How Google search engine really works is a fascinating exploration of the intricate processes behind the world’s most popular search engine. This journey delves into the core mechanisms, from the initial crawling and indexing of web pages to the sophisticated algorithms that deliver relevant results, considering user interaction and privacy concerns.
We’ll examine the vast network of interconnected web pages, the complex ranking systems that determine which pages appear first, and the vital role of user experience and feedback in shaping the search engine’s functionality. We’ll also uncover the impressive security measures Google employs to maintain a safe and trustworthy search environment.
Crawling and Indexing
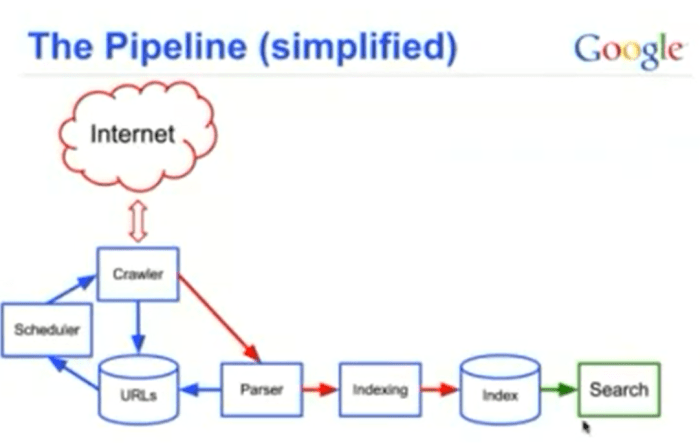
Google’s search engine operates on a vast network of interconnected web pages. To present relevant results, it needs a sophisticated system for discovering and understanding these pages. This system involves two crucial processes: crawling and indexing. Crawling discovers new and updated pages, while indexing meticulously organizes the extracted information for rapid retrieval.The process of crawling and indexing is a continuous cycle.
Google’s crawlers, often called spiders or bots, systematically traverse the web, following links to discover new content. This newly discovered content is then processed and added to Google’s massive index. This index acts as a vast library, enabling Google to quickly locate and retrieve relevant information when a user submits a search query.
Methods of Discovery and Update
Google employs various methods to discover new web pages and keep its index up-to-date. These methods are constantly evolving to adapt to the ever-changing web landscape. One key method is following links from already-indexed pages. The crawler follows hyperlinks, traversing the web like a digital explorer, discovering new content in the process.Another vital method is sitemaps. Webmasters submit sitemaps, which are essentially blueprints of their websites, detailing the structure and organization of the content.
These sitemaps provide Google’s crawlers with a structured pathway to navigate the website, ensuring comprehensive coverage. This helps in discovering content that might be difficult to find via link traversal alone. Google also uses other signals, including updates to web pages and user behavior, to determine which pages need re-crawling and updating.
Information Extracted During Indexing
During the indexing process, Google’s crawlers don’t just collect the text content of a page. They extract a wide range of information to create a comprehensive understanding of the page. This includes the title, meta descriptions, headings, and other HTML tags. Furthermore, the crawlers analyze the text content, identifying s and phrases that reflect the page’s topic.
The crawler also takes into account the structure and layout of the page, such as images, videos, and other multimedia elements. Finally, the crawler considers the page’s overall context, evaluating factors such as the domain authority and the links pointing to the page.
Understanding how Google’s search engine works is key to getting your website noticed. It’s a complex system, evaluating billions of web pages based on various factors, like the content’s relevance and authority. To boost your site’s ranking, earning high-quality backlinks is crucial, and strategies like getting a first DA 80 backlink get first da 80 backlink can be a powerful step.
Ultimately, a deep understanding of these search algorithms remains the foundation for sustainable online visibility.
Types of Crawled Content and Indexing Strategies
- Static content: Pages with fixed content, such as news articles or product descriptions. These are typically indexed using a standard approach, focusing on the textual content and metadata.
- Dynamic content: Pages whose content changes based on user input or other parameters. This requires more sophisticated indexing techniques. Google uses techniques like rendering the page as it would appear to a user and indexing the rendered content.
- Structured data: Data presented in a structured format, often using schema markup. This enables Google to understand the data better, potentially displaying richer results in search results. The structured data is used to create a more detailed understanding of the data on the page, often enhancing search results.
