and iterations, fostering a collaborative environment between the firm and the client.
Initial Assessment
The initial assessment phase focuses on understanding the client’s current situation and future aspirations. This involves in-depth stakeholder interviews, thorough market analysis, and competitive landscape evaluation. Key stakeholders include clients, internal teams, and potential users. These interviews aim to uncover the client’s pain points, desired outcomes, and expectations for the design solution. The market analysis examines industry trends, competitor strategies, and emerging technologies.
By gathering this comprehensive information, a clear project brief and design vision are developed, forming the foundation for the subsequent stages.
Strategy Development
Building upon the initial assessment, the strategy development phase involves collaborative workshops and in-depth analysis. These workshops, involving key stakeholders, help refine the project vision, explore potential solutions, and identify the most effective strategies. Competitor analysis identifies areas of strength and weakness, helping to pinpoint opportunities for differentiation and value creation. The output of this phase is a strategic design roadmap that Artikels the proposed solutions, timelines, and resource allocation.
This roadmap provides a shared understanding of the project’s direction.
Design Implementation
The design implementation phase focuses on translating the strategic roadmap into tangible deliverables. This involves prototyping, rigorous testing, and iterative refinement. Prototypes allow for early testing and feedback, ensuring the solution aligns with user needs and expectations. Testing methodologies are employed to assess usability, functionality, and overall effectiveness. This iterative approach allows for continuous improvement and adjustments based on client feedback.
The result of this phase is a finalized design specification document that provides detailed instructions for the implementation team.
Deployment & Monitoring
The final phase, deployment and monitoring, focuses on successfully launching the designed solution and tracking its performance. This includes comprehensive training for client staff on the new system or process. A crucial aspect of this phase is establishing robust feedback mechanisms to capture client experience and identify areas for improvement. Monitoring performance metrics helps identify areas where adjustments are needed.
Strategic design in professional services is crucial for standing out. Knowing how to effectively present information is key, and that includes knowing how to highlight text in your WordPress posts. Learning how to properly highlight key points, like using how to highlight text in wordpress , can greatly enhance your client engagement and make your content more digestible.
This ultimately strengthens your strategic design approach.
This phase ensures a smooth transition and ongoing value realization for the client.
Key Phases and Deliverables
| Phase | Activities | Deliverables | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Assessment | Stakeholder interviews, market analysis, competitor analysis | Project brief, design vision, project scope | 2-4 weeks |
| Strategy Development | Design workshops, SWOT analysis, solution prioritization | Strategic design roadmap, project plan | 4-6 weeks |
| Design Implementation | Prototyping, user testing, design refinement | Final design specifications, user manuals | 6-8 weeks |
| Deployment & Monitoring | Training, launch, performance tracking, feedback collection | Feedback mechanisms, ongoing support | 8+ weeks |
Tools and Techniques for Strategic Design
Strategic design in professional services goes beyond simply creating aesthetically pleasing materials. It’s about understanding the deep-seated needs and motivations of clients and crafting solutions that deliver measurable value. This involves employing a range of tools and techniques that facilitate a clear understanding of the landscape, the client’s pain points, and the desired outcomes. Effective strategic design in this sector necessitates a blend of analytical rigor and creative problem-solving.Effective strategic design in professional services requires a thorough understanding of the client’s needs and challenges.
This understanding can be achieved through a variety of tools and techniques that provide valuable insights into the intricacies of the service delivery process. Employing user-centered design principles ensures that the design solutions resonate with the target audience and address their specific needs effectively.
User Research and Insights Gathering
Gathering insights from target users is crucial for creating effective and valuable solutions. This includes understanding their needs, identifying pain points, and understanding their motivations. Direct engagement with potential and current clients is key to developing a nuanced understanding of the service landscape. This can be achieved through various methods like user interviews, surveys, and focus groups.
Strategic design is key in professional services, especially for firms looking to stand out. Take Northwood Construction, for example; they’ve clearly nailed their strategy, becoming a local hero by focusing on community engagement and high-quality work, as detailed in their inspiring story how northwood construction became a local hero. This demonstrates how a well-defined approach to design can translate into real-world success and build a strong brand reputation within the professional services industry.
