Seo a b split testing 101 – A/B split testing 101 provides a comprehensive guide to optimizing your website’s search engine performance through data-driven experimentation. Learn how to use variations and control groups to identify what truly resonates with search engines and users. This guide will take you through the entire process, from setting up your tests to analyzing the results and implementing winning strategies.
We’ll cover everything from choosing the right metrics to implementing different types of tests, including practical examples and case studies. Understanding the common pitfalls and advanced strategies will help you avoid costly mistakes and maximize your efforts.
Introduction to A/B Split Testing
A/B split testing is a powerful method for comparing two versions of a webpage or marketing campaign to determine which performs better. It’s a cornerstone of optimizing online experiences and achieving better results. By systematically varying elements and tracking the impact on key metrics, businesses can identify the most effective strategies for their specific audience.This process involves creating two versions of a webpage (Variation A and Variation B), exposing each version to a different segment of the target audience, and analyzing the performance of each version based on specific metrics.
The goal is to understand which variation resonates most strongly with the target audience, leading to increased engagement, conversions, or other desired outcomes. The fundamental principle is to compare a new version (Variation B) against a proven, existing version (Variation A).
Understanding Variations and Control Groups
A/B testing hinges on the concept of variations and control groups. The control group, often Variation A, serves as the baseline for comparison. Variation B introduces a change, such as a different headline, button color, or layout. This systematic comparison allows businesses to isolate the effect of specific changes on user behavior.
Importance of Split Testing in
Split testing is crucial for because it enables data-driven optimization of website elements. By identifying which variations yield better results in terms of user engagement and conversion rates, businesses can optimize their content, structure, and overall site experience to attract and retain visitors. isn’t just about s; it’s about creating a website that resonates with users.
Key Metrics for A/B Testing in
A critical aspect of A/B testing is defining the metrics that will measure the success of each variation. These metrics will depend on the specific goals of the test. Common metrics include click-through rates (CTR), bounce rates, time on page, conversion rates, and organic traffic. A thorough understanding of these metrics is crucial for accurate interpretation of results.
Example A/B Test Setup
| Variation A | Variation B | Key Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Original website layout with standard call-to-action button | Revised layout with a more prominent call-to-action button | Click-through rate (CTR), Conversion rate, Time on page, Bounce rate |
In this example, Variation A represents the existing, established website layout, while Variation B introduces a revised layout with a more prominent call-to-action button. Tracking CTR, conversion rate, time on page, and bounce rate will reveal the impact of the change on user behavior.
Implementing A/B Tests
A/B testing is a crucial part of optimizing strategies. It allows you to compare different versions of your website elements to see which performs better. This iterative process helps you understand what resonates with your target audience and drives the best results in terms of search engine rankings and user engagement. By systematically testing variations, you can continuously refine your tactics to maximize their impact.Implementing A/B tests for requires careful planning and execution.
This involves identifying specific areas for improvement, creating variations, and choosing the right tools for measurement and analysis. The ultimate goal is to gain a data-driven understanding of what elements enhance your website’s visibility and user experience.
Methods for Implementing A/B Tests
Different methods can be used for A/B testing elements. These methods range from simple modifications to more complex setups, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The best method depends on the specific element being tested and the resources available. Some popular methods include modifying page titles, meta descriptions, headings, and image alt text.
Tools for Conducting A/B Tests in
Various tools are available for conducting A/B tests in . These tools offer different features and functionalities, making them suitable for different needs and budgets. The choice of tool often depends on the complexity of the tests, the volume of data to be analyzed, and the level of customization required.
- Google Optimize: A powerful tool from Google that allows you to A/B test various elements on your website, including meta descriptions, page titles, and other -related components. It integrates seamlessly with Google Analytics, providing comprehensive insights into user behavior and conversion rates. It’s a free option for basic testing and can be scaled up to handle more complex testing scenarios.
- VWO (Visual Website Optimizer): Another popular choice, VWO provides robust A/B testing capabilities. It offers a user-friendly interface and a wide array of features for advanced testing and analysis. VWO’s flexibility is helpful for testing different variations of page layouts, elements, and components. It provides more detailed reporting compared to some other tools.
