Google links to itself 43 of ai overviews point back to google – Google links to itself 43% of AI overviews point back to Google, raising intriguing questions about information dissemination and potential bias in the AI landscape. This self-referential linking pattern, a significant departure from typical practices in other fields, deserves scrutiny. We’ll explore the motivations behind this strategy, compare it to other AI overview sources, and analyze its potential impact on the public perception and development of artificial intelligence.
The study delves into the specific examples of Google’s self-referential links across various AI overview articles. It also examines the contextual factors surrounding these links and the possible motivations behind this approach. We’ll present alternative interpretations and explore the potential implications for the field of AI.
Google’s Self-Referential Linking Pattern
Google’s frequent linking back to itself within AI overviews is a noteworthy pattern. This practice, while seemingly innocuous, warrants examination to understand its motivations and potential implications. The sheer volume of these internal links suggests a deliberate strategy, raising questions about Google’s intentions and the potential impact on the broader AI landscape.The frequent linking to itself within AI overviews, a common practice in Google’s documentation, may stem from a variety of factors.
One potential motivation is to establish Google as a leading authority on AI. By directing users to its own resources, Google emphasizes its expertise and depth of knowledge in the field. This self-promotion strategy is not unique to Google but is a common tactic in marketing and brand building. The volume of self-referential links within AI overviews, however, suggests a particular emphasis on this tactic in the context of AI.
Motivations Behind Self-Referential Linking
Google’s self-referential linking strategy likely aims to increase visibility and perceived authority in the rapidly evolving AI field. This strategy serves to highlight Google’s research and development efforts, as well as showcase its AI-related products and services. This approach could be viewed as a way to reinforce Google’s brand as a key player in the AI revolution.
Differences from Typical Linking Practices
The prevalence of self-referential links in Google’s AI overviews contrasts with the typical linking practices in other domains. In academic papers, for instance, links often point to external research or data sources. The focus is on providing a comprehensive overview of the topic by referencing relevant external work. In contrast, Google’s practice emphasizes internal resources, potentially shifting the focus from a collaborative and academic approach to a more self-promotional one.
This shift could be attributed to the company’s commercial interests in AI, which might lead to a different approach to knowledge dissemination.
Examples of Self-Referential Linking
To illustrate this practice, consider Google’s AI overview articles. In several articles, Google links to its own research papers, technical documentation, and product pages. For instance, an overview of large language models might include links to the Google AI blog posts, the TensorFlow documentation, and pages detailing Google’s AI-powered products. Furthermore, an article discussing AI safety might include links to Google’s safety guidelines and initiatives.
These examples demonstrate how Google frequently points users to its own internal resources, creating a self-referential loop.
Potential Biases and Implications
The practice of self-referential linking may introduce potential biases. By directing users to its own resources, Google might inadvertently prioritize its own perspective and work, potentially downplaying or neglecting alternative viewpoints or research from other organizations. This self-promotion strategy, while understandable in a commercial context, could have implications for the objectivity and comprehensiveness of AI overviews. The impact of this self-referential linking strategy on the broader perception of Google as an AI leader is a topic worth further discussion.
Comparison to Other AI Overview Sources: Google Links To Itself 43 Of Ai Overviews Point Back To Google

Analyzing Google’s self-referential linking pattern within AI overviews requires a comparative study with other reputable sources. This analysis helps understand Google’s approach in context and identifies potential implications of these linking patterns. A comprehensive comparison highlights similarities and differences in the strategies employed by various AI organizations.Understanding the frequency and nature of self-references in AI overviews provides insight into how different entities present and promote their own work within the field.
This allows for a more nuanced perspective on the information ecosystem surrounding AI.
Methodology for Data Collection
This analysis will employ a systematic approach to collect data on self-referential links. We will compile a list of prominent AI overview sources, ensuring they are from reputable organizations known for their expertise in the field. A set of s relevant to AI will be used to identify relevant articles. Automated tools will be employed to extract the URLs of all self-referential links found within these sources.