- Multimedia content: Images, videos, and other multimedia elements. These elements are often indexed using specialized techniques, extracting relevant information from the content. The information is also analyzed for visual features and context.
| Type of Crawled Content | Indexing Strategies |
|---|---|
| Static Content | Standard approach, focusing on text and metadata. |
| Dynamic Content | Rendering the page and indexing the rendered content. |
| Structured Data | Utilizing schema markup for better understanding and richer search results. |
| Multimedia Content | Specialized techniques for extracting information from images, videos, etc. |
Comparison of Crawling Techniques
| Search Engine | Crawling Techniques |
|---|---|
| Link following, sitemaps, user behavior signals, and more. | |
| Bing | Similar to Google’s approach, with a focus on real-time data and updates. |
| DuckDuckGo | Emphasizes privacy and focuses on a more comprehensive web coverage. |
Google employs advanced techniques to handle dynamic content, such as using JavaScript rendering to create a virtual user experience and capture the dynamic content as it appears to a user. It also uses sophisticated techniques to handle structured data, using schema markup to extract and understand specific data points, enhancing search results with more detailed information.
Search Algorithm
Google’s search algorithm is a complex and constantly evolving system designed to deliver the most relevant and helpful results to users. It’s a sophisticated blend of technical processes and intricate ranking factors that sift through billions of web pages to pinpoint the most suitable content for any given query. Understanding its inner workings provides insight into the mechanisms behind effective online searching.The algorithm works behind the scenes, meticulously analyzing countless signals to produce a ranked list of search results.
This process involves not only understanding the words in a query but also comprehending the intent behind the query, which allows the search engine to provide a more tailored and useful experience.
Core Components of the Algorithm
The core components of Google’s search algorithm are multifaceted and intertwined. These components include sophisticated natural language processing, machine learning models, and a vast network of data centers. These components work together to understand the user’s intent and deliver relevant results.
Ranking Factors
Google’s ranking algorithm considers a multitude of factors when determining the order of search results. These factors are designed to provide a comprehensive and holistic view of the content’s relevance, authority, and user experience. The algorithm’s complexity ensures that the results are not simply based on matching, but also on a wider array of factors that indicate quality.
Relevance, Authority, and User Experience
Relevance, authority, and user experience are crucial components in Google’s search algorithm. Relevance is determined by how well the content addresses the user’s query. Authority signifies the trustworthiness and credibility of the source. User experience encompasses aspects like website speed, design, and mobile-friendliness. These factors are carefully weighted to provide a balanced and helpful search experience.
Key Ranking Factors and Weightings (Hypothetical)
| Ranking Factor | Hypothetical Weighting |
|---|---|
| Page Content Relevance | 40% |
| Backlinks (Quality and Quantity) | 30% |
| Website Authority (Domain Age, Trust Score) | 15% |
| User Engagement (Click-Through Rate, Dwell Time) | 10% |
| Mobile-Friendliness | 5% |
Note: These weightings are hypothetical and do not reflect the actual algorithm.
Flowchart of the Search Algorithm
Start
|
V
User Enters Query
|
V
Query Processing (Understanding Intent)
|
V
Index Retrieval (Identifying Relevant Pages)
|
V
Ranking (Applying Algorithm Factors)
|
V
Result Display (Ordered List of Pages)
|
V
End
Multilingual and Cultural Considerations
Google’s search algorithm is designed to consider different languages and cultural contexts in its results.
It uses advanced language models and machine translation to ensure that search results are relevant to users across the globe. Google’s understanding of different languages and cultural nuances is crucial for providing a truly global search experience.
PageRank and Link Analysis: How Google Search Engine Really Works
PageRank, a cornerstone of Google’s search algorithm, revolutionized how web pages are ranked. It goes beyond simple matching to understand the relationships between websites, assigning a numerical value to each page reflecting its importance within the vast web. This importance is heavily influenced by the quality and quantity of backlinks pointing to the page.
Understanding how Google analyzes these connections is crucial for anyone looking to improve their website’s visibility. This analysis delves into the intricacies of PageRank, backlinks, and the impact of manipulative link-building tactics.
PageRank: Determining Page Importance
PageRank assigns a score to each page based on the importance of the pages linking to it. A higher PageRank score indicates a more authoritative and trustworthy source, reflecting the collective judgment of the web. Pages with many links from high-ranking pages receive a boost in their own PageRank, creating a complex network of influence. This process considers the quality and quantity of inbound links, effectively modeling the web’s interconnectedness.
Backlinks and Search Rankings
Backlinks are crucial for search rankings. They represent a vote of confidence from other websites, suggesting the linked page’s value and relevance. High-quality backlinks from reputable sources significantly boost a page’s PageRank and search visibility. The quality of a backlink is often more important than its quantity. A backlink from a highly authoritative website carries more weight than numerous backlinks from less relevant sites.
