Google reminds that hreflang tags are hints not directives, setting a crucial foundation for international . This means understanding the nuances of how these tags work is essential for effective multilingual website optimization. Proper implementation avoids confusion for search engines and users, ensuring a smooth experience for everyone.
Hreflang tags are fundamental to helping search engines understand the language and region-specific versions of your content. They essentially tell search engines which version of a page to show to users based on their location and language preference. While powerful, they are not absolute directives; they are suggestions. This post delves into the intricacies of hreflang tags, exploring their function, best practices, and common pitfalls.
We’ll also discuss alternatives to hreflang and how to troubleshoot implementation issues.
Understanding the Concept of Hreflang Tags
Hreflang tags are crucial for search engine optimization () when your website is available in multiple languages or has localized versions for different regions. They act as a communication channel between search engines and your site, helping them understand the appropriate version of your content for each user based on their location and language preferences. This accurate identification improves the user experience and ultimately enhances your website’s ranking in search results.Hreflang tags function as a set of instructions that guide search engine crawlers to identify the correct language and regional version of a web page for a specific user.
This ensures that the most relevant content is displayed to the user, leading to higher click-through rates and better search engine rankings. This targeted approach can improve the overall user experience and contribute significantly to performance.
Fundamental Purpose of Hreflang Tags
Hreflang tags primarily aim to prevent duplicate content issues and ensure that search engines correctly understand the relationships between different language and regional versions of a website. By providing explicit instructions, hreflang tags help search engines deliver the most relevant page to each user, improving the overall user experience.
How Hreflang Tags Function
Hreflang tags work by providing search engines with information about the different versions of a page available for various languages and regions. This information allows search engines to choose the most appropriate version for each user, enhancing the overall user experience. This process is crucial for websites with global reach, enabling search engines to provide the right content to the right users.
Hreflang Attributes and Their Roles
The primary attributes within hreflang tags dictate the relationship between different versions of a page. Understanding these attributes is vital for effective implementation and ensures search engines accurately identify the correct version of the content for each user. Each attribute carries specific information about the targeted audience, allowing search engines to tailor the user experience.
Structure of Hreflang Tags in HTML
Hreflang tags are implemented as HTML attributes within the ` ` tag. They are typically placed within the `
` section of the HTML document. The structure ensures search engines can easily interpret the information and make the right decisions about delivering the appropriate content. This standardized approach facilitates a smooth and accurate process of delivering localized content to users.Common Hreflang Tag Attributes and Uses
| Attribute | Value | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
hreflang |
en-US, fr-CA, etc. |
Specifies the language and region code. | |
href |
URL of the alternate page. | Provides the URL for the alternate version. | |
Importance of Hreflang Tags: Google Reminds That Hreflang Tags Are Hints Not Directives
Hreflang tags are critical for international , guiding search engines and users to the correct localized versions of your website. They act as a roadmap, ensuring that the right content reaches the right audience, regardless of their geographical location or language preference. A well-implemented hreflang strategy can significantly improve your website’s visibility and performance in international markets.Accurate hreflang implementation is crucial for ensuring a seamless user experience and optimal search engine ranking.
Incorrect implementation, on the other hand, can lead to frustrating user experiences and negatively impact your site’s search visibility. This comprehensive discussion delves into the significance of proper hreflang usage.
Crucial Role in International
Hreflang tags are essential for international because they tell search engines which version of your website is intended for which geographic location and language. Without them, search engines might struggle to identify the appropriate version for users, potentially showing irrelevant content or even penalizing your site for duplicate content issues. This is particularly important for websites with multilingual or multi-regional content.
Impact on User Experience
Incorrect hreflang implementation can lead to a poor user experience. If a user in France is directed to an English version of your site, they’ll likely encounter difficulties navigating and finding the information they need. This can lead to frustration, and ultimately, a higher bounce rate. Conversely, proper hreflang tags ensure users are directed to the most relevant and accessible content, improving their overall satisfaction.
