Google nofollow link attributes are crucial for . Understanding how these attributes work and how Google interprets them is vital for maintaining a healthy website. This exploration dives into the nuances of the nofollow attribute, from its historical context to its practical applications and potential impact.
This in-depth guide covers everything from the fundamental definition of the nofollow attribute to its intricate relationship with other ranking factors. We’ll also look at best practices, common errors, and troubleshooting techniques to ensure you’re using nofollow effectively.
Understanding the ‘nofollow’ attribute
The ‘nofollow’ attribute in HTML is a crucial element for search engine optimization () and maintaining the integrity of online content. It signals to search engines that a hyperlink should not pass along PageRank, effectively preventing the link from influencing the search engine ranking of the linked page. This attribute has evolved over time, adapting to the changing landscape of the web and the increasing sophistication of search engine algorithms.The ‘nofollow’ attribute’s core function is to indicate to search engines that a website owner doesn’t endorse the linked page.
This can be useful in a variety of situations, from preventing spam to managing the quality of links on a website.
Historical Context and Evolution
The ‘nofollow’ attribute emerged as a response to the growing problem of spam and manipulative link building practices. Early search engines relied heavily on link popularity as a ranking factor. This made websites vulnerable to manipulation, as spammers could create artificial links to boost their rankings. The introduction of the ‘nofollow’ attribute provided a mechanism to counteract these issues.
Various Ways the ‘nofollow’ Attribute is Used
The ‘nofollow’ attribute is employed in numerous ways to control the flow of link equity in the web. It’s used to prevent the passing of PageRank to potentially undesirable or inappropriate links. This is often seen in links from user-generated content, such as comments, forum posts, and social media, where the site owner cannot always control the quality or intent of the links.
Syntax for Implementing the ‘nofollow’ Attribute
The ‘nofollow’ attribute is implemented by adding the attribute to the tag. The most common syntax is:
<a href="http://example.com" rel="nofollow">Link Text</a>
The `rel=”nofollow”` attribute is placed directly within the opening ` ` tag, following the `href` attribute. This simple addition effectively communicates to search engines that the link should not be considered for ranking purposes. Variations are possible but this is the standard.
Different Usage Contexts
The ‘nofollow’ attribute is valuable in various contexts.
- Links from Comments: Many blogs and forums use comments sections to allow users to engage with the content. The ‘nofollow’ attribute is frequently used on links within comments to prevent spammy links from influencing the site’s ranking.
- Social Media Links: When sharing links from social media platforms, such as Twitter or Facebook, the ‘nofollow’ attribute can be employed. This is particularly important when dealing with links from users or external sources that the website owner doesn’t directly control.
- Forum Posts: In online forums, user-generated content frequently includes links. Applying the ‘nofollow’ attribute to these links can be beneficial in preventing ranking issues.
- Sponsored Content: When displaying sponsored links or advertising content, the ‘nofollow’ attribute helps clearly delineate between organic and paid links, ensuring accurate representation in search engine results.
The ‘nofollow’ attribute is a vital tool for maintaining the integrity of website content and managing the flow of link equity on the web. Its application ensures a more accurate reflection of website popularity and helps prevent the spread of spam.
Google’s Interpretation and Enforcement
Google’s interpretation of the nofollow attribute is crucial for understanding how search engines like Google process links. It signals to Google that the link should not be considered a vote of endorsement or trust for the linked page. This is a fundamental aspect of link building and website optimization.
Google’s nofollow link attributes are crucial for SEO, but frankly, focusing too much on landing pages might be a wasted effort. Many marketers get caught up in optimizing these pages, often to the detriment of a broader strategy. In fact, the whole concept of landing pages as a primary focus is arguably a bit outdated, as explored in this insightful article about landing pages being overrated.
Ultimately, the best use of nofollow links is in directing traffic to high-quality content that truly engages your audience, not just to a page designed to convert.
Google doesn’t automatically ignore nofollow links. Instead, it acknowledges their intent. These links are not used to boost the ranking of the linked page, but Google might still consider them in other ways. This understanding is vital for building a healthy and trustworthy online ecosystem.
Understanding Google’s nofollow link attributes is crucial for SEO, especially when linking to other websites. When building a landing page, remember that strategically placed links, like those from authoritative resources, can help improve your page’s ranking. A well-structured landing page, such as the one described in this guide on how to build a landing page , will benefit from careful consideration of nofollow links, ensuring that you don’t dilute your site’s authority by linking to low-quality or spammy sites.
Google’s Understanding of the ‘nofollow’ Attribute
Google interprets the nofollow attribute as a signal that the link should not influence the PageRank of the linked page. This means Google won’t consider the link as a vote of endorsement. The intent is clear: the linking page doesn’t endorse the linked page’s content or authority. This allows website owners to control the influence of their links.
Factors Google Considers
Google assesses several factors when evaluating links with the nofollow attribute, but the primary concern is the link’s purpose. These factors include:
- Link Context: The surrounding text and content of the linking page are significant. If the link is embedded in spammy or manipulative content, Google will likely treat it with less weight, regardless of the nofollow tag.
- Linking Page Quality: The overall authority and reputation of the linking page play a role. A high-quality, reputable page carries more weight in Google’s eyes.
- Link Purpose: Google attempts to discern whether the nofollow attribute is legitimately used to prevent ranking manipulation or if it’s used to circumvent search engine rules.
How Google Handles ‘nofollow’ Links in its Algorithm
Google’s algorithm doesn’t ignore nofollow links entirely. Instead, these links might be used for other purposes within the algorithm. These purposes might include:
- Understanding Link Networks: Google uses the information from nofollow links to understand the overall link network and the relationships between websites.
- Content Understanding: Google might consider nofollow links for understanding the context and topic of the linking page, which can be helpful for determining relevance.
- Spam Detection: In cases of potentially manipulative link building, nofollow links can help Google identify and penalize those practices.
Potential Impact on Website Ranking
Using the nofollow attribute doesn’t guarantee a positive or negative impact on website ranking. It simply indicates that a link shouldn’t be considered a direct vote of endorsement. There are situations where the impact is significant, and others where the impact is minimal.
- Beneficial Scenarios: Using nofollow for links to affiliate products or third-party content allows you to promote these without directly influencing their rankings. This maintains your site’s integrity. You can also use it for forum discussions or comments where you don’t endorse the specific content linked.
- Detrimental Scenarios: Overusing nofollow can sometimes reduce the overall signal of authority from external sources to your site. If links are being nofollowed when they should not be, then this might signal to Google a lack of genuine value in the content.
Examples of ‘nofollow’ Usage
The proper use of nofollow is crucial for ethical practices. Using it for the right reasons and in the right situations maintains the integrity of search results. Examples of beneficial usage include:
- External links to competitor websites: Providing information or context about the competition without endorsing them.
- Links to third-party resources: Referencing external information that is relevant to your content but not affiliated with your site.
- Forum comments or social media posts: Sharing links within a forum or social media context where you don’t endorse the linked content.
Practical Applications and Best Practices: Google Nofollow Link Attributes
The ‘nofollow’ attribute, while straightforward in its implementation, plays a crucial role in website management and . Understanding its proper application is key to maintaining a healthy website and avoiding penalties. This section delves into specific scenarios, comparing its use with other link attributes, and showcasing best practices.
Applying the ‘nofollow’ attribute is not just about avoiding spam; it’s about ensuring your site’s integrity and maintaining a positive relationship with search engines. This approach also helps manage the spread of potentially harmful links, promoting a healthier online environment.
Scenarios for Using the ‘nofollow’ Attribute
Using the ‘nofollow’ attribute is not always about avoiding backlinks; sometimes, it’s about controlling the impact of links on your site’s ranking. Here’s a breakdown of common scenarios:
| Scenario | Justification | HTML Implementation | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guest posts on low-quality or spammy blogs | Preventing your site’s association with potentially harmful content. | Link to low-quality blog | Reduces the likelihood of your site being penalized for links from low-quality sources. |
| Comments on forums or blogs where spam is prevalent | Avoiding the transfer of ranking signals to spammy comments. | Link to spammy forum comment | Helps maintain a positive profile by separating your site from potentially harmful links. |
| Affiliate links where commission is not the primary goal | Acknowledging the link’s commercial nature without impacting rankings. | Link to affiliate site | Allows users to click the link without affecting your site’s performance. |
| Links to articles or pages that aren’t related to your content | Maintaining a strong, thematic connection between your site and the pages you link to. | Link to irrelevant page | Keeps your site’s focus on a particular topic and avoids unnatural links. |
Comparison with Other Link Attributes
Understanding how ‘nofollow’ compares to other link attributes helps you choose the right approach for each situation.
