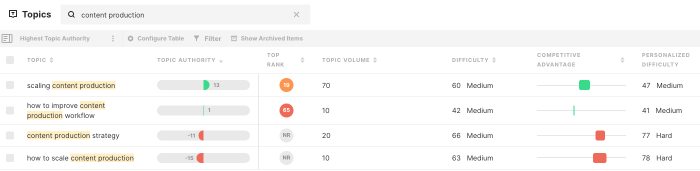
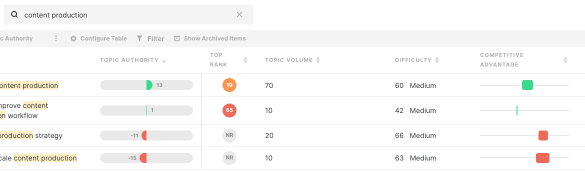
Helpful content topic modeling topic clusters sets the stage for understanding how to create truly valuable content. This exploration delves into defining helpful content, identifying effective topic modeling techniques, and organizing topic clusters for maximum impact. We’ll cover everything from structuring content for comprehension to tailoring it for diverse audiences and measuring its effectiveness.
The process of organizing content around carefully selected topic clusters is crucial for creating a well-structured and user-friendly experience. By understanding how different topic modeling techniques impact the generation of helpful content, we can develop a framework for optimal content creation.
Defining Helpful Content
Helpful content, in the context of topic modeling and topic clusters, is information that effectively addresses user needs and expectations within a specific domain. It goes beyond simple presentation of facts; it facilitates understanding, application, and problem-solving. This requires a deep understanding of the user’s intent and the context surrounding the topic. This definition applies across various content formats, from articles and videos to infographics and interactive tools.Helpful content is not just informative; it’s actionable.
It empowers users to navigate complex topics, make informed decisions, and solve problems related to topic modeling and topic clusters. This focus on user empowerment is crucial for driving engagement and fostering a positive user experience.
Key Characteristics of Helpful Content
Helpful content possesses specific characteristics that distinguish it from less helpful content. These characteristics are essential for creating content that resonates with users and meets their needs.
- Accuracy and Validity: Information presented must be accurate and verifiable. Inaccurate data or misleading information can erode trust and undermine the helpfulness of the content. This is particularly important in the context of topic modeling, where precise terminology and methodology are critical.
- Clarity and Conciseness: Complex concepts should be explained in a clear and concise manner. Jargon and technical terms should be defined and explained, ensuring accessibility for a broad audience. This includes appropriate structuring and use of visuals to enhance understanding.
- Relevance and Focus: The content must directly address the specific topic and the needs of the target audience. Unnecessary information or tangential discussions can detract from the core message and reduce helpfulness.
- Engagement and Interactivity: Content that engages the user, such as interactive elements, visualizations, and calls to action, can significantly enhance the user experience and improve comprehension. This might involve providing practical examples, downloadable templates, or interactive simulations related to topic modeling.
- Accessibility and Usability: Content should be easily accessible and usable across different platforms and devices. This includes considerations for design, readability, and navigation.
Content Format Considerations
The concept of helpfulness applies differently across various content formats. Each format has its strengths and weaknesses in conveying information effectively.
Helpful content topic modeling topic clusters are great for organizing information. For instance, if you’re looking to boost your WooCommerce store’s sales, understanding how to customize WooCommerce product pages is key. Learning how to do this, as detailed in this guide how to customize woocommerce product pages , can significantly improve user experience and ultimately drive conversions.
This kind of targeted information fits perfectly within these helpful content topic modeling topic clusters.
- Articles: Articles should present in-depth information, structured logically with headings, subheadings, and supporting evidence. Examples and case studies can make complex concepts more understandable. The use of clear language and a logical flow of information are key for helpful articles.
- Videos: Videos can effectively communicate information through visual aids, demonstrations, and interviews. They are particularly useful for demonstrating processes or explaining complex concepts through visual examples. Videos should be concise and well-structured, with clear audio and visuals.