- Optimizely: A highly sophisticated platform that empowers businesses to execute sophisticated A/B tests. Optimizely’s capabilities extend beyond simple tests, enabling businesses to conduct multivariate tests and personalization strategies. It provides advanced analytics and reporting tools for in-depth analysis.
Best Practices for Setting Up a Testing Environment
Establishing a robust testing environment is critical for reliable results. It involves careful planning and execution to ensure the test environment accurately reflects the production environment. This method helps minimize any external factors that might skew the results.
- Define Clear Objectives: Before starting any test, clearly define the goals and metrics you want to track. This clarity will guide your decisions throughout the testing process.
- Select Representative Traffic: Ensure that the traffic participating in the A/B test is representative of your target audience. This ensures that the results are meaningful and applicable to your overall marketing strategy.
- Control External Factors: Try to minimize any external factors that could influence the results of the test, such as changes in advertising campaigns or promotions. Maintaining a consistent testing environment helps avoid unexpected variables.
Creating Variations of Elements
Creating variations of elements requires careful consideration of different approaches. It’s crucial to identify areas for improvement and create variations that target specific improvements. This includes using different s, phrasing, and styles.
- Headlines: Experiment with different headline structures, lengths, and tones. Test headlines with strong calls to action or that highlight unique selling points.
- Meta Descriptions: Craft multiple meta descriptions with varying placements and language. Test different lengths and formats to see what performs best.
- Image Alt Text: Optimize image alt text with descriptive s that accurately reflect the image’s content. Test different variations to see which descriptions generate more clicks.
Tools Comparison Table
The following table summarizes the pros and cons of various A/B testing tools for :
| Tool | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Google Optimize | Free, integrated with Google Analytics, easy to use. | Limited advanced features compared to paid tools. |
| VWO | User-friendly interface, robust features, detailed reporting. | Higher cost compared to Google Optimize. |
| Optimizely | Advanced features, multivariate testing capabilities, robust analytics. | Most expensive option, steeper learning curve. |
Analyzing Results and Making Decisions
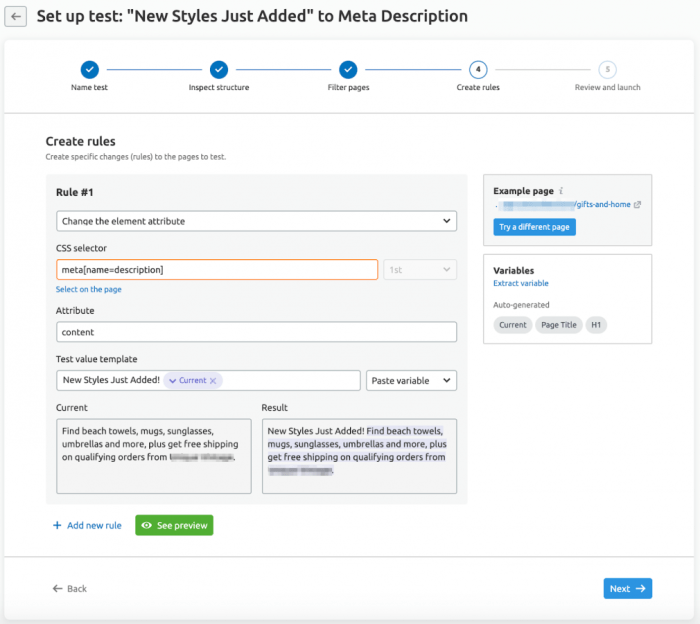
A/B testing for is about more than just running experiments; it’s about understanding the results and using them to optimize your website. This crucial step involves interpreting data, identifying statistically significant variations, and ultimately, deciding which changes to implement for improved performance. Successful A/B testing relies heavily on meticulous analysis.Thorough analysis of A/B test results allows you to identify patterns and trends that might otherwise be missed.
This analysis not only helps in deciding which variation is superior but also reveals insights into user behavior and preferences, which can be valuable in future strategies. Understanding statistical significance is paramount to avoid drawing conclusions based on random fluctuations.
