Microsoft Internet Explorer cache is a crucial component of browsing, but understanding its complexities can be tricky. This comprehensive guide delves into the purpose, management, impact, troubleshooting, security considerations, and even the tools to optimize this often-overlooked aspect of your browsing experience.
The cache acts as a temporary storage for frequently accessed website data, significantly speeding up subsequent visits. However, a poorly managed cache can lead to slowdowns, display errors, and even security vulnerabilities. This post will dissect the intricacies of the Internet Explorer cache, offering practical insights into its functionality and maintenance.
Understanding the Microsoft Internet Explorer Cache
The Internet Explorer cache is a crucial component of the browsing experience, significantly impacting page load times and overall efficiency. It’s a temporary storage space on your computer that saves frequently accessed data from websites. This data includes images, scripts, and other elements that make up web pages. Understanding how this cache functions can help optimize your browsing and troubleshoot potential issues.The Internet Explorer cache acts as a local repository for web resources.
By storing copies of these resources, the browser can retrieve them faster upon subsequent visits to the same website, thus accelerating loading times. This efficiency gain is especially noticeable when dealing with sites with frequent updates or those with a large number of embedded assets.
Purpose and Function of the Internet Explorer Cache
The primary purpose of the Internet Explorer cache is to speed up browsing by storing frequently accessed web page components. This stored data, known as cached content, is retrieved from the local computer’s storage rather than having to download it from the server every time the user visits the same website. This process dramatically reduces the time needed to load pages, improving overall browsing speed.
Ever wondered why your Microsoft Internet Explorer cache might be acting up? It’s often a symptom of broader server issues. For example, ensuring your WordPress website’s server is consistently online is crucial. This is easily monitored using tools like the ones explained in how to monitor your WordPress website server uptime. A stable server, in turn, keeps your Internet Explorer cache functioning smoothly.
If your server’s uptime is consistently good, your cache should be fine. Ultimately, a healthy server translates to a smooth browsing experience when using Microsoft Internet Explorer.
Types of Data Stored in the Cache
The Internet Explorer cache stores various types of data crucial for web page display. This includes images, scripts, stylesheets, and other resources required to render a webpage. These cached elements can range from simple graphic images to complex JavaScript code that handles dynamic page content. Storing these components locally allows for quicker retrieval, minimizing the need for repeated downloads from the server.
Improvement of Browsing Speed and Efficiency
The cache dramatically improves browsing speed and efficiency by reducing the amount of data that needs to be downloaded from the internet. When a user visits a website for the second or subsequent time, the browser can often retrieve the needed data directly from the cache. This reduces network traffic, lowers latency, and allows for a faster display of the webpage’s elements.
Structure and Organization of Cache Files
The cache files are structured and organized to optimize retrieval speed. The cache typically contains a directory structure reflecting the website’s domain and file paths. This hierarchical organization enables the browser to locate specific cached files quickly and efficiently. A well-organized cache structure reduces the time required to locate the necessary data, ensuring smooth and rapid browsing.
Comparison with Other Browser Caching Mechanisms
| Feature | Internet Explorer Cache | Other Browser Caching Mechanisms (e.g., Chrome, Firefox) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Stores frequently accessed web resources. | Stores similar resources in a structured format for faster retrieval. |
| Retrieval Speed | Retrieves data from local storage, leading to faster page loads. | Employs similar mechanisms for rapid retrieval, improving browsing performance. |
| Cache Management | Automatically manages the cache to store and remove data as needed. | Has similar mechanisms for handling cache content, ensuring efficient usage. |
| Expiration Policies | Typically follows expiration policies defined by the server. | Applies similar policies, ensuring freshness and validity of cached data. |
The table above provides a basic comparison. Modern browser caching mechanisms, including those found in Chrome and Firefox, are highly sophisticated, with features like cache invalidation and more advanced storage strategies to further enhance efficiency. These features ensure the data remains fresh and relevant to the user’s experience.
Managing the Internet Explorer Cache
The Microsoft Internet Explorer cache, while crucial for faster browsing, can sometimes become cluttered, impacting performance. Proper management of this cache is vital for optimal browsing speed and a smooth user experience. Knowing how to clear the cache effectively and understanding when it’s necessary can significantly improve your online experience.Effective cache management involves more than just knowing how to clear it.
