Pagination seo what you need to know – Pagination : What You Need to Know is your essential guide to optimizing paginated content for search engines. This deep dive covers everything from understanding different pagination methods and their implications, to technical considerations like canonicalization and mobile-friendliness. We’ll also explore how to improve user experience, boost search engine crawlability, and fine-tune performance for optimal results.
Imagine a website with tons of content – articles, products, or anything else. Pagination breaks it into manageable chunks, making it easier for users to navigate and search engines to crawl. But, proper pagination is crucial for . This guide will show you how to get it right, ensuring your content is discoverable and accessible.
Understanding Pagination
Pagination is a crucial aspect of web design, especially for websites displaying large amounts of content. It allows users to navigate through numerous pages of information, making it easier to browse and discover relevant material without overwhelming them with a single, extensive page. Effective pagination improves user experience and, when implemented correctly, can enhance a website’s search engine optimization () performance.Pagination is essential for sites with extensive archives, news feeds, product catalogs, and blog posts.
It breaks down lengthy content into manageable portions, improving the user experience and the overall efficiency of site navigation. This approach significantly reduces the cognitive load on users and ensures they can easily find the specific information they need.
Different Pagination Methods
Various methods exist for handling pagination, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these methods is crucial for choosing the best approach for your website.
- Simple Pagination: This traditional method uses numbered page links to navigate between different content segments. It’s a straightforward approach that’s widely understood by users.
- Infinite Scroll: This method loads content dynamically as the user scrolls down the page, without requiring separate page transitions. It enhances user experience by providing a seamless browsing experience.
- Load More: This approach displays a “Load More” button, which, when clicked, retrieves and displays additional content. It offers a visually appealing and interactive alternative to traditional pagination.
Examples of Pagination in Action
Pagination is commonly employed on e-commerce websites for displaying product listings, news sites for presenting articles, and social media platforms for showing posts or comments. For instance, Amazon frequently utilizes pagination to display large inventories of products. Similarly, major news outlets often utilize pagination for news articles.
Importance of Pagination for User Experience
Pagination plays a vital role in user experience by optimizing the browsing process. By breaking down lengthy content into manageable portions, it prevents overwhelming users and ensures that they can easily find the specific information they need. It simplifies navigation and enhances the overall efficiency of site exploration. This, in turn, leads to increased user satisfaction and a more positive user experience.
Comparing Pagination Methods
| Pagination Method | Pros (for ) | Cons (for ) | User Experience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Pagination | Clearer link structure, easy for search engines to crawl and index all pages, explicit indication of content depth. | Potentially more complex URL structure, might not be ideal for very long lists, less dynamic for the user. | Familiar and easy to use, good for users accustomed to traditional page navigation. |
| Infinite Scroll | Simpler URL structure (often just one URL), potentially faster loading time for initial page load. | Search engines may have difficulty indexing all pages, less explicit indication of content depth, potential for missed content in search results. | Seamless and dynamic experience, good for users who prefer continuous scrolling. |
| Load More | Simpler URL structure (often just one URL), potentially faster loading time for initial page load. | Search engines may have difficulty indexing all pages, less explicit indication of content depth, potential for missed content in search results. | Interactive and visually appealing, good for users who appreciate an interactive experience. |
Pagination and Search Engine Crawlability
Pagination is crucial for websites with extensive content. However, its implementation can impact how search engines crawl and index your site’s pages. Understanding this interplay is essential for maximizing your website’s visibility and organic search traffic. Proper pagination strategies ensure search engines can effectively navigate and index all relevant content.Search engines use sophisticated algorithms to crawl and index web pages.
They follow links to discover new content, and the way pagination is handled significantly affects this process. Poorly implemented pagination can lead to critical indexing issues, resulting in parts of your site not being discovered or ranked as highly as they could be. Conversely, well-optimized pagination allows search engines to easily access all content, boosting your site’s overall .
Search Engine Crawling of Pagination
Search engines follow links to discover new pages. In the context of pagination, these links often represent pages of results. Effective pagination ensures search engines can easily follow the links to all the pages within a set of results. If the pagination links are not properly structured, or if there are obstacles preventing crawlers from accessing these links, search engines may not fully index your site’s content.