The insights gleaned from these methods form the bedrock of effective strategic design.
Digital Tools for Design Support
Digital tools play a critical role in facilitating the strategic design process. They streamline the workflow, enhance collaboration, and provide powerful visualization capabilities. Examples of these tools include collaborative platforms for project management, design software for creating prototypes and wireframes, and data visualization tools for presenting insights.
Application of Design Principles
Applying design principles, such as user-centered design, is essential in professional services. User-centered design ensures that the design solutions are tailored to meet the specific needs and preferences of the target audience. This approach involves actively involving users in the design process, gathering their feedback, and iterating on solutions based on their input. By placing the user at the heart of the design process, the resulting solutions are more likely to be effective and valuable.
Comparison of Methodologies
Various methodologies are employed in strategic design, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Agile methodologies, for example, emphasize iterative development and flexibility, while Lean methodologies focus on eliminating waste and maximizing efficiency. The choice of methodology depends on the specific project goals, the nature of the client, and the resources available. Each approach offers a unique perspective and set of tools for tackling design challenges.
Design Tools and Techniques in Professional Services
A range of tools and techniques are utilized in strategic design for professional services, each serving a specific purpose. The appropriate tools and techniques should be carefully selected based on the project’s specific needs. Their application can be illustrated by their usage in specific scenarios, as detailed in the table below.
| Tool/Technique | Description | Application in Professional Services | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| User Interviews | Gathering insights from target users through one-on-one conversations. | Understanding client needs, identifying pain points, and uncovering unmet expectations. | Interviewing potential clients to gather their perspectives on existing services and identify areas for improvement. |
| Personas | Representing user groups with detailed profiles, encompassing their needs, motivations, and behaviors. | Creating empathetic design solutions by embodying the client’s perspective. | Developing a persona for a specific segment of clients, for example, “The Budget-Conscious Entrepreneur,” to tailor solutions to their unique needs. |
| Journey Mapping | Visualizing the user’s experience through a service or product. | Identifying opportunities for improvement in the client’s experience, from initial contact to final outcome. | Mapping the client’s journey through the service process, highlighting pain points and areas for enhancement. |
| Competitive Analysis | Examining the offerings and strategies of competitors to identify opportunities and gaps in the market. | Gaining insights into the competitive landscape, benchmarking against industry leaders, and understanding differentiation strategies. | Analyzing competitor offerings to identify unique selling propositions and develop competitive advantages. |
Measuring the Impact of Strategic Design
Strategic design in professional services isn’t just about creating visually appealing deliverables; it’s about driving tangible business value. Effective measurement is crucial to demonstrate the return on investment (ROI) and justify future design initiatives. This involves understanding the specific goals and objectives of the design project and aligning metrics to track progress and success.Measuring the impact of strategic design requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond simple aesthetics.
Strategic design in professional services is crucial for attracting and retaining clients. A key part of that design often involves updating your website’s content, and if you’re using a Just Another WordPress site, learning how to easily change the text is a must. Check out this helpful guide on how to easily change the just another WordPress site text for a straightforward walkthrough.
By implementing these changes, you’ll be able to fine-tune your website’s message to resonate with your target audience, which is a significant component of effective strategic design.
It necessitates a clear understanding of how design choices translate into quantifiable results, such as increased efficiency, improved client satisfaction, or enhanced profitability. By meticulously tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), businesses can build a strong case for the value of design-led strategies.
Metrics and KPIs for Design Effectiveness
Understanding the metrics and KPIs relevant to a specific design initiative is paramount. This requires careful consideration of the project’s goals and how design elements contribute to achieving those objectives. For instance, a design focused on streamlining internal processes might measure efficiency gains in terms of reduced time spent on tasks or improved task completion rates.
- Client Satisfaction: Surveys, feedback forms, and Net Promoter Scores (NPS) provide valuable insights into client satisfaction with design-related services. Higher scores indicate improved client experience and loyalty.
- Employee Engagement: Improved workflow design can positively influence employee morale and engagement. Tracking metrics such as employee satisfaction surveys, retention rates, and reduced employee turnover can demonstrate the positive impact of design on the internal work environment.