Understanding the implications of cache clearing on browsing experience, as well as the various methods for achieving this, are essential for making informed decisions. This section delves into the practical aspects of managing the Internet Explorer cache.
Methods for Clearing the Cache
Various methods exist for clearing the Internet Explorer cache. These methods range from simple, automated tools to manual, step-by-step procedures. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the user’s needs and technical proficiency. The optimal approach often depends on the specific situation and the desired level of control.
Manual Clearing of Cache in Different Versions
Internet Explorer versions vary in their cache management interfaces. The steps for clearing the cache manually differ slightly across these versions. Understanding these differences is key to effectively managing your cache.
Internet Explorer 11
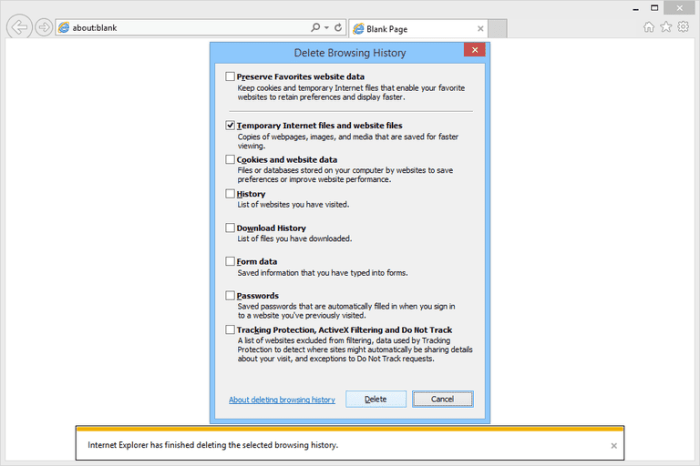
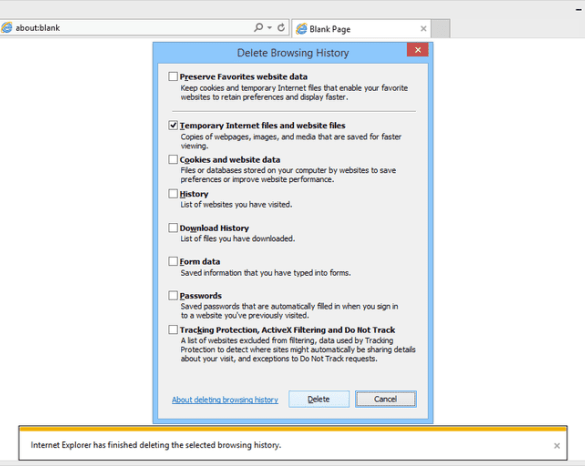
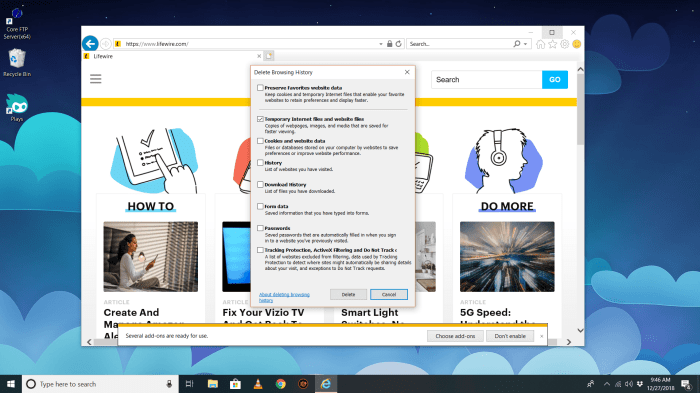
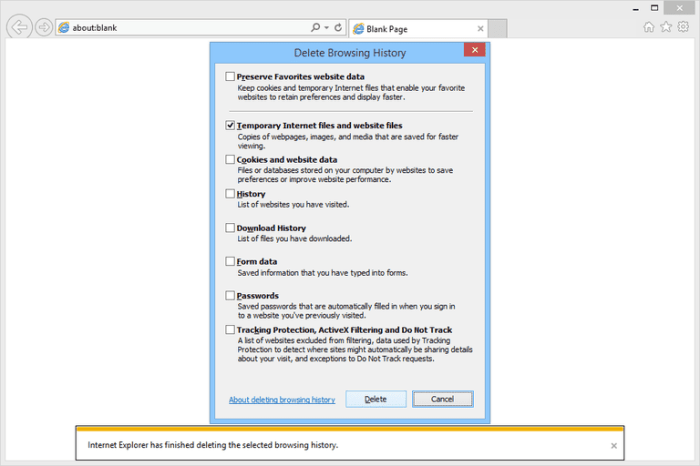
To clear the cache in Internet Explorer 11, open Internet Options. Navigate to the “General” tab and locate the “Browsing history” section. Click the “Delete” button. A dialog box will appear, allowing you to choose what data to delete. Select “Temporary Internet Files and website files” and click “Delete.” Confirm the deletion.
