Google tag manager what it is 3 fixes to common problems – Google Tag Manager: What it is 3 fixes to common problems. This guide dives deep into the world of tag management, explaining what Google Tag Manager (GTM) is and how to troubleshoot common implementation issues. We’ll explore the core functionalities, common pitfalls, and practical solutions, providing a comprehensive overview for effective tag management.
Understanding GTM is crucial for website owners and marketers seeking to optimize data collection and analysis. From real-time tag management to integrations with other tools, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and solutions to overcome common challenges and ensure seamless data tracking.
Introduction to Google Tag Manager
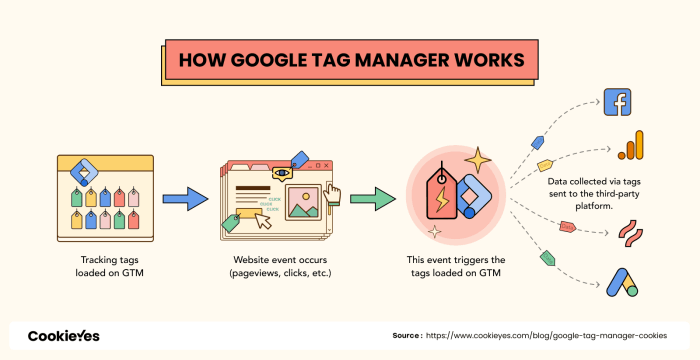
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a free tag management system offered by Google. It’s a powerful tool for managing and deploying tags on your website or app without needing to directly edit the code. GTM streamlines the process of adding, updating, and removing tracking tags, which is essential for analytics, marketing, and other important functionalities. Think of it as a central hub for all your website tags, allowing you to control them all from one place.GTM simplifies the process of adding and updating tracking tags, crucial for website analytics, marketing, and other functionalities.
By acting as a centralized platform for tag management, GTM avoids the need for direct code editing, reducing errors and improving efficiency. This centralized approach ensures all your tags are consistently updated, simplifying maintenance and preventing potential issues caused by manual changes.
Core Functionalities of GTM
GTM allows for the management of various tags and tracking codes across your website or application. This includes, but is not limited to, tags for analytics platforms like Google Analytics, marketing platforms like Google Ads, social media platforms, and custom tags for specific tracking needs. Its core functionality lies in its ability to deploy and manage these tags without altering the underlying code of your website or app.
This separation of tag management from the core code ensures maintainability and reduces the risk of errors.
How GTM Differs from Other Tag Management Solutions
GTM stands out from other tag management systems through its ease of use and integration with Google’s ecosystem. It’s free to use and integrates seamlessly with other Google services like Google Analytics and Google Ads. This streamlined integration often simplifies setup and maintenance, making it a preferred choice for many. While other platforms may offer similar functionalities, GTM’s extensive integration with the Google ecosystem provides a convenient and powerful solution for users already deeply involved with Google’s tools.
Key Features and Benefits of GTM
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time Tag Management | GTM allows for the dynamic deployment and management of tags without requiring changes to the website’s source code. This enables real-time updates to tags, ensuring accurate data collection and consistent tracking. | Faster implementation and updates of tags, minimizing downtime and errors associated with manual code modifications. |
| Simplified Tag Deployment | GTM provides a user-friendly interface to add, edit, and remove tags without direct access to the website’s code. This reduces the risk of introducing errors and simplifies tag management for non-technical users. | Improved efficiency in tag management for both technical and non-technical users, enabling quicker implementation of tracking solutions. |
| Enhanced Tag Management Flexibility | GTM offers advanced functionalities such as triggers, variables, and containers, allowing for highly customized tag deployment based on specific website events or user actions. This flexibility enables precise tracking of user interactions. | Increased control and accuracy in tracking user behavior, enabling tailored marketing campaigns and data-driven decisions. |
Common GTM Implementation Issues: Google Tag Manager What It Is 3 Fixes To Common Problems

Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a powerful tool for managing tags on your website, but implementation challenges can arise. Understanding these common issues is crucial for smooth tag management and achieving desired results. Incorrect configurations or misunderstandings of GTM’s functionality can lead to inaccurate data collection and ineffective marketing campaigns. This section will delve into three prevalent problems encountered during GTM implementation, offering examples and potential causes for each.