- Infographics: Infographics use visual elements to present complex data or information in a concise and easily digestible format. They are highly effective for highlighting key insights and trends in topic modeling and topic clusters. Infographics should be clear, visually appealing, and accurately represent the data they display.
User Intent and Needs
Understanding user intent and needs is crucial for creating helpful content. What are users hoping to achieve by interacting with the content?
- Understanding the basics: Some users may be new to topic modeling and need a foundational understanding of the concepts. Helpful content in this case should be introductory and focused on core principles.
- Applying techniques: Other users may want to apply specific techniques to their own data. Helpful content for these users should include practical examples and step-by-step guides.
- Troubleshooting issues: Some users might be experiencing problems and need help resolving them. Helpful content in this scenario should offer clear solutions and troubleshooting advice.
Evaluation Framework
A framework for evaluating the helpfulness of content related to topic modeling and topic clusters should consider the following:
- Accuracy of information: Is the information presented accurate and up-to-date?
- Clarity and conciseness: Is the information presented in a clear and concise manner?
- Relevance to user needs: Does the content directly address the user’s specific needs and expectations?
- Engagement and interactivity: Does the content encourage user interaction and engagement?
- Accessibility and usability: Is the content easily accessible and usable across different platforms and devices?
Identifying Topic Modeling Techniques: Helpful Content Topic Modeling Topic Clusters
Topic modeling, a powerful technique in natural language processing, helps uncover hidden patterns and themes within large datasets of text. Understanding the nuances of different topic modeling methods is crucial for extracting meaningful insights and creating helpful content. This exploration delves into various techniques, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses, and guiding you in selecting the optimal approach for your specific needs.Different topic modeling techniques offer unique approaches to uncover latent topics within a corpus of text.
The choice of technique heavily influences the resulting topic clusters and the interpretability of the results. Choosing the right method depends on the characteristics of the dataset, desired level of detail, and computational resources available.
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA)
LDA, a generative probabilistic model, assumes that each document is a mixture of topics. Each topic is characterized by a probability distribution over words. LDA excels at identifying topics that are represented by a mix of words and at finding relationships between documents. This method is often favored for its ability to uncover nuanced and complex relationships within text data.
- Strengths: LDA is relatively straightforward to implement and interpret. It provides a clear probabilistic framework for understanding topic distributions.
- Weaknesses: LDA can be computationally intensive for large datasets. The resulting topics can sometimes be difficult to interpret, requiring careful analysis.
- Application in Helpful Content: LDA can be used to discover topic clusters relevant to specific domains, allowing for the creation of content categorized around specific themes. For instance, in a dataset of blog posts, LDA can identify topics like “machine learning,” “data visualization,” or “cloud computing.” This facilitates the creation of focused and comprehensive content within each identified topic cluster.
Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF)
NMF is an alternative topic modeling approach that seeks to decompose a document-term matrix into two non-negative matrices. This method is particularly useful for identifying topics with clear and distinct word associations.
- Strengths: NMF is computationally faster than LDA, making it suitable for large datasets. The resulting topics are often more interpretable, as the words associated with each topic are more explicitly connected.
- Weaknesses: NMF may not capture nuanced or complex relationships between topics as effectively as LDA. The interpretation of the results might need additional contextual analysis.
- Application in Helpful Content: NMF can be effectively employed to identify topic clusters in user reviews or customer feedback data. For example, in a dataset of restaurant reviews, NMF might uncover topics like “food quality,” “service,” or “ambience.” This information can be leveraged to create content that addresses customer concerns and enhances user experience.
Choosing the Right Technique
Several factors influence the choice between LDA and NMF:
- Dataset size and complexity: NMF is faster for larger datasets.
- Desired level of topic nuance: LDA might be better for capturing intricate topic relationships.
- Computational resources: NMF requires fewer resources than LDA for larger datasets.
Practical Example (LDA)
Consider a dataset of articles about sustainable agriculture. Using LDA, we can identify key themes. The output might include topics like “organic farming,” “water conservation,” “soil health,” and “alternative energy.” These topics can be further explored to develop targeted content around these themes.