Internet Explorer 10
Clearing the cache in Internet Explorer 10 is similar to Internet Explorer 11. Open Internet Options, navigate to the “General” tab, and click “Delete.” Choose “Temporary Internet Files and website files” and click “Delete.” Confirm the deletion.
Internet Explorer 9 and Earlier
Clearing the cache in earlier versions, such as Internet Explorer 9 and earlier, follows a similar procedure. Open Internet Options, navigate to the “General” tab, and click “Delete.” Choose “Temporary Internet Files and website files” and click “Delete.” Confirm the deletion.
Impact of Clearing the Cache on Browsing Experience
Clearing the cache can have a noticeable impact on the browsing experience. Clearing the cache can improve page load times, particularly for frequently visited websites, by eliminating outdated data. This process can also address issues related to website display errors, where cached data may be corrupt or outdated.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Emptying Cache and Temporary Internet Files
The following steps Artikel a standardized procedure for emptying the cache and temporary Internet files in Internet Explorer:
- Open Internet Explorer.
- Click on the “Tools” menu (or the gear icon in newer versions).
- Select “Internet Options.”
- Navigate to the “General” tab.
- Click on the “Delete” button under Browsing history.
- Check the box for “Temporary Internet Files and website files.”
- Click “Delete.”
- Confirm the deletion.
Scenarios Requiring Cache Clearing
Clearing the cache can resolve various issues, including:* Slow website loading: If websites take longer than usual to load, clearing the cache can improve performance by removing outdated or corrupted data.
Display problems
Issues with website rendering or incorrect display can often be resolved by clearing the cache.
Login issues
Problems logging into websites may be resolved by removing cached login credentials.
Outdated content
Websites may not display the most current content if cached versions are used instead of the latest data.
Pros and Cons of Frequent Cache Clearing
| Feature | Pros | Cons ||—|—|—|| Improved performance | Faster page load times | Potential loss of saved logins and settings for websites || Reduced storage usage | Keeps the browser’s storage more organized | Can disrupt the user’s customized browsing experience || Fixes display errors | Eliminates outdated or corrupted cached data | Potential need to re-enter saved website login information || Security enhancement (in some cases) | Reduces the risk of encountering malicious cached data | Can potentially clear necessary website settings or data |
Impact of Cache on Website Performance
The Internet Explorer cache, while crucial for speeding up browsing, can sometimes have a detrimental effect on website performance if not managed properly. A poorly managed cache can lead to slow loading times, display issues, and even a negative user experience. Understanding the nuances of how the cache affects websites is essential for optimizing their speed and reliability.A full cache, overflowing with outdated or irrelevant data, can significantly slow down website loading times.
Imagine a cluttered storage room; finding the right item becomes increasingly difficult and time-consuming. Similarly, a full cache forces the browser to search through a vast amount of stored data to locate the needed resources, resulting in longer loading times. This directly translates into a frustrating user experience, leading to potential loss of visitors and diminished engagement.
Ever wondered why your Microsoft Internet Explorer cache might be acting up? Sometimes, seemingly unrelated issues, like unassigned traffic in Google Analytics 4, can actually be linked to browser caching. For example, if you’re having trouble figuring out where your GA4 traffic is going, checking your browser’s cache settings might be a good first step. Troubleshooting unassigned traffic in GA4 can involve a variety of techniques, as outlined in this helpful guide: how to fix unassigned traffic in ga4.
