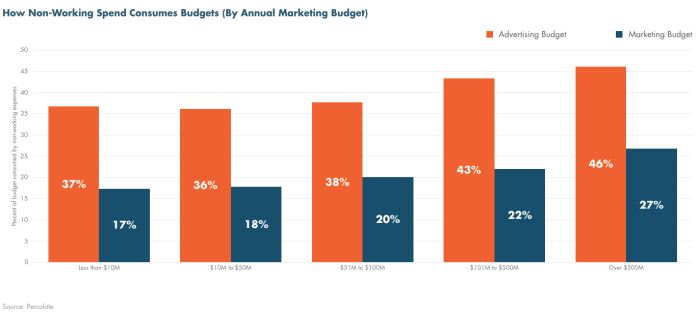
Measuring the true cost of marketing sets the stage for a crucial conversation about maximizing ROI. This isn’t just about crunching numbers; it’s about understanding the hidden expenses and intangible factors that often get overlooked in traditional marketing budgets. We’ll explore how to move beyond perceived costs and delve into the actual, comprehensive expenses associated with different marketing initiatives.
From defining “true cost” and identifying key cost drivers to measuring marketing effectiveness and conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis, we’ll cover a range of strategies for optimizing your marketing spend. Real-world case studies and actionable tools will help you apply these principles to your own campaigns. Get ready to uncover the hidden costs and boost your bottom line!
Defining True Cost
Understanding the true cost of marketing goes beyond the initial budget. It encompasses all the expenses directly and indirectly associated with a campaign, revealing the complete financial picture. This holistic view is crucial for effective resource allocation and accurate return on investment (ROI) analysis. A deeper dive into the concept of true cost is necessary to make informed decisions and avoid costly miscalculations.The perceived cost of a marketing campaign often represents only the upfront expenses.
This frequently leads to a skewed perspective on the overall investment. True cost, however, includes all the associated expenses that contribute to the success or failure of the campaign, thus providing a more realistic and comprehensive picture.
Components of True Cost
The true cost of a marketing initiative extends beyond the obvious. It incorporates various elements, each playing a vital role in the overall campaign performance. These include not only direct costs but also indirect costs, which can sometimes be more substantial than anticipated.
Perceived Cost vs. True Cost
Perceived cost in marketing often focuses on tangible expenses like advertising spend and design fees. However, true cost goes beyond these, encompassing hidden costs like time spent on project management, staff salaries, and potential opportunity costs. These hidden costs can significantly impact the profitability of a campaign, making a true cost analysis essential for informed decision-making.
Cost Breakdown by Marketing Activity
Understanding the cost breakdown across different marketing activities provides a clear picture of where resources are being allocated. A detailed analysis of each activity helps pinpoint areas where efficiency can be improved or where adjustments are needed.
| Marketing Activity | Cost Breakdown Categories |
|---|---|
| Advertising (e.g., TV, radio, social media) | Media buys, production costs, creative agency fees, ad placement, campaign management, tracking & analytics. |
| Content Creation (e.g., blog posts, articles, videos) | Writer fees, editor fees, graphic designer fees, video production costs, platform costs, optimization. |
| Influencer Marketing | Influencer fees, campaign management, content creation support, monitoring and analysis. |
| Search Engine Optimization () | consultant fees, website optimization, content creation, research, link building, ongoing maintenance. |
| Email Marketing | Email platform subscription fees, design costs, list building, content creation, campaign management, analysis. |
Identifying Cost Drivers
Unpacking the true cost of marketing isn’t just about adding up expenses; it’s about understanding the intricate factors driving those costs. Modern marketing landscapes are complex, with numerous moving parts and technological influences. Pinpointing these cost drivers allows for more effective budgeting, optimized campaigns, and ultimately, a better return on investment.This exploration delves into the core cost drivers, examining how technology shapes these costs, and contrasting the financial burdens of various marketing channels.
We’ll present a structured approach for analyzing campaign expenses, making the entire process more transparent and manageable.
Key Cost Drivers in Modern Marketing
Understanding the various elements that contribute to marketing expenses is crucial for effective cost management. These elements span across different stages and aspects of a marketing campaign.
- Personnel Costs: Salaries for marketing teams, including strategists, designers, content creators, and social media managers, are a significant expense. Specialized roles like data analysts and specialists add to this personnel burden. The cost of outsourcing certain tasks or hiring freelancers can also vary greatly depending on the scope of the project.
- Technology Costs: Software subscriptions, cloud storage, and marketing automation tools are integral to modern marketing efforts. The cost of maintaining and upgrading these technologies can be substantial, particularly for complex systems and high-volume campaigns. Choosing the right technology is key to balancing functionality with affordability.
- Advertising Costs: The expense associated with various advertising channels (e.g., social media ads, search engine ads, display ads) varies significantly depending on factors like target audience, bidding strategies, and campaign duration. Highly competitive markets often result in higher ad costs.
- Content Creation Costs: Producing high-quality written, visual, or audio content requires investment in time, resources, and potentially freelance talent. Costs associated with photography, videography, and graphic design play a vital role in determining the overall content budget.
- Agency Fees: When engaging external marketing agencies, the fees for services such as strategy development, campaign execution, and reporting must be factored into the overall marketing budget. The cost of agencies can vary greatly depending on their experience, expertise, and the scope of the project.
Impact of Technology on Marketing Costs, Measuring the true cost of marketing
Technology’s profound influence on marketing has led to both cost savings and increased expenses. Automation tools, for instance, can streamline tasks, reducing labor costs. However, implementing and maintaining these systems often involves substantial initial investment.
- Automation Tools: While automating repetitive tasks can decrease labor costs, the initial investment in software licenses and training can be significant. Ongoing maintenance and upgrades further contribute to the overall cost.
- Data Analytics: Leveraging data analytics to gain deeper insights into customer behavior is invaluable for optimizing marketing campaigns. However, this often requires specialized software and personnel to interpret the data, increasing the technological and human resource cost.
- Digital Marketing Channels: The rise of digital channels like social media and search engines has made marketing more accessible, but the ongoing cost of managing campaigns and staying current with evolving algorithms can be significant. Competitive advertising costs can also be high on these platforms.
Cost Comparison Across Marketing Channels
The cost of marketing campaigns varies greatly depending on the chosen channels. This section provides a comparative overview, highlighting the factors influencing the expenses.
| Marketing Channel | Key Cost Drivers | Typical Cost Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Social Media Marketing | Advertising costs, content creation, community management | Variable; depends on platform, targeting, and campaign scope |
| Search Engine Optimization () | Content creation, research, technical optimization | Ongoing; requires investment in time and resources |
| Email Marketing | List building, email design, campaign management, email service provider (ESP) | Variable; depends on list size, email frequency, and sophistication of campaigns |
Framework for Analyzing Marketing Campaign Costs
A structured approach to analyzing marketing campaign costs is crucial for informed decision-making. This framework provides a systematic method for evaluating expenses.
- Define Objectives: Clearly Artikel the goals of the marketing campaign, which directly influences the resources needed.
- Identify Target Audience: Knowing the target audience informs the choice of channels and the type of content to be created, impacting costs.
- Estimate Resource Requirements: Accurately assess the personnel, technology, and materials needed for campaign execution, including content creation, marketing tools, and ad spend.
- Track Expenses: Implement a system for diligently recording all expenses related to the campaign, enabling a precise cost analysis.
- Analyze ROI: Evaluate the return on investment of the campaign against the total cost incurred. This provides crucial feedback for future campaigns.
Measuring Marketing Effectiveness
Pinpointing the true cost of marketing isn’t just about identifying expenses; it’s equally crucial to understand how effectively those investments are generating desired outcomes. This involves a rigorous examination of the metrics that quantify marketing campaign success and the return on investment (ROI) achieved. Without accurate measurement, it’s impossible to optimize strategies and ensure marketing dollars are spent wisely.
Effective measurement allows businesses to identify what works, what doesn’t, and where adjustments are needed to improve future campaigns.