Impact on Search Engine Rankings
Search engines rely heavily on hreflang tags to understand the internationalization of your website. By providing clear instructions on which content belongs to which region, you help search engines serve the correct results to the right users. Proper implementation can lead to improved search rankings and higher visibility for your website in specific target markets. Failure to implement them correctly can lead to decreased rankings as search engines struggle to understand the content’s target audience.
Comparison: Hreflang Implementation vs. No Hreflang Implementation
The difference between using and not using hreflang tags can be significant. Websites with proper hreflang implementation typically see improved search engine rankings, increased user engagement, and a higher conversion rate from international visitors. Conversely, websites without hreflang tags may face lower rankings, difficulties reaching target audiences in different regions, and a potentially frustrating experience for users searching for content in their preferred language.
This can significantly impact the potential for sales and growth in international markets.
Google’s recent reminder that hreflang tags are hints, not directives, highlights the importance of understanding how these tags function. While you’re focusing on international SEO, it’s crucial to consider buyer persona examples beyond the basics, like those detailed in buyer persona examples beyond basics. Ultimately, remembering that hreflang tags are suggestions, not commands, ensures your international strategy isn’t just technically correct but also deeply connected to your target audience’s needs.
Avoiding Duplicate Content Issues
Proper hreflang implementation plays a vital role in avoiding duplicate content issues. By specifying the language and region for each version of your website’s content, you clearly signal to search engines that these versions are distinct. This avoids potential penalties for duplicate content, which can negatively affect your website’s overall search ranking.
Hreflang Tags as Hints, Not Directives
Hreflang tags are a crucial part of internationalization for websites, helping search engines understand which version of a page is relevant to a user based on their location. While they are intended to guide search engines, it’s important to understand their limitations. They function as hints, not commands, and their effectiveness depends on several factors.Understanding this distinction is vital for implementing a robust internationalization strategy.
A well-informed approach will not only enhance user experience but also improve search engine visibility. Search engines interpret these hints and use them as a guide, but they are not obligated to follow them blindly.
Hreflang as a Suggestion, Not a Command
Hreflang tags provide search engines with suggestions about which version of a page is best suited for a particular user. However, they aren’t absolute directives. Search engines can and do use other factors to determine the best page to show, and sometimes these factors override the suggestions given by the hreflang tags.
Scenarios Where Hreflang Might Not Be Sufficient
Hreflang tags are not a magic bullet. There are situations where they might not be enough to direct search engines to the appropriate page, especially when dealing with complex localization or when the website’s structure doesn’t perfectly align with the suggestions.
- Dynamic content and localized pages: If a page’s content dynamically changes based on the user’s location, hreflang tags might not fully capture the nuances. For instance, a page with a specific product’s pricing based on location, or a page showing content based on user’s language.
- Significant discrepancies in content: If the content on different language versions is drastically different, the search engine might not understand the link and might not pick the suggested version.
- Complex URLs: URLs with numerous parameters can make it difficult for hreflang tags to effectively map to the appropriate localized pages.
Limitations of Relying Solely on Hreflang Tags
Search engines are intelligent and have their own mechanisms to assess the quality and relevance of pages. Hreflang tags are only one piece of the puzzle.
- Search engine algorithms: Search engines may prioritize pages based on factors other than hreflang tags, such as content quality, user engagement, and site structure. This means that even with correctly implemented hreflang tags, a poorly optimized page might not rank well.
- Crawl frequency: Search engines may not crawl all pages frequently enough for hreflang tags to be effectively utilized.
- Page availability: If the page suggested by the hreflang tag is unavailable or inaccessible, search engines may not be able to utilize the hint effectively.
When Search Engines Might Ignore Hreflang Tags
Search engines aren’t obligated to follow hreflang tags; they are guidelines. There are instances where they might choose to ignore them, particularly when the tags are implemented incorrectly or don’t align with the actual content of the website.
- Incorrect implementation: If the hreflang tags are not implemented correctly or contain errors, search engines might not interpret them properly.
- Inconsistency between tags and content: If the hreflang tags suggest a page for a specific language or location, but the actual content doesn’t match, search engines may disregard the tag.