Impact of Pagination on Crawlability
Pagination’s impact on crawlability can be significant. Issues arise when search engines encounter difficulty in discovering all the pages within a set of results. Common issues include pagination links that are not accessible, or pagination structures that are difficult for bots to follow. This can lead to missing pages, incomplete indexing, and a diminished search ranking. For example, if pagination links are not properly linked, the crawler may not follow all the pages, leading to incomplete indexing.
Optimizing Pagination for Search Engine Bots
Several techniques can optimize pagination for search engine bots. These include using clean and well-structured URLs for each page, ensuring all pagination links are accessible, and providing the crawler with clear signals that indicate the existence of more content. Implementing clear, consistent, and properly structured pagination links helps search engines easily determine the presence of further pages within a set of results.
Best Practices for Pagination
Best practices for pagination emphasize ease of navigation for both users and search engine crawlers. These practices include using clear and concise pagination links, incorporating rel=”next” and rel=”prev” attributes in the HTML to signal the sequence of pages, and ensuring the pagination links are included in the sitemap. Using the rel=”next” and rel=”prev” attributes provides a clear signal to search engines regarding the order of pages.
By properly implementing these elements, the crawler can effectively understand the hierarchy and structure of your content.
Table of Common Crawl Errors and Solutions
| Crawl Error | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Missing or inaccessible pagination links | Search engine bots cannot find links to subsequent pages. | Ensure pagination links are present and accessible, using proper HTML structure. |
| Duplicate content across pages | Repeated content across multiple pages of results, hindering unique indexing. | Ensure unique content on each page, avoiding exact duplicates. |
| Incorrect or inconsistent pagination structure | Complex or inconsistent pagination structure that makes it difficult for bots to navigate. | Use a consistent pagination structure across your website, employing clear and predictable patterns. |
| Slow loading pagination links | Slow loading of pagination pages, affecting crawling speed. | Optimize pagination links for speed, reducing loading time and improving crawler efficiency. |
Pagination and User Experience
Pagination, the division of content into multiple pages, is a common practice on websites, especially for extensive articles, product listings, or blog posts. A well-designed pagination system can significantly improve the user experience by making information more accessible and manageable. Conversely, a poorly designed system can frustrate users and negatively impact engagement.Effective pagination goes beyond simply displaying page numbers.
It involves understanding user behavior and creating a seamless browsing experience. A good pagination system should consider how users interact with the content, how they anticipate information retrieval, and how they respond to the presentation of that information. This is crucial for maintaining user satisfaction and encouraging them to continue exploring the site.
Impact on User Experience
Pagination directly influences how users navigate and interact with a website. A user-friendly pagination system enhances comprehension, improves efficiency, and reduces frustration. Conversely, poorly designed pagination can be a major hurdle, leading to decreased engagement and potentially impacting conversions. This is because a complicated or confusing system discourages users from exploring further content. Effective pagination provides clear and consistent navigation, allowing users to easily locate desired information without feeling overwhelmed.
Knowing pagination SEO is crucial for website optimization. It directly impacts how Google crawls and indexes your content, influencing rankings. Understanding user behavior and their engagement with different page numbers is key. A powerful tool for analyzing this is a Google Analytics custom audience report, like the one detailed on this resource. This allows you to see which pages are most popular and which pagination methods work best, enabling adjustments to enhance user experience and improve SEO.
Ultimately, optimizing your pagination structure leads to higher search engine rankings and better user engagement.
Benefits of Intuitive Pagination Designs
Intuitive pagination designs create a positive user experience. Clear visual cues, logical organization, and straightforward navigation are key components. Users appreciate the ability to quickly scan the content and easily jump to the desired section. This improves the efficiency of information retrieval. Predictable layout and consistent labeling streamline the user’s journey, leading to higher satisfaction.
Importance of Clear Navigation
Clear navigation within paginated content is critical. Users should instantly understand where they are within the overall content set and how to easily move to the next or previous pages. This includes using descriptive labels (e.g., “Page 1 of 10”), clear visual separators between pages, and readily accessible “next” and “previous” buttons. Good pagination makes the information retrieval process effortless and user-centric.