Critical Marketing Metrics
Understanding the impact of marketing activities requires tracking various key metrics. These metrics offer insights into campaign performance, audience engagement, and overall business growth. They provide the data needed to make informed decisions and refine marketing strategies. Focusing on the right metrics ensures that the evaluation process isn’t just a collection of numbers, but a meaningful assessment of campaign effectiveness.
- Website Traffic: Website traffic metrics, such as unique visitors, page views, and bounce rate, offer a clear picture of audience engagement with the marketing content. Tracking these metrics allows for identification of high-performing campaigns that drive significant traffic to the website.
- Conversion Rates: Conversion rates are crucial for measuring the effectiveness of marketing in driving desired actions, such as completing a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or requesting a demo. Conversion rates help to quantify the effectiveness of marketing channels in generating leads and ultimately sales.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The cost of acquiring a new customer provides a vital metric for evaluating the efficiency of marketing campaigns. Lowering CAC is often a primary goal for businesses looking to maximize profitability and improve the overall return on investment from marketing activities. This metric provides valuable insights into the overall cost-effectiveness of marketing efforts.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): This metric estimates the total revenue a customer is expected to generate throughout their relationship with a company. A high CLTV indicates that marketing investments are yielding substantial long-term returns, highlighting the importance of customer retention strategies.
Return on Investment (ROI) Calculation
Calculating ROI is fundamental to assessing the profitability of marketing campaigns. It compares the net profit generated from a marketing campaign to the total costs associated with that campaign. This calculation provides a clear understanding of the financial return on each marketing dollar spent.
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Marketing) – 100%
For example, if a marketing campaign generates $10,000 in profit with $5,000 in costs, the ROI would be 100% [(10,000/5,000)100%]. This means for every dollar invested, one dollar was returned.
Figuring out the true cost of marketing campaigns can be tricky, right? It’s not just about ad spend. You need to factor in everything from design and development to the time spent strategizing. And that’s where optimizing your website for search engines becomes crucial. Knowing how to build a single-page website that truly resonates with search algorithms can save you a bundle, as outlined in the ultimate guide to single page websites and seo.
This comprehensive approach allows you to focus your marketing efforts more efficiently and get a better return on your investment. Ultimately, measuring the true cost of marketing comes down to understanding how each element impacts your overall bottom line.
Attribution Modeling
Attribution modeling is essential for understanding which marketing channels or campaigns contribute most significantly to conversions. By tracking the customer journey, attribution models help determine the touchpoints that influence a customer’s decision to purchase. This granular understanding allows for optimized marketing budgets and strategic adjustments to maximize ROI across various channels.
- First-Touch Attribution: This model assigns credit to the first marketing touchpoint a customer interacts with before making a purchase. It’s straightforward but may not accurately reflect the impact of subsequent interactions.
- Last-Touch Attribution: This model assigns credit to the last marketing touchpoint a customer interacts with before making a purchase. It might overestimate the impact of the final interaction and undervalue earlier touchpoints.
- Multi-Touch Attribution: This model assigns credit across multiple touchpoints based on their influence throughout the customer journey. It’s often the most accurate method for understanding the overall impact of different marketing efforts.
Marketing Metrics Table
| Metric | Calculation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Website Traffic | Unique Visitors + Page Views | Measures overall website engagement. |
| Conversion Rate | (Conversions / Total Visits) – 100% | Measures the percentage of visitors who complete a desired action. |
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | Total Marketing Cost / Number of Customers Acquired | Calculates the cost to acquire each new customer. |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) | Average Purchase Value
|
Estimates the total revenue a customer will generate over their relationship with the company. |
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Understanding the true return on your marketing investment requires a rigorous cost-benefit analysis. This step goes beyond simply identifying costs; it delves into quantifying the value generated by each marketing strategy. A thorough analysis allows for informed decisions, optimizing resource allocation, and ultimately maximizing profitability. It’s the bridge between spending money and achieving measurable results.
Conducting a Thorough Cost-Benefit Analysis
A cost-benefit analysis is a systematic process of evaluating the financial implications of a marketing strategy. It involves identifying all costs associated with a campaign, including direct costs like advertising spend and indirect costs like staff time. Crucially, it also requires estimating the benefits derived from the campaign, such as increased sales, lead generation, or brand awareness. This analysis should be tailored to the specific marketing strategy and target audience, ensuring accurate estimations of both costs and benefits.