Configuration Errors
Proper configuration is fundamental to GTM’s effectiveness. Mistakes in setting up tags, triggers, or variables can lead to inaccurate data reporting. For instance, a wrongly configured event tracking tag might not fire correctly, resulting in missing data about user interactions. A common scenario involves mismatching tag names or incorrectly defining event parameters in the tag configuration. This can happen if the code on the website differs from what’s expected in GTM, leading to a failure to capture specific events.
Another example involves the incorrect setup of triggers, which could prevent a tag from firing when intended. In short, mismatches in configurations between the website’s structure and the GTM setup are the leading cause of these errors. The consequence is unreliable data, making informed decisions difficult.
Trigger Misconfigurations
Triggers determine when a tag should fire. Incorrectly configured triggers can lead to tags firing at the wrong time or not at all. For example, a tag designed to fire on page load might not be firing, potentially due to a misconfigured trigger. If a trigger is set to fire on a specific event, like a button click, but the event isn’t correctly mapped in the trigger, the tag will not fire.
Ever tripped over Google Tag Manager? It’s a powerful tool, but sometimes it throws a wrench in the works. I’ve tackled common issues like tags not firing and misconfigured triggers. Fortunately, mkg google premier agency partner mkg google premier agency partner can help you get the most out of your Google Tag Manager setup.
They’ve got the expertise to diagnose and resolve even the trickiest tag manager problems, ensuring smooth sailing with your marketing efforts. So, if you’re facing a tag manager snag, remember the importance of a strong partner.
Similarly, if the trigger conditions are too broad, the tag may fire in unwanted contexts, resulting in data inaccuracies. The core problem often stems from a mismatch between the expected user actions and the defined trigger rules. A lack of thorough testing and understanding of the website’s behavior can contribute to this issue.
Figuring out Google Tag Manager (GTM) can be tricky, but it’s a powerful tool. Three common problems often stump people, but luckily, there are fixes! While you’re wondering about GTM, it’s also natural to consider broader questions like privacy concerns with voice assistants. Are you worried about whether Ok Google is secretly gathering data? Dive into the potential privacy issues with voice assistants by checking out this article about Ok Google are you spying on me.
Regardless, mastering GTM is key for a smooth online experience. Understanding its ins and outs will ultimately help you avoid those common pitfalls.
Tag Firing Issues
Even with correct configuration, tags might not fire as expected. This could be due to conflicts with other tags or scripts on the page. Imagine a scenario where a custom JavaScript tracking code interferes with a GTM tag, causing it not to fire. Another instance involves the tag firing multiple times when it should fire only once, leading to inflated data and incorrect reporting.
Often, this problem stems from conflicts between different scripts on the page. Poorly maintained or updated scripts can lead to unforeseen conflicts and unpredictable tag behavior. The inability to isolate and diagnose the conflict often leads to frustrating troubleshooting.
Figuring out Google Tag Manager can be tricky, but thankfully, there are some common problems with easy fixes. Learning how to use AI tools like the ones discussed in boost your content marketing with these expert ai tips and prompts can also significantly boost your content creation. Ultimately, mastering Google Tag Manager is about streamlining your website tracking, and these fixes will help you achieve that goal effectively.
Potential Error Messages and Causes
| Error Message | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Tag not firing | Incorrect trigger configuration, conflicts with other tags, or incorrect tag setup |
| Multiple tag firings | Conflicting tags or scripts on the page, trigger configured too broadly |
| Data inconsistencies | Incorrect variable setup, mismatched tag parameters, or trigger misfires |
Fixing Common GTM Implementation Issues
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a powerful tool for managing tags on your website, but implementing it correctly can sometimes be tricky. Common issues can arise from misconfigurations, incorrect tag setups, or misunderstandings of GTM’s functionality. Addressing these issues proactively is crucial for ensuring accurate tracking and data collection. This section dives into three common implementation problems and provides solutions with step-by-step instructions and best practices.
Troubleshooting Tag Firing Issues
Tag firing issues are a frequent concern in GTM implementation. These issues can stem from incorrect trigger configurations, conflicting tags, or problems with the tag’s structure. Identifying and resolving these problems requires careful examination of tag configurations and triggers.
- Incorrect Trigger Configuration: A common cause of tag firing problems is an incorrectly configured trigger. This can result in tags firing at the wrong time or not firing at all, impacting the accuracy of collected data.