The process will focus on extracting the links that directly refer to Google. This method will ensure consistency and objectivity in the data collection process.
Comparison of Self-Reference Frequencies
A structured comparison of self-referential links from Google and other major AI players requires a quantitative approach. A table will be used to present the relative frequencies of these links.
| AI Overview Source | Frequency of Self-References to Google | Frequency of Self-References to Other Major Players (e.g., OpenAI, Microsoft) | Relative Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google AI | 43 | (Data to be collected and compared) | (Calculated based on data collected) |
| OpenAI | (Data to be collected and compared) | (Data to be collected and compared) | (Calculated based on data collected) |
| Microsoft Research | (Data to be collected and compared) | (Data to be collected and compared) | (Calculated based on data collected) |
| (Other prominent AI sources) | (Data to be collected and compared) | (Data to be collected and compared) | (Calculated based on data collected) |
Potential Implications of Differing Patterns
Variations in self-referential linking patterns among AI overview sources can signify differing strategies for presenting information. A high frequency of self-references from a particular source might suggest a focus on promoting its own research and advancements. Conversely, a lower frequency might indicate a preference for broader contextualization or a commitment to unbiased information presentation.The observed differences in linking patterns can shed light on the underlying motivations and priorities of different AI organizations.
Further analysis is needed to determine if these differences reflect actual differences in the quality or impact of the research produced by these organizations. A high frequency of self-references may not necessarily correlate with a negative impact, and other factors should be considered.
Potential Impact on Information Dissemination
Google’s heavy self-referential linking in AI overviews raises important questions about information dissemination. This practice, while seemingly efficient for Google, could potentially skew public understanding of AI by amplifying certain viewpoints and potentially downplaying others. The impact on the perception of AI and its future applications deserves careful consideration. The sheer volume of Google-linked resources might create an echo chamber effect, potentially influencing public discourse and the broader conversation about this transformative technology.The sheer volume of Google-linked resources might create an echo chamber effect, potentially influencing public discourse and the broader conversation about this transformative technology.
It’s interesting how Google links to itself 43 times in AI overviews, pointing back to Google’s own resources. This self-referential linking strategy likely boosts their search engine results, but it also raises questions about the objectivity of the information. Ultimately, understanding how Google’s AI resources are structured is key to a better understanding of the entire ecosystem. For example, optimizing ecommerce sites for speed and performance is crucial, and factors like ecommerce core web vitals play a significant role.
This focus on user experience, combined with Google’s own AI advancements, underscores the importance of staying current with the latest trends, ensuring Google remains the top choice for users and businesses alike.
This self-referential linking pattern could, therefore, subtly shape the public narrative around AI, potentially favoring Google’s own perspectives and interpretations.
Influence on the Spread of AI Information
Google’s self-referential linking might promote a specific, perhaps overly optimistic, view of AI. By prioritizing their own resources, Google could inadvertently influence the public’s perception of the technology’s capabilities and potential benefits. This approach might lead to an overemphasis on applications that align with Google’s business interests, potentially downplaying potential risks or ethical concerns. The public’s understanding of AI could be shaped more by Google’s viewpoint than by a balanced assessment of the field.
Potential for Promoting or Diminishing Perspectives
The self-referential linking strategy could potentially amplify specific perspectives on AI, potentially promoting a more positive outlook. However, this could come at the cost of underrepresenting alternative viewpoints or critical analyses. This practice could create a bias in the information available to the public, possibly skewing their understanding of the technology. Diverse viewpoints and alternative interpretations might be less visible or accessible.