Interpreting A/B Test Results for
Analyzing A/B test results involves scrutinizing key metrics to see if variations in your website’s content or design have impacted important metrics like organic traffic, rankings, time on page, and conversion rates. The goal is to understand whether a specific change, such as a new headline or meta description, has led to an improvement or decline in these metrics.
So, you’re diving into SEO A/B split testing 101? It’s all about tweaking your website to see what resonates best with users. With Google recently announcing plans to expand their Discover section on the desktop homepage, this expansion could significantly impact search results. This means understanding how users interact with that section is crucial for any successful SEO A/B split testing strategy.
Think about how those changes will influence click-through rates and organic traffic, and how you’ll adjust your approach accordingly.
A clear understanding of how these metrics correlate to your overall strategy is essential.
Determining Statistical Significance
To ensure that observed differences between variations aren’t due to chance, statistical significance must be established. Statistical tools calculate the probability that the observed difference in results between variations is not merely a random occurrence.
A common threshold for statistical significance is a p-value of 0.05. This means there’s only a 5% chance that the observed difference occurred by chance.
Using statistical significance helps prevent inaccurate conclusions. For example, if a variation shows a slight increase in traffic, but the difference isn’t statistically significant, implementing that change might not be worthwhile. Employing statistical methods helps filter out minor fluctuations and focus on meaningful improvements.
So, you’re diving into SEO A/B split testing 101? Knowing your WordPress platform inside and out is crucial for success. Check out the 11 best ways to learn WordPress before and after launching your blog for expert tips on mastering the platform, from basic navigation to advanced plugins. Once you’ve got your WordPress skills dialed in, you’ll be well-equipped to really nail those A/B split tests and boost your SEO results!
Identifying Better or Worse Variations
Once statistical significance is established, determining whether a variation is better or worse than the control involves comparing the key metrics. For example, if a variation resulted in a statistically significant increase in time on page, it’s likely a positive change. Conversely, a decrease in rankings after a variation might signal a negative impact. By focusing on metrics relevant to your objectives, you can make informed decisions.
Structured Reporting and Presentation of Results
A structured method for reporting A/B test results is crucial for effective communication and decision-making. A clear report should include the following:
- Test Objectives: Clearly state the goals of the A/B test.
- Methodology: Detail the methods used for the experiment, including sample size and duration.
- Results: Present a summary table with key metrics for both variations and the control group, including statistical significance (p-value).
- Analysis: Interpret the results, highlighting the impact on key metrics. Explain the reasons behind the variations.
- Recommendations: Suggest concrete actions based on the findings.
Sample A/B Test Result Table
This table illustrates a sample A/B test result, highlighting statistical significance and key metrics.
| Metric | Control | Variation A | Statistical Significance (p-value) | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Traffic (monthly) | 10,000 | 11,500 | 0.03 | +1,500 |
| Rankings (top 10) | 50 | 55 | 0.02 | +5 |
| Time on Page (average) | 2 minutes | 2.5 minutes | 0.01 | +0.5 minutes |
| Conversion Rate | 5% | 6% | 0.04 | +1% |
Key Elements for A/B Testing

A/B testing is a powerful tool for optimizing website performance, including . By systematically testing different versions of key elements, you can identify which variations resonate best with search engines and users, leading to improved rankings and increased organic traffic. This process requires careful consideration of the elements most likely to influence search engine algorithms and user behavior.Testing different elements is crucial for achieving optimal results in organic search.
Search engines constantly evolve, and user preferences shift. Understanding how these changes impact your site’s performance through A/B testing allows you to adapt your strategy to maintain a strong presence in search results.
Identifying Critical Elements for Testing
Various elements can significantly impact a website’s performance in search results. Identifying these elements and testing their variations allows for the optimization of content to resonate better with both search engines and users. This involves understanding the impact of different variations on user engagement and metrics.
Impact of Content Variations on User Engagement and
The content on your website is paramount for both user engagement and success. Variations in content, including headlines, meta descriptions, and body text, can directly influence user engagement metrics, like time on page, bounce rate, and click-through rate. These metrics, in turn, are signals that search engines use to assess the quality and relevance of your content.
