How to get GA4 site annotations and notes in WordPress? This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about integrating Google Analytics 4 (GA4) annotations into your WordPress website. We’ll explore different methods, from simple plugin integrations to custom code implementations, providing a clear and practical approach for anyone looking to enhance their website analytics with GA4 annotations.
Understanding how to utilize GA4 annotations is crucial for gaining valuable insights into user behavior and website performance. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to effectively collect and analyze data, ultimately helping you improve your site’s functionality and user experience.
Introduction to Google Analytics 4 (GA4) Site Annotations in WordPress
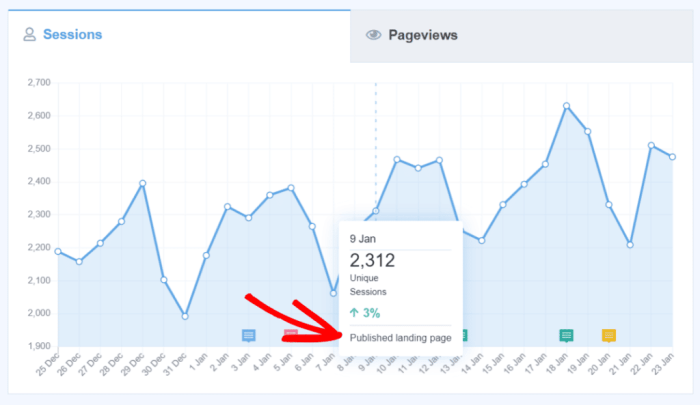
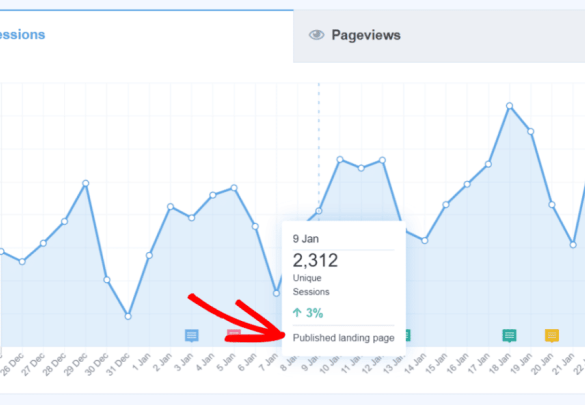
Site annotations in Google Analytics 4 (GA4) are powerful tools for adding contextual information to your website data. Imagine trying to understand why traffic to a specific page spiked one day – annotations provide a timestamped record of events, allowing you to quickly connect that spike to a specific marketing campaign, a product launch, or even a social media post.
Annotations help you interpret the data, understand user behavior, and improve your website. They are especially valuable in the WordPress context, where understanding visitor actions alongside your content management system activities is critical.Annotations function as a digital diary for your website’s activity. They allow you to associate notes with specific timeframes within your GA4 data, enabling deeper insights into user behavior and website performance.
This is incredibly useful when you need to correlate website events with external factors like marketing campaigns or news events. They are not limited to one website, so they can be used on a wide variety of platforms.
GA4 Site Annotations in WordPress
Annotations in GA4 aren’t specific to WordPress; they’re a feature of the platform itself. However, their value is magnified within the WordPress environment. WordPress sites are often used for content publishing, e-commerce, and community forums, so understanding how different actions affect visitor behavior is crucial for optimizing performance.
How Annotations Improve Website Analysis
Annotations enhance your website analysis by providing a direct link between data points and real-world events. This makes identifying trends and patterns much easier. For instance, if you notice a drop in conversion rates, you can look at the corresponding annotations to see if there was a major update to your website, a temporary technical issue, or a change in your marketing strategy.
This helps to understand what caused the drop in conversion rates and implement solutions.
Integrating GA4 into WordPress
Integrating GA4 into your WordPress site is a straightforward process, often managed through a plugin. You’ll typically install the Google Analytics 4 plugin, then connect your WordPress site to your GA4 account. The plugin handles the tracking code, which sends data to GA4. Once the integration is complete, you can use the annotations to record and track important events, which in turn helps with analyzing user behavior.
The actual implementation involves using the Google Analytics 4 plugin or a similar integration tool, but the basic concept remains the same.
Methods for Implementing GA4 Annotations in WordPress
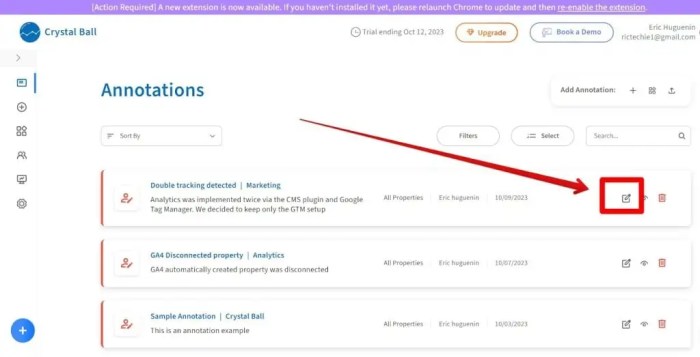
Implementing GA4 annotations in WordPress allows for enhanced tracking and analysis of user interactions on your website. This granular level of data is crucial for understanding user journeys and optimizing your website’s performance. Proper implementation ensures accurate data collection and actionable insights.Implementing GA4 annotations within your WordPress website involves choosing between utilizing plugins or crafting custom code snippets.
Figuring out how to get those GA4 site annotations and notes in WordPress can be tricky, but it’s totally doable! Learning about how to effectively leverage social media marketing strategies, like those discussed by Xenia Muntean in her work on xenia muntean democratizing social media marketing , can help your website’s performance. Ultimately, integrating these insights can lead to improved website analytics and a more insightful understanding of your audience’s behavior, making it easier to get those crucial GA4 site annotations and notes.
Each approach presents distinct advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice depends on your technical expertise and project needs. Careful consideration of the trade-offs between ease of use and customization will determine the most suitable path for your WordPress site.
Plugin Integrations
Several plugins facilitate the integration of GA4 annotations into WordPress. These plugins often simplify the process by offering user-friendly interfaces to manage annotations.
- Many popular WordPress plugins offer GA4 integration, enabling you to easily add annotations to your website’s pages and posts. These plugins usually come with pre-built configurations for various annotation types. This approach requires minimal coding knowledge, streamlining the implementation process.
- Examples of such plugins might include those specifically designed for enhanced analytics or general website optimization, providing dedicated sections for setting up GA4 annotations. These often offer a wizard-like interface, making setup straightforward for users with varying levels of technical expertise.
- While these plugins simplify implementation, they might have limitations in terms of customization. Users seeking advanced control over annotation parameters or unique annotation types might find the plugin approach less flexible than custom code solutions.
Custom Code Snippets, How to get ga4 site annotations and notes in wordpress
For more advanced control and customization, implementing GA4 annotations with custom code snippets offers significant advantages. This approach gives you complete flexibility in tailoring the annotation process to your website’s specific requirements.
- Using custom code allows for precise control over the annotation parameters. You can modify and adapt the code to align with your website’s unique data tracking needs, providing detailed control over the annotation process.
- Implementing custom code snippets can involve inserting JavaScript code directly into your theme files or utilizing a child theme for modifications. This approach offers a more granular level of customization, allowing you to integrate GA4 annotations precisely where needed.
- Custom code solutions often require a working knowledge of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. This approach might demand more time and technical skill, but the result is greater control and potential for intricate data tracking scenarios.
Comparison of Plugin and Code-Based Approaches
| Feature | Plugin Approach | Code-Based Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | High | Low |
| Customization | Low | High |
| Technical Expertise Required | Low | High |
| Learning Curve | Short | Steep |
| Flexibility | Limited | Extensive |
| Potential for Errors | Lower | Higher |
WordPress Plugins for GA4 Annotations
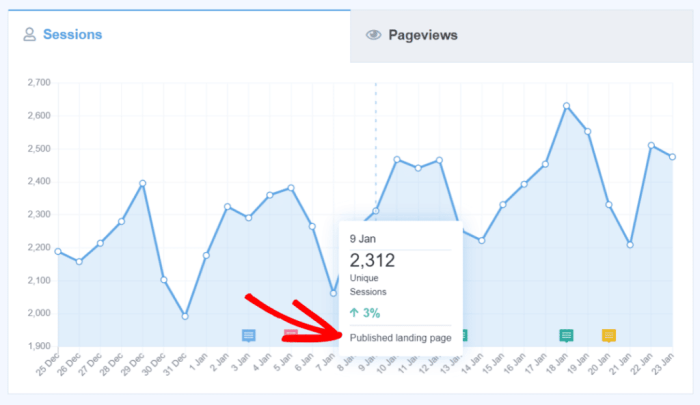
While manually adding GA4 site annotations to WordPress is possible, utilizing dedicated plugins can streamline the process and often provide additional features. These plugins can automate the annotation process, reduce the risk of errors, and potentially offer other valuable functionalities. This section dives into the world of WordPress plugins for GA4 annotations, exploring their benefits, drawbacks, and key features.Implementing GA4 annotations in WordPress often requires modifying the theme’s code or using custom functions.
Plugins provide a simpler, often more user-friendly, approach. However, understanding the potential trade-offs is crucial for making an informed decision.
Popular WordPress Plugins for GA4 Annotations
Plugins designed for event tracking and custom analytics often integrate GA4 annotations. Finding plugins explicitly dedicated to GA4 annotations might be less common, but the functionality is often embedded within more comprehensive analytics tools.
-
Advanced Custom Fields (ACF): This popular plugin allows for creating custom fields and meta boxes in WordPress posts and pages. While not directly for GA4 annotations, ACF can be used to store annotation data which can then be used with a GA4 tracking script. This approach allows for flexibility and customizability. ACF excels at handling complex custom data needs, making it a powerful tool for those with intricate annotation requirements.
-
Google Analytics for WordPress by MonsterInsights: This plugin offers robust GA4 integration. While not exclusively focused on annotations, it provides comprehensive tracking features that can be leveraged for implementing annotations within the context of event tracking. It allows you to set up custom dimensions, which can be used to capture annotation data. This solution is particularly useful for those already using MonsterInsights for their analytics.
-
WPForms: For forms and contact forms, WPForms is a widely used plugin. It’s useful in tracking user interactions with forms and can capture annotation data, especially if the forms are designed to collect specific information about user activity.
Benefits of Using Plugins
Plugins offer several advantages over manual implementation:
- Ease of Use: Plugins usually have user-friendly interfaces, simplifying the implementation process. This reduces the technical overhead for users with limited coding experience.
- Reduced Errors: Well-designed plugins handle the complexities of code integration, reducing the chance of errors that can occur when manually modifying theme files.
- Customization Options: Many plugins offer customization options for annotations, allowing you to tailor them to your specific needs.
- Additional Features: Some plugins might include additional features such as reporting dashboards or integrations with other tools.
Drawbacks of Using Plugins
Despite the benefits, plugins also have some drawbacks:
- Plugin Conflicts: There’s a possibility of plugin conflicts, especially with other plugins that handle similar functionalities.
- Maintenance: Plugin updates can sometimes introduce compatibility issues, requiring ongoing maintenance.
- Limited Control: Depending on the plugin, you might have limited control over certain aspects of the annotation process.
- Security Risks: In rare cases, poorly maintained plugins might introduce security vulnerabilities.
Comparison of Plugin Features
The following table provides a basic comparison of the features and functionalities of different plugins mentioned above.
| Plugin | Ease of Use | Customization | Additional Features | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Custom Fields | High | High | Limited | Paid |
| Google Analytics for WordPress by MonsterInsights | Medium | Medium | High | Paid |
| WPForms | Medium | Medium | Medium | Paid |
Custom Code Implementation for GA4 Annotations
Adding GA4 annotations via custom code provides maximum flexibility for tailoring your tracking to specific needs. This method lets you dynamically create annotations based on user interactions or other data, surpassing the limitations of pre-defined annotations. However, this approach requires a deeper understanding of both JavaScript and PHP.Implementing custom code involves writing scripts that capture data points relevant to your annotations, then sending this data to Google Analytics 4.
This allows for more complex and granular tracking of user behavior, enabling highly targeted analysis. This method also gives complete control over the annotation process, letting you integrate it seamlessly with your existing WordPress functionality.
Step-by-Step Guide
To implement custom code for GA4 annotations, follow these crucial steps:
-
Identify the Triggering Event: Determine the specific actions or events that should trigger the annotation creation. Examples include a user clicking a specific button, navigating to a particular page, or completing a form.
This initial step dictates the logic for your custom code. Understanding what actions prompt the annotation is crucial for accurate and relevant tracking.
-
JavaScript Implementation (Client-Side): Use JavaScript to capture the event data when the triggering action occurs. This JavaScript code will send the annotation data to the server.
The JavaScript portion acts as the “sensor” for your annotations. It gathers data and sends it to the PHP code on the server for processing and sending to GA4.
// Example JavaScript snippet document.getElementById('myButton').addEventListener('click', function() // Get relevant data (e.g., page URL, form values) const pageUrl = window.location.href; const formValue = document.getElementById('myForm').value; // Construct annotation data object const annotationData = event: 'buttonClick', page: pageUrl, form: formValue ; // Send data to server (using AJAX or fetch API) fetch('/ga4-annotation-endpoint', method: 'POST', headers: 'Content-Type': 'application/json' , body: JSON.stringify(annotationData) ) .then(response => response.json()) .catch(error => console.error('Error sending annotation:', error)); ); -
PHP Implementation (Server-Side): Develop a PHP script to receive and process the annotation data sent from the JavaScript code. This script should then send the data to the GA4 measurement ID.
The PHP code acts as the “hub” for the annotation data. It receives data from the client-side, formats it correctly, and sends it to GA4.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues: How To Get Ga4 Site Annotations And Notes In WordPress
Implementing Google Analytics 4 (GA4) site annotations in WordPress can sometimes encounter hurdles. Understanding potential conflicts and troubleshooting steps is crucial for a seamless integration. This section details common issues and provides solutions to help you overcome these challenges. Proper implementation is essential for accurate data collection and analysis.
Troubleshooting GA4 annotations involves identifying and resolving discrepancies between the GA4 setup and your WordPress environment. Conflicts with existing plugins or themes, incorrect code implementations, and issues with tracking IDs are all potential stumbling blocks. This section will guide you through identifying and rectifying these problems.
Common Integration Conflicts
Incorrectly configured tracking IDs, outdated plugins, or conflicts with active themes can cause integration problems. Ensure the GA4 tracking ID is correctly implemented in the chosen method (plugin or custom code). Double-checking for conflicts between plugins and themes is crucial. Verify the compatibility of the chosen GA4 plugin with your WordPress version.
Troubleshooting Steps for Various Issues
A systematic approach is essential for troubleshooting integration problems. Begin by checking the GA4 tracking ID for accuracy and verifying the implementation method. Examine your WordPress logs for error messages that might provide clues. If using a plugin, check for plugin updates. If using custom code, review the code for syntax errors.
Isolate the problem by temporarily disabling plugins or themes to see if they’re causing conflicts.
Figuring out how to get GA4 site annotations and notes in WordPress can be tricky, but it’s crucial for understanding user behavior. Once you’ve got that nailed down, you can start building a comprehensive content library, like creating your company content library , to organize and access all your valuable insights. This will help you track which content resonates most with your audience and optimize your strategy accordingly.
So, diving into GA4 annotations and notes is key to maximizing your WordPress site’s performance.
Examples of Common Errors and Solutions
| Error | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| GA4 tracking not working | Incorrect tracking ID, implementation errors, plugin conflicts, or theme conflicts | Verify the tracking ID, check the implementation method (plugin or custom code), update plugins/themes, and isolate conflicts by temporarily disabling them. Review error messages in WordPress logs. |
| Tracking events not showing up in GA4 | Missing event parameters, incorrect event names, or issues with event triggering | Check event parameters (e.g., category, action, label), ensure the event name is correct, and verify event triggering. Inspect the code for the specific events that aren’t showing up. Use the WordPress debugging tools. |
| Annotations not displaying in the WordPress dashboard | Incorrect data format or incorrect implementation of the annotation method. | Verify that the annotation data is in the expected format (e.g., JSON, string). Review the custom code or plugin implementation. Ensure that the WordPress theme and other plugins are not interfering. |
| Slow website performance after GA4 implementation | Excessive data calls to GA4 or improperly implemented code. | Optimize GA4 code for performance. Reduce unnecessary data calls. Check for any excessive or unnecessary calls to Google Analytics 4. Check code for potential issues or slow-down. Implement code optimizations. |
Best Practices and Recommendations
Implementing Google Analytics 4 (GA4) site annotations in WordPress offers valuable insights into user behavior. However, effective utilization requires careful planning and execution. Properly managing annotations ensures accurate data collection, facilitating informed decisions regarding website improvements and user experience enhancements.
Careful consideration of best practices ensures that GA4 annotations provide meaningful data. This involves not only the technical implementation but also the strategic approach to data analysis and interpretation. Understanding the various use cases and potential pitfalls is critical for maximizing the benefits of site annotations.
Figuring out how to get those GA4 site annotations and notes in WordPress can be tricky, but it’s a crucial part of site optimization. First, you need to make sure you’ve set up your GA4 tracking correctly. Then, understanding how to choose the best premium WordPress theme for your site like this one is important for compatibility and performance.
Ultimately, proper theme selection will significantly impact your ability to effectively access and utilize those annotations and notes. It’s all about a smooth workflow when working with GA4 data in WordPress.
Managing and Utilizing GA4 Annotations
Effective annotation management involves a multi-faceted approach. Firstly, establish a clear taxonomy for annotations. This taxonomy should be easily understood and maintained, enabling consistent data collection across different projects or initiatives. Secondly, develop a system for regularly reviewing and updating annotations. This ensures the annotations remain relevant and accurate, avoiding outdated or irrelevant information.
Strategies for Efficient Data Collection and Analysis
Efficient data collection and analysis using site annotations rely on strategic planning. A crucial aspect is defining specific goals for annotation use. For example, identifying areas of high user interaction or analyzing the impact of specific website changes on user behavior. This targeted approach ensures that the data collected is directly relevant to the objectives. The data should be meticulously organized for easy retrieval and analysis.
Employing analytical tools, such as spreadsheets or specialized reporting platforms, can greatly facilitate the process.
Optimizing Site Annotations for Specific Use Cases
Optimizing site annotations for various use cases requires a tailored approach. For example, for A/B testing, annotations can be used to record which version of a webpage or feature was being tested. This allows for precise analysis of the performance of different variations. Similarly, for content audits, annotations can track user engagement with specific pages or elements within a page.
This detailed information allows for targeted improvement efforts. Using different annotation colors or tags can help to categorize and filter the annotations easily, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of the data.
Data Security Considerations
Data security is paramount when using site annotations. Annotations often contain sensitive information, such as user actions or specific events. Implementing robust security measures is critical to protect this data. This includes access control measures, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access the annotation data. Furthermore, data encryption methods should be implemented to protect the integrity of the annotations.
Regular audits of annotation data security practices should be performed to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Examples of GA4 Annotations in Action
GA4 annotations, when implemented correctly, offer a powerful lens into user behavior on your website. They go beyond basic page views and event tracking, providing rich context to understand why users interact with specific elements. This contextual understanding is crucial for optimizing website performance and enhancing the user experience. This section delves into real-world examples showcasing the value of annotations.
Annotations are not just about labeling events; they’re about adding meaningful descriptions that help you understand the “why” behind user actions. Imagine a user clicking a “Contact Us” button, but instead of leaving a message, they abandon the form. An annotation explaining the reason (e.g., “Form fields too complex,” or “Missing instructions”) allows you to address the underlying problem and improve the conversion process.
Illustrative Examples of Annotation Use Cases
Annotations offer valuable insights into diverse website interactions. They provide detailed context to enhance analysis, leading to targeted improvements. Consider these scenarios:
- Product Page Interactions: Annotations can track user actions on a specific product page. For example, annotating a user’s time spent on a product detail page with the text “Reviewed specifications” helps identify how users interact with product information. This can lead to optimizing the page’s layout or content for better understanding.
- Cart Abandonment Analysis: Annotating reasons for cart abandonment (e.g., “Shipping cost too high,” “Payment gateway issues”) reveals crucial pain points in the checkout process. This data allows you to offer tailored solutions and improve conversion rates. You can then address the issues through discounts, free shipping, or improved payment gateway integration.
- Support Ticket Generation: Annotations can be used to identify user issues and needs. If a user clicks a “Help” button multiple times and then submits a support ticket, annotating this behavior with “Confused about return policy” provides context for support teams to proactively address common questions and expedite issue resolution.
Different Types of Annotations and Their Data
Annotations can be categorized into different types, each providing a specific layer of understanding. The table below illustrates how annotations provide valuable context, helping to understand user behavior and website performance.
| Annotation Type | Description | Data Example |
|---|---|---|
| Product Interest | Captures user interest in specific products. | “Viewed high-end laptop,” “Compared feature X and Y,” “Added to wishlist” |
| Navigation Path | Details the user’s journey through the website. | “Navigated from homepage to category page to product page,” “Searched for term ‘running shoes'” |
| Checkout Issues | Documents problems encountered during the checkout process. | “Shipping cost too high,” “Payment declined,” “Forgot password” |
| Support Interactions | Records user interaction with support channels. | “Asked about return policy,” “Requested a refund,” “Viewed FAQs” |
Understanding User Behavior and Website Performance
Annotations provide a rich understanding of user behavior and website performance. Analyzing annotation data reveals patterns in user interactions and identifies areas for improvement. For example, if users frequently annotate a specific form field as “Difficult to understand,” the website design needs review and adjustments. This iterative approach to user feedback is critical for optimization.
Last Point
In conclusion, adding GA4 annotations to your WordPress site is achievable through various methods. Whether you opt for a plugin-based solution or a custom code approach, this guide has provided you with the tools and knowledge to make informed decisions. Remember to consider the specific needs of your website and choose the method that best suits your technical expertise.
By following the best practices and troubleshooting advice, you’ll be well-equipped to effectively leverage GA4 annotations for a deeper understanding of your website’s performance.