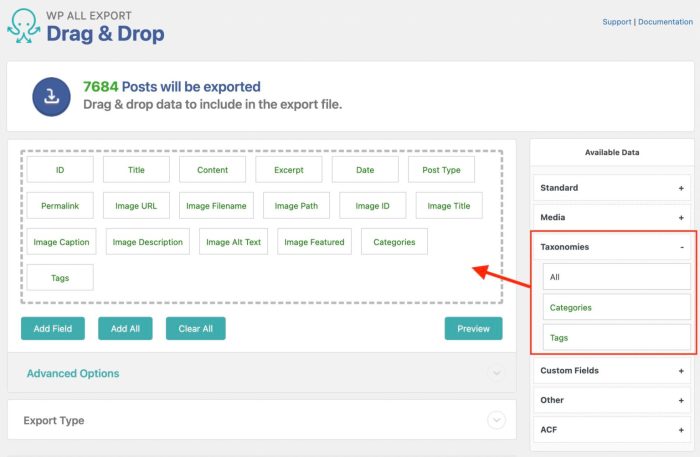
How to import post for WordPress is a crucial skill for anyone managing a WordPress site, especially when inheriting content or expanding their blog. This guide dives deep into the world of importing posts, covering various file formats, plugins, and potential pitfalls. We’ll explore different import methods, helping you choose the right approach for your needs, and provide a step-by-step walkthrough of the process.
From understanding the importance of post imports to optimizing WordPress for large-scale imports, this comprehensive guide covers all aspects of bringing your content to your WordPress site. We’ll also touch on critical security considerations to protect your website during the import process.
Introduction to WordPress Post Imports
WordPress post imports are a crucial tool for transferring content from other platforms to your WordPress website. Whether you’re migrating from a previous blog, consolidating content from multiple sources, or simply needing a quick way to add a large number of posts, imports offer a streamlined solution. They save significant time and effort compared to manually creating each post, especially when dealing with hundreds or thousands of entries.Import methods are essential for maintaining a consistent and organized workflow.
They enable seamless integration of various content formats, including XML, CSV, and others, making the transition from one platform to WordPress efficient. This versatility is crucial for users with diverse content needs.
Want to know how to import posts into your WordPress site? It’s a straightforward process, but understanding the underlying dynamics of ecommerce platforms like Shopify is helpful. For example, understanding how Shopify is impacting the ecommerce landscape can be insightful, especially when considering how to import data from one platform to another. This insightful article on tracking Shopify’s boom in ecommerce business dives into that, and it can help inform your approach to importing posts if you’re migrating from a Shopify store.
Ultimately, understanding these connections helps you choose the best methods for importing posts effectively into your WordPress blog.
Different Import Methods
Different file formats require different import methods. Understanding these distinctions ensures successful data migration. XML imports are often preferred for their structured nature, enabling WordPress to easily parse and interpret the data. CSV imports are suitable for data that’s organized in tabular format, like lists or tables. Specific plugins may support importing from other formats, such as JSON or custom databases, depending on their functionality.
The choice of import method directly impacts the efficiency and accuracy of the transfer process.
Importing posts into WordPress can be a breeze, but sometimes technical glitches like a DNS server not responding can throw a wrench in the works. If you’re encountering that frustrating error, check out this helpful guide on how to fix DNS server not responding error in WordPress 5 ways to get your site back online. Once you’ve resolved those server issues, importing your posts should go smoothly again.
Import Plugins vs. Manual Methods
Import plugins offer a significant advantage over manual methods, particularly for large-scale transfers. They automate the import process, reducing the risk of errors and saving considerable time. However, manual methods, while potentially more customizable, can be extremely time-consuming and error-prone for large volumes of content. The optimal choice depends on the scale of the import and the user’s technical expertise.