Analyzing Web Page Relationships
Google analyzes the relationships between web pages using sophisticated algorithms. These algorithms examine not only the number of links pointing to a page but also the quality and context of those links. The process involves evaluating factors such as the authority of the linking page, the relevance of the linking page to the target page’s content, and the overall context of the link within the linking page’s content.
This analysis enables Google to understand the relationships and importance of different web pages, forming a comprehensive view of the web’s structure.
Ever wondered how Google’s search engine actually works its magic? It’s a complex system, but essentially, it crawls the web, indexes pages, and ranks them based on relevance. This intricate process is deeply intertwined with effective inbound marketing strategies, like guest blogging. A data-driven approach, as outlined in this excellent piece on why guest blogging is the best inbound marketing strategy a data driven answer , demonstrates how high-quality content, strategically placed on other relevant websites, boosts your website’s visibility.
Ultimately, this improves your search engine ranking and enhances your overall online presence.
Comparison of PageRank with Other Link Analysis Algorithms
| Feature | PageRank | Other Link Analysis Algorithms (e.g., HITS) |
|—————–|———————————————|—————————————————-|
| Core Idea | Measures the importance of a page based on the importance of its inbound links.
| Often uses two scores: authority and hub, reflecting the importance of a page for providing information and for summarizing information respectively. |
| Link Weighting | Considers the importance of the linking page. | May assign different weights to links based on various factors. |
| Data Structure | Employs a recursive algorithm. | Often involves iterative processes to refine the scores.
|
| Computational Cost| Relatively high for large web graphs. | Computational cost may vary depending on the specific algorithm. |
Impact of Spam and Manipulative Link Building
Spam and manipulative link building techniques, like buying backlinks or creating artificial links, can harm search results. These practices undermine the integrity of the search process by artificially inflating a page’s PageRank and artificially enhancing its visibility. Such activities deceive search engines and ultimately harm the user experience by providing irrelevant and low-quality results.
Strategies for Improving Link Profile Naturally
Creating a natural and high-quality link profile requires a focus on creating valuable content and building genuine relationships with other websites. Strategies include guest blogging on relevant sites, creating shareable content, and participating in online communities. These activities help to earn backlinks organically, which significantly contribute to improving a website’s PageRank and search visibility.
User Interaction and Feedback
Google’s search algorithm isn’t static. It’s a dynamic system constantly learning and adapting to user behavior. This feedback loop, powered by user interactions, plays a crucial role in refining search results and ensuring relevance. Understanding how users interact with search results is paramount to Google’s mission of providing the most helpful and informative answers.
Impact of User Behavior on Search Results
User behavior significantly influences search results. Factors like the queries users submit, the pages they click on, and how long they spend on those pages all contribute to the algorithm’s understanding of what constitutes a relevant and valuable result. This continuous feedback loop is a core aspect of Google’s search engine, enabling it to evolve and improve its ability to provide users with the information they need.
Click-Through Rates and Dwell Time
Click-through rate (CTR) and dwell time are crucial metrics in evaluating the quality of search results. A high CTR indicates that users find the displayed results relevant and useful, while a low CTR suggests that the results might not be meeting user expectations. Dwell time, the amount of time a user spends on a webpage after clicking on a search result, further provides insight.
Understanding how Google’s search engine works is crucial for online success. It’s a complex system, but essentially, Google crawls the web, indexes billions of pages, and then ranks them based on relevance and quality. To optimize your website for those rankings, consider using tools like 12 tools that can help you build high converting landing pages to create engaging, high-quality landing pages.
This directly impacts how well your site performs in search results, ultimately boosting your visibility and driving traffic. In essence, understanding Google’s algorithm and utilizing effective strategies are key to maximizing your online presence.
A longer dwell time suggests the page is engaging and informative, reinforcing its relevance. Google uses these metrics to understand the quality and value of web pages.
Analysis of User Interactions
Google analyzes various user interactions with search results to refine the algorithm. This includes not only CTR and dwell time but also the specific queries users ask, the pages they visit after clicking on a search result, and the overall user experience. This comprehensive data collection enables Google to identify trends and patterns that inform adjustments to the search ranking system.