Organizing Topic Clusters
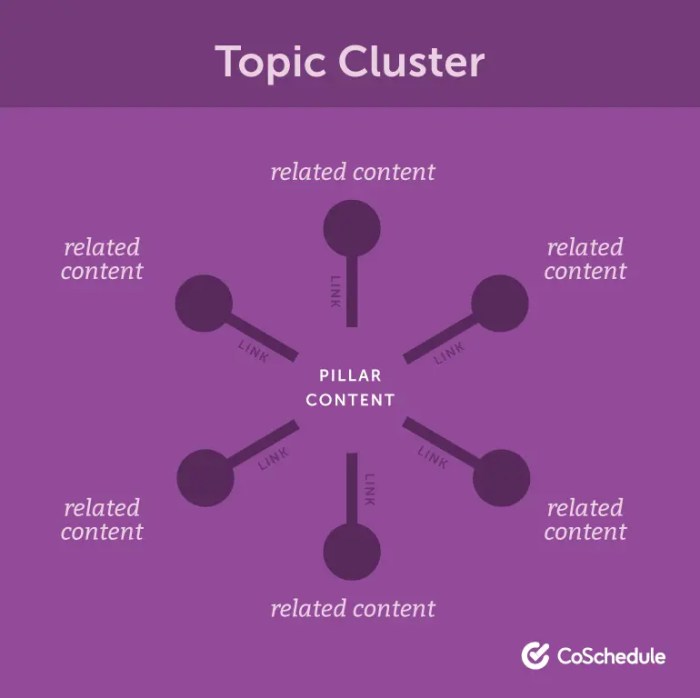
Organizing topic clusters is crucial for creating a user-friendly and easily navigable knowledge base. A well-structured hierarchy allows users to quickly find the information they need, enhancing the overall experience and effectiveness of the content. This process goes beyond simply grouping topics; it involves understanding the relationships between them and prioritizing content for maximum impact.Effective topic clustering creates a clear pathway for users to explore related concepts, making it easier to grasp complex subjects.
By strategically organizing these clusters, we can improve the discoverability and accessibility of information, leading to a more efficient knowledge management system.
Hierarchical Structure of Topic Clusters
Topic clusters should be organized in a hierarchical structure, mirroring the relationships between concepts. This structure facilitates easy navigation and promotes a deeper understanding of the subject matter. A well-organized hierarchy, akin to a tree structure, enables users to drill down into specific details while also providing context from broader perspectives.
- Root Topics: These are the broadest categories that encompass the entire scope of the knowledge base. They serve as entry points for users seeking general information. For example, a root topic for a software development knowledge base could be “Software Development Lifecycle.”
- s: These delve deeper into the root topics, providing more specific information. Continuing the example, s under “Software Development Lifecycle” might include “Requirements Gathering,” “Design,” and “Testing.”
- Detailed Topics: These are the most specific topics within the s, offering detailed explanations, instructions, or examples. Examples within “Requirements Gathering” could be “User Interviews,” “Surveys,” and “Document Analysis.”
Impact of Organization on Discoverability and Accessibility
The way topic clusters are organized directly affects how easily users can find and access relevant information. A well-structured hierarchy allows users to navigate efficiently, quickly identifying the information they need. Conversely, a poorly organized structure can lead to frustration and wasted time. A clear structure improves the user experience and makes the knowledge base more valuable.
- Intuitive Navigation: A clear hierarchy makes it easy for users to navigate from broad concepts to specific details. This is akin to using a table of contents in a book.
- Improved Search Functionality: A hierarchical structure helps search engines and internal search tools understand the relationships between topics, improving search accuracy and relevance.
- Enhanced Learning and Understanding: By presenting information in a logical sequence, the hierarchy promotes a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Prioritizing Topics Within a Cluster
Prioritizing topics within a cluster is essential for creating helpful content. This process focuses on identifying the most valuable and frequently accessed information within each cluster.