Regardless of the solution, ensuring your Internet Explorer cache is properly managed can prevent future issues, ensuring smooth browsing experiences.
Impact on Website Loading Times
A large cache can dramatically affect loading times, particularly for static assets like images, stylesheets, and scripts. When a user requests a page, the browser first checks the cache. If the requested resources are found, they are loaded directly from the cache, skipping the step of downloading them from the server. However, if the cache is full of outdated or unnecessary items, the browser has to search through a massive amount of data to find the correct file.
This extra search time directly contributes to the overall loading time of the website. This is especially noticeable for websites that have a large amount of static content, such as e-commerce platforms or news sites.
Ever wondered about the Microsoft Internet Explorer cache? It’s essentially a temporary storage area for webpages, and while useful, it can sometimes slow things down. Luckily, with initiatives like clicta digital agency launches google ad grants management to support nonprofits , organizations are finding new ways to streamline their online presence. Clearing your browser’s cache regularly can significantly improve your browsing experience, which is key to keeping your online presence optimized.
Ultimately, a well-maintained cache is crucial for a fast and efficient browsing experience.
Potential Issues from a Large Cache
A large, unmanaged cache can lead to various problems. First, it consumes significant disk space, potentially impacting system performance. Second, it can increase the time required for the browser to locate the necessary files, leading to slower loading times. Third, it can store outdated or irrelevant data, leading to inconsistent or incorrect displays on the website. Fourth, if the cache is not regularly invalidated, it can present outdated versions of resources, leading to broken links, missing images, or incorrect styles.
This is more pronounced on frequently updated websites.
Impact of Cache Size on System Performance
A large cache can strain system resources, impacting not only website performance but also overall system responsiveness. The more data stored in the cache, the more memory and disk space are consumed. This can lead to slower system speeds, reduced efficiency, and potentially cause instability. In extreme cases, a very large cache can even cause the system to freeze or crash.
The impact of cache size on system performance is a key consideration for website administrators.
Effects of Cache Invalidation Strategies
Different cache invalidation strategies have different impacts on website loading speed. A proactive invalidation strategy, where cached data is automatically updated or removed, can significantly improve loading times. This prevents the display of outdated content and ensures users always see the most up-to-date version of the website. In contrast, a passive invalidation strategy, where the cache is only updated periodically, can lead to slower loading times, especially for frequently updated websites.
Website administrators need to choose a strategy that balances the need for speed with the need for maintaining a valid cache.
Impact of a Stale Cache on Website Display
A stale cache can result in an inaccurate or outdated display of a website. Outdated stylesheets can lead to incorrect formatting and layout, while stale images can display incorrect versions. Users may experience missing images, incorrect text, or a visually inconsistent website. The impact is most evident when a website has frequently updated content, such as news articles or product listings.
For example, a news portal with a stale cache may display old headlines or articles, making the content appear out of date.
Effect of Cache on Website Responsiveness
A large and inefficient cache can negatively affect website responsiveness. A sluggish or unresponsive website is a common user experience problem. The time required to retrieve data from the cache directly impacts the overall responsiveness of the website. A large cache can cause delays in loading dynamic content, resulting in a slow and frustrating user experience. The responsiveness of a website depends on the efficient management of its cache.
Troubleshooting Cache-Related Issues
Internet Explorer’s cache, while crucial for faster page loading, can sometimes become a source of problems. Corrupted or outdated cache files can lead to slowdowns, broken links, and display inconsistencies. Understanding how to identify and resolve these issues is essential for maintaining a smooth browsing experience.
Common Cache-Related Problems
Internet Explorer cache issues manifest in various ways. Slow loading times, missing images, or incorrect display of web pages are common symptoms. Sometimes, entire websites might not load at all, or parts of them might load incorrectly. Users might encounter error messages or notice inconsistencies in the layout or design of a website.
Identifying Cache-Related Problems
Identifying the source of a cache-related problem often involves a combination of observation and testing. Users should pay attention to the specific symptoms they encounter. Are images missing? Are web pages loading slowly? Are there error messages displayed?
The nature of the problem can help pinpoint the cause.
