Opting out of a featured snippet a quick guide – Opting out of a featured snippet: a quick guide. Tired of your website content being overshadowed by a search engine’s featured snippet? This guide dives deep into understanding featured snippets, identifying when to opt out, the various methods for doing so, and how to effectively implement and monitor your opt-out strategy. We’ll explore the benefits and drawbacks, and arm you with actionable steps to reclaim control over your website’s visibility.
Featured snippets, while often beneficial, can sometimes hinder a website’s performance. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the process, covering the reasons behind wanting to opt out, the technical methods available, and the key metrics to track for optimal results. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a newcomer to website optimization, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to confidently navigate this aspect of search engine optimization.
Understanding Featured Snippets
Featured snippets are concise answers to user queries that appear directly in the search engine results page (SERP). They aim to provide users with quick, relevant information without requiring them to click through to a website. Understanding how featured snippets work can significantly impact a website’s visibility and traffic.Featured snippets are not just a single, static answer format.
They come in various forms tailored to different search queries, offering diverse information types to the user. Knowing these types allows website owners to optimize their content for a broader range of potential snippet placements.
Definition of Featured Snippets
Featured snippets are concise answers displayed directly on the search engine results page (SERP) in response to user queries. They often appear above the organic search results, potentially drawing significant user attention. These concise answers can range from a simple definition to a more comprehensive summary. The key aspect is their direct answer to the search query.
Types of Featured Snippets
Featured snippets can take several formats to effectively address different user needs. The formats can include paragraphs, lists, tables, and even images.
- Paragraph Snippets: These are the most common type, providing a short, concise answer to the user’s query in a paragraph format. They are often used for questions that require a straightforward explanation.
- List Snippets: These snippets present information in an ordered or unordered list format. They are suitable for queries that require a series of steps, points, or a collection of items. Examples include “steps to boil an egg” or “types of coffee beans”.
- Table Snippets: These snippets present data in a tabular format, ideal for comparisons, specifications, or presenting factual data. An example might be a comparison of different car models or the nutritional information for various foods.
- Image Snippets: These snippets feature an image with a brief caption or description directly in the search results. They are particularly relevant for queries that involve visual information, such as “what does a spider look like” or “what is a sunflower”.
How Search Engines Identify and Select Featured Snippets
Search engines use complex algorithms to identify and select featured snippets. These algorithms analyze the content on web pages, assess its relevance to the user query, and evaluate the quality and accuracy of the information. Factors considered include the page’s authority, the clarity and conciseness of the content, and the overall user experience. A key aspect of the selection process is ensuring the snippet’s content directly addresses the user’s query.
Benefits of Featured Snippets for Websites
Featured snippets can significantly benefit websites. High placement in the SERP often leads to increased visibility and traffic. This can improve brand awareness and lead to more conversions.
- Increased Visibility: Featured snippets place websites prominently on the SERP, increasing their visibility to potential users.
- Higher Click-Through Rates: The high position and concise nature of featured snippets can often result in higher click-through rates compared to organic results.
- Enhanced Brand Authority: Being featured in a snippet can establish a website as a trustworthy source of information.
Potential Drawbacks of Featured Snippets for Websites, Opting out of a featured snippet a quick guide
While featured snippets can be beneficial, they also present potential drawbacks. If a website’s content is not optimized for featured snippets, it might not be selected. Additionally, the snippet may not always accurately reflect the website’s full content.
Comparison of Featured Snippet Types
| Snippet Type | Structure | Typical Content |
|---|---|---|
| Paragraph | A concise paragraph answering the query | Definition, explanation, or summary |
| List | Ordered or unordered list of items | Steps, points, or a collection of items |
| Table | Rows and columns of data | Comparisons, specifications, or factual data |
| Image | Image with caption or description | Visual information, examples |
Identifying When to Opt Out

Choosing whether or not to participate in Google’s featured snippet program is a crucial decision for website owners. A well-optimized featured snippet can significantly boost traffic and visibility. However, in certain circumstances, opting out might be the better strategy. Understanding when to opt out can protect your website’s performance and ensure your content is presented accurately to searchers.Knowing when to opt out of a featured snippet involves careful consideration of various factors.
A nuanced understanding of the potential pitfalls and benefits is essential for making informed decisions. This guide will detail specific scenarios where opting out might improve your website’s performance and user experience.