- Solution: Verify that the trigger’s conditions align with the desired actions. Ensure that the trigger’s event type and selector match the event being tracked.
- Step-by-Step Procedure:
- Open the trigger configuration in GTM.
- Review the event type and selector settings.
- Verify that the trigger’s conditions are consistent with the website’s behavior.
- If necessary, modify the trigger settings to match the desired event.
- Test the trigger by simulating the event on the website.
- Best Practices: Thoroughly test each trigger with various user interactions. Document the expected behavior and trigger conditions. Maintain a consistent naming convention for triggers to improve organization.
- Conflicting Tags: Conflicting tags can sometimes lead to inaccurate data or unexpected behaviors. This can happen if multiple tags try to execute actions on the same event.
- Solution: Review the order of tags in the GTM container. Prioritize tags that need to fire first.
- Step-by-Step Procedure:
- Open the GTM container.
- Identify potential conflicts between tags.
- Arrange tags in the desired order, prioritizing those that need to fire first.
- Test the tag order to ensure accurate firing sequences.
- Best Practices: Utilize tag preview mode to monitor tag firing sequences. Use unique names for tags to avoid ambiguity.
- Invalid Tag Structure: Errors in the tag structure can prevent the tag from firing correctly. This might include issues with the tag’s configuration, syntax, or the integration with the tracking platform.
- Solution: Carefully review the tag’s configuration. Verify the accuracy of the tag’s settings, including the tracking code and data layer variables.
- Step-by-Step Procedure:
- Double-check the tag’s configuration in GTM.
- Verify that the tag’s settings match the tracking platform’s requirements.
- Validate the tracking code and ensure its correctness.
- Test the tag’s functionality using tag preview mode.
- Best Practices: Utilize the tag preview mode to simulate user interactions and observe tag firing behavior. Maintain a clear documentation of the tag’s purpose and configuration.
Data Layer Issues
Data layer issues are common when dealing with GTM implementations. Problems with the data layer structure, incorrect variable names, or the lack of necessary data points in the layer can lead to inaccurate data. Identifying and fixing these problems is crucial for obtaining reliable insights.
Troubleshooting Tag Firing Order
If tags aren’t firing in the expected order, a GTM implementation issue is likely. Misaligned tag firing sequences can lead to inaccurate data collection and reporting.
Advanced GTM Techniques
Google Tag Manager (GTM) offers a powerful platform for managing tags, but maximizing its potential often requires advanced techniques. These techniques go beyond basic implementation and delve into optimizing performance, troubleshooting complexities, and harnessing GTM’s full capabilities. Mastering these advanced approaches allows for greater efficiency, reduced errors, and enhanced tracking insights.Optimizing GTM performance often involves careful consideration of various factors.
This includes managing the size and complexity of your containers, effectively utilizing triggers, and strategically deploying tags. Troubleshooting complex issues frequently requires a methodical approach, involving thorough debugging, and understanding the interactions between different components within the GTM environment.
Container Configuration
Efficient container configuration is crucial for performance. A well-structured container minimizes the loading time of the GTM container itself. This involves careful organization of tags, triggers, and variables. Employing best practices in variable organization, such as grouping related variables together and using descriptive names, simplifies management and reduces confusion. Furthermore, a modular approach to tag grouping, with specific containers for different types of tags (e.g., analytics, marketing, social media), can greatly improve performance by preventing unnecessary loading of tags.
Triggering
Optimizing triggering mechanisms significantly improves the efficiency of tag firing. Carefully crafted triggers ensure tags are activated only when necessary. Understanding the differences between various trigger types (e.g., page view, event, custom) is essential. Complex scenarios often require a combination of triggers, which necessitates a deep understanding of trigger logic and interaction with variables. For example, triggering a specific tag only on certain product pages within a large e-commerce website reduces unnecessary requests.
Tag Management
Efficient tag management is a cornerstone of GTM optimization. A well-structured tag hierarchy, employing logical naming conventions and categorized groupings, promotes ease of maintenance and troubleshooting. Strategic deployment of tags, firing only necessary tags for specific events, minimizes overhead and improves performance. This ensures that only the relevant tags execute, reducing the load on the website. For instance, loading analytics tags only on pages with conversions reduces the impact on the website’s loading time.