Evaluating Profitability of Marketing Channels
Different marketing channels have varying costs and potential returns. A key aspect of a cost-benefit analysis is evaluating the profitability of each channel. This involves assessing the cost per acquisition (CPA) for each channel, comparing it to the average revenue generated per customer acquired through that channel. For example, social media marketing might have a lower CPA than traditional print advertising, but the return on investment (ROI) may vary depending on the specific strategy and target audience.
Analyzing data on customer acquisition costs and revenue generated from each channel is critical for informed decision-making.
Comparing Profitability of Diverse Marketing Strategies
Comparing the profitability of various marketing strategies necessitates a standardized approach. One method is to calculate the ROI for each strategy, expressing the gain or loss as a percentage of the initial investment. For instance, a strategy with a higher ROI suggests a greater return for every dollar invested. Alternatively, a cost-per-lead (CPL) analysis can be used to compare the efficiency of strategies in generating leads.
By focusing on metrics like ROI and CPL, businesses can assess which strategies yield the best return on investment.
Steps in a Cost-Benefit Analysis for a Marketing Campaign
A structured approach simplifies the process. This detailed table Artikels the key steps involved in a cost-benefit analysis for a marketing campaign:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Define Objectives | Clearly articulate the goals of the marketing campaign, such as increasing brand awareness, driving sales, or generating leads. |
| 2. Identify Costs | Detail all costs associated with the campaign, including advertising spend, staff time, marketing materials, and any other relevant expenses. |
| 3. Estimate Benefits | Quantify the anticipated benefits from the campaign, such as increased sales, leads generated, or improved brand awareness. Use historical data or market research to support these estimations. |
| 4. Calculate ROI | Divide the total benefits by the total costs to arrive at the ROI. Express the ROI as a percentage. |
| 5. Analyze Results | Compare the ROI of different marketing strategies to identify the most profitable approaches. Consider factors like target audience, campaign duration, and market conditions. |
| 6. Adjust Strategy | Based on the analysis, adjust the marketing strategy to optimize resource allocation and maximize returns. |
Case Studies and Examples: Measuring The True Cost Of Marketing

Understanding the true cost of marketing isn’t just about crunching numbers; it’s about understanding the impact of different strategies on overall profitability. Real-world examples of successful cost measurement provide invaluable insights, highlighting both effective and ineffective approaches. Analyzing both successes and failures reveals critical factors for optimizing marketing budgets and achieving desired outcomes.
Successful Cost Measurement Case Studies
Companies that accurately measure the true cost of marketing campaigns often see significant returns. This approach allows for precise resource allocation and better campaign performance tracking.
- A software company meticulously tracked the cost per lead generated from different marketing channels (social media, content marketing, paid advertising). By analyzing the cost of acquiring each lead across various platforms, they were able to optimize their budget, focusing on the channels that yielded the highest conversion rates. This led to a 20% increase in sales qualified leads over the next quarter.
- A retail brand implemented a robust marketing attribution model. This allowed them to pinpoint the exact contribution of each marketing touchpoint in the customer journey, from initial awareness to final purchase. This enabled them to identify and eliminate inefficient marketing activities, thereby reducing the overall cost per customer acquisition by 15%.
Miscalculated Marketing Costs and Consequences
Sometimes, a lack of accurate cost measurement leads to significant financial losses and missed opportunities.
- A startup launched a large-scale social media campaign without considering the cost of managing and moderating the influx of comments and interactions. The significant increase in customer service workload overwhelmed the support team, resulting in a drop in customer satisfaction and a substantial increase in operational costs. This ultimately led to a decrease in customer retention and a reduced return on investment.
- A company invested heavily in a print advertising campaign without considering the cost of design, printing, and distribution. They failed to measure the campaign’s reach and effectiveness, leading to wasted resources and a poor return on investment. This led to a decline in brand awareness and a loss of market share compared to competitors.