- Efficiency Gains: Reduced processing time, streamlined workflows, and improved task completion rates are all quantifiable indicators of increased efficiency. Tools like time tracking software can be invaluable for this kind of analysis.
- Cost Savings: Strategic design can lead to cost savings through improved resource allocation, optimized processes, and reduced errors. This can be measured through comparative financial data from before and after the design implementation.
Evaluating Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculating ROI for strategic design projects is essential for demonstrating their value to stakeholders. The calculation often involves comparing the costs of the design project against the benefits it generates.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: This method involves identifying all costs associated with the design project (e.g., design fees, development time) and comparing them to the quantifiable benefits derived (e.g., increased revenue, reduced operational costs). The result, often expressed as a percentage, demonstrates the return on investment.
- Projected Revenue Growth: Strategic design can positively influence revenue streams by increasing customer engagement, conversion rates, or market share. Projecting future revenue growth, based on design-driven improvements, can highlight the potential ROI.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Streamlined processes, improved efficiency, and reduced errors can lead to substantial cost reductions. Comparing pre- and post-design operational costs can illustrate the financial impact.
Tracking and Analyzing Data Related to Design Outcomes
A structured approach to data collection and analysis is essential for assessing design impact. Regular monitoring and analysis of data allow for adjustments to the design process and the optimization of results.
- Data Collection Methods: A combination of quantitative and qualitative methods is typically most effective. Quantitative methods, like surveys and data analytics, provide numerical data, while qualitative methods, like interviews and focus groups, offer insights into the user experience and feedback.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Specific KPIs should be established at the outset of the design project, aligned with the project’s goals. These KPIs should be measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART goals). Examples of KPIs include client satisfaction scores, conversion rates, and customer retention rates.
- Regular Reporting: Regular reports, summarizing the performance of the design initiative, provide an up-to-date view of progress and impact. These reports should include data visualizations (graphs, charts) for effective communication of key trends.
Examples of Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection Methods
Choosing appropriate data collection methods is crucial for accurate and comprehensive evaluation.
- Quantitative Methods: Surveys, A/B testing, clickstream analysis, and website analytics are examples of quantitative methods. These methods provide numerical data that can be statistically analyzed to determine the effectiveness of design changes.
- Qualitative Methods: Interviews, focus groups, usability testing, and user feedback forms are examples of qualitative methods. These methods offer valuable insights into user perceptions, experiences, and feedback on design choices.
Challenges and Considerations in Strategic Design
Strategic design, while offering significant potential for professional services firms, faces inherent challenges. Successfully implementing a strategic design approach requires a deep understanding of these obstacles and proactive strategies for overcoming them. This section delves into common hurdles, the importance of cultural alignment, and methods for fostering a design-centric culture within professional services organizations.Understanding the nuances of these challenges is crucial for successful strategic design implementation, allowing firms to adapt and optimize their approach for maximum impact.
Addressing these obstacles head-on empowers firms to leverage design thinking for lasting competitive advantage.
Common Challenges in Implementing Strategic Design
Successfully integrating strategic design into a professional services firm’s operations often encounters obstacles stemming from organizational structure, culture, and individual resistance to change. Overcoming these obstacles is critical for achieving desired outcomes.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new design methodologies or tools, fearing disruption to established processes or concerns about skill gaps. This resistance can manifest in passive opposition or outright rejection of new approaches.
- Lack of Internal Buy-In: Without senior leadership endorsement and active participation, strategic design initiatives may struggle to gain traction and resources. This lack of buy-in can stifle the project’s progress and limit its potential impact.
- Cultural Misalignment: A firm’s existing culture might not be conducive to a design-focused approach. Values emphasizing efficiency, tradition, or a rigid hierarchical structure can impede the flexibility and creativity required for successful design implementation.
- Defining Design Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly outlining roles and responsibilities for design teams, and how they integrate with existing departments, is essential to avoid duplication of effort and ensure effective communication. Ambiguity in roles can lead to confusion and inefficiency.
- Measuring Design Impact: Quantifying the impact of design interventions can be challenging, particularly in professional services where intangible benefits are prevalent. Establishing clear metrics and demonstrating the return on investment is essential to securing ongoing support and investment.
Addressing Design-Related Challenges
This section Artikels a systematic approach to tackling challenges and fostering a design-focused culture. A structured process is vital to ensure effective problem-solving and long-term success.
- Identify the Challenge: Thoroughly document and understand the specific design-related obstacles facing the firm. This includes identifying the source and impact of the challenge.
- Analyze Root Cause: Dive deeper to understand the underlying reasons for the challenge. Is it a lack of resources, a skill gap, or cultural resistance? Identifying the root cause is essential for developing targeted solutions.
- Develop Solution: Generate creative and practical solutions to address the identified challenges. These solutions should be tailored to the firm’s specific context and aligned with its strategic goals.
- Implement Solution: Execute the chosen solution with a clear plan, assigning responsibilities, and establishing timelines. Communication and stakeholder engagement are critical during implementation.
- Evaluate Results: Monitor the effectiveness of the implemented solution. Use data and feedback to assess its impact on the firm’s design efforts.
- Close Loop/Iterate: Continuously refine the approach based on the evaluation results. Adapt and iterate on the solutions to improve their effectiveness and ensure ongoing alignment with the firm’s goals.
Flowchart for Addressing Design Challenges
The following flowchart illustrates a structured process for addressing design-related challenges in a professional services firm:
Future Trends in Strategic Design for Professional Services
Strategic design in professional services is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements, shifting client expectations, and a more competitive market landscape. This evolution demands a proactive approach, one that anticipates future trends and adapts design strategies accordingly. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for professional service firms to maintain a competitive edge and deliver value to clients in the years to come.The future of strategic design in professional services will be characterized by a heightened focus on user-centricity, leveraging technology to enhance efficiency and effectiveness, and a deeper understanding of emerging market dynamics.
Successful firms will not just adapt, but proactively shape the future by anticipating evolving client needs and integrating innovative design methodologies into their core operations.
Emerging Trends in Strategic Design
The field is seeing a convergence of design thinking principles with data-driven insights and AI-powered tools. This fusion enables a more precise and targeted approach to problem-solving, leading to more impactful and efficient strategic designs. Companies are now utilizing advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and trends in client data, allowing for more personalized and effective service delivery.
Role of Technology and Innovation
Technology plays a pivotal role in shaping future strategic design approaches. Cloud-based platforms, collaborative tools, and AI-powered analytics are transforming how firms gather, analyze, and act on client data. For instance, AI-driven tools can automate tasks like market research and competitive analysis, freeing up designers to focus on higher-level strategic thinking and creative problem-solving.
Potential Future Applications of Strategic Design
Strategic design in professional services can be applied to a wide range of areas. Imagine using design thinking to optimize internal processes, streamlining workflows and enhancing employee experience. Another application involves crafting client onboarding experiences that are seamless and intuitive, fostering stronger client relationships and loyalty. The design process can also be leveraged to create innovative solutions to complex industry challenges, leading to new revenue streams and competitive advantages.
Adapting to Evolving Client Expectations, Strategic design in the professional services
Clients today are increasingly demanding personalized and seamless experiences. They expect quick responses, clear communication, and solutions tailored to their specific needs. Professional service firms must adapt their design strategies to meet these expectations. For example, the use of interactive dashboards and personalized reporting tools can significantly improve client communication and transparency, fostering trust and satisfaction.
Anticipating Future Trends and Developing Proactive Design Strategies
Proactive design strategies are crucial for success in the future. This involves continuously monitoring industry trends, understanding emerging technologies, and proactively incorporating these elements into strategic design frameworks. Staying informed about the latest research and best practices in user experience (UX) design and human-centered design principles is paramount. Furthermore, fostering a culture of continuous learning and experimentation within the firm is essential for adapting to the evolving landscape and anticipating future challenges.
By proactively anticipating these trends, firms can develop strategies that position them for long-term success in the ever-changing professional services industry.
Last Point
In conclusion, strategic design in professional services is not just a trend, but a crucial aspect for success in today’s competitive landscape. By understanding the principles, process, and tools discussed, firms can gain a competitive edge by enhancing client experiences, driving revenue growth, and adapting to evolving market demands. This guide provides a roadmap for implementing effective strategic design strategies and navigating the challenges along the way.