Scenarios Where Opting Out Might Be Beneficial
Understanding when to opt out requires recognizing when a featured snippet could be inaccurate, misleading, or detrimental to your website’s performance. A well-crafted featured snippet can significantly improve a site’s visibility and ranking, but there are instances where opting out is the better choice.
- Inaccurate or Misleading Information: A featured snippet that presents incorrect or incomplete information about your website’s content can harm your reputation and credibility. For instance, if a featured snippet misrepresents the scope of your service or misquotes a key piece of information, it can lead to user frustration and potentially damage your business.
- Competition for s: If your website is competing with others for specific s, and the featured snippet consistently displays content from a competitor, opting out might be beneficial. A competitor might be able to present their content better than yours, potentially driving traffic away from your site.
- Content Misrepresentation: A featured snippet might summarize or highlight a portion of your content in a way that misrepresents the overall message or intent. This can lead to users clicking on the snippet, expecting a certain type of content, but finding something different on your page.
- Impact on Traffic and Conversions: A featured snippet, while initially increasing visibility, might not translate into actual conversions. If the snippet’s summary isn’t enticing enough or if users are not finding what they’re looking for on your site, it could decrease overall engagement and conversions.
- Control Over Content Presentation: Sometimes, a featured snippet might not accurately represent the user’s intent or the most relevant content on your page. Opting out allows you to control the content presented in the search results, ensuring the user is directed to the most appropriate information on your website.
Specific Examples of Negative Impacts
In certain situations, a featured snippet can negatively affect your website’s performance. Here are some examples.
- Reduced Click-Through Rate (CTR): If the featured snippet doesn’t accurately reflect the page content, users might click on the snippet, only to be disappointed when they land on a page that doesn’t meet their expectations. This can lead to a decrease in click-through rates.
- Increased Bounce Rate: A poor featured snippet can lead to a higher bounce rate. Users who click on a snippet expecting one thing and finding another on your site are more likely to leave immediately.
- Damage to Brand Reputation: If the featured snippet presents inaccurate or misleading information, it can damage your brand’s reputation and trustworthiness. This can affect your credibility with potential customers.
Table of Scenarios Requiring Opt-Out
This table illustrates situations where opting out of a featured snippet might be necessary.
| Scenario | Example | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Inaccurate Information | A featured snippet states a product is available in red, but the website shows only blue options. | The snippet misrepresents the product availability, potentially leading to customer frustration. |
| Content Misrepresentation | A featured snippet summarizes a complex article about a specific software feature as simple steps, whereas the actual article provides in-depth details. | The snippet doesn’t capture the complexity of the content, leading users to a different experience than expected. |
| Competition | A competitor’s website consistently appears in featured snippets for a key , potentially diverting traffic away from your site. | Your website’s content is less prominent, despite potentially being equally or more relevant. |
Methods for Opting Out
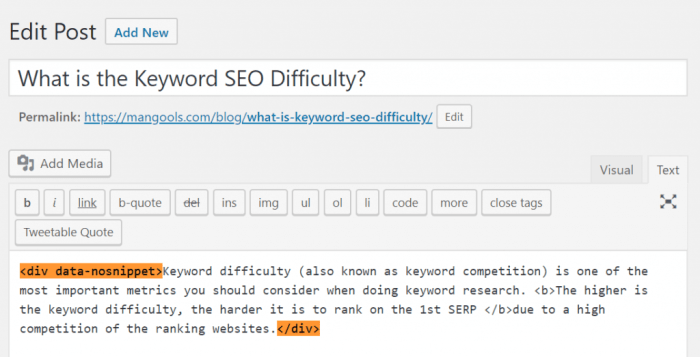
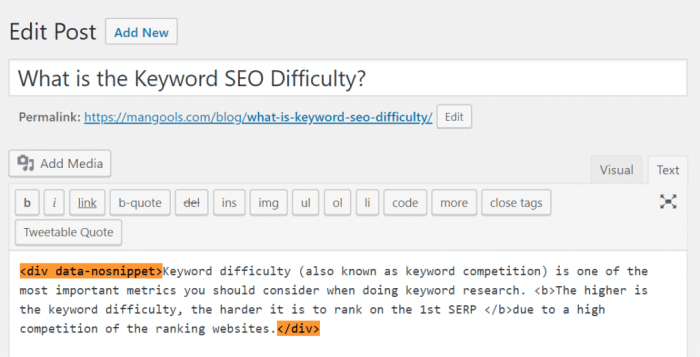
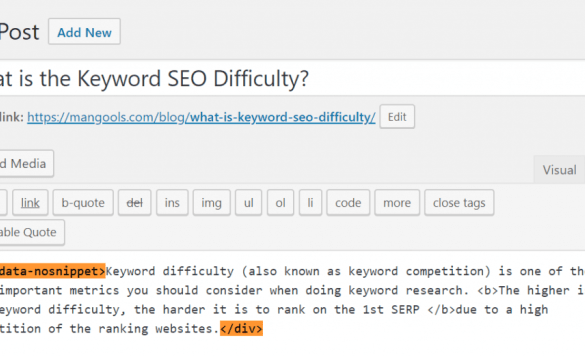
Choosing not to appear in Google’s featured snippets is a strategic decision, often made to maintain control over the user experience on your site. This section details the various methods available, along with their effectiveness and potential drawbacks. Understanding these methods allows you to fine-tune your strategy and manage your website’s visibility in search results.Effective strategies for preventing your pages from being featured snippets hinge on several techniques, each with its own implications for search engine optimization.
By strategically implementing these techniques, you can tailor your site’s presentation in search results to your specific needs.
Noindex Directives
Noindex directives are powerful tools for excluding specific pages or content from Google’s index. Implementing them prevents those pages from appearing in search results, including featured snippets.This involves adding a tag to the HTML head of the targeted page. This tells search engines not to index the page. This is a straightforward way to exclude specific content.
Meta Tags for Featured Snippet Prevention
Meta tags, specifically the “meta robots” tag, provide another avenue for managing a page’s visibility in search results. The “meta robots” tag can be utilized to exclude a page from being considered for featured snippets, alongside other indexing directives.A meta tag like will prevent indexing and following, thereby effectively excluding the page from the featured snippet display. Note that this method often works in conjunction with other techniques for comprehensive exclusion.
Robots.txt Exclusion
The robots.txt file is a crucial component of website management, offering a way to communicate with search engines about what parts of your site they should and shouldn’t crawl. A strategically placed directive in your robots.txt file can prevent featured snippets from appearing.By adding a rule to the robots.txt file that excludes the specific page, you effectively instruct search engines to avoid crawling and indexing that page, preventing it from becoming a featured snippet.
Want a quick guide on opting out of a featured snippet? Understanding how search engine optimization (SEO) and paid advertising (PPC) impact your website traffic, like seo ppc website traffic , is key. Knowing how to control your visibility in search results, including featured snippets, is crucial for your online presence. This guide will walk you through the steps to effectively opt out.
However, this method often requires precise specification of the target URL.
Structured Data Markup Impact
Structured data markup, often using schema.org vocabulary, plays a role in how search engines understand the content of a webpage. Improperly structured or missing markup can indirectly affect a page’s likelihood of being selected for a featured snippet.Incorrect structured data markup can sometimes misrepresent the content of the page, potentially hindering its suitability for a featured snippet. Using schema markup appropriately can help to correctly represent content and potentially influence snippet selection.
Looking for a quick guide on opting out of a featured snippet? Understanding how search engines prioritize content is key, and future content distribution leveraging multi channel strategies like SEO, social media, and email marketing can significantly impact your visibility. By strategically distributing your content across various platforms, you’re more likely to reach a wider audience and potentially reduce your reliance on a featured snippet.
This guide will provide actionable steps to effectively opt out of a featured snippet, helping you control your content’s online presence. future content distribution leveraging multi channel strategies will help you understand how to position your content for success.
Implementing Noindex Directives: A Step-by-Step Procedure
This procedure Artikels how to effectively implement noindex directives for specific pages.
Want a quick guide on opting out of a featured snippet? Sometimes, you might want to fine-tune your website’s visibility in search results. For instance, if you’re looking to control how visitors are shown tailored messages on your WordPress site, exploring how to use cookie retargeting in WordPress to show custom on-site messages here could be a great strategy.
This could be a helpful step towards managing your site’s SEO and user experience. Ultimately, understanding how to control featured snippets is a key part of a broader SEO strategy.
- Identify the page(s) you want to exclude from featured snippets.
- Open the HTML source code of the target page.
- Locate the head section of the HTML code.
- Add the meta tag `` within the head section.
- Save the modified HTML file.
- Verify the change by checking Google Search Console for the updated status of the page.