Industry-Specific Approaches
Different industries have unique approaches to measuring the true cost of marketing. Understanding these variations is crucial for tailoring strategies to specific market needs and constraints.
| Industry | Typical Cost Measurement Approach |
|---|---|
| E-commerce | Emphasis on customer lifetime value (CLTV), cost per acquisition (CPA), and return on ad spend (ROAS). Detailed tracking of online advertising performance and website analytics is essential. |
| Financial Services | Strict adherence to regulatory compliance and compliance costs are factored into the marketing budget. Focus on lead quality and customer acquisition cost (CAC) is paramount. |
| Healthcare | Highly regulated environment with stringent guidelines regarding marketing communication. Cost measurement often involves a blend of traditional media analysis and digital campaign tracking, with a strong focus on compliance and ethical advertising practices. |
Future Trends and Projections
The landscape of marketing is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting consumer behaviors. Predicting the future of measuring marketing costs requires understanding these dynamic forces. This section explores emerging trends impacting the measurement of marketing costs, from new technologies to the increasing role of data analytics.
Emerging Technologies and Strategies
Several emerging technologies and strategies are reshaping the way marketers approach campaign execution and measurement. These innovations significantly influence the true cost of marketing by altering the methods and channels used. AI-powered tools, for example, are automating tasks, optimizing campaigns, and personalizing customer experiences, which can impact costs through efficiency gains or targeted spending. Similarly, the rise of influencer marketing and its associated metrics are complicating the traditional attribution models.
Measuring the effectiveness and cost of influencer campaigns requires unique frameworks that consider the reach, engagement, and conversion rates specific to each platform.
Data Analytics and Cost Measurement
Data analytics will play a pivotal role in shaping future cost measurement in marketing. The increasing volume, velocity, and variety of data available allow marketers to track and analyze campaign performance with greater precision. Real-time data dashboards will allow for dynamic adjustments to campaigns, optimizing spending based on immediate results. Predictive analytics can forecast future outcomes and identify potential cost savings or risks.
This data-driven approach enables marketers to measure not only the direct costs but also the indirect costs associated with marketing efforts.
Figuring out the true cost of marketing campaigns can be tricky. You need to account for more than just ad spend. Tools like social media monitoring tools help track the impact of your efforts across various channels, which is crucial for accurately assessing the overall marketing investment. This detailed data helps pinpoint where your budget is performing best and where it might need adjustments, leading to a clearer understanding of the true cost of your marketing initiatives.
Evolving Landscape of True Cost Measurement
The measurement of marketing costs is evolving rapidly. In the next five years, we can expect a shift towards more granular and holistic approaches. Marketing attribution models will become more sophisticated, encompassing a wider range of touchpoints and channels. Advanced analytics will enable marketers to accurately measure the return on investment (ROI) for each marketing activity, allowing for more precise cost allocation.
Figuring out the true cost of marketing can be tricky, but it’s essential. Knowing which marketing strategies deliver the biggest bang for your buck is key. For example, exploring 5 techniques with the greatest return on marketing investment can help you identify the most effective approaches. 5 techniques with the greatest return on marketing investment will highlight areas where you can maximize your budget and achieve better results.
Ultimately, understanding the true cost of your marketing efforts is crucial for making smart decisions and optimizing your ROI.
This evolution is crucial for organizations to optimize their marketing budgets and ensure they are getting the most out of their investments. For example, companies might adopt more complex attribution models, such as multi-touch attribution, to trace customer journeys across multiple touchpoints. The shift toward more sophisticated models is driven by the need for a deeper understanding of the customer journey and the need to measure the impact of marketing campaigns on a more granular level.
Practical Applications and Tools
Putting the theory of marketing cost analysis into practice requires the right tools and a well-defined process. This section dives into the practical applications, showing how to track and manage marketing expenses effectively. From simple spreadsheets to sophisticated software solutions, we’ll explore various options to ensure you’re getting the most out of your marketing budget.