- User Demand: Analyze user behavior to identify the most requested or searched topics. This can be done by tracking search queries, click-through rates, and user feedback.
- Content Quality: Assess the quality of existing content, ensuring that the most accurate and comprehensive information is prioritized.
- Content Completeness: Determine if any critical topics are missing within the cluster. This involves looking at the overall scope and identifying gaps in the existing information.
Identifying Potential Gaps in Topic Coverage, Helpful content topic modeling topic clusters
Identifying gaps in topic coverage involves scrutinizing the existing clusters to uncover missing information. This can be achieved through a systematic approach that compares the current content against industry best practices, user needs, and relevant research.
- Benchmarking: Compare the current content to similar knowledge bases or industry standards to identify areas where the coverage may be insufficient.
- User Research: Conduct user interviews and surveys to understand user needs and identify topics they are looking for but haven’t found.
- Competitor Analysis: Analyze the content offered by competitors to identify gaps in the current topic coverage that could provide an advantage.
Role of User Feedback in Refining Topic Clusters
User feedback plays a vital role in refining topic cluster structures. It provides valuable insights into how users interact with the content and identify areas that need improvement. Gathering and analyzing user feedback is essential for iterative refinement of the knowledge base.
- Collecting Feedback: Implement mechanisms for gathering user feedback, such as surveys, feedback forms, and user forums.
- Analyzing Feedback: Carefully analyze user feedback to identify patterns and common concerns.
- Iterative Improvement: Use the feedback to make adjustments to the topic cluster structure, content, and navigation to enhance the user experience.
Structuring Content for Understanding
Organizing content around topic clusters is crucial for a seamless user experience. This involves creating a logical flow of information that guides readers through the core concepts, maximizing their comprehension and retention. Effective structuring ensures that related information is grouped together, facilitating easy navigation and cross-referencing. Clear headings and subheadings, combined with appropriate formatting, dramatically improve readability and help users quickly locate the specific information they need.A well-structured content piece resembles a roadmap, guiding the reader through the topic’s landscape.
This approach not only enhances understanding but also promotes engagement and encourages deeper exploration of the subject matter.
Organizing Content Around Topic Clusters
To organize content around topic clusters, begin by creating a hierarchical structure. Place related content together. For instance, if your topic cluster is “Social Media Marketing Strategies,” articles on “Content Optimization,” “Paid Advertising,” and “Community Building” should reside within that cluster, enabling users to find all relevant materials in one location. This clustering ensures a focused presentation of related concepts.
Logical Flow of Information
A logical flow within content pieces is essential for user comprehension. Start with a general overview, gradually introducing specific details and examples. Use transitional phrases to connect ideas and show the relationships between concepts. For example, “Building upon the previous point…” or “As a result of this…” create a cohesive narrative, moving from broad strokes to granular details.
Helpful content topic modeling, especially when focusing on topic clusters, is crucial for creating impactful content. For example, if you’re a professional services firm looking to refresh your image, a detailed rebranding essential guide professional services firms like this one can be invaluable. Understanding the key themes and subtopics related to rebranding allows you to tailor your content strategy, ensuring it resonates with your target audience.
This targeted approach, ultimately, strengthens your overall topic modeling strategy.
This gradual unveiling of information allows readers to absorb and process the content effectively.
Cross-Referencing Content Pieces
Cross-referencing allows users to connect different pieces of content related to a topic cluster. Use internal links to direct readers to relevant articles or sections. For example, if an article on “Content Optimization” mentions ” best practices,” include a link to a separate article detailing techniques. This interconnected structure allows users to explore related concepts more deeply, enhancing their understanding of the overall topic.
Using Headings and Formatting
Clear headings and subheadings are vital for readability and navigation. Employ a hierarchical structure, using H1, H2, H3 tags to delineate main topics, s, and further subdivisions. Use bullet points or numbered lists where appropriate for concise presentation of key ideas. Emphasis on key terms using bold text improves readability.
Example Structure with HTML Table
This table demonstrates a structured approach for content, particularly useful for displaying information across multiple topics. The 4-column format allows for a responsive layout, adapting to various screen sizes.
| Topic | Description | Key Techniques | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content Optimization | Improving the quality and relevance of content to attract and engage readers. | research, content audit, user experience optimization | Creating high-quality, informative blog posts |
| Paid Advertising | Using paid channels to reach a wider audience and drive conversions. | Targeted campaigns, budget optimization, A/B testing | Running Facebook or Google Ads |
| Community Building | Cultivating a loyal following and fostering engagement through interaction. | Social listening, community management, interactive content | Hosting webinars or Q&A sessions |
| Social Media Analytics | Monitoring and analyzing social media performance to understand trends. | Engagement rate tracking, follower growth, sentiment analysis | Using tools like Hootsuite or SproutSocial |
Creating Content for Different Audiences
Crafting helpful content isn’t a one-size-fits-all endeavor. Different users have varying levels of prior knowledge, diverse learning styles, and unique needs. To truly deliver value, content must be adaptable to meet these diverse requirements. Understanding these nuances is key to making your topic modeling and topic cluster content truly helpful.Tailoring content for different user profiles and knowledge levels, incorporating visuals, and ensuring accessibility are crucial for creating a positive user experience and maximizing the impact of your content.
This approach not only engages a wider audience but also fosters a more inclusive and effective learning environment.
Tailoring Content for Different Knowledge Levels
Understanding your audience’s existing knowledge base is paramount. For beginners, introduce foundational concepts in a clear and concise manner, using simple language and avoiding jargon. Include illustrative examples and analogies to facilitate understanding. For advanced users, delve deeper into complex topics, explore advanced techniques, and incorporate nuanced discussions. Provide links to further resources for those seeking more in-depth exploration.
By considering varying knowledge levels, you create a more comprehensive learning experience for all.
Enhancing Content with Visuals
Visual aids significantly enhance the comprehension and engagement of your content. High-quality images, diagrams, and short videos can break up large blocks of text, making the information more digestible and memorable. For example, a diagram illustrating a topic modeling algorithm can make abstract concepts more tangible and understandable. Videos can demonstrate the practical application of the techniques, while images can showcase real-world use cases or the different stages of a topic modeling workflow.
Accessibility for Users with Disabilities
Creating accessible content is crucial for inclusivity. Ensure your content is accessible to users with visual impairments by providing alternative text descriptions for images and using sufficient color contrast. Offer transcripts for videos and audio descriptions for visual elements. Consider using screen reader-compatible formatting and keyboard navigation. By making your content accessible, you expand your reach and make it valuable to a broader audience.
Maintaining a Consistent Voice and Tone
Consistency in voice and tone across all content is essential for establishing brand identity and ensuring clarity. Develop a style guide outlining the specific tone, language, and formatting preferences to be employed in all topic cluster materials. This consistency builds familiarity and trust with your audience, and promotes a cohesive understanding of your topic clusters.
Comparing Content Formats and Effectiveness
| Content Format | Description | Effectiveness for Beginners | Effectiveness for Advanced Users |
|---|---|---|---|
| Written Articles | Detailed explanations, in-depth analyses | Good for introducing fundamental concepts | Excellent for exploring intricate techniques |
| Interactive Tutorials | Step-by-step instructions, exercises | Excellent for hands-on learning | Provides practical application and reinforcement |
| Videos | Demonstrations, explanations, interviews | Engaging for visual learners | Provides concise explanations and real-world examples |
| Infographics | Visual representation of data and concepts | Excellent for summarizing key information | Provides quick overview and comparisons |
This table summarizes the strengths of different content formats for different audience segments. Each format can be effectively used in combination to enhance the overall user experience and learning outcome.
Measuring Content Helpfulness
Assessing the helpfulness of content is crucial for optimizing topic modeling and topic cluster strategies. It’s not enough to simply create content; we need to understand if it’s effectively meeting user needs. This involves a multi-faceted approach encompassing user feedback, analytics, and iterative improvement. A well-defined system for measuring helpfulness ensures content remains relevant and valuable.Understanding user interaction with content is paramount.