By A/B testing different content variations, you can identify the versions that lead to higher user engagement and improved rankings. This iterative process allows for continuous optimization and adaptation to changing search engine algorithms and user behavior.
SEO A/B split testing 101 is all about figuring out what works best for your site visitors, and a crucial part of that is understanding your users’ needs. A great example of this is creating a truly excellent support system for your SaaS product, like the perfect saas support system. By optimizing your support, you can drastically improve user experience, leading to higher conversion rates and better SEO results overall.
This in turn directly influences your SEO A/B split testing results.
Testing Different Headings and Their Impact on
Headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.) are essential for structuring content and signaling its hierarchy to both users and search engines. Different heading variations can influence how users perceive the content and how search engines interpret its importance. Testing variations in heading text, structure, and placement allows for an optimization of content relevance and presentation. For example, a headline like “Best Strategies for 2024″ might be more engaging and perform better in search results than ” Tips.” Through A/B testing, you can measure the impact of these variations on click-through rates, time on page, and overall user engagement.
Comparing Element Types and Potential Impact
| Element | Potential Impact | Testing Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Site Structure | Improved user experience, enhanced crawlability, and better indexing by search engines. | Test different site navigation structures, menus, and page organization. |
| Content Optimization | Increased relevance to user searches, improved rankings, and enhanced user engagement. | Test variations in usage, content length, and readability. |
| Image Optimization | Faster page loading speeds, improved user experience, and potential ranking boosts from image search. | Test different image formats, sizes, and alt text descriptions. |
| Meta Descriptions | Increased click-through rates from search engine results pages (SERPs). | Test variations in length, inclusion, and overall persuasiveness. |
| Internal Linking | Improved site navigation, enhanced user experience, and increased visibility of important pages to search engines. | Test different link anchor text, placement, and target pages. |
Common Mistakes to Avoid: Seo A B Split Testing 101
A/B testing for is a powerful tool, but it’s easy to make mistakes that undermine its effectiveness. Understanding potential pitfalls is crucial for getting accurate and actionable insights. Errors can range from flawed experimental design to misinterpreting the results, leading to wasted resources and potentially harmful decisions. This section highlights common mistakes and provides solutions to help you avoid them.
Sample Size Considerations
Proper sample size is essential for statistically significant results. Insufficient data can lead to unreliable conclusions, while excessive data can be inefficient. Understanding the necessary sample size depends on the variability of the results and the desired level of confidence. Failing to account for this critical aspect can result in missed opportunities or implementing changes that don’t actually improve performance.
Calculating the appropriate sample size using statistical formulas is crucial.
Data Interpretation Pitfalls, Seo a b split testing 101
Interpreting A/B test results requires careful consideration. A common mistake is to focus solely on the most significant differences, ignoring potentially important nuances in the data. Correlation does not equal causation, and it’s essential to avoid jumping to conclusions without rigorous analysis. Also, factors external to the tested elements can influence the results, making it difficult to isolate the impact of the changes.
Statistical Significance and Bias
Statistical significance is a crucial concept in A/B testing. Without it, any observed differences between groups might be due to random chance rather than a genuine effect. Failing to achieve statistical significance means the results aren’t reliable, potentially leading to the implementation of ineffective changes. Bias in the experimental design, such as selecting participants or measuring outcomes in a skewed way, can also undermine the validity of the results.
Understanding and mitigating potential sources of bias is vital.
Guidelines for Avoiding Common Errors
To minimize errors in A/B testing, follow these guidelines:
- Clearly define the specific elements to be tested, ensuring measurable metrics are identified.
- Establish a statistically significant sample size before beginning the test.
- Control for external factors that might influence the results.
- Avoid making changes to other elements during the testing period.
- Use appropriate statistical tools and methods for data analysis.
- Be cautious about drawing conclusions from small or insignificant results.
Common Mistakes and Solutions
The table below Artikels common mistakes and their corresponding solutions for A/B testing.
| Mistake | Solution |
|---|---|
| Insufficient sample size | Calculate the appropriate sample size based on desired confidence level and expected effect size using statistical power analysis tools. |
| Ignoring external factors | Control for external factors by isolating the testing period and ensuring a consistent environment for all participants. |
| Misinterpreting correlation as causation | Focus on analyzing the data for a causal relationship rather than simply identifying correlation. Use rigorous analysis techniques to establish causality. |
| Lack of statistical significance | Ensure the chosen sample size is sufficient to detect meaningful differences. Use appropriate statistical tests (e.g., t-tests, chi-squared tests) to assess statistical significance. |
| Bias in the experimental design | Randomly assign participants to groups to minimize bias. Carefully consider potential sources of bias and implement controls to mitigate them. |
Advanced A/B Testing Strategies
A/B testing in is more than just comparing two versions of a webpage. Advanced strategies unlock deeper insights and optimize for more complex variables. These strategies move beyond simple variations to consider user behavior, long-term impact, and multiple factors influencing conversions. We’ll explore multivariate testing, UX integration, feedback incorporation, and long-term measurement to elevate your A/B testing.Advanced A/B testing goes beyond the simple two-option comparison.
It allows for the examination of more complex interactions and the identification of crucial factors driving conversions. By incorporating various factors into a single test, we gain a more holistic understanding of user behavior and can make more informed decisions for optimization.
Multivariate Testing
Multivariate testing (MVT) allows for testing multiple variations of multiple elements simultaneously. Instead of just changing one aspect, MVT evaluates the combined effect of different changes to titles, meta descriptions, headings, and even content structure. This comprehensive approach identifies the most effective combination of elements, yielding significant improvements in performance. For example, a company testing a product page might simultaneously alter the headline, image, and call-to-action button.
MVT will pinpoint which combination of these variations drives the most conversions and organic traffic.
User Experience (UX) in A/B Testing
User experience (UX) is intrinsically linked to A/B testing. A website that is easy to navigate and understand is more likely to rank well in search engines. UX testing within A/B testing ensures that the changes being tested not only improve metrics but also enhance the user experience. This synergy is critical for long-term success, as a positive user experience often leads to higher engagement, more conversions, and increased time spent on the site.
Incorporating UX testing into the process helps ensure the changes aren’t just about but also about providing a positive user experience.
Incorporating User Feedback
User feedback is invaluable in the A/B testing process. Gathering feedback from users who interact with the different versions of a page allows for a deeper understanding of user preferences and pain points. Collecting and analyzing user feedback helps refine and improve test variations. Tools like surveys, feedback forms, and user interviews can provide invaluable insights into user reactions to different design elements.
Measuring Long-Term Effects
A/B testing shouldn’t be viewed as a short-term sprint. Long-term effects of changes are crucial. Tracking metrics beyond immediate conversions, such as organic traffic growth, rankings, and domain authority, provides a more comprehensive understanding of the lasting impact of the variations. Analyzing these metrics over a significant period reveals the true effectiveness of implemented changes, indicating long-term benefits.
For instance, a change in content structure might not show immediate results but could gradually improve organic rankings and traffic over months.
Comparison of A/B Testing Methodologies
| Methodology | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| A/B Testing | Compares two variations of a single element. | Simple, easy to implement. | Limited scope; doesn’t evaluate interactions between elements. |
| Multivariate Testing | Simultaneously tests multiple variations of multiple elements. | Comprehensive analysis of interactions; identifies optimal combinations. | Complex to design and analyze; requires more resources. |
| Multivariate Testing with User Feedback | Combines MVT with user feedback to enhance insights. | More nuanced understanding of user preferences; informed decision-making. | Requires user testing and feedback collection. |
Last Word
In conclusion, A/B split testing is a powerful tool for improving your website’s search engine visibility. By understanding the principles, implementing the strategies, and analyzing the results, you can refine your approach and achieve better rankings, more traffic, and ultimately, increased conversions. Don’t just guess, test and optimize! This comprehensive guide will empower you to do just that.