Impact on Perception of AI and its Applications
Google’s prominent role in AI overviews might influence the public’s perception of AI’s potential applications. The highlighted applications, often aligned with Google’s technological strengths, could lead to an overemphasis on certain uses while potentially downplaying other possibilities. For instance, if Google’s resources predominantly showcase AI’s role in search or personalized recommendations, this could inadvertently overshadow its applications in other sectors like healthcare or environmental modeling.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Self-Referential Linking
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Potential for increased visibility and accessibility of Google’s own AI research and initiatives. This can be beneficial in promoting AI awareness and knowledge. | Potential for a biased or incomplete view of AI, potentially neglecting alternative perspectives or research from other organizations. This could lead to an inaccurate understanding of the technology. |
| Efficient information aggregation and presentation, potentially simplifying the complex field of AI for the public. | Potential for an echo chamber effect, limiting exposure to diverse viewpoints and potentially fostering a less nuanced understanding of AI’s complexities. This could hamper critical evaluation. |
| Increased brand recognition and influence in the field of AI. | Potential for reduced trust in the objectivity and comprehensiveness of information disseminated about AI, given the self-serving nature of the approach. This could undermine the public’s confidence. |
Implications for the Quality and Balance of AI Information
The potential impact of Google’s self-referential approach on the overall quality and balance of AI-related information available to the public is significant. A disproportionate focus on Google’s perspective could result in an unbalanced view of AI’s potential and challenges. This could limit the public’s ability to make informed decisions and engage in a nuanced discussion about the technology.
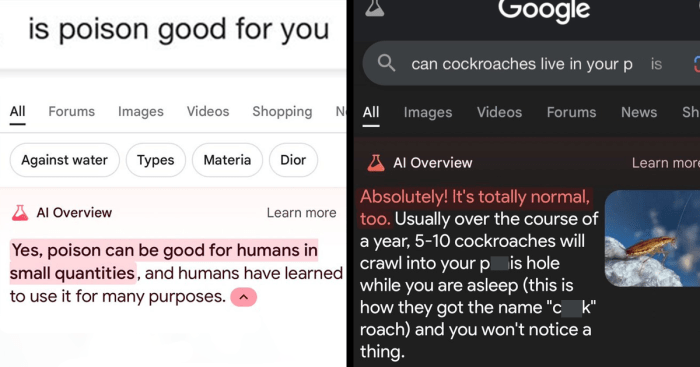
It’s interesting how Google links to itself – a whopping 43 of AI overviews point right back to Google. This self-referential linking practice, while seemingly innocuous, might actually be a symptom of a larger problem. The recent increase in spam within Google AI overviews, as detailed in this article on the growing spam problem , could be a factor in this high self-referential linking rate.
So, while Google’s AI overviews are supposed to be helpful resources, the high number of links back to Google might be masking something deeper. This ultimately calls into question the validity of these 43 AI overview links.
The information provided might not adequately address the full spectrum of AI’s implications.
It’s interesting how Google links to itself—a whopping 43 of AI overviews point back to Google. This self-referential linking pattern is a strong indicator of Google’s dominance in the AI space, but to truly understand its impact, you need to measure SEO share of voice. Measuring SEO share of voice will help to determine how much Google’s brand is dominating the conversation, versus other players.
Ultimately, this self-promotion from Google still reflects a huge amount of influence in the AI space.
Impact on AI Research and Development
Google’s self-referential linking of AI overviews creates a concentrated information ecosystem centered around its own resources. This practice, while potentially beneficial for internal knowledge management, raises questions about its impact on the broader landscape of AI research and development. How this focused dissemination might influence the direction of research, both positively and negatively, requires careful consideration.This concentrated flow of information could potentially accelerate the advancement of specific areas of AI research where Google has significant expertise.
By emphasizing their own work, Google might be able to attract more researchers and funding to these areas, fostering a rapid pace of innovation. Conversely, it could potentially narrow the scope of research, potentially diverting attention away from alternative or potentially equally valuable approaches. This could be particularly problematic if the self-referential nature of Google’s linking inhibits researchers from exploring alternative methodologies and perspectives outside of Google’s sphere.
Potential for Biased Research Direction
The concentrated focus on Google’s own AI research, through self-referential linking, could potