How to fix err ssl version or cipher mismatch in WordPress? This guide delves into the common SSL/TLS errors plaguing WordPress websites, offering practical solutions to restore secure connections. We’ll explore the technical aspects of SSL certificates, cipher suites, and versions, and then dive into troubleshooting steps specific to WordPress, servers, and plugins. From identifying the error to implementing fixes, we’ll cover everything you need to resolve these frustrating issues.
Understanding SSL/TLS is crucial for website security. This guide will walk you through common error messages, how to diagnose the specific problem, and the necessary steps to fix it. We’ll look at WordPress-specific configurations, server-side settings, and practical examples, ultimately empowering you to maintain a secure and functioning WordPress site.
Understanding SSL/TLS Errors
Secure communication over the internet is crucial for protecting sensitive data. SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) plays a vital role in ensuring this security. It’s a standard protocol that establishes an encrypted connection between a web server and a web browser. This encrypted connection prevents eavesdropping and tampering with data during transmission.SSL/TLS accomplishes this encryption by using a combination of technologies, including digital certificates, cipher suites, and SSL versions.
Understanding these components is essential for diagnosing and resolving SSL/TLS errors.
SSL/TLS and Website Security
SSL/TLS is a fundamental component of modern website security. It establishes a secure channel between a web browser and a web server, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information like usernames, passwords, and financial data. This encrypted connection uses cryptography to scramble data transmitted between the two points.
SSL Certificates
SSL certificates are digital documents that verify the identity of a website. They act as proof of ownership, issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). These certificates contain the website’s public key, which is used to encrypt data sent to the server. The server’s private key is kept secret and used to decrypt the data. A valid SSL certificate is essential for establishing a secure connection.
Troubleshooting SSL version or cipher mismatches in WordPress can be tricky, but it’s crucial for site security. Fortunately, there are straightforward fixes. However, remember that even with a perfect SSL configuration, the time it takes for SEO to show results the time it takes for SEO to show results can vary, depending on factors like your website’s content and backlink profile.
So, while you’re diligently fixing those SSL issues, be patient with the SEO process. Once those initial technical hurdles are cleared, you can focus on content creation and building your authority.
Cipher Suites and SSL Versions
Cipher suites are sets of cryptographic algorithms used for encryption and decryption during SSL/TLS connections. They specify the encryption method, hashing algorithm, and key exchange method. SSL versions define the protocol versions used for the communication. Different cipher suites and versions have varying levels of security. For example, older versions like TLS 1.0 are considered less secure than newer versions like TLS 1.3.
Secure Communication Between Website and Browser
The SSL/TLS handshake is the process that establishes a secure connection between a web browser and a web server. It involves a series of steps:
- The browser requests a secure connection from the server.
- The server sends its SSL certificate, which includes the server’s public key.
- The browser verifies the certificate’s authenticity and validity, ensuring it’s issued by a trusted Certificate Authority.
- The browser and server negotiate a cipher suite and SSL version.
- Both sides exchange encryption keys, establishing a secure communication channel.
This process ensures that only the intended recipient can read the data exchanged.
Importance of a Valid SSL Certificate for WordPress Websites
A valid SSL certificate is crucial for WordPress websites, particularly for e-commerce sites and those handling sensitive user data. It establishes trust with visitors and ensures secure communication, thus safeguarding against potential security threats. This trust is built through a visible padlock icon in the browser’s address bar.
Comparison of SSL Versions
| SSL Version | Security Features | Security Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| TLS 1.0 | Early version, limited security features. | Vulnerable to various attacks, should be avoided. |
| TLS 1.2 | Significantly improved security over TLS 1.0. | Still vulnerable to some attacks compared to TLS 1.3. |
| TLS 1.3 | Modern version with enhanced security and performance. | Latest version, considered the most secure. |
This table highlights the evolution of SSL versions and their relative security levels. Newer versions offer stronger protection against evolving threats.
Identifying the Error: How To Fix Err Ssl Version Or Cipher Mismatch In WordPress
Pinpointing the specific SSL/TLS version or cipher suite mismatch is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Incorrect configurations can lead to frustrating website errors and impede user access. Understanding the error messages and associated symptoms empowers you to quickly diagnose and resolve these issues.Identifying the root cause often involves deciphering cryptic error messages, understanding the different SSL/TLS versions and cipher suites, and meticulously reviewing server logs.
This section provides a detailed analysis of error messages, symptoms, and log locations to assist in accurate identification.
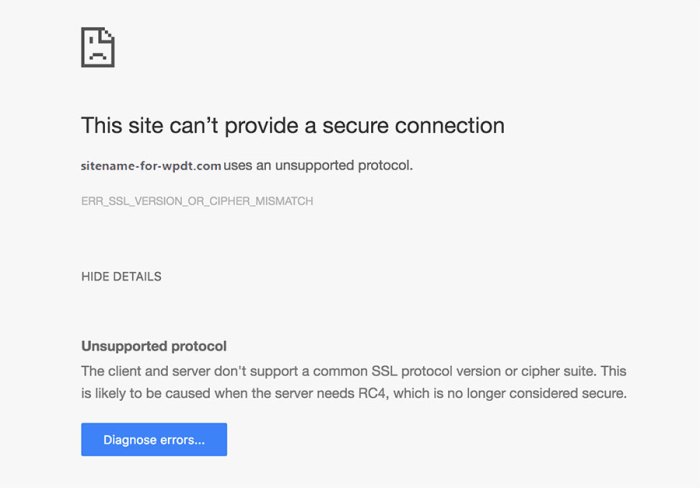
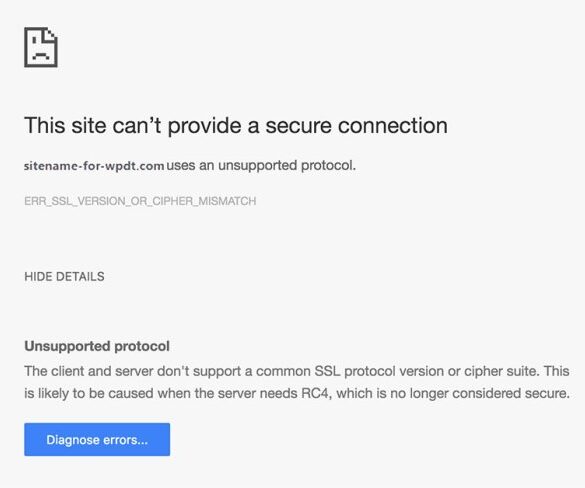
Common Error Messages
Various error messages signal SSL/TLS version or cipher suite mismatches. These messages can vary in complexity, but often include terms like “SSL_ERROR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH,” “ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH,” or similar strings. These errors frequently manifest in web browsers as an inability to load the site.
Examples of Error Messages, How to fix err ssl version or cipher mismatch in wordpress
Users might encounter several error messages. Some examples include:
- “ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH” (a common browser error)
- “SSL_ERROR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH” (a server-side error)
- “The connection was reset” (a symptom, often linked to a mismatch)
- “Your connection is not private” (a message from browsers indicating security issues)
Identifying the Mismatch
Determining the precise SSL/TLS version and cipher suite issue necessitates a multi-faceted approach. Examining browser error messages and server logs is paramount. Careful attention to detail in these messages will reveal the specific incompatibility.
Analyzing Error Logs
Error logs contain invaluable information for troubleshooting SSL/TLS issues. These logs provide a detailed record of events, including errors, warnings, and successful connections.
- Identifying the specific log file containing the error message is vital.
- Common locations for these logs include web server directories (e.g., Apache, Nginx) and system-wide log directories.
- Searching for s like “SSL_ERROR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH” or “ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH” will help pinpoint the error.
Error Type, Causes, and Symptoms Table
This table illustrates different error types, potential causes, and typical symptoms:
| Error Type | Potential Causes | Typical Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| SSL Version Mismatch | Client or server using incompatible SSL versions | Connection failure, inability to establish secure connection, error messages related to version mismatch. |
| Cipher Suite Mismatch | Client or server supporting incompatible encryption algorithms | Connection failure, inability to establish secure connection, error messages related to cipher mismatch. |
| Certificate Issues | Expired, invalid, or mismatched certificates | Error messages related to certificate verification, inability to establish secure connection. |
| Server Configuration Issues | Incorrect SSL/TLS settings on the server | Connection failure, inability to establish secure connection, error messages indicating server-side configuration problems. |
Troubleshooting Steps
Pinpointing the root cause of an SSL/TLS error, like a version or cipher mismatch, requires a systematic approach. Incorrect SSL configurations on either the server or the WordPress installation can lead to these errors. By following these troubleshooting steps, you can effectively diagnose the issue and implement the necessary fixes.Understanding the fundamental components of SSL/TLS configurations is key to effectively identifying and resolving these errors.
This involves checking certificate installations, server configurations, and WordPress settings.
Initial Troubleshooting Steps
A methodical approach to diagnosing the issue is essential. Begin by checking the most obvious points: site accessibility, server logs, and basic error messages. Reviewing error messages from the browser or server logs will provide crucial information about the specific nature of the SSL/TLS error.
Checking SSL Certificate Installation and Validity
Ensuring the SSL certificate is correctly installed and valid is paramount. A misconfigured or expired certificate can trigger errors.
- Verify the certificate is properly installed on the web server. This usually involves checking the server’s configuration files, like Apache’s httpd.conf or Nginx’s nginx.conf.
- Validate the certificate’s validity using tools like OpenSSL. Check the certificate’s expiration date and any intermediate certificates involved in the chain. This process confirms the certificate is legitimate and hasn’t expired.
- Confirm the certificate is issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). A non-trusted certificate will trigger security warnings in browsers, preventing access.
Verifying Server’s SSL Configuration
Server-side configurations play a crucial role in SSL/TLS settings. Incorrect configurations can lead to mismatches and errors.
- Examine the server’s SSL/TLS configuration files (e.g., `httpd.conf` for Apache, `nginx.conf` for Nginx). Verify that the correct protocols and cipher suites are enabled. Ensure that the configuration aligns with your needs and security best practices.
- Use the `openssl s_client` command to test the server’s SSL/TLS configuration. This tool allows you to check if the server supports the required protocols and ciphers.
Role of Server-Side Settings in SSL/TLS Configuration
The server’s settings directly impact how SSL/TLS communication is handled. The correct configuration is crucial for smooth communication.
- Review the server’s SSL/TLS protocols and cipher suites. These settings dictate which encryption methods are supported. Ensure that both the server and client support the required protocols and ciphers.
- Verify the server’s SSL/TLS port configuration. The correct port must be used for SSL/TLS connections. Incorrect port settings can cause communication failures.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Checking SSL Certificate Details
This table Artikels a systematic approach to verify SSL certificate details:
| Step | Action | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Retrieve the certificate from the server. | Obtain the certificate file(s). |
| 2 | Use OpenSSL to examine the certificate details. | Verify the certificate’s validity, issuer, and expiration date. |
| 3 | Check the certificate chain. | Ensure all intermediate certificates are present and valid. |
| 4 | Verify the server’s SSL configuration. | Confirm that the server supports the required protocols and ciphers. |
WordPress-Specific Configurations
WordPress, while user-friendly, can sometimes be the source of SSL/TLS errors. Plugins and themes, often downloaded from third-party sources, can introduce conflicts that disrupt the secure connection. Understanding how WordPress interacts with SSL configurations is crucial for resolving these issues.
Plugins and Themes: Potential Conflicts
Plugins and themes are extensions that enhance WordPress functionality. However, some poorly coded or outdated extensions can interfere with the server’s SSL configuration, leading to mismatches in protocols or cipher suites. Identifying and resolving these conflicts is vital to maintaining a secure website.
Troubleshooting SSL errors like “ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCH” in WordPress can be tricky. Sometimes, it’s a simple server configuration issue, but other times, it requires more in-depth investigation. Fortunately, there are plenty of resources online to help you through the process, including comprehensive guides to understanding Pendo vs. Walkme for smoother client onboarding, like this helpful comparison: pendo vs walkme comparison new client onboarding made easy.
Once you’ve got a good grasp of those tools, you can better diagnose and fix your SSL issues in WordPress, ensuring a secure and seamless experience for your website visitors.
Checking for Conflicting Plugins or Themes
To pinpoint the problematic plugin or theme, systematically disable or deactivate them one by one. This process helps isolate the source of the error. Actively monitor the website’s behavior after each deactivation. If the error disappears, the deactivated plugin or theme is the culprit. A step-by-step approach ensures a targeted resolution.
Updating or Disabling Problematic Plugins and Themes
Once the problematic plugin or theme is identified, updating it to the latest version is often the solution. Outdated extensions may contain vulnerabilities or incompatible configurations. If updating isn’t possible, consider disabling the extension temporarily. This method allows you to continue testing and further isolating the source of the issue.
WordPress Settings for SSL
WordPress settings provide configuration options to enable and manage SSL/TLS. Properly configuring these settings is critical for a secure connection. Access the WordPress dashboard, navigate to the settings area, and look for SSL/TLS related options. Carefully review and adjust the configurations to ensure they align with your server’s SSL setup.
Potential Conflicts Between WordPress Plugins and SSL Configurations
| Plugin Category | Potential Conflict | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Security Plugins | Incorrect cipher suite or protocol restrictions. | Update the plugin or adjust server settings to match the plugin’s requirements. |
| Caching Plugins | Cache issues with SSL certificates or configurations. | Clear the cache, update the plugin, or adjust cache settings to accommodate SSL. |
| E-commerce Plugins | Payment gateway incompatibility with SSL configurations. | Verify payment gateway compatibility with SSL configurations and update the plugin or gateway if needed. |
| Contact Form Plugins | SSL misconfiguration within the plugin’s form submission process. | Update the plugin or adjust the plugin settings for proper SSL handling. |
| Third-party Integrations | API or integration issues with SSL certificates. | Verify the compatibility of the integration with SSL certificates. Update the plugin if possible or adjust the server settings if necessary. |
Server Configuration
Server-side SSL/TLS configurations are crucial for securing WordPress websites. Incorrect or outdated server settings can lead to SSL/TLS errors, impacting user experience and potentially exposing sensitive data. Properly configured servers ensure secure connections and maintain trust with users. This section dives into the technical aspects of configuring your web server for secure communication.Robust server-side SSL/TLS configuration is paramount for safeguarding WordPress websites.
It’s not just about enabling SSL; it’s about ensuring the correct protocols, ciphers, and certificates are employed. A poorly configured server can result in connection errors, impacting site performance and potentially exposing your site to vulnerabilities.
Web Server Configuration (Apache/Nginx)
Proper web server configuration is essential for handling SSL requests correctly. Apache and Nginx are popular choices, each with its own configuration syntax. Correctly configuring the server to understand and process SSL requests is a critical step in achieving secure connections.
Troubleshooting SSL errors like “SSL version or cipher mismatch” in WordPress can be a real pain, but thankfully, there are solutions. A strong online presence is key for any business, especially for a dispensary. Optimizing your SEO strategy, like learning how to properly target keywords and create compelling content, can dramatically improve your search engine rankings, leading to more customers.
Fortunately, understanding how to fix SSL issues will also improve your site’s security, ultimately boosting your overall online reputation and making your website trustworthy. Check out grow cannabis dispensary SEO presence for more insights on building a successful online presence for your dispensary. Once your SSL is working correctly, your website will function smoothly and customers can enjoy a seamless experience.
- Apache Configuration: Apache’s configuration typically involves modifying the `httpd.conf` or `apache2.conf` file to include virtual host directives that specify SSL settings. These directives define the SSL protocol, cipher suites, and certificate locations for each domain. Careful attention to detail is required to avoid potential conflicts or misconfigurations.
- Nginx Configuration: Nginx utilizes a similar approach. Within the server block, you configure SSL settings like the protocol, cipher suites, and the location of the SSL certificate and key files. The configuration files need to be carefully reviewed to ensure they match the desired security level and prevent errors.
Updating SSL/TLS Libraries and Certificates
Keeping your server’s SSL/TLS libraries and certificates up-to-date is vital. Outdated libraries can have known vulnerabilities, making your website susceptible to attacks. Regular updates patch security flaws, ensuring the highest level of security for your site.
- Library Updates: Periodically check for updates to your server’s OpenSSL library. This involves running appropriate update commands specific to your operating system and server distribution. This process should be carefully documented to avoid accidental data loss or service disruptions.
- Certificate Management: Certificates should be renewed regularly. Expired certificates will result in connection errors. Automated renewal processes are highly recommended to ensure continuous secure operation. You should have a plan for certificate rotation and replacement, ensuring seamless transitions and minimal downtime.
Verifying Server SSL Configuration
Thorough verification of the server’s SSL configuration is essential. This involves testing the configuration and identifying potential problems before deploying to production. Tools and methods are available to validate the server’s SSL setup.
- SSL/TLS Testing Tools: Utilize online tools designed for SSL/TLS testing. These tools assess the server’s configuration, identifying potential issues like unsupported ciphers, outdated protocols, or mismatched certificates. These tools provide detailed reports, aiding in diagnosing configuration problems.
- Command-Line Tools: Command-line tools like `openssl` can be used to verify the server’s SSL configuration. These tools can check for various aspects of the configuration, including the certificate’s validity and the supported cipher suites. These tools provide a comprehensive assessment of the SSL/TLS implementation.
Server-Side Settings for SSL/TLS
The following table Artikels common server-side settings for SSL/TLS, along with their potential impact on website security and performance.
| Setting | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| SSL Protocol | Specifies the SSL/TLS protocols supported by the server. | Supporting outdated protocols may expose vulnerabilities. |
| Cipher Suites | Defines the cryptographic algorithms used for encryption. | Using weak ciphers can compromise security. |
| Certificate | Digital certificate used for authentication. | Expired or invalid certificates lead to connection errors. |
| Key | Private key corresponding to the certificate. | Compromised keys can expose sensitive data. |
| Session Resumption | Enables reusing session information. | Improves performance by reducing initial handshake time. |
Practical Solutions and Examples

Fixing SSL version or cipher mismatch errors often involves adjusting server configurations and client settings. This section provides practical solutions, detailed methods for upgrading SSL versions and cipher suites, and examples tailored to various server setups. Understanding the specific error messages and the implications of the mismatch is crucial for implementing the correct solution.The effectiveness of a solution depends on the server’s operating system, the web server software (like Apache or Nginx), and the specific SSL/TLS library used.
A precise diagnosis and targeted approach are key to successful resolution.
Upgrading SSL/TLS Version
Modifying the SSL/TLS version supported by your server involves changing the server configuration files. Different web servers have different ways of configuring SSL/TLS. The goal is to enable the highest supported version while ensuring compatibility with most clients.
- Apache HTTP Server: The `ssl.conf` file (or a dedicated `ssl.crt` file) usually controls SSL/TLS versions. Look for directives like `SSLProtocol` and `SSLHonorCipherOrder`. For example, to enable TLS 1.3, add `TLSv1.3` to the `SSLProtocol` directive. Ensure this matches the client’s capabilities. Carefully review the documentation for your Apache version to understand the exact syntax and possible conflicts.
- Nginx Web Server: Nginx configuration files (typically `nginx.conf` and `ssl.conf`) control SSL/TLS versions. The `ssl_protocols` directive specifies the enabled protocols. For instance, `ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;` enables TLS 1.2 and 1.3. Again, verify compatibility with your clients.
Modifying Cipher Suites
Cipher suites determine the encryption methods used during SSL/TLS handshakes. Selecting appropriate and compatible cipher suites is essential. Avoid outdated or weak cipher suites to prevent security vulnerabilities.
- Apache HTTP Server: The `SSLCipherSuite` directive in the `ssl.conf` file defines the available cipher suites. Example: `SSLCipherSuite HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5` removes weak ciphers and allows only strong options. Always check compatibility with the latest standards and avoid any known vulnerabilities.
- Nginx Web Server: The `ssl_ciphers` directive in the `nginx.conf` file configures cipher suites. Using a modern, well-vetted list is recommended. For example: `ssl_ciphers TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384:TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256:TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256:HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5:!DSS`; always ensure that the order of cipher suites reflects the security levels and prioritizes strong ciphers.