Examples of Good and Bad Pagination Designs
A good pagination design might use a clean, minimalist layout with clear labels, consistent spacing, and easy-to-use navigation controls. It would clearly indicate the current page and the total number of pages. A bad pagination design, on the other hand, might use a cluttered layout, confusing labeling, or non-intuitive navigation controls. This can disorient users and create a negative experience.
For instance, a poorly designed pagination system might place the navigation elements at the very bottom of the page, making it hard to locate them, or use obscure terminology for next/previous pages.
Table Demonstrating Impact on User Engagement
| Pagination Design | User Engagement Metrics | User Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Good | Higher click-through rates to subsequent pages, reduced bounce rates, longer session durations, increased page views per session. Users consistently engaged with the content. | Positive comments regarding ease of navigation, clarity of presentation, and intuitive design. Users often praised the efficiency of the system. |
| Bad | Lower click-through rates to subsequent pages, higher bounce rates, shorter session durations, fewer page views per session. Users demonstrated a clear lack of interest. | Negative comments regarding confusing navigation, unclear labeling, and frustrating design. Users frequently complained about the difficulty of accessing information. |
Technical Considerations for Pagination
Pagination is crucial for websites with extensive content, enabling users to navigate through numerous pages of results. However, proper technical implementation is vital to ensure search engines understand and index these pages correctly, avoiding duplicate content issues and maximizing user experience. This section delves into the technical aspects of pagination, focusing on canonicalization, site structure, and structured data.Implementing pagination correctly is essential for a positive user experience and optimal search engine visibility.
Ignoring technical considerations can lead to decreased organic traffic, lower rankings, and a less effective overall strategy.
Canonicalization for Paginated Content
Proper canonicalization is paramount for paginated content. Search engines need clear signals indicating which version of a page is the primary one. Without proper canonicalization, search engines might index multiple versions of the same content, diluting your site’s authority and potentially causing ranking issues. This section will cover the significance of canonicalization and how to correctly implement it.
- Importance of Canonical Tags: Canonical tags are essential for telling search engines which URL is the preferred version of a page. This prevents duplicate content issues and ensures search engines index the intended version. Without canonical tags, search engines might crawl and index multiple versions of a single page, resulting in decreased rankings.
- Correct Implementation of Canonical Tags: A canonical tag should point to the URL of the primary version of the page, and it should be placed within the section of the HTML document. For paginated content, the canonical tag should point to the main, or first, page. Subsequent pages should use a canonical tag that points back to the first page. This helps search engines understand the relationship between pages.
Improving Website Structure with Pagination
Pagination can enhance site structure by logically organizing large amounts of information. A well-structured site architecture is easier for both users and search engines to navigate, leading to better user experience and improved search engine rankings.
- Logical Page Numbering: Using logical page numbers (e.g., 1, 2, 3, etc.) helps users understand their location within the content. Avoid using non-sequential or cryptic page numbers, as this can confuse users and search engines.
- Clear Navigation: Providing clear navigation elements like “Previous” and “Next” buttons is essential for user-friendly navigation. The navigation should be easily accessible and prominent on each page.
- Hierarchical Structure: Implement a clear hierarchy to organize your content. This makes it easier for users and search engines to find relevant information.
Example of Proper Canonicalization
Imagine a product listing page with pagination. The main product page is `https://www.example.com/products`. The second page is `https://www.example.com/products/page/2`.
- Main Product Page (Canonical): The canonical tag on `https://www.example.com/products` would point to itself: ` `.
- Second Page (Canonical): The canonical tag on `https://www.example.com/products/page/2` would point to the main product page: ` `.
Pagination and Structured Data
Structured data markup helps search engines understand the content on your pages. Implementing structured data for paginated results can lead to rich snippets in search results, improving click-through rates and visibility.
- Using Schema.org for Rich Snippets: Use schema.org markup to define the content on each page within a paginated series. The structured data should highlight the pagination information. For instance, if you have a blog post, the schema.org markup could indicate the total number of pages and the current page number.
- Benefits of Structured Data: Rich snippets often display more information in search results, including page numbers. This often leads to a higher click-through rate compared to results without rich snippets. This makes your website stand out in search results, leading to increased visibility.