Table: User Interactions and Potential Impact on Search Rankings
| User Interaction | Potential Impact on Search Ranking |
|---|---|
| High Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Positive impact; indicates relevance and usefulness of the result. The result is more likely to be ranked higher in future searches. |
| Low CTR | Negative impact; suggests the result might not be relevant or useful to users. The result is less likely to be ranked highly. |
| Long Dwell Time | Positive impact; indicates the result is engaging and informative. The result is more likely to be ranked higher. |
| Short Dwell Time | Negative impact; suggests the result might not be fulfilling user needs. The result is less likely to be ranked highly. |
| Negative User Feedback (e.g., marking a result as unhelpful) | Negative impact; directly signals the result is not helpful, leading to a lower ranking. |
| Frequent Visits to a Specific Result | Positive impact; shows consistent user engagement and relevance. The result is more likely to be ranked higher. |
Machine Learning and Adaptation
Google utilizes machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of user interaction data. This allows the search engine to dynamically adjust search results based on observed patterns and feedback. The algorithms learn from user behavior, continually refining the ranking system to deliver more relevant and valuable results. This iterative process ensures that search results adapt to evolving user needs.
Personalization in Search Results, How google search engine really works
Personalization is a crucial aspect of providing relevant search results. Google tailors search results based on factors like user location, search history, and past interactions. This approach enhances the user experience by presenting results that are more likely to be relevant to individual needs. Personalized results aim to anticipate user needs and provide results tailored to their specific interests and contexts.
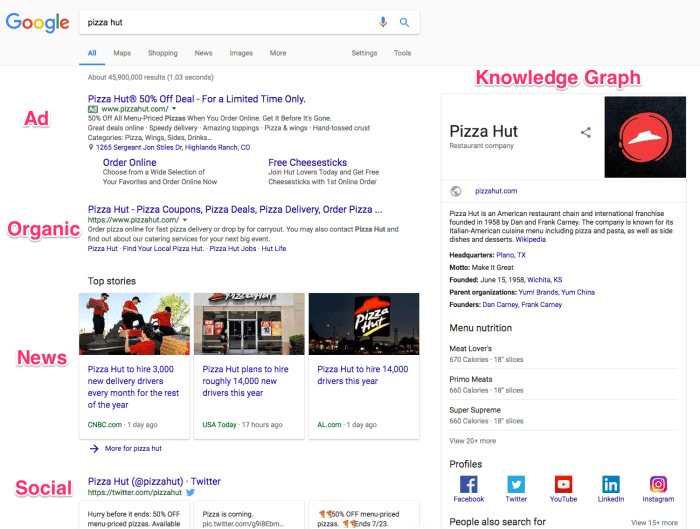
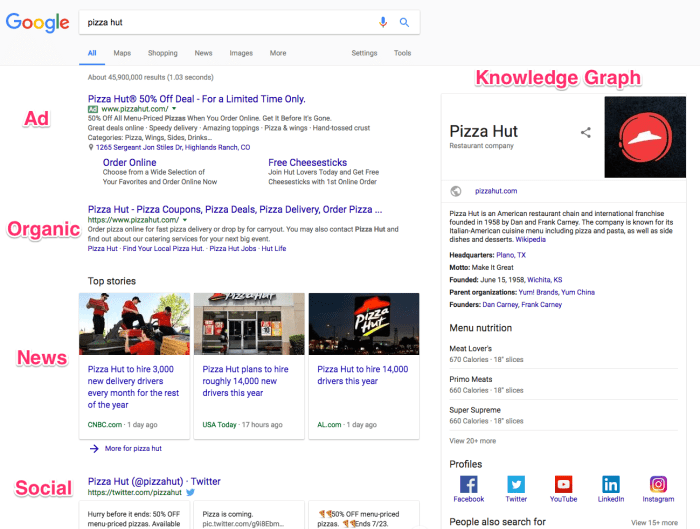
Search Result Display
Google’s search results aren’t just a list of links; they’re a carefully crafted presentation designed to provide the most relevant and helpful information quickly. The display meticulously considers user context, search query, and the type of content being presented, ensuring a seamless and efficient user experience. This process goes beyond simply displaying links; it involves a dynamic arrangement of various result types, prioritizing those deemed most valuable to the user.
Structure of a Search Result Page
A typical Google search result page presents results in a visually organized manner. The layout prioritizes the most relevant results at the top, often including a snippet of the webpage’s content directly within the result itself. This snippet aids users in quickly assessing the page’s relevance to their query. Further down, additional results, categorized by type (e.g., images, videos, news), are presented in a visually distinct fashion.
A prominent feature is the search query itself, displayed prominently at the top, followed by the search results in a clear, easy-to-scan format.