Command-Line Tools for Verification
Command-line tools can help verify server configurations and identify potential issues.
- OpenSSL: The `openssl s_client` command allows testing the SSL/TLS configuration of your server. It can show which ciphers and protocols are supported. Use this to ensure that the configured ciphers and protocols are compatible with the expected clients. Examples: `openssl s_client -connect example.com:443` and `openssl s_client -connect example.com:443 -cipher TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384`.
Practical Solutions Table
| Scenario | Solution | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Outdated SSL version detected | Upgrade SSL version in server configuration | High |
| Weak cipher suite detected | Modify cipher suites to include strong algorithms | High |
| Client reports compatibility issue | Identify the unsupported cipher suite and adjust the server configuration accordingly | High |
Preventing Future Issues

Fixing SSL/TLS errors is crucial, but proactive measures are equally important to prevent future problems. A proactive approach involves understanding the root causes of these errors and implementing strategies to maintain a secure environment. This includes staying updated on security best practices and server configurations.By understanding and implementing the preventative measures Artikeld below, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering SSL/TLS errors in the future.
This ensures your WordPress website remains accessible and secure for your visitors.
Keeping Server and WordPress Software Up-to-Date
Regular updates for your server operating system and WordPress software are essential for security. Outdated software often contains vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Patches released by software providers frequently address these vulnerabilities.
- Server Operating System Updates: Regularly update your server’s operating system. Security patches often address critical vulnerabilities. This ensures the underlying platform is protected against known exploits. Check your hosting provider’s recommendations for update schedules.
- WordPress Core Updates: WordPress releases regular updates with security enhancements. Keeping your WordPress installation updated is critical. These updates often address vulnerabilities and improve overall security.
- Plugin and Theme Updates: Plugins and themes, often extensions to your WordPress website, also need to be updated. Outdated plugins and themes are potential entry points for attackers. Always ensure that your plugins and themes are up-to-date.
Best Practices for Configuring SSL/TLS on a WordPress Website
Proper SSL/TLS configuration is vital for secure communication. Incorrect configurations can lead to errors. These best practices help ensure proper implementation.
- Using HTTPS: Ensure your website uses HTTPS, the secure protocol. This encrypts communications between the server and users’ browsers. Using HTTPS is essential for protecting sensitive data.
- Valid SSL Certificate: Use a valid SSL certificate issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). A valid certificate ensures secure connections. Avoid self-signed certificates, as they can lead to security warnings for users.
- Strong Cipher Suites: Configure your server to use strong cipher suites that support modern encryption algorithms. Avoid outdated cipher suites, which may be vulnerable to attacks.
- Strict Security Policies: Configure your web server to enforce strict security policies, such as HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS). This helps prevent man-in-the-middle attacks.
Regularly Reviewing Server Configurations for SSL/TLS
Regularly checking your server configurations ensures that SSL/TLS settings remain optimal and up-to-date.
- Automated Checks: Implement automated checks to scan your server’s SSL/TLS configuration regularly. This helps identify potential issues promptly.
- Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits of your server’s SSL/TLS configuration. This helps identify and address any vulnerabilities or misconfigurations.
- Checking Logs: Regularly review server logs for errors related to SSL/TLS connections. This helps identify potential problems early on.
Best Practices for WordPress Security in Relation to SSL
Implementing these best practices enhances WordPress security and reduces the risk of SSL/TLS errors.
- Enable HTTPS by default: Configure your server to enforce HTTPS for all connections.
- Use strong passwords: Employ strong, unique passwords for all accounts and services related to your website.
- Regular security scans: Implement security scans to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
- Firewall protection: Implement a firewall to block unauthorized access.
- Limit login attempts: Implement measures to limit the number of failed login attempts.
Last Word
In conclusion, fixing SSL/TLS errors in WordPress involves a multi-faceted approach, encompassing certificate validation, server configuration, and WordPress plugin checks. By following the detailed steps in this guide, you can effectively diagnose and resolve cipher mismatch errors. Proactive measures, like keeping your software updated and regularly reviewing configurations, are essential to prevent future issues. A secure website is essential, and this guide empowers you to keep your WordPress site running smoothly and securely.