Mobile-Friendly Pagination: Pagination Seo What You Need To Know
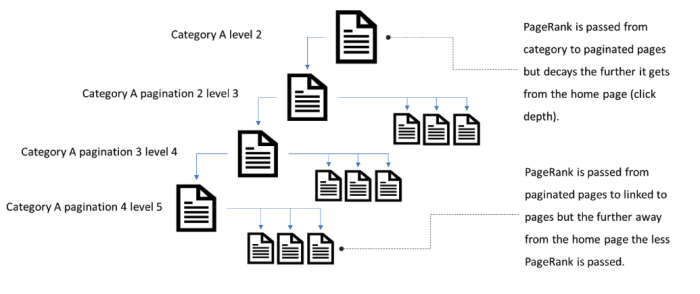
Mobile-friendly pagination is crucial for a positive user experience and improved search engine visibility. Users increasingly access websites on smartphones and tablets, making it vital to ensure a seamless and intuitive pagination experience on these devices. Failing to optimize pagination for mobile can lead to a poor user experience, potentially resulting in high bounce rates and decreased engagement.Responsive pagination design is essential for adapting to different screen sizes and orientations.
This allows users to navigate effortlessly through multiple pages, whether they are using a desktop computer, a tablet, or a smartphone. This responsive design is key to maximizing user engagement and providing a consistent and enjoyable experience across all devices.
Responsive Pagination Design Considerations
Properly implementing responsive pagination requires careful consideration of several factors. The layout should adjust dynamically to fit the available screen space, ensuring all pagination elements, such as the page numbers, are easily clickable and readable. Accessibility is also important. The pagination should be usable by people with disabilities using assistive technologies. Clear visual cues should be used to indicate the current page and allow users to easily move to previous and next pages.
Mobile-Specific Pagination Examples
Implementing pagination that works seamlessly on various mobile devices requires a nuanced approach. For example, a single-line pagination design that displays all page numbers horizontally may work well on desktops but may be overwhelming and difficult to read on smaller mobile screens. A more concise design, perhaps with a series of clickable dots, would be better suited to the mobile experience.
Using a drop-down menu or an expanded view that becomes available on tap is also a valid approach.
Best Practices for Mobile-Friendly Pagination
Best practices for mobile-friendly pagination include: Prioritizing a clean and uncluttered design. Ensuring page numbers are large and easily clickable. Using clear visual cues to highlight the current page. Implementing touch-friendly interactions for mobile devices. Including clear and concise labels for each button and functionality.
Testing on various mobile devices and screen sizes to ensure a consistent and functional user experience. Testing is crucial to verify functionality and aesthetics across different mobile devices.
Comparison of Responsive Pagination Designs
| Responsive Design | Mobile View | Desktop View |
|---|---|---|
| Single-line horizontal pagination | Overwhelming; difficult to read on smaller screens; may require scrolling. | Easy to read and scan all pages at once. |
| Dot-based pagination | Easy to use; allows for quick navigation; compact. | Simple and effective; user can quickly see all pages. |
| Dropdown pagination | Accessible and intuitive; allows for page selection from a list. | Compact and efficient; users can quickly browse all pages. |
| Pagination with infinite scroll | Smooth scrolling experience; improved loading performance; may require extra design consideration for user engagement. | Smooth scrolling experience; improved loading performance; less visible page count information. |
Performance Optimization
Pagination, while crucial for user experience and , can significantly impact website performance if not optimized. Slow-loading paginated pages lead to higher bounce rates and lower user engagement. Understanding how pagination affects performance and employing strategies to improve it are essential for a successful online presence.Efficient pagination ensures that users can access the desired content quickly and easily, preventing frustration and boosting their overall experience.
Knowing pagination SEO is crucial for website success. You need to ensure your pages are crawlable and easily understood by search engines. Understanding how Google Analytics’ enhanced ecommerce features track user behavior, like purchases and product views, can significantly improve your pagination strategy. By analyzing this data, you can optimize your pagination for better user experience and, in turn, boost rankings.
Using these insights to improve your pagination structure will lead to better site performance. Learn more about Google Analytics’ enhanced ecommerce features here: google analytics enhanced ecommerce features. Ultimately, effective pagination SEO is about creating a seamless and efficient user journey.
A well-optimized pagination system contributes to better search engine rankings and ultimately, higher conversion rates.