Methods for Opting Out: Effectiveness and Drawbacks
This table summarizes the methods for opting out of featured snippets, considering their effectiveness and potential drawbacks.
| Method | Effectiveness | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Noindex Directives | High | Requires modification of the page’s HTML; may not prevent all cases. |
| Meta Tags | High | Similar to noindex, needs careful implementation; not always foolproof. |
| Robots.txt | Medium | More general exclusion; may not address specific pages; requires careful URL matching. |
| Structured Data Markup | Indirect | Improperly implemented markup can cause unexpected results; needs to be correct to be helpful. |
Implementing Opt-Out Strategies
Successfully opting out of featured snippets requires a multifaceted approach. Simply adding a meta tag or a line in your robots.txt file isn’t always enough. Understanding the intricacies of search engine algorithms and the nuances of your specific website’s structure is key to preventing your content from appearing in featured snippets where you don’t want it. This section provides a practical guide on implementing effective opt-out strategies, covering crucial technical aspects.Implementing the chosen opt-out method requires a precise and consistent approach.
Different methods target different aspects of search engine crawlers’ understanding of your website’s structure. This careful approach ensures your content remains hidden from featured snippet display while still allowing other important content to be indexed.
Noindex Directives
Noindex directives instruct search engines not to index specific pages or content. This is a powerful tool to prevent featured snippet inclusion. Implementing noindex effectively requires understanding the different ways it can be applied.
- Implementing noindex directives via robots.txt: A robots.txt file is a crucial component of a website’s architecture. It guides search engine crawlers, telling them which pages to index and which to avoid. Adding a “Disallow” rule to your robots.txt file is a basic method. For instance, adding a line like “Disallow: /page-to-exclude/” will prevent the search engine from indexing the specified page, effectively preventing it from appearing in featured snippets.
- Implementing noindex directives via meta tags: You can directly instruct search engines not to index specific pages using meta tags within the HTML code of the page itself. The ` ` tag within the `` section of the page’s HTML is a common way to do this. This is particularly useful for pages that are dynamic or generated by a system, as robots.txt might not be sufficient in these cases.
Modifying Meta Tags
Meta tags provide crucial information to search engines about your web pages. Adjusting meta tags can significantly influence how your content is displayed and indexed.
- Adding the `noindex` attribute: Including the `noindex` attribute within the `robots` meta tag, as mentioned earlier, will prevent the page from being indexed. This is a direct way to prevent the page from appearing in any search results, including featured snippets.
- Modifying the `description` meta tag: While not directly preventing featured snippets, altering the description meta tag can subtly influence how search engines understand the page’s content. A well-crafted description can still influence the displayed snippet, though it doesn’t prevent the snippet from being selected altogether.
Updating Robots.txt Files
The robots.txt file is a crucial tool for controlling how search engines crawl your website. Updating it requires careful consideration of its structure and directives.
- Understanding Disallow directives: The “Disallow” directive in robots.txt tells search engines which parts of your site they should not crawl. You need to specify the exact URLs or patterns to exclude. For example, a `Disallow: /category/featured-snippet-articles/` would prevent all pages under the `featured-snippet-articles` category from being indexed.
- Ensuring proper syntax: Accuracy in syntax is critical when modifying robots.txt. Errors can lead to unintended consequences, including indexing issues or incorrect crawl behavior. Carefully review your robots.txt file before uploading changes.
Modifying Structured Data Markup
Structured data markup provides search engines with a detailed understanding of your content. Carefully crafting structured data can significantly influence how your content is presented.
- Preventing misinterpretation: If your structured data markup is incorrectly formatted, search engines might misinterpret it, potentially leading to your content appearing in featured snippets. Correctly defining schema types and properties is critical.
- Removing or modifying schema properties: If specific properties within your structured data markup are causing misinterpretations or are unnecessary for featured snippet avoidance, you can remove or modify them. This precise approach helps to control how search engines understand your content.
Troubleshooting Opt-Out Issues
Troubleshooting problems when opting out of featured snippets involves several steps.
| Potential Issue | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|
| Page still appearing in featured snippets | Verify noindex directives, check for errors in robots.txt, and ensure structured data is correctly formatted. |
| Unclear crawl behavior | Check your robots.txt file for any syntax errors, re-crawl the site using the search console, and check for any crawl errors reported. |
| Delayed changes taking effect | Verify Google Search Console crawl rate, and ensure your sitemap is updated to reflect changes. |
Monitoring and Evaluating Results: Opting Out Of A Featured Snippet A Quick Guide
Tracking the effectiveness of opting out of featured snippets requires a structured approach to measure the impact on website traffic and conversions. Understanding the potential consequences of this change is crucial for adapting your strategy and ensuring a positive outcome. This involves not only measuring changes but also identifying any negative effects and making adjustments to your strategy accordingly.Monitoring the impact of opting out of featured snippets is vital to understand if the strategy is beneficial or if adjustments are needed.