Tools and Techniques for Calculating and Managing Marketing Costs
Effective marketing cost management relies on a variety of tools and techniques. Choosing the right ones depends on the size and complexity of your marketing operations, as well as your budget. Spreadsheet software like Google Sheets or Microsoft Excel are excellent for basic tracking. For more complex needs, dedicated marketing analytics platforms offer comprehensive solutions. These platforms typically include features for campaign tracking, cost allocation, and performance reporting.
For instance, HubSpot, Google Analytics, and Salesforce Marketing Cloud are popular choices for businesses of varying sizes. Moreover, social media management tools can provide insights into ad spending and engagement metrics, allowing you to refine your strategy and optimize your return on investment.
Setting Up a System for Tracking and Measuring Marketing Costs
Establishing a robust system for tracking marketing costs is crucial for understanding ROI and making informed decisions. This involves creating a clear process for recording all marketing expenses, from ad spend to content creation costs. Key elements include:
- Defining categories: Categorize marketing expenses into specific campaigns, channels, or activities. This detailed breakdown allows for accurate allocation of costs and facilitates performance analysis.
- Implementing a centralized database: Use a spreadsheet, database, or dedicated software to store and manage marketing cost data. Maintaining a single source of truth streamlines reporting and analysis.
- Establishing a regular reporting schedule: Regular reporting (e.g., weekly, monthly) allows you to monitor cost trends, identify areas for improvement, and adjust strategies accordingly.
Integrating Cost Analysis into the Marketing Workflow
Integrating cost analysis into the marketing workflow requires a proactive approach. Regularly review marketing spend against performance metrics, and adjust strategies as needed. This proactive approach helps to ensure that marketing activities are not only effective but also cost-efficient.
- Pre-campaign cost estimation: Before launching a new marketing campaign, estimate the associated costs, including materials, labor, and advertising expenses. This step enables budgeting and resource allocation.
- Real-time monitoring: Use dashboards and reporting tools to monitor campaign performance and costs in real time. This allows for quick adjustments if the campaign is not meeting its objectives or exceeding its budget.
- Post-campaign analysis: After a campaign concludes, thoroughly analyze the costs and results. Identify areas of efficiency and areas where costs can be reduced for future campaigns.
Comparison of Marketing Cost-Tracking Tools
Different tools offer varying features and functionalities. This table provides a concise overview of common marketing cost-tracking tools and their key capabilities.
| Tool | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Analytics | Website traffic analysis, campaign tracking, conversion tracking | Free, comprehensive data | Requires technical understanding, may not be ideal for complex marketing setups |
| HubSpot | CRM, marketing automation, analytics, reporting | All-in-one solution, robust reporting features | Can be expensive for extensive use |
| Salesforce Marketing Cloud | Marketing automation, email marketing, social media management | Powerful for large-scale marketing campaigns | Very expensive, requires technical expertise |
| Excel/Google Sheets | Basic tracking, formulas, calculations | Low cost, customizable | Limited capabilities for complex analysis, not suitable for large-scale operations |
Optimizing Marketing Spend
Knowing the true cost of marketing is crucial, but it’s equally important to understand how to leverage that knowledge to improve your return on investment. Optimizing your marketing spend isn’t about cutting corners; it’s about strategically allocating resources to maximize effectiveness and minimize waste. This involves a shift from reactive spending to proactive resource management, fueled by data-driven insights and a clear understanding of your target audience.Effective optimization relies on understanding the interconnectedness of marketing activities and their impact on overall business goals.
It’s not just about reducing costs; it’s about reallocating funds to channels that deliver the best results, based on measurable ROI. This proactive approach, coupled with a deep understanding of your customer base, leads to significant improvements in marketing campaign performance.
Strategies for Budget Optimization
Effective budget optimization begins with a detailed analysis of current marketing activities. This includes identifying high-performing channels, identifying areas where inefficiencies exist, and understanding which channels yield the lowest return on investment. This crucial analysis should guide future marketing decisions and inform resource allocation.
- Prioritize high-performing channels: Identify and focus on channels demonstrating the highest ROI. This often involves analyzing data on click-through rates, conversion rates, and customer lifetime value associated with different marketing campaigns and channels. For example, if email marketing consistently generates higher conversion rates than social media advertising, a larger budget allocation to email campaigns might be warranted.