Impact of Pagination on Website Performance
Pagination introduces overhead by requiring multiple requests to the server for each page of results. This can lead to longer loading times, especially for users with slower internet connections. The number of requests increases linearly with the number of pages, which directly impacts the overall time it takes to display the entire content set. The delay between requests can be noticeable, particularly on mobile devices with limited bandwidth.
Furthermore, complex queries and large result sets compound the problem.
Strategies for Faster Loading Times
Several strategies can significantly improve the performance of paginated pages. Implementing server-side pagination, optimizing image sizes, and utilizing caching mechanisms are critical for a smooth user experience.
- Server-Side Pagination: Instead of generating each page on the client-side, generating the pagination links on the server dramatically reduces the amount of data transferred to the browser. This reduces the load on the server and the client’s resources, resulting in faster page load times. This is especially critical for sites handling large amounts of data, as client-side processing can become very slow and inefficient.
It’s crucial to evaluate server-side capabilities and limitations before deciding on this approach.
- Client-Side Caching: Utilizing browser caching allows for the storage of frequently accessed assets, reducing the number of requests needed for subsequent visits. This strategy is particularly beneficial for static assets like images and CSS files. Proper implementation of caching directives and strategies is essential for avoiding performance degradation. This involves setting appropriate cache headers and configuring the caching mechanism correctly.
Knowing pagination SEO is crucial for site performance, but did you know that A/B testing can significantly boost your conversions? For instance, you can use 9 ab tests that you can run tomorrow to double your conversions to optimize your pagination structure, like the placement of next/previous buttons, to improve user experience and search engine ranking. This leads to better user engagement and higher organic traffic, ultimately enhancing your pagination SEO strategy.
- Image Optimization: Images are often a significant source of page load times. Optimizing images for web use, including compression and appropriate formats, is vital. Using optimized image formats such as WebP can significantly reduce file sizes without compromising quality. Techniques like responsive image delivery and lazy loading further reduce the load on the initial page load.
Minimizing Server-Side Processing for Pagination
Client-side pagination, though simpler to implement, can be detrimental to performance. Instead, server-side pagination is the preferred approach, especially for large datasets. Server-side rendering of pagination links avoids multiple round trips to the server, thus significantly reducing the loading time.
- Database Optimization: Using efficient database queries to retrieve only the necessary data for each page, rather than the entire dataset, reduces the server-side processing required. Indexing and query optimization play a critical role in this strategy.
- API-Based Data Fetching: Utilizing an Application Programming Interface (API) to fetch and process data can further reduce server-side processing demands. APIs provide a layer of abstraction that allows for more granular control over the data retrieved, thus reducing unnecessary overhead. This also allows for a more modular approach to handling data, making the code more scalable and easier to maintain.
The use of caching with APIs can further optimize the fetching process.
- Asynchronous Operations: Employing asynchronous operations, where possible, allows the server to continue processing other requests while waiting for data to be fetched. This strategy reduces latency and enhances the overall performance of the pagination system.
Optimizing Image Sizes and Page Elements
Image sizes and page elements significantly influence loading times. Reducing file sizes without compromising quality and optimizing elements can significantly improve page speed.
- Choosing Appropriate Image Formats: WebP, a modern image format, offers excellent compression, potentially reducing file sizes compared to JPEG or PNG. Choosing the correct image format based on the image’s content and desired level of quality is crucial.
- Image Compression: Lossless compression techniques for images can reduce file sizes without compromising quality. Lossy compression, on the other hand, can reduce file sizes further but may lead to a slight decrease in image quality.
- Responsive Images: Serving images in different sizes based on the user’s device and screen resolution optimizes page load times. This ensures that users are served images that are optimized for their specific devices.
Caching to Speed Up Paginated Pages
Caching mechanisms significantly improve the performance of paginated pages by storing frequently accessed data. This reduces the load on the server and results in faster loading times for subsequent requests.
- Server-Side Caching: Server-side caching stores frequently accessed data on the server, allowing for faster retrieval. This approach is particularly beneficial for frequently requested pages or data.
- Browser Caching: Implementing appropriate caching headers allows the browser to store static assets like images, CSS, and JavaScript, thus reducing the need for repeated downloads. Correctly configured caching headers are crucial for optimal performance.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Utilizing CDNs can deliver static assets from servers closer to users, reducing latency and improving page load times.
Testing and Monitoring

Thorough testing and monitoring are crucial for ensuring paginated content delivers a positive user experience and performs well in search engine results. Effective strategies for testing and monitoring help identify and rectify issues before they negatively impact users or rankings. This section delves into key aspects of testing pagination across different platforms and monitoring its performance and user engagement.Comprehensive testing and ongoing monitoring are essential for maintaining a high-quality user experience and optimal search engine performance for paginated content.
This proactive approach ensures that pagination elements are functional and meet user expectations across various devices and browsers. Monitoring tools provide insights into performance bottlenecks and user behavior, facilitating necessary adjustments to enhance the overall user experience and visibility.
Strategies for Testing Pagination
Effective testing involves simulating real-world scenarios to identify potential usability problems. This encompasses various devices and browsers to ensure consistent performance across a wide range of user environments.
- Cross-browser testing: Testing across different browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge) is critical. Variations in rendering and handling of pagination elements can lead to inconsistencies and user experience issues. Using browser developer tools is essential for inspecting pagination elements, ensuring proper styling, and verifying functionality.
- Cross-device testing: Different devices (desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones) exhibit diverse screen sizes and resolutions. Ensuring proper scaling and responsiveness of pagination elements is vital to prevent content from being truncated or overlapping. Responsive design principles and viewport meta tags are key considerations.
- Simulated user flows: Creating scenarios that mimic real-world user interactions is crucial. This involves simulating navigation through multiple pages, checking for pagination errors, and verifying loading times. Automated testing tools can effectively execute these simulated flows, producing comprehensive reports of any discovered issues.
Tools for Monitoring Pagination Performance, Pagination seo what you need to know
Various tools are available to track and analyze the performance of paginated content. Understanding performance bottlenecks and user behavior is vital for optimization.
- Web performance testing tools: Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, and WebPageTest analyze loading times, identify bottlenecks, and provide recommendations for optimization. These tools are crucial for evaluating the impact of pagination on site speed and identifying areas needing improvement.
- Server logs: Analyzing server logs reveals detailed information about pagination requests, errors, and response times. This analysis helps identify patterns and trends that can indicate performance issues or errors in the pagination logic.
- Analytics platforms: Platforms like Google Analytics provide insights into user behavior, such as bounce rates, time on page, and clicks on pagination links. This data is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of pagination in driving user engagement and determining areas for enhancement.
Methods for Measuring User Engagement
Understanding how users interact with paginated content is vital for optimization.
- Click-through rates (CTR) on pagination links: Analyzing the percentage of users who click through to subsequent pages within a pagination set provides insights into user interest and engagement with the content. High CTRs indicate that users are actively navigating through the pages, whereas low CTRs may suggest a need for improvement in content relevance or presentation.
- Time spent on each page: Tracking the average time spent on each paginated page can indicate user engagement. Longer times spent often correlate with more in-depth content exploration and higher user satisfaction.
- Bounce rate: Analyzing the bounce rate, or the percentage of users who leave after viewing only the first page, can highlight issues with the content or its presentation. High bounce rates might indicate that the first page isn’t compelling enough to encourage users to explore further.
Techniques for Tracking Pagination-Related Metrics
Monitoring metrics is vital for evaluating the impact of pagination on search engine rankings.
- Indexation of pagination links: Ensuring search engines properly index all pagination links is crucial for crawling and indexing the entire content set. This involves optimizing the structure and linking strategy of the pagination.
- Rank tracking: Regularly monitoring the rankings of individual pages within the paginated content set allows for evaluation of the impact of pagination on . This data reveals any fluctuations or patterns that might suggest areas requiring adjustments to improve rankings.
- Crawled pages: Tracking the number of pages crawled by search engines is crucial. It provides insights into how well search engines can access and process the paginated content. A high number of crawled pages typically indicates that the pagination is functioning correctly and search engines can effectively access the entire content set.
Closure
In conclusion, optimizing pagination for is a multifaceted approach that encompasses technical, user experience, and performance aspects. By understanding the nuances of different pagination methods, addressing potential crawl errors, and ensuring a seamless user experience across devices, you can significantly improve your website’s visibility and user engagement. This guide has equipped you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of paginated content and achieve optimal results.