Advanced Techniques for Improved Performance
- Lazy Loading: Implementing lazy loading for tags can significantly reduce the initial page load time by deferring the loading of some tags until they are needed. This is particularly effective for tags that are not essential for the initial page rendering.
- Asynchronous Tag Loading: Using asynchronous loading methods for tags reduces the impact on the page’s loading speed. This technique allows tags to load concurrently without blocking the browser’s rendering process.
- Data Layer Optimization: A well-structured and optimized data layer is crucial for efficient tag firing. This involves minimizing the data passed to the data layer, using appropriate data types, and structuring data for efficient use.
Troubleshooting Complex GTM Issues
Diagnosing complex GTM issues often involves a systematic approach. Comprehensive debugging tools, including GTM’s built-in debugging features and browser developer tools, are invaluable in isolating the root cause of problems. Understanding the relationships between tags, triggers, and variables is critical to identifying and resolving intricate issues. For instance, a comprehensive error log, detailing the timing and status of each tag firing, provides invaluable insight into the cause of issues.
GTM Best Practices
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a powerful tool for managing tags on your website, but its effectiveness hinges on following best practices. A well-structured and maintained GTM account ensures smooth tag deployments, efficient data collection, and robust troubleshooting capabilities. This section details key best practices to optimize your GTM setup.Effective GTM implementations require a proactive approach to organization and maintenance.
These practices streamline tag management, leading to a more manageable and reliable system.
Maintaining a Well-Organized GTM Configuration
A well-organized GTM configuration is crucial for efficient tag management and troubleshooting. A clear structure within the GTM workspace makes identifying and managing tags much easier. Employing a consistent naming convention for containers, tags, and triggers helps maintain order.
- Consistent Naming Conventions: Using a standardized naming convention for tags, triggers, and containers makes it easier to identify and manage components within your GTM account. For example, use prefixes like “analytics,” “marketing,” or “ecommerce” to categorize tags logically.
- Modular Structure: Break down complex configurations into smaller, manageable modules. This modular approach allows for easier maintenance and troubleshooting of individual components. Grouping similar tags and triggers into logical units enhances readability and maintainability.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of your GTM containers to identify any outdated or unnecessary tags. Removing unused tags keeps the workspace clean and efficient.
Robust Data Collection Best Practices
Implementing robust data collection is paramount for meaningful insights. Ensure that your tags capture the right data points, accurately and reliably.
- Define Clear Data Requirements: Before implementing any tags, define the specific data you need to collect. This ensures you’re not collecting unnecessary data and that the collected data aligns with your business goals.
- Prioritize Data Accuracy: Implement validation checks to ensure the accuracy of collected data. This involves verifying the correct data format and ensuring data integrity.
- Utilize Data Layer: Utilize the data layer effectively to pass data from your website to your tags. Ensure the data layer is structured correctly, making it easier to access and use the data within your tags.
Troubleshooting Complex Implementations
Troubleshooting complex GTM implementations can be challenging. A systematic approach helps to pinpoint the root cause of any issues.
- Establish a Troubleshooting Workflow: Develop a clear troubleshooting workflow that includes steps for isolating the problem, checking logs, and identifying potential conflicts.
- Utilize Debug Mode: Leverage the GTM debug mode to identify the source of any tag firing issues. Debug mode provides detailed information about the tag execution.
- Document Steps: Document all steps taken to troubleshoot any issues. This detailed record allows for faster resolution if similar problems arise in the future.
Key Takeaway
Always thoroughly test your changes before deploying them to production. Testing prevents unexpected errors and ensures that your changes have the desired effect.
GTM and Other Tools Integration
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a powerful tool for managing tags on your website, but its true potential shines when integrated with other marketing tools. This integration allows for seamless data flow and streamlined workflows, leading to more efficient campaign management and enhanced analytics. By connecting GTM with platforms like analytics tools and advertising platforms, you gain a holistic view of your marketing performance, enabling data-driven decisions and optimized campaigns.GTM acts as a central hub, collecting data from various sources and feeding it into other tools.
This centralized approach simplifies tag management, reduces errors, and streamlines the entire process of tracking and analyzing website performance. The ability to easily modify tags and trigger actions within GTM without altering the website’s code makes integration with other tools crucial for adaptability and flexibility in marketing strategies.
Common Integrations, Google tag manager what it is 3 fixes to common problems
Integrating GTM with other tools is crucial for effective marketing. It allows for a unified view of campaign performance and streamlined data analysis. Several common integrations are used to achieve this. For instance, linking GTM with analytics platforms provides detailed website traffic insights, while integrating with ad platforms enables targeted ad campaigns and performance measurement.
Integration with Analytics Platforms
Connecting GTM with analytics platforms like Google Analytics provides a rich source of data about user behavior on your website. This integration allows for detailed tracking of website traffic, user engagement, and conversion rates. GTM can send data from various website events (page views, button clicks, form submissions) to Google Analytics, enabling in-depth analysis of user journeys. For example, you can track how users interact with specific content or products and identify areas for improvement.
Integration with Advertising Platforms
Integrating GTM with advertising platforms (like Google Ads) allows for dynamic ad targeting and improved campaign performance. GTM can be used to collect data about user interactions with ads and feed this data back into the ad platform. This enables the platform to tailor ads based on user behavior and preferences, leading to higher conversion rates. For example, GTM can track which ads lead to specific actions, like a purchase or a signup.
This granular data allows for more effective ad spending and campaign optimization.
Benefits of Integration
The benefits of integrating GTM with other marketing tools are substantial. Centralized tag management reduces errors and streamlines workflows. Data consistency across platforms provides a holistic view of marketing performance. Enhanced campaign optimization leads to improved efficiency and better return on investment.
Integration Table
| Tool Integrated | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Google Analytics | Collects website data (page views, events, conversions) and provides insights into user behavior. | Detailed website traffic analysis, user engagement tracking, conversion rate optimization. |
| Google Ads | Tracks ad performance and user interactions with ads, enabling dynamic ad targeting. | Improved ad targeting, higher conversion rates, optimized ad spending, better campaign performance. |
| Facebook Ads | Tracks user interactions with Facebook ads, enabling targeted ad campaigns. | Enhanced targeting options, better campaign performance, insights into user engagement with Facebook ads. |
| Marketing Automation Platforms (e.g., HubSpot, Marketo) | Collects user data and triggers automated actions based on predefined rules. | Improved lead nurturing, personalized user experiences, enhanced customer journey management. |
GTM Case Studies (Illustrative)
Google Tag Manager (GTM) implementation, when done correctly, can significantly improve website analytics and marketing effectiveness. However, poor setup can lead to wasted resources and ineffective tracking. Examining successful and unsuccessful implementations provides valuable insights into best practices and potential pitfalls.Effective GTM implementations are crucial for businesses seeking to understand user behavior, optimize marketing campaigns, and ultimately drive conversions.
This section presents case studies showcasing successful and problematic GTM setups, highlighting the key factors that contribute to each outcome.
Successful GTM Implementation Case Study
A major e-commerce company successfully implemented GTM to enhance its marketing tracking. Initial challenges included disparate tracking systems, making data analysis complex. The solution involved a phased implementation, consolidating data streams and standardizing event definitions. A dedicated GTM team ensured proper configuration and ongoing maintenance. This streamlined approach enabled real-time tracking of customer journeys, allowing for targeted marketing campaigns and significant improvements in conversion rates.
The company observed a 15% increase in conversion rates within the first six months of implementation, demonstrating the positive impact of a well-structured GTM setup.
Poorly Designed GTM Setup Case Study
A small business attempted a DIY GTM implementation, lacking proper planning and training. The setup resulted in numerous errors, causing inconsistent data collection and hindering analysis. Duplicate tags were implemented, leading to inaccurate reporting. The lack of a clear documentation strategy meant debugging and maintenance were extremely difficult. This led to delays in campaign optimization and a missed opportunity to identify critical user behaviors.
Benefits of a Well-Designed GTM Setup
A well-designed GTM setup offers numerous advantages. It allows for efficient and accurate data collection, empowering informed decision-making. Centralized management streamlines tag updates and maintenance, reducing errors and wasted time. This leads to consistent data across all marketing channels and improved ROI. Furthermore, a well-defined structure facilitates collaboration and knowledge sharing within a company.
By creating a unified data ecosystem, the company gains a holistic view of its user base, enabling more targeted and effective campaigns.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering Google Tag Manager involves understanding its core functionalities, troubleshooting common implementation issues, and implementing effective solutions. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of GTM, equipping you with the knowledge and best practices to effectively manage tags on your website. Remember, thorough testing is key to a successful GTM implementation.