Diagnosing Cache Problems
Several methods can help diagnose cache-related issues. First, try clearing the cache and cookies. If the problem persists, check for corrupted files within the cache folder. If you suspect a specific website is causing the issue, temporarily disabling caching for that site might offer insights.
Common Causes of Slow Loading Times
Several factors can contribute to slow loading times due to cache issues. Outdated or corrupted cache files can lead to unnecessary re-downloads of content, slowing down the entire process. If the cache contains outdated or corrupted versions of files, the browser might attempt to reload those files from the server, which can significantly extend the loading time.
Troubleshooting Cached Content
Troubleshooting cached content involves a series of steps. First, clear the cache and cookies. If the issue persists, try disabling caching for specific websites. If possible, contact the website administrator to determine if there are any issues on their end that might be contributing to the problem.
Resolving Corrupted Cache Files
Corrupted cache files can lead to numerous issues. The cache folder can become fragmented, leading to slow loading times or display problems. It’s crucial to understand that manually altering or deleting files within the cache folder without proper understanding could further damage the browser’s functionality. In such cases, clearing the cache and cookies is often the safest solution.
Troubleshooting Steps for Cache Problems
- Clear the cache and cookies: This is the first and often most effective step. Clearing the cache removes outdated or corrupted files, allowing the browser to download the most up-to-date versions of web pages and their components.
- Disable caching for specific websites: If the problem seems isolated to a particular website, disabling caching for that site can help determine if the issue lies with the website or with your browser’s cache.
- Check for corrupted files: Examine the cache folder for any damaged or corrupted files. If such files are found, deleting them may resolve the problem.
- Contact the website administrator: If the problem persists after clearing the cache and cookies, contact the website administrator to see if they are experiencing any issues on their end.
Common Cache-Related Errors and Solutions
| Error | Solution |
|---|---|
| Images not displaying | Clear cache and cookies, disable caching for the website, check for corrupted files. |
| Slow loading times | Clear cache and cookies, disable caching for the website, check for corrupted files, optimize network connection. |
| Incorrect display of web pages | Clear cache and cookies, disable caching for the website, check for corrupted files. |
| Website not loading at all | Clear cache and cookies, disable caching for the website, check network connection, check for server issues. |
Security Considerations Regarding the Cache: Microsoft Internet Explorer Cache
The Internet Explorer cache, while speeding up browsing, can become a security vulnerability if not managed properly. Storing temporary files, including potentially sensitive information, raises concerns about data breaches and malicious attacks. Understanding the security implications and implementing appropriate security measures is crucial for protecting user data and maintaining a secure browsing environment.The cache, acting as a repository for web pages and files, can inadvertently store sensitive data, like login credentials or personal information, if not properly secured.
This data can be exploited by attackers if the cache is compromised, leading to unauthorized access or identity theft. Furthermore, the cache can be a target for malicious attacks, potentially exposing the user to various security risks.
Vulnerabilities of the Internet Explorer Cache
The cache can be a vulnerable point of entry for attackers. Compromised websites can inject malicious code into cached files. If a user accesses a compromised site, the cached version, now containing the malicious code, could execute on the user’s system. This vulnerability is especially relevant in situations where users frequently revisit websites or use cached versions of web pages.
Risks Associated with Sensitive Data in the Cache, Microsoft internet explorer cache
Storing sensitive data, like passwords and credit card information, in the cache poses significant security risks. If the cache is compromised, this sensitive data can be exposed, leading to potential identity theft or financial fraud. This is a critical concern, as users often unknowingly retain sensitive data within the cache.
Best Practices for Securing the Cache
Regularly clearing the cache is a fundamental security measure. Deleting cached files removes potentially compromised data and reduces the risk of exposure. Strong passwords and security software are also essential for protecting the user’s entire system, including the cache.
- Regular Cache Clearing: Regularly clearing the cache is crucial for preventing security breaches. This practice eliminates potentially compromised data and reduces the attack surface. Regular clearing ensures that sensitive information is not retained in the cache, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. Consider scheduling regular cache clearing, such as weekly or monthly, as a preventative measure.
- Robust Password Management: Implementing strong and unique passwords for online accounts is vital. This measure strengthens overall security and protects against various attacks, including those targeting cached data. Utilizing a password manager can help generate and store strong passwords securely, further enhancing security protocols.