| Attribute | Purpose | Implementation | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
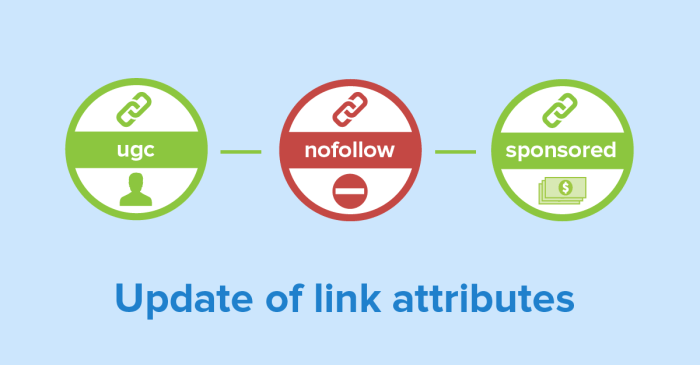
| rel=”nofollow” | Signals to search engines not to follow a link. | Link | Reduces or eliminates the impact of the link on the site’s ranking. |
| rel=”sponsored” | Indicates a link is sponsored or paid for. | Link | Provides transparency to users about the commercial nature of the link. |
| rel=”ugc” | Identifies the link as a user-generated content link. | Link | Indicates to search engines that the link’s value may be less influential. |
Effective Use Cases
Several websites successfully utilize the ‘nofollow’ attribute. For example, reputable news sites often use it for links to comment sections, ensuring that the comments themselves don’t negatively impact their . Similarly, blogs use it on guest posts or affiliate links where they are not necessarily endorsing the content.
Proper Use in Different Contexts
Implementing ‘nofollow’ correctly is crucial for different types of content. In comment sections, using ‘nofollow’ for user-generated content ensures that comments don’t artificially inflate the site’s link profile. In forum posts, if a link is not directly related to the discussion, ‘nofollow’ is a best practice. For affiliate links, using ‘nofollow’ is essential to avoid the risk of penalties while still allowing users to access the linked content.
Potential Implications of Misuse
Misusing or overusing the ‘nofollow’ attribute can have unintended consequences. Overusing it can lead to a decrease in link diversity, which can affect your site’s search ranking. Conversely, failing to use it appropriately when needed can expose your site to potential penalties. Careful consideration of each link is vital for maintaining a positive profile.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
The “nofollow” attribute, while seemingly straightforward, interacts with other search ranking factors and HTML elements in complex ways. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective and avoiding unintended consequences. This section delves into advanced techniques and considerations surrounding the proper application of the “nofollow” attribute.
Effective strategies often involve a nuanced approach, and the “nofollow” attribute is no exception. Applying it correctly requires an understanding of its relationship with other search ranking factors, its interaction with HTML, and the importance of context.
Relationship with Other Ranking Factors
The “nofollow” attribute doesn’t directly affect search engine rankings of the page containing the link. However, its impact can be indirect. A large number of “nofollow” links pointing to a page could potentially signal a lack of authoritative endorsements, potentially influencing rankings. Similarly, the absence of “nofollow” attributes on links can indicate trust and quality, potentially contributing positively to ranking.
Google considers a multitude of factors when assessing page quality, and “nofollow” is just one element in that complex equation.
Interaction with Other HTML Elements
The “nofollow” attribute primarily affects the link element ( ). Its impact is limited to the specific link being marked, and doesn’t influence other elements on the page. For example, the “nofollow” attribute won’t affect the page’s content, title, or meta descriptions. Its function is strictly confined to the link itself. Careful consideration of surrounding elements is still important.
Identifying Links Requiring “nofollow”
Determining which links should be marked with “nofollow” requires careful evaluation of the source and context. Links from spammy or low-quality websites should generally be marked. Guest posts from dubious sources are a prime example. Self-promotional links from your own domain should be considered, as should links to pages that aren’t aligned with the overall content strategy.
A useful method is to analyze the referring page’s content, checking for signs of spam, manipulation, or questionable authority.
Contextual Considerations
The appropriate use of “nofollow” is highly contextual. For example, a link to a news article reporting on your company might be a valuable reference, while a link to a promotional blog post on your product might warrant a “nofollow” attribute. Contextually, links to user-generated content, such as comments or forum posts, often benefit from the “nofollow” attribute.
The aim is to differentiate between endorsements and mere citations.
Comparison of Approaches to Problematic Links, Google nofollow link attributes
Dealing with problematic links requires a nuanced approach. One approach is to disavow spammy links, which can sometimes help mitigate the negative impact on rankings. Another approach involves using the “nofollow” attribute to manage problematic links from the source. Choosing the appropriate method requires evaluating the nature of the problematic link and its potential impact. Sometimes, the best solution is to simply remove the link entirely.
A comprehensive approach considers the nature and source of the problematic link and the overall context of the page.
Impact on

The ‘nofollow’ attribute, while seemingly innocuous, can significantly impact a website’s search engine optimization () efforts. Its effect isn’t always straightforward, and understanding its influence on traffic, rankings, and potential manipulation is crucial for any website owner or professional.
Google’s nofollow link attributes are crucial for SEO, preventing link juice from flowing to sites you don’t want to endorse. But when evaluating AI-generated content versus human-written content, AI vs human content becomes a key factor. High-quality, human-written content often carries more weight and authority, which can indirectly influence how Google views those links. Therefore, careful consideration of the nofollow attribute is paramount when dealing with potentially less valuable content sources.
Implementing ‘nofollow’ attributes strategically can prevent unwanted consequences. However, a careless or unethical application can harm a website’s visibility and reputation. Knowing how to use it properly and avoid its misuse is essential for sustainable and ethical practices.
Impact on Website Traffic
The ‘nofollow’ attribute directly impacts website traffic by reducing the perceived authority a website gains from inbound links. Links marked as ‘nofollow’ do not pass link equity, a crucial element in Google’s ranking algorithm. This reduced influence can result in lower referral traffic from sites that link to a website with ‘nofollow’ tags, as search engines interpret this as a weaker signal of the linked page’s importance.
Correlation with Search Engine Ranking
A strong correlation exists between the presence of ‘nofollow’ attributes and a website’s search engine ranking. While ‘nofollow’ links do not directly contribute to a website’s ranking, their excessive use can indicate a lack of quality inbound links. A website relying heavily on ‘nofollow’ links might appear less trustworthy and relevant to search engines, potentially hindering its ranking in search results.
Potential for Manipulating Search Results
The ‘nofollow’ attribute, if misused, can potentially contribute to search result manipulation. A website could engage in link schemes, where they generate a large number of ‘nofollow’ links from irrelevant or low-quality sites. While these links won’t directly boost the target website’s ranking, they might artificially inflate the appearance of authority, misleading search engine algorithms and potentially harming other legitimate websites.
Consequences of Unethical Link-Building Practices
Unethical link-building practices involving ‘nofollow’ attributes can lead to severe consequences. Search engines can penalize websites engaging in such practices, leading to a significant drop in search engine rankings. This can result in a loss of organic traffic and negatively impact the website’s overall online visibility. Further, such practices can damage the website’s reputation and erode trust with users.
Alternative Methods for Desired Outcomes
To achieve positive outcomes without resorting to unethical practices, focusing on high-quality content and building natural, relevant backlinks is crucial. Creating valuable content that attracts natural links from reputable websites is a sustainable approach. Promoting content through social media, outreach to relevant influencers, and participating in industry forums can also generate valuable backlinks without employing manipulative techniques.
Developing a strong, trustworthy online presence through consistent content creation and engaging with the community is a more ethical and long-term strategy for improving search engine rankings.
Troubleshooting and Error Handling
Navigating the complexities of can be challenging, and the ‘nofollow’ attribute, while seemingly straightforward, can present unexpected hurdles. Understanding how to troubleshoot potential issues is crucial for maintaining a healthy website structure and avoiding penalties. This section delves into common pitfalls, misconceptions, and effective debugging strategies to help you master the implementation of this attribute.
Common Errors in Using the ‘nofollow’ Attribute
A thorough understanding of potential errors is essential for effective troubleshooting. Incorrect implementation can lead to unintended consequences and impact your website’s search visibility.
| Error | Description | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Syntax | The ‘nofollow’ attribute is not applied correctly within the HTML tag. | Incorrect use of the attribute, such as missing quotes or incorrect placement within the HTML structure. | Ensure the attribute is applied correctly to the link tag () using the format: `Link Text`. Double-check the syntax and the surrounding HTML elements. |
| Incorrect Placement of ‘rel=”nofollow”‘ | The ‘nofollow’ attribute is applied in the wrong location within the HTML structure, or not applied to the appropriate link element. | Applying the attribute to the wrong element, or failing to apply it to the relevant link element (such as a hyperlink or anchor). | Verify that the ‘rel=”nofollow”‘ attribute is applied directly to the anchor tag () containing the link. Avoid applying it to the parent element. |
| Missing ‘nofollow’ attribute | The ‘nofollow’ attribute is absent from the link element, making the link potentially susceptible to ranking issues. | Oversight during implementation or the absence of explicit instructions to use the ‘nofollow’ attribute. | Carefully review the link’s HTML structure to ensure the ‘rel=”nofollow”‘ attribute is present. |
| Incorrect use of multiple rel attributes | Multiple conflicting ‘rel’ attributes are used on the same link element. | Multiple ‘rel’ attributes applied to the link, such as applying `rel=”nofollow”`, `rel=”sponsored”`, and `rel=”noopener”` together. | Ensure only one `rel` attribute is used for the link element. Use `rel=”nofollow”` for links where you want Google to ignore the link for ranking purposes. |
Common Misconceptions about the ‘nofollow’ Attribute
Addressing common misconceptions is crucial for implementing the ‘nofollow’ attribute correctly. These misconceptions often lead to confusion and potential issues in your strategy.
- Misconception: ‘nofollow’ prevents link juice transfer entirely. Reality: ‘nofollow’ prevents Google from considering the link for ranking purposes, but it does not entirely prevent the link from affecting the page’s visibility in other ways. There might be some indirect impact.
- Misconception: Using ‘nofollow’ is a guaranteed way to avoid penalties. Reality: While using ‘nofollow’ appropriately helps avoid certain issues, spammy links or malicious practices may still attract penalties. It is just one element in a larger strategy.
- Misconception: ‘nofollow’ is a universally accepted signal for all search engines. Reality: While widely adopted by Google, other search engines may not necessarily interpret ‘nofollow’ in the same way. It’s not a universal standard across all search engines.
Debugging ‘nofollow’ Link Issues
Effective debugging requires a systematic approach. Identify the source of the problem and implement appropriate solutions.
- Inspect the HTML: Use developer tools to thoroughly inspect the HTML structure of the problematic links. Verify the presence and correct syntax of the ‘nofollow’ attribute. Check for any potential conflicting attributes.
- Check for Broken Links: Ensure that the links themselves are functional and point to the correct destinations. Broken links can be a source of errors.
- Utilize Audits: Use specialized tools or conduct manual audits to pinpoint specific areas where the ‘nofollow’ attribute may be incorrectly implemented. Look for inconsistencies and missing attributes.
Validating HTML Implementation
Ensuring the correct HTML implementation of the ‘nofollow’ attribute is essential for preventing issues. Using a validator tool is a crucial step in maintaining a healthy website structure.
Auditing Websites for ‘nofollow’ Issues
Systematic auditing helps prevent issues related to the ‘nofollow’ attribute. A structured approach can uncover potential problems before they impact your .
- Comprehensive Link Analysis: Identify all links on your website, and review them for the presence and correct application of the ‘nofollow’ attribute.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly audit your website to catch and fix any issues that might arise.
- Automated Tools: Use specialized tools for automated link audits to identify and resolve ‘nofollow’ attribute errors across your website.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, mastering Google’s nofollow link attributes is a key element in building a successful online presence. By understanding the nuances and best practices Artikeld in this guide, you can avoid pitfalls and optimize your website for search engines. Proper implementation of nofollow is not just about avoiding penalties; it’s about ensuring your links contribute positively to your overall strategy.