This goes beyond simple page views and involves a deeper dive into user behavior, such as time spent on pages, click-through rates, and the types of content users engage with most within topic clusters. This data provides invaluable insights into content effectiveness.
Metrics for Assessing Content Helpfulness
Several metrics can gauge the effectiveness of content related to topic modeling and topic clusters. These metrics are vital in identifying what resonates with users and what areas need improvement. Quantitative data, when analyzed alongside qualitative feedback, provides a comprehensive picture of content performance.
- Engagement Metrics: These metrics track user interaction with the content. Key metrics include time spent on page, bounce rate, click-through rates (CTR) to related articles, and the number of shares or comments. High engagement often indicates content that successfully addresses user needs. For example, if a user spends a considerable amount of time on a specific topic cluster, it suggests that the content within the cluster is relevant and useful to their needs.
- Completion Rates: If the content involves a process or a tutorial, measuring the completion rate of the process is vital. A higher completion rate indicates that the content is easy to follow and understand. For instance, in a step-by-step guide, if users are successfully completing each step, it’s a strong indicator of clarity and comprehensibility.
- Conversion Rates: If the content aims to drive specific actions (like sign-ups, downloads, or purchases), conversion rates are key indicators. For example, a higher conversion rate for a lead magnet download after reading a specific topic cluster indicates that the cluster’s content is persuading and motivating users to take the desired action.
Collecting User Feedback
Gathering user feedback is essential to understand the perceived helpfulness of content. Qualitative data from users provides context and insight into quantitative metrics. Constructive feedback helps identify areas where content can be improved and adapted to better address user needs.
- Surveys: Surveys can be deployed to target specific questions related to user experience. For example, users can be asked about the clarity of explanations, the relevance of information, and the overall usefulness of the topic cluster.
- User Reviews and Comments: Actively soliciting and reviewing user comments on articles and topic clusters is crucial. Comments provide valuable direct feedback on specific aspects of the content, allowing for targeted improvements. These comments should be categorized and analyzed to identify recurring themes and patterns.
- Focus Groups: In-depth discussions with smaller groups of users can provide rich insights into their experiences with the topic modeling content. These groups can provide detailed feedback and insights on specific aspects of the content’s organization and clarity.
Role of Analytics in Understanding User Engagement
Analytics tools provide valuable insights into user engagement with topic modeling content. Understanding user behavior within topic clusters allows for content optimization.
- Identifying Patterns: Analytics tools can identify patterns in user behavior within specific topic clusters. For instance, if users are frequently navigating away from a particular section, it indicates a need for improvement or a potential disconnect between the content and user expectations.
- Tracking User Journeys: Tracking the path users take through the topic cluster allows for a deeper understanding of their engagement and whether the flow effectively leads them to the desired outcomes. A detailed analysis of user journeys within a topic cluster helps identify bottlenecks and areas where the content is less effective.
- A/B Testing: Analytics tools can be used to conduct A/B testing of different versions of content, such as headlines, images, or structure, to determine which performs better. A/B testing different content iterations provides measurable data to optimize for better engagement.
Improving Future Content
User feedback and analytics provide a roadmap for improving future content. Applying these insights ensures continued relevance and value for users.
Helpful content topic modeling topic clusters are crucial for understanding audience interests. Knowing what resonates with your target audience directly impacts your success, whether you’re crafting engaging blog posts or optimizing your Amazon retail ad service campaigns. A strong understanding of these clusters helps you target the right keywords and create content that genuinely connects with your customers.
This in turn, leads to improved visibility and ultimately, greater returns. For a deeper dive into leveraging Amazon’s retail ad service, check out this resource: amazon retail ad service. Ultimately, mastering topic modeling will be key to creating helpful and effective content.
- Content Updates: Identifying areas of low engagement or negative feedback enables focused updates to address specific shortcomings in the content. This could involve clarifying unclear points, expanding on topics, or restructuring the content flow.
- Topic Clustering Refinement: If a particular topic cluster is not resonating with users, it may indicate that the underlying topic structure needs adjustment. The clustering strategy might require re-evaluation and refinement to better align with user needs.
- Content Format Adjustment: Analyzing user engagement with different content formats (e.g., videos, infographics, interactive elements) helps determine the optimal approach for conveying information within specific topic clusters. Users may respond better to certain formats than others.
Metrics and Application Table
| Metric | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement Metrics (Time on Page, Bounce Rate, CTR) | Measure user interaction with the content. | Identify areas of high and low engagement within topic clusters. |
| Completion Rates | Measure the completion of a process or tutorial. | Assess the clarity and understandability of step-by-step guides or tutorials. |
| Conversion Rates | Measure the successful completion of a desired action. | Evaluate the effectiveness of content in motivating users to take specific actions. |
Illustrative Examples
Topic modeling and topic clustering are powerful techniques for understanding large datasets. Illustrative examples are crucial for visualizing complex concepts and demonstrating the practical application of these techniques. They help bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world implementation, making the process more tangible and accessible.
Data Visualization for Complex Relationships
Visualizing the relationships between topics is essential for understanding how different concepts connect and influence each other. A well-designed data visualization can reveal hidden patterns and trends, making it easier to interpret the results of topic modeling. For instance, a network graph can illustrate the connections between topics. Nodes in the graph represent topics, and edges represent the strength of the relationship between them.
A stronger connection is represented by a thicker edge. The color of the nodes could correspond to the frequency of each topic, allowing for a visual representation of the importance of each topic. Another visualization option is a word cloud, where the size of each word corresponds to its frequency within a specific topic. This method allows for quick identification of dominant s.
Illustrating Key Concepts with Blockquotes
Blockquotes are an effective way to highlight key concepts and findings. They allow for clear separation of important ideas, making them stand out from the surrounding text. For example, consider a finding from a topic model that suggests a strong relationship between “sustainable agriculture” and “climate change.” The following blockquote could be used to emphasize this finding:
“Our analysis reveals a strong connection between sustainable agriculture practices and the mitigation of climate change effects. The results suggest a high correlation between these two topics, highlighting the potential of sustainable agriculture as a crucial strategy for addressing climate change.”
Topic Cluster Structure Visualization
A visual representation of a topic cluster structure is crucial for understanding the hierarchical relationships within the dataset. A tree diagram is a good way to visualize the hierarchy of topic clusters. The root of the tree represents the overarching topic, and branches represent s. The branches further divide into sub-clusters, creating a hierarchical structure. The width of each branch could reflect the size of the topic cluster, with wider branches representing larger clusters.
Different colors could represent different types of clusters or different levels of detail. A simple tree diagram could represent topics like “Natural Disasters,” “Mitigation,” and “Recovery,” with “Natural Disasters” at the root and “Mitigation” and “Recovery” as the main branches. Further branching could represent specific types of disasters or recovery strategies.
Hypothetical Example of Content Organization
A hypothetical example of content organization can be demonstrated through a fictional scenario. Imagine a news website dedicated to covering technology trends. They are using topic modeling to categorize news articles. One prominent topic cluster is “Artificial Intelligence.” s within this cluster could include “AI in Healthcare,” “AI in Finance,” “AI Ethics,” and “AI Job Market.” Within each , articles could be further organized based on specific advancements, challenges, or applications.
This structure allows readers to easily find information related to their interests, ensuring a smooth and intuitive user experience. The website could provide a navigation system based on the topic clusters, allowing users to easily explore related topics and gain a deeper understanding of the news.
Last Word
In conclusion, crafting helpful content around topic clusters involves a multifaceted approach. From defining helpful content and choosing appropriate topic modeling techniques to structuring content for understanding and measuring its effectiveness, we’ve explored a comprehensive strategy. By implementing these methods, you can significantly improve the discoverability and usability of your content, leading to a more rewarding user experience.