- Reduce or eliminate low-performing channels: Conversely, identify and eliminate channels with a demonstrably low ROI. This might involve discontinuing advertising campaigns on platforms that fail to generate meaningful leads or conversions. By cutting unproductive spending, companies can redirect funds to more profitable areas.
- Implement automated marketing: Leverage automation tools to streamline repetitive tasks, improve efficiency, and potentially reduce labor costs. This might include automating email marketing sequences, social media posting schedules, or lead nurturing campaigns. Automation tools can free up marketing teams to focus on higher-value tasks.
- Refine targeting: Ensure that marketing efforts are reaching the most relevant audience. This requires detailed analysis of customer data, understanding customer demographics, interests, and behaviors, and using this knowledge to tailor marketing messaging and channels. Precise targeting minimizes wasted ad spend by concentrating efforts on the most receptive audience.
Allocating Resources Based on ROI
Allocating resources based on measurable ROI is a critical component of optimization. This requires establishing clear metrics for success and tracking the performance of each marketing initiative. This data-driven approach helps ensure that marketing dollars are invested in strategies that demonstrably contribute to business objectives.
- Establish clear key performance indicators (KPIs): Define specific and measurable KPIs that align with overall business goals. Examples include website traffic, lead generation, sales conversions, and customer acquisition cost (CAC). These should be consistently tracked and analyzed.
- Track and analyze results: Monitor the performance of each marketing initiative against established KPIs. This ongoing analysis provides valuable insights into what’s working and what’s not, allowing for adjustments and reallocation of resources.
- Regularly review and adjust: The marketing landscape is dynamic. Regularly review marketing performance and adjust strategies based on the data. This adaptability ensures that marketing efforts remain aligned with current trends and customer needs.
Real-World Examples of Optimization Success
Many businesses have experienced significant improvements by optimizing their marketing spend. A retailer, for example, might have seen a substantial increase in sales by shifting a portion of its budget from print advertising to targeted online ads. Similarly, a software company could have boosted lead generation by focusing its efforts on content marketing and search engine optimization ().
These are just a few examples, and the specific improvements will vary depending on the industry, business model, and specific marketing strategies employed.
Identifying Areas for Cost Reduction
While optimizing marketing spend often involves strategic reallocation, it also includes identifying areas where costs can be reduced without compromising effectiveness. This might involve renegotiating contracts with advertising agencies or exploring alternative marketing channels that offer comparable results at a lower price.
- Negotiate contracts: Negotiate better rates with advertising agencies, social media platforms, or other marketing partners.
- Explore alternative channels: Evaluate and implement alternative marketing channels with a potentially lower cost per acquisition. This might involve leveraging social media marketing, content marketing, or influencer marketing.
- Optimize existing campaigns: Refine existing marketing campaigns by analyzing performance data and making adjustments to messaging, targeting, or ad creatives. This might include testing different variations of ads to see which perform best.
Epilogue
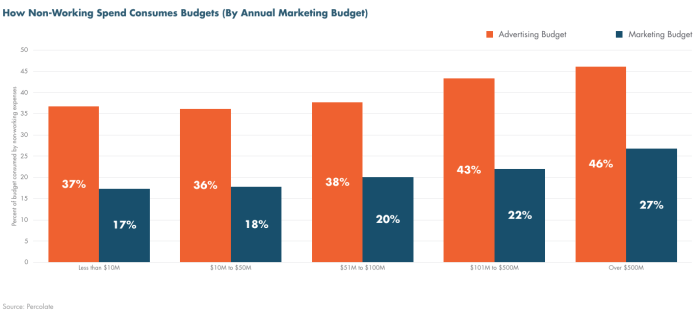
In conclusion, measuring the true cost of marketing is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor. It requires careful consideration of diverse factors, from the initial planning stages to ongoing evaluation and optimization. By understanding the complete cost picture, you can make informed decisions about resource allocation, channel selection, and overall marketing strategy. Ultimately, this deep dive into the true cost of marketing will empower you to make smarter choices and drive tangible results for your business.