It involves meticulous tracking of key performance indicators (KPIs) and analyzing any changes in website traffic and conversion rates.
Tracking Opt-Out Strategy Effectiveness
To effectively monitor the impact of opting out of featured snippets, a systematic approach is necessary. This involves regularly collecting data and analyzing trends to identify any patterns or correlations. A key aspect is to identify and measure the impact on organic traffic and conversion rates. This will help determine if the opt-out strategy is producing the desired results.
Metrics for Measuring Changes
Several metrics can be used to track changes in website traffic and conversions following the opt-out decision. These include:
- Organic Search Traffic: Monitor the volume of visitors arriving at your website through organic search results. Tools like Google Analytics provide detailed data on traffic sources, allowing you to see if traffic has increased, decreased, or remained stable after opting out.
- Conversion Rates: Measure the percentage of visitors who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase, filling out a form, or signing up for a newsletter. A decrease in conversion rates might indicate a negative impact on your website’s effectiveness.
- Time on Site: Analyze the average time visitors spend on your website. A significant drop in time on site could suggest that the content is not engaging or relevant enough.
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of visitors who leave your website after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate might indicate that the content is not relevant to the user’s search query or that the landing page is not optimized.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Track the percentage of users who click on your website link from search results. A decrease in CTR might suggest that your website is no longer appearing prominently in search results or that the content is not compelling.
Identifying Negative Consequences
Carefully monitoring for negative consequences is essential. These can include:
- Reduced Organic Traffic: A significant drop in organic search traffic after opting out of featured snippets could indicate a negative impact on your search engine ranking.
- Lower Conversion Rates: If the conversion rate decreases, it might indicate that users are less likely to engage with your website content or make desired actions.
- Increased Bounce Rate: A rise in bounce rate suggests that users are leaving your website immediately after viewing a single page, possibly due to a mismatch between the content and their search intent.
Adjusting Strategies Based on Performance Data
Analyzing the collected data is crucial for making informed decisions. This involves identifying patterns and correlations between specific actions and observed outcomes.
- Adapt your content strategy: If organic traffic decreases, consider revising your content to align better with user search intent. Focus on creating more comprehensive and informative content to attract visitors and maintain a higher ranking in search results.
- Improve website optimization: Evaluate the technical aspects of your website to ensure it is easily accessible and user-friendly. Make necessary improvements to enhance the user experience and ensure faster loading times.
- Reassess strategy: If conversion rates decline, analyze the s you are targeting and ensure they accurately reflect user intent. Consider adding or adjusting relevant s to enhance visibility.
Data Analysis Reports
Regular reports provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of your opt-out strategy. These reports should include data visualizations, such as charts and graphs, to present the information in an easily understandable format.
| Date | Organic Traffic (Visits) | Conversion Rate (%) | Time on Site (Avg.) | Bounce Rate (%) | CTR (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024-08-15 | 10,000 | 5% | 2:30 | 40% | 2% | Initial data post opt-out |
| 2024-08-22 | 9,500 | 4.5% | 2:00 | 45% | 1.8% | Slight decrease in traffic and conversion |
| 2024-08-29 | 9,800 | 5.2% | 2:15 | 42% | 2.1% | Slight recovery; need further analysis |
Tracking Opt-Out Results Template
A template for tracking opt-out results can help organize data collection and analysis.
- Date: The date of data collection.
- Organic Traffic (Visits): The number of visitors coming from organic search.
- Conversion Rate (%): The percentage of visitors who complete a desired action.
- Time on Site (Avg.): The average time visitors spend on your website.
- Bounce Rate (%): The percentage of visitors who leave after viewing only one page.
- CTR (%): The percentage of users who click on your website link from search results.
- Notes: Any observations or comments about the data.
Epilogue
In conclusion, opting out of featured snippets can be a crucial strategy for controlling your website’s online presence. By understanding the different types of snippets, recognizing when opting out is beneficial, and mastering the available methods, you can regain control and tailor your content to better serve your audience. Remember to consistently monitor and evaluate the results to fine-tune your strategy and ensure it aligns with your website’s goals.