- Poor site structure: If the site structure doesn’t align with the hreflang suggestions, search engines might not effectively follow the intended links.
Alternative Approaches When Hreflang Tags Prove Insufficient
When hreflang tags alone aren’t enough, a multi-pronged approach may be necessary.
- Canonicalization: Properly using canonical tags can ensure that search engines understand the primary version of a page.
- Content quality: High-quality content tailored to each language and region will increase relevance for users and improve search rankings.
- Site structure: A well-organized site structure makes it easier for search engines to understand the relationship between different versions of pages.
Hreflang as a Suggestion: Illustrative Table
This table demonstrates hreflang as a suggestion, showing how search engines use various factors to determine the best page for a user.
| User Location | Hreflang Tag Suggestion | Search Engine Considerations | Final Page Displayed |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States (English) | |
Content quality, user experience, site structure | https://example.com/en-US (if it meets search engine criteria) |
| United Kingdom (English) | |
Content quality, user experience, site structure | https://example.com/en-GB (if it meets search engine criteria) |
| France (French) | |
Content quality, user experience, site structure | https://example.com/fr (if it meets search engine criteria) |
Best Practices for Implementing Hreflang Tags

Hreflang tags are crucial for helping search engines understand the language and location-specific versions of your website. Proper implementation is essential for ensuring that users in different regions see the most relevant content and avoiding issues with duplicate content penalties. This section delves into best practices for setting up hreflang tags, including strategies for different locales, examples of appropriate usage, the importance of canonical tags, and common pitfalls.Implementing hreflang tags effectively is more than just slapping some code on your site.
It requires careful consideration of your target audience and their geographical location. You need to understand how your website’s content relates to various regions and languages, and how hreflang tags can facilitate this connection.
Setting Up Hreflang Tags for Different Locales
To effectively target various locales, your hreflang tags need to meticulously map your website’s content to specific regions and languages. This involves identifying the correct language codes and country codes. For instance, if you have a version of your site in Spanish for Spain, the hreflang tag should point to the Spanish version of the page. The language code should be “es” and the country code “es”.
Similarly, for a Spanish version targeted at Mexico, the code would be “es-MX”.
Examples of Hreflang Tag Usage Across Various Scenarios
Consider these examples demonstrating how hreflang tags work in different scenarios:
- English website with a Spanish version: If your English website (en) has a corresponding Spanish (es) version, you would use an hreflang tag for the Spanish version that links to the English page, making sure to use the correct country codes if applicable.
- Multi-country targeting: If your website targets users in the United States (en-US) and the United Kingdom (en-GB), you’d use separate hreflang tags to specify the correct version for each country. The crucial point here is to accurately match the target country and language code to the correct URL.
- Dynamic URLs: For dynamic content, the hreflang tags should be adapted to accurately reflect the language and region. For example, if a user navigates to a product page on your site, the hreflang tags for that specific page need to adapt accordingly.
Significance of Using Canonical Tags in Conjunction with Hreflang
Canonical tags play a vital role in guiding search engines. Using canonical tags in conjunction with hreflang tags ensures search engines understand the primary version of a page, especially when multiple language versions exist. They clarify the main version for indexing, helping prevent duplicate content issues.
Hreflang Implementation Pitfalls and Solutions
| Pitfall | Description | Example | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Language Codes | Using the wrong language codes (e.g., using “sp” instead of “es”). | `` | Ensure correct language codes are used, referencing ISO 639-1 and ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 standards. |
| Missing Canonical Tags | Omitting canonical tags for pages with multiple language versions. | No canonical tag on the page. | Include canonical tags to identify the preferred version for search engines. |
| Incorrect URL Structure | Using incorrect URL structures for different locales. | Using `/en` and `/es` for both static and dynamic content. | Maintain a consistent URL structure for different languages and regions. |
Hreflang Tag Validation Checklist
- Verify Language Codes: Double-check all language codes align with ISO standards (e.g., ISO 639-1). Consistency is key here.
- Validate URL Structure: Ensure URLs are consistent across all language versions.
- Canonical Tag Integration: Confirm canonical tags correctly identify the primary page version.
- Test Across Different Browsers: Evaluate how the hreflang tags function on various browsers.
- Regular Auditing: Periodically review your implementation to ensure it remains accurate and up-to-date.
Troubleshooting Hreflang Implementation
Troubleshooting hreflang implementation is crucial for ensuring accurate website rendering for different user locations. Incorrectly implemented hreflang tags can lead to wasted crawl budget, reduced rankings, and a poor user experience. This section details common issues, diagnostic steps, and solutions for effective hreflang tag management.Identifying and resolving hreflang implementation problems often requires a systematic approach. Careful analysis of the website’s structure, target audiences, and crawl data is necessary.
The goal is to pinpoint the root cause of the issue and apply the appropriate corrective measures.
Common Hreflang Implementation Errors
Common errors in hreflang implementation can stem from various factors, including incorrect tag syntax, missing or duplicated tags, incorrect language or country codes, or inconsistencies with the website’s structure. These errors can significantly impact search engine crawlers’ understanding of the site’s multilingual or multi-regional presence.
Diagnosing Hreflang Tag Issues
Diagnosing hreflang tag problems involves several key steps. First, meticulously examine the HTML source code of the affected pages for any discrepancies in the hreflang tags. Pay close attention to the syntax, target URLs, and language/country codes. Next, analyze the site’s crawl data using Google Search Console or similar tools to identify any issues with how search engines are indexing the pages.
Google’s recent reminder that hreflang tags are hints, not directives, is crucial for any digital marketer. Understanding this nuance is key to crafting effective strategies, especially when dealing with bots. A well-defined bot digital marketing strategy, like the one outlined in this detailed guide, bots digital marketing strategy , can help you ensure your site is presented correctly to search engine bots.
Ultimately, though, remember that hreflang tags are still essential for guiding search engine crawlers, and this crucial hint is a key component of a successful SEO strategy.
A thorough understanding of the website’s structure and content organization is vital in determining if the issue is systemic or localized to specific pages.
Common Errors and Solutions
Various errors can arise during hreflang implementation. Addressing these issues often involves a combination of code modification, structural adjustments, and thorough testing. Incorrect tag placement, missing attributes, and inconsistent usage across different pages are among the most common problems.
- Incorrect Tag Placement: Ensure hreflang tags are placed correctly within the ` ` section of the HTML document on the relevant pages. Incorrect placement can lead to search engines not recognizing the tags or misinterpreting their purpose.
- Missing or Duplicate Tags: Double-check that the necessary hreflang tags are present on all relevant pages. Duplicated or missing tags can confuse search engines, leading to indexing issues.
- Incorrect Language/Country Codes: Verify that the language and country codes in the hreflang tags accurately reflect the content’s target audience. Using incorrect codes can result in the wrong content being displayed for specific regions.
- Inconsistency with Website Structure: Ensure that the hreflang tags align with the website’s structure and content organization. Inconsistencies can lead to inaccurate content rendering for different user locations.
Example Troubleshooting Scenarios
Let’s consider a scenario where a website serves English content for the US and UK. If the hreflang tag for the UK page points to the US page, the search engine might incorrectly index the UK content as US content, leading to a poor user experience and potential ranking issues.
Troubleshooting Table
| Potential Error | Description | Diagnostic Steps | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Tag Placement | Hreflang tags not within the `` section | Inspect HTML source code for placement | Move tags to the `` section |
| Missing Tags | Required hreflang tags are absent | Verify presence of tags on all relevant pages | Add missing tags |
| Incorrect Language Codes | Language codes do not match the content | Compare language codes with content | Update codes to accurately reflect target audience |
| Inconsistency with Website Structure | Hreflang tags don’t align with site structure | Examine sitemap and content organization | Modify tags to reflect structure and content |
Alternative Approaches and Strategies
Hreflang tags, while powerful, aren’t the only path to international success. Understanding alternative strategies can significantly enhance your reach and allow for flexibility when dealing with multilingual content or regional variations. This section explores alternative approaches to achieving international goals without relying solely on hreflang.Alternative methods for international can be just as effective as using hreflang tags, particularly when specific nuances of content organization or website architecture are critical.
They offer unique advantages, particularly in situations where a complex multilingual structure or handling region-specific content is needed.
Content Segmentation and Localization
Effective multilingual content management doesn’t always necessitate hreflang. A well-structured approach to content segmentation and localization can yield similar results. This method involves creating distinct URLs for different language versions of the same content. Each version targets a specific audience, and the URL structure clearly indicates the language.
URL Parameters for Language Selection
Utilizing URL parameters for language selection offers a flexible way to manage multilingual content. For instance, appending a parameter like “?lang=fr” to a URL will display the French version of the page. This method is particularly useful for websites with a substantial amount of content and when you want to avoid creating a separate URL for each language variation.
It allows users to easily switch between languages without needing to navigate to a new page. This method is also more dynamic than statically creating separate URLs.
Subdirectories for Language-Specific Content
Organizing content by subdirectories for different languages can be an efficient method. A website could use a structure like `example.com/en/` for English content and `example.com/fr/` for French content. This approach is straightforward and can be readily integrated into existing website architectures. It’s crucial for clarity and user experience.
Website Design with Multiple Domains
Employing separate domains for different language versions is another strategy. For instance, a German-language site might be hosted at `de.example.com`. This approach, though technically distinct from hreflang, offers the benefit of a dedicated domain for each language, improving regional search engine rankings. However, it’s more complex and costly than other methods.
Multilingual Content Creation Strategies
Content creation for specific regions without hreflang tags involves tailoring content to local preferences, cultural nuances, and search engine algorithms. This includes using culturally relevant s, phrases, and imagery that resonate with the target audience. It is a crucial aspect of effective multilingual content.
Example Website Structure (without hreflang)
| URL | Content | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| example.com/en/products | English product descriptions | English-speaking customers |
| example.com/es/productos | Spanish product descriptions | Spanish-speaking customers |
| example.com/fr/produits | French product descriptions | French-speaking customers |
This example demonstrates a structure where each language has a dedicated subdirectory. This structure improves by allowing search engines to understand the language of the content easily. It promotes a more localized experience for users.
Limitations and Advantages of Alternative Approaches
Alternative approaches to hreflang have limitations and advantages. While methods like URL parameters or subdirectories are often simpler to implement, they may not be as comprehensive as hreflang tags for complex multilingual setups. However, these methods can be more effective for simpler situations and offer more flexibility for dynamically adjusting content.
Illustrative Examples
Now that we’ve explored the theoretical underpinnings of hreflang tags and their crucial role in international , let’s delve into practical examples. These examples will demonstrate how hreflang tags are implemented, highlighting both successful strategies and common pitfalls to avoid. Understanding how to apply hreflang correctly is vital for reaching global audiences and optimizing your website for diverse search queries.
Hypothetical Website with International Content
Imagine a clothing retailer, “Global Threads,” with a presence in the US, UK, and Germany. Their website (globalthreads.com) offers identical product listings but in different languages (English, German, and British English) and with prices adjusted for each region. The key here is that the content is largely the same, but the presentation and pricing need to be region-specific.
Setting up Hreflang Tags for Global Threads
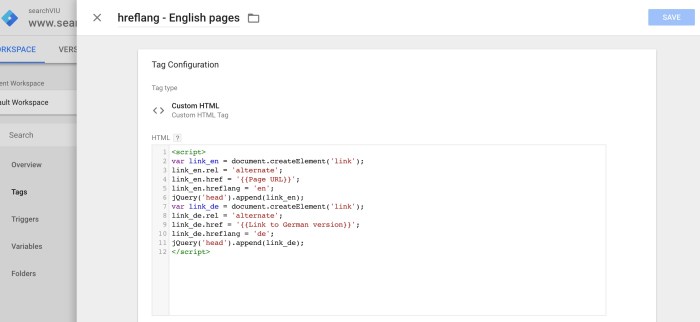
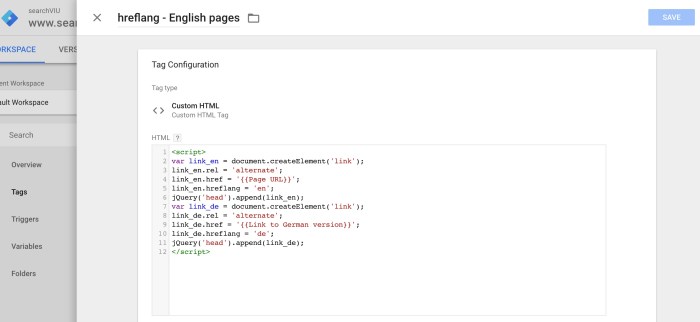
To ensure proper hreflang implementation, Global Threads would include the following tags in the HTML header of each page:
- For the English (US) page (e.g., globalthreads.com/product-A):
<link rel="alternate" href="https://globalthreads.com/product-A" hreflang="en-US">This tag specifies the English (US) version of the page.
- For the German page (e.g., globalthreads.com/de/product-A):
<link rel="alternate" href="https://globalthreads.com/de/product-A" hreflang="de-DE">This tag specifies the German version of the page.
- For the British English page (e.g., globalthreads.com/uk/product-A):
<link rel="alternate" href="https://globalthreads.com/uk/product-A" hreflang="en-GB">This tag specifies the British English version of the page.
These tags would need to be implemented for every page that has a translated or region-specific version. Crucially, each language-specific page would also need its own set of hreflang tags linking back to the original English (US) page.
Alternative Approach: Effective Multilingual Website without Hreflang Tags
Global Threads could use a robust multilingual CMS or platform. This approach allows them to have separate URLs for different languages without the need for explicit hreflang tags. For example, they might use a subdirectory structure (e.g., globalthreads.com/de/ for German). In this case, the CMS would handle the routing and presentation of content in the correct language for each user’s location.
This would effectively serve as a fallback for users who are not specifically targeting the relevant language-specific URL. The CMS’s sophisticated routing can handle the localization without the direct use of hreflang tags.
Google’s reminder that hreflang tags are hints, not directives, is crucial for SEO. Understanding how these tags work is vital for effective cross-channel personalization, like strategies discussed in this insightful piece on cross channel personalization what works now across generations and channels. Ultimately, remembering that hreflang tags are suggestions, not mandates, allows for a more nuanced and effective approach to optimizing content delivery across various platforms and audiences.
Summary Table: Hreflang Scenarios and Solutions
| Scenario | Website Structure | Hreflang Implementation | Alternative Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identical product pages, different languages/regions | Separate URLs for each language/region | Include hreflang tags linking to each version | Multilingual CMS with appropriate URL structure |
| Different product pages, different languages/regions | Separate URLs for each language/region | Include hreflang tags linking to each version | Multilingual CMS with separate product pages for each region |
| Large e-commerce site with many product variations | Complex URL structure | Utilize a structured approach for hreflang implementation, mapping all versions | Employ a sophisticated multilingual platform to handle routing and localization |
| Dynamically generated content | URLs are generated on the fly | Use server-side directives to dynamically generate hreflang tags based on user location or language preference | Employ a robust multilingual platform with dynamic content support |
Technical Considerations for Hreflang
Hreflang tags, while powerful for international , require careful technical implementation. Proper server configuration and URL structure are crucial for ensuring that search engines and users receive accurate information about the available language and regional variations of your website. This section delves into the technical aspects of implementing hreflang, including server configuration, URL structure, and potential challenges.Server configuration plays a pivotal role in effectively communicating hreflang information to search engines.
The server needs to correctly identify the appropriate language or region for each URL and return the relevant hreflang tags within the HTTP headers. This involves careful consideration of the server-side logic and the way URLs are handled. Misconfigurations can lead to duplicate content issues and wasted crawl budget.
Server-Side Configuration, Google reminds that hreflang tags are hints not directives
Accurate URL structures are paramount for the success of hreflang implementation. The structure of URLs should be consistent and predictable across different language and regional versions of the site. This consistency allows search engines to correctly associate URLs and understand the relationships between different versions of the site. Avoid inconsistent or ambiguous URL structures.
- URL Structure Consistency: Employ a consistent structure for URLs representing different language or regional variations of your website. Using clear, descriptive naming conventions for these variations can aid in accurate identification by search engines and users. Avoid using parameters that are not relevant to the site content. For instance, use “/en” or “/fr” in the URL for English and French versions instead of a query parameter like “?lang=en”.
- Using HTTP Headers: The server should return hreflang tags within the HTTP headers of each page. This direct communication is vital for search engines to process the information correctly. The correct HTTP headers need to be added to the server response for each page, indicating the language or region targeted by the URL.
- Implementing Redirects: For cases where users navigate to a non-canonical URL, redirects play a crucial role in guiding users to the correct canonical page. Implementing 301 redirects for non-canonical URLs helps maintain user experience and preserve value.
Accurate URL Structures
URLs are the fundamental building blocks of your website’s structure. Their accuracy and clarity directly impact how search engines understand your site’s content. Well-structured URLs enable search engines to easily discern the intended language and region, and consequently provide accurate results to users.
- Descriptive URLs: Use descriptive and relevant s in your URLs to aid search engines in understanding the content of each page. For instance, using “/en/products/shoes” for English shoe products rather than a complex, non-descriptive URL is more effective.
- Consistency in URL Parameters: Ensure consistency in URL parameters across different language or regional versions of the site. For instance, if the site uses a query parameter for language selection, ensure that the parameter is consistently used across all pages and variations.
- Avoid Unnecessary Parameters: Remove or minimize unnecessary parameters from your URLs, as these can add complexity for search engines and can confuse users. The use of query parameters like ‘?lang=en’ should be minimized.
Common Technical Challenges
Several technical challenges can hinder the successful implementation of hreflang tags. These range from server-side configurations to ensuring correct URL structures. Understanding these challenges is crucial for implementing a robust and effective hreflang strategy.
- Incorrect HTTP Headers: One of the common problems is the incorrect implementation of HTTP headers. Failure to include or format the hreflang tags correctly within the HTTP headers can result in the search engines not understanding the intended language or region for a page.
- Implementation Errors: Implementation errors can lead to unexpected results. These errors can range from missing hreflang tags to incorrect usage. Carefully review the implementation process to avoid these errors.
- Maintaining Consistency: Maintaining consistency across all URLs and pages is critical. Inconsistent hreflang implementation across different pages can confuse search engines and harm your website’s performance.
Examples of Server Configurations
| Server Configuration Type | Configuration Example | Description | Technical Considerations ||—|—|—|—|| Apache | `
`RewriteCond %HTTP:Accept-Language ^en-US.*$`
`RewriteRule ^/products$ /en/products [L,R=301]`
`return 301 /en/products;`
“ | Similar to Apache, redirecting based on Accept-Language header.
| Needs Nginx configuration and correct language matching. || Custom Server | Custom PHP code to determine the appropriate language based on user location or browser preferences. | More flexible and adaptable, allows custom logic. | Requires PHP or similar scripting knowledge and careful implementation. || Cloud Platform (e.g., AWS, GCP) | Use the platform’s load balancing and routing capabilities to implement hreflang redirects.
| Efficient and scalable solution, leverages the platform’s infrastructure. | Requires understanding of the platform’s configuration and routing mechanisms. |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, while hreflang tags are valuable tools for international , they are hints, not commands. Understanding their limitations and exploring alternative approaches is critical for effective multilingual website management. This article provides a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the complexities of hreflang implementation, ensuring optimal performance and user experience. Remember, a well-structured strategy often involves a combination of techniques to best serve your audience.