- Employing Security Software: Employing reliable anti-virus and anti-malware software is essential. This software actively scans for and neutralizes threats, including those targeting the cache. Regular updates to security software ensure that it can detect and mitigate emerging threats.
- Secure Browsing Habits: Avoid accessing potentially compromised websites. Exercise caution when clicking links, especially those from unknown or suspicious sources. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of malicious code being injected into the cache. Always verifying the legitimacy of a website before entering sensitive information is critical.
Preventative Measures for Cache Security
Implementing preventative measures is vital for safeguarding the cache and mitigating security risks. A proactive approach reduces the potential for attacks and protects sensitive data.
- Enable Browser Security Features: Utilize browser security features, such as enhanced protection or phishing filters. These features often include the ability to identify and block potentially malicious websites or content, preventing the cache from storing harmful elements.
- Review Browser Settings: Regularly review browser settings, especially those related to privacy and security. Ensure that appropriate security features are enabled to protect against cache-related vulnerabilities. This includes understanding and adjusting cache settings within the browser to minimize risks.
- Educate Users: Educating users about cache security risks is vital. By informing users about the implications of storing sensitive data in the cache and best practices for secure browsing, organizations can empower users to protect themselves. This includes awareness training about identifying phishing attempts and suspicious websites.
Cache Management Tools and Techniques
The Internet Explorer cache, while crucial for website performance, can sometimes become bloated and negatively impact browsing speed. Proper management of this cache is vital for a smooth and efficient browsing experience. This section explores tools and techniques for effective Internet Explorer cache management.Understanding the tools and methods available to manage the cache empowers users to optimize their browsing experience and maintain a healthy system.
The efficiency of your browsing is directly related to how effectively you manage the cache.
Identifying Cache Management Tools
Various tools can assist in managing the Internet Explorer cache, ranging from built-in options to third-party applications. Knowing these options gives you control over your browsing experience. Some tools provide a more comprehensive approach than others, allowing you to fine-tune your cache management strategy.
Using Third-Party Tools to Clear the Cache
Several third-party tools are designed to manage the Internet Explorer cache with greater control than the built-in options. These tools often provide additional features beyond simply clearing the cache, such as managing cookies, browsing history, and temporary files. They provide a more comprehensive approach to browser management. Some tools offer options for scheduling automatic cache clearing, or allow customization of which specific cache entries are cleared.
Using Tools for Effective Cache Management
Effective cache management involves understanding how each tool works and selecting the one that best suits your needs. A crucial step is learning how to use the selected tools effectively. This requires familiarizing yourself with the specific features and functionalities.
Optimizing Cache Management for Better Performance
Optimizing cache management involves understanding the trade-offs between speed and storage space. A well-managed cache reduces load times while minimizing storage demands. Knowing how to effectively manage the cache enhances website performance and reduces the strain on system resources. This can significantly impact overall system performance.
Cache Management Tools Comparison
The following table Artikels some popular cache management tools and their functionalities.
| Tool Name | Functionality | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| CCleaner | Clears cache, cookies, browsing history, and temporary files. Provides options for selective clearing and scheduling. | Comprehensive cleaning, scheduling options, and a user-friendly interface. |
| IObit Advanced SystemCare | Offers a suite of system optimization tools, including cache management. Provides a graphical interface for managing cache, cookies, and other browser data. | Comprehensive system optimization, including cache management, alongside other system-level improvements. |
| Wise Cache Cleaner | Specializes in cleaning cache files and temporary files. Often provides advanced settings for precise control over cache management. | Focuses specifically on cache cleanup, providing precise control over the files to be removed. |
Benefits of Specialized Cache Management Tools
Specialized cache management tools offer several advantages over the built-in Internet Explorer options. These tools provide advanced features and customization options, allowing users to fine-tune their cache management strategy for optimal performance. They provide a more streamlined and user-friendly approach to managing cache.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, understanding the Microsoft Internet Explorer cache is key to maximizing your browsing experience. Proper management, from clearing outdated data to utilizing appropriate tools, ensures optimal website performance and security. We’ve explored the entire lifecycle of the cache, from its role in enhancing speed to its potential for security risks, empowering you to take control and navigate the web smoothly.