Presenting Search Results Visually
Google employs a user-friendly design to display search results. The layout is deliberately uncluttered, allowing users to quickly locate and scan relevant information. Clear visual cues differentiate different result types, making it straightforward for users to understand the nature of each result. Visual hierarchy is key; more important results are displayed more prominently. The visual presentation adapts to various screen sizes (desktop vs.
mobile) to ensure optimal readability and usability.
Different Types of Search Results
Google’s search results extend beyond simple text links. Users can find images, videos, news articles, and more. This diverse offering ensures that the search experience caters to a wide range of information needs.
Comparison of Result Types
| Result Type | Description | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Web Pages | Standard search results displaying snippets of web content. | High relevance to the query; typically links to full webpages. |
| Images | Visual results directly related to the query. | Visual representation of relevant images; often with high resolution. |
| Videos | Video clips and channels relevant to the query. | Embed videos directly within the results; user can preview content without leaving the search page. |
| News | Recent news articles related to the query. | Featured news stories with timestamps; often from reputable news sources. |
Prioritization and Organization of Results
Google’s algorithm prioritizes results based on relevance, authority, and user engagement. Web pages with high authority, frequently updated content, and strong user signals (e.g., high click-through rates) are often presented higher in the results. This ensures that users are presented with the most informative and credible results first. The organization of results is further enhanced by the categorization of results by type.
Contextual Presentation of Results
Google dynamically adapts the presentation of search results to the user’s context. Mobile users, for instance, will see results optimized for smaller screens, featuring larger images and concise information. Desktop users, on the other hand, may be presented with a wider array of results and a more detailed layout. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining a seamless and efficient user experience across all devices.
Security and Privacy
Google prioritizes user security and privacy, recognizing it as a fundamental aspect of its service. Robust security measures are integral to maintaining user trust and preventing malicious activities. This commitment extends to safeguarding user data throughout the entire search process, from crawling and indexing to displaying search results. A strong focus on privacy and security allows Google to maintain a reliable and trustworthy platform for users globally.
Google employs a multi-layered approach to protect user data and prevent abuse. This approach includes advanced technologies, rigorous policies, and a commitment to continuous improvement. These safeguards aim to ensure that user information remains confidential and that the search experience remains safe and reliable.
Security Measures to Protect User Data
Google implements a variety of security measures to protect user data, including encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems. These measures help prevent unauthorized access and misuse of user information. Strong authentication protocols are critical to protecting user accounts and preventing fraudulent activities. Data is encrypted both in transit and at rest to protect it from potential breaches.
Importance of User Privacy in Search Engine Operation
User privacy is paramount in search engine operation. Google’s commitment to privacy is evident in its design principles, which prioritize user control over their data. This includes providing users with options to manage their search history, personalize their experience, and control the visibility of their information. Respect for user privacy fosters trust and encourages responsible use of the search engine.
Google’s Safety Guidelines for Handling Inappropriate Content
Google employs a sophisticated system for identifying and handling inappropriate content. This system involves automated detection and human review to ensure compliance with safety guidelines. These guidelines are regularly updated and refined to address emerging threats and ensure a safe environment for all users. The goal is to strike a balance between providing access to information and preventing the dissemination of harmful content.
Security Protocols Used by Google
| Aspect of Search Engine Operation | Security Protocols |
|---|---|
| Data Storage | Encryption at rest, access controls, regular security audits |
| Data Transmission | Encryption in transit, secure protocols (HTTPS), regular security assessments |
| User Accounts | Multi-factor authentication, strong passwords, account recovery mechanisms |
| Malicious Activity Detection | Intrusion detection systems, threat intelligence, automated detection systems, human review |
Safeguarding Against Spam and Malicious Websites
Google employs sophisticated algorithms and technologies to detect and filter spam and malicious websites. These techniques include analyzing website content, backlinks, and user behavior. Regular updates to these algorithms are crucial to maintaining a high quality search experience, free from spam and harmful content. This involves continuous monitoring and adaptation to new threats.
Challenges of Maintaining Security and Privacy in a Global Context
Maintaining security and privacy in a global context presents unique challenges. Different regions have varying legal and regulatory frameworks, which can impact how Google operates. Compliance with these diverse regulations requires careful consideration and adaptation. Navigating international data transfer laws and respecting different cultural sensitivities are crucial components of maintaining trust and security globally. Moreover, the constant evolution of technology and cyber threats demands a proactive approach to security.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, understanding how Google search engine really works reveals a powerful blend of technology, data analysis, and user-centric design. From crawling and indexing to the final presentation of results, every aspect plays a crucial role in the seamless user experience. The constant evolution of algorithms and the incorporation of user feedback highlight the ongoing effort to refine and optimize this fundamental online tool.