Comparison of Import Plugins
The following table provides a comparative overview of popular import plugins, highlighting key features, user reviews, and ease of use. It’s crucial to consider these factors when selecting a plugin for your specific needs.
| Plugin Name | Key Features | User Reviews | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Import/Export WP | Handles XML, CSV, and other formats; supports bulk import and export; good for general use. | Generally positive, with some users reporting issues with complex setups. | Medium. Requires some technical understanding to use effectively. |
| WP All Import | Highly versatile; supports many formats and custom data mapping; excellent for complex imports. | Very positive, praised for its flexibility and extensive features. | High. The extensive options can make it somewhat daunting for beginners. |
| WP Migrate DB | Excellent for complete website migrations, including posts, pages, users, and other data. | Generally positive, but some users find the learning curve steep for non-technical users. | Medium. User experience varies based on technical knowledge. |
| Advanced Custom Fields Import Export | Specifically designed for importing and exporting data from custom fields, crucial for complex content structures. | Mostly positive, emphasizing its tailored solutions for custom field data. | Medium to High. Ease of use depends on the complexity of custom fields being imported. |
Choosing the Right Import Method
Deciding on the appropriate import method for your WordPress posts is crucial for a smooth and efficient migration. The chosen format significantly impacts the import process’s speed, accuracy, and potential for errors. Different file formats offer various advantages and disadvantages, each tailored to specific data structures and import scenarios. Understanding these nuances is key to a successful WordPress import.
Common File Formats for Post Imports
Various file formats are commonly used for importing WordPress posts. These include CSV (Comma Separated Values), XML (Extensible Markup Language), and JSON (JavaScript Object Notation). Each format possesses unique characteristics influencing its suitability for different import tasks.
Comparison of Import Formats
- CSV (Comma Separated Values): This format excels at handling simple data structures. It’s straightforward to create and edit using spreadsheet software. However, it lacks the flexibility and structure of XML or JSON for complex data. Importantly, CSV files often require meticulous preparation to ensure compatibility with WordPress import plugins.
- XML (Extensible Markup Language): XML offers a structured format ideal for complex data with multiple fields and nested relationships. This structured approach can lead to more accurate and less error-prone imports compared to CSV. However, creating and manipulating XML files often demands more technical expertise than CSV.
- JSON (JavaScript Object Notation): JSON, similar to XML, provides structured data, making it suitable for intricate information. It’s widely used for its human-readable format and efficient data transfer. JSON’s popularity stems from its ease of use, particularly for web applications and data exchange. Import plugins may offer varying degrees of support for JSON.
Data Preparation for Import
Proper data preparation is vital for successful WordPress post imports. The method employed hinges on the chosen file format. Carefully mapping fields in the import file to WordPress’s corresponding fields ensures accurate data transfer.
Import Steps for Different Formats
| File Format | Preparation Steps | Import Plugin | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSV | Ensure consistent formatting (e.g., comma delimiter), accurate field names corresponding to WordPress categories, and validate data types (e.g., date, number). | Various plugins support CSV import; select one compatible with your data structure. | Inconsistent delimiters, incorrect field mappings, and missing data can lead to errors during import. |
| XML | Structure the XML file with appropriate tags corresponding to WordPress fields, validating the structure to avoid errors, and ensuring correct encoding. | WordPress often includes XML import capabilities or use dedicated plugins for intricate XML structures. | Incorrect XML structure, missing or malformed tags, and encoding issues can result in data loss or corruption during import. |
| JSON | Validate the JSON structure, ensuring correct field names match WordPress fields, verify data types (e.g., strings, numbers, dates) and correct encoding. | Select a plugin explicitly designed to import JSON data into WordPress. | Incorrect JSON structure, field mismatch, and data type discrepancies can cause issues during import. |
Handling Issues During the WordPress Post Import Process: How To Import Post For WordPress
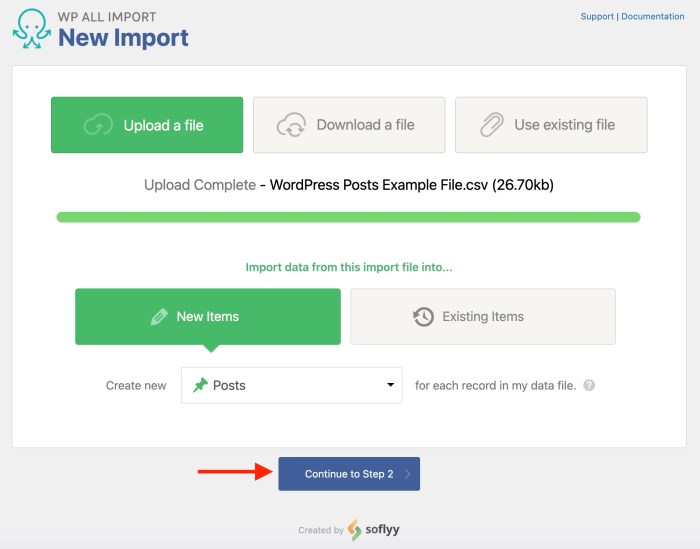
Importing content from other platforms to WordPress can sometimes lead to unexpected hiccups. Knowing how to identify and resolve these issues is crucial for a smooth migration. This section dives into common problems and effective troubleshooting strategies.Importing data, while often straightforward, can sometimes encounter problems. These problems range from seemingly minor glitches to major setbacks. Understanding the root causes of these problems and knowing how to address them is key to a successful import.
Common Import Errors and Their Causes
A variety of errors can occur during a WordPress import, stemming from various factors. These include inconsistencies in data formats, missing or incorrect data in the source file, and issues with the target WordPress installation. Identifying the source of the problem is the first step towards a successful resolution.
Identifying and Resolving Missing Fields, How to import post for wordpress
Sometimes, critical information might be missing from the import file. This can lead to incomplete or inaccurate posts and pages on your WordPress site. Carefully reviewing the import file and the destination WordPress settings can help pinpoint the missing fields. If the import tool allows it, using a spreadsheet or similar program to fill in the gaps beforehand can be a helpful preventive measure.
This is a crucial step as missing data can hinder the import process.
Importing posts into WordPress can be a breeze, but sometimes you need a little extra help. Understanding the intricacies of things like “billed cost served cost adwords breakout” billed cost served cost adwords breakout can be crucial for optimizing your site. Luckily, there are plenty of helpful resources online to walk you through the process of getting your posts uploaded.
Dealing with Duplicate Entries
Duplicate entries can cause significant problems, especially if the import process doesn’t account for them. It’s essential to anticipate this possibility. Most import plugins have options to handle duplicates, allowing you to either skip them, update existing entries, or merge them. Choosing the right option depends on the specific data and the desired outcome.
Recovering from a Failed Import
A failed import can be frustrating, but it’s not necessarily the end of the world. A crucial aspect of recovery is understanding why the import failed. If the error logs are available, carefully examine them to identify the root cause. Recovering from a failed import often involves revisiting the import process, reviewing the data source, and using a more appropriate import method.
Troubleshooting Import Problems
The following table provides a breakdown of common import errors, their potential causes, solutions, and preventive measures.
| Error | Cause | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Missing Fields | Incomplete data in the source file, incorrect file format, or issues with the import plugin. | Check the source file for missing data, ensure the file format is compatible, and verify that the WordPress import plugin is properly configured. Consider editing the source file before import to address missing fields. | Validate the source data before importing, ensuring all required fields are present and correctly formatted. |
| Duplicate Entries | Identical data present in the source file, or import process failing to recognize unique identifiers. | Configure the import plugin to handle duplicates (e.g., skip duplicates, update existing entries). If using a spreadsheet, use unique identifiers. | Ensure unique identifiers in the source file to prevent duplicates. |
| Import Timeout | Large dataset, slow internet connection, or server limitations. | Break down the import into smaller chunks, use a faster internet connection, or increase server resources. | Test the import with a smaller subset of data before importing the entire dataset. |
| File Format Issues | Incorrect file format, missing headers, or corrupted data. | Validate the file format, fix any corrupted data, ensure correct headers, and verify compatibility with the WordPress import plugin. | Use a compatible file format (e.g., CSV), and validate the data integrity before the import. |
Optimizing WordPress for Imports
Large-scale WordPress post imports can significantly strain your website’s resources, potentially leading to slow loading times, errors, and even site downtime. Optimizing your WordPress environment for these imports is crucial to ensure a smooth and efficient process. This section delves into strategies for managing resource consumption, choosing appropriate import settings, and optimizing your WordPress installation for high-volume data transfers.Proper optimization ensures your website handles the import without hiccups, preserving user experience and preventing performance issues.
It’s essential to anticipate potential resource bottlenecks and proactively address them to avoid a negative impact on your site’s functionality.
Optimizing Performance for Large Imports
Import processes, especially with substantial data volumes, can overwhelm WordPress’s resources. Strategies like utilizing caching plugins and ensuring adequate server resources are vital for maintaining website responsiveness. Failing to optimize for large imports could result in prolonged loading times and potentially interrupt your website’s operations.
Managing Resource Consumption During the Import
Managing resource consumption is key to avoiding performance problems during large-scale imports. Using optimized import plugins and adjusting server settings for increased memory and processing power can mitigate issues. It’s essential to understand the resource demands of the import process to prevent slowdowns or errors.
- Utilizing Optimized Import Plugins: Employing plugins specifically designed for large-scale imports can greatly enhance the process’s efficiency. These plugins often include features for handling data in chunks, which reduces memory strain and minimizes the risk of script timeouts. Plugins like WP All Import or similar specialized import tools are excellent examples.
- Adjusting Server Resources: Ensure your web hosting server has sufficient RAM and processing power to handle the import task. Increasing server resources allows for a more efficient and faster import. Check your hosting provider’s resources to understand the limits and plan accordingly. Consider contacting your hosting provider if you anticipate exceeding your server’s limits.
- Data Chunking: Dividing the import process into smaller, manageable chunks can dramatically improve performance. Importing data in batches reduces the amount of data held in memory at any one time. This minimizes memory strain and prevents the import process from crashing. Tools like the built-in WordPress import functionality might have options to import data in chunks.
Choosing Appropriate Import Settings for Different Volumes of Data
Choosing the right import settings is crucial for optimal performance. Different import methods may be suitable for various data volumes. A well-defined approach can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering errors or delays.
- Small Datasets: For smaller datasets, standard WordPress import settings may suffice. The process should be straightforward and efficient.
- Medium Datasets: For medium-sized imports, consider using plugins designed for handling larger volumes of data. These plugins often allow for data chunking or other optimization techniques.
- Large Datasets: For substantial data imports, the most critical factor is ensuring your server resources are sufficient. Utilizing plugins for handling large data sets and employing strategies for data chunking are essential for avoiding resource exhaustion.
Checklist for Optimizing WordPress for Large-Scale Imports
A structured approach to optimizing your WordPress installation for large-scale imports is essential for avoiding potential issues.
- Assess Server Resources: Determine the available RAM and processing power of your hosting server. This helps to identify potential limitations early on.
- Choose the Right Import Plugin: Select a plugin optimized for large-scale imports to ensure data is processed efficiently.
- Test Import Process with Smaller Datasets: Before importing a large dataset, test the import process with a smaller, representative sample to identify any potential issues and fine-tune settings.
- Monitor Resource Usage During Import: Continuously monitor server resources during the import process to detect any signs of excessive load. This enables timely intervention if needed.
- Use Data Chunking Techniques: Employ strategies like data chunking to handle large imports effectively and prevent resource exhaustion.
- Optimize Database Queries: Optimize database queries to enhance the import process’s efficiency. Check for any potential performance bottlenecks within your database structure.
Security Considerations for Imports
Importing content into your WordPress site can be a powerful way to expand your site’s content quickly, but it also introduces potential security risks if not handled properly. A poorly executed import can leave your site vulnerable to malicious attacks, compromise user data, or even lead to complete site takedown. Understanding the security implications and employing best practices during the import process is crucial for maintaining a secure and reliable WordPress site.Careful consideration of the source of the imported content is paramount.
Untrusted sources can contain malicious code, potentially leading to significant security breaches. The process itself also requires stringent measures to protect against data manipulation or corruption. This includes verifying the integrity of the imported data and implementing safeguards to prevent unauthorized access.
Assessing the Source of Imported Content
A crucial first step is to thoroughly vet the source of the imported data. If the content originates from an untrusted source, such as a file downloaded from an unknown website or an unverified online repository, proceed with extreme caution. Import data only from reputable sources and be prepared to conduct additional checks.
Data Validation and Sanitization
Before importing any data, ensure that it undergoes rigorous validation and sanitization. This involves scrutinizing the content for malicious code, unexpected characters, or potentially harmful patterns. Implement filters to remove or modify any potentially harmful elements. Use robust libraries or tools that can identify and neutralize malicious code. Remember, even seemingly harmless data can contain hidden vulnerabilities if not thoroughly inspected.
Verification of Imported Data Integrity
Verifying the integrity of the imported data is critical to preventing the introduction of malicious code. Employ checksums to compare the imported data with the original data, ensuring no tampering has occurred during the transfer. Check the content for unusual or suspicious patterns that might indicate the presence of malicious code. Consider using specialized security scanners to identify potential threats within the imported data.
Specific Examples of Security Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Strategies
- Malicious Scripts in Imported Content: If the imported content includes hidden JavaScript or other scripts, these could execute unwanted actions on your site. Mitigation: Use security plugins and perform rigorous checks for malicious code and scripts before import. Implement a secure content filtering system to automatically remove or modify potentially harmful scripts.
- SQL Injection Vulnerabilities: Imported data might contain SQL code that could exploit vulnerabilities in your WordPress database. Mitigation: Employ parameterized queries or prepared statements when handling imported data. Use database-level security measures to limit user access and permissions.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attacks: Imported content that includes malicious scripts can lead to XSS attacks, allowing attackers to inject code into your site. Mitigation: Use input validation to sanitize and escape user-supplied data, especially during import. Implement a strong output encoding mechanism to prevent malicious script execution.
Implementing Secure Import Processes
Implementing secure import processes is paramount for protecting your WordPress site from security risks. Utilize secure file transfer protocols (e.g., HTTPS) for transferring files containing imported data. Employ strong passwords and multi-factor authentication for all accounts involved in the import process. Keep your WordPress installation and plugins updated to patch known vulnerabilities.
Final Wrap-Up
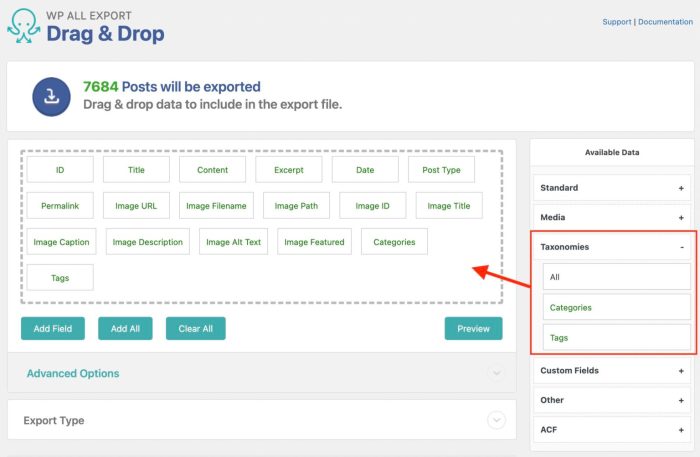
In conclusion, importing posts into WordPress is a manageable task, even for beginners. By understanding the different methods, choosing the right plugin, and meticulously following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can seamlessly integrate content from various sources into your WordPress site. Remember to prioritize security and optimize for large imports, ensuring a smooth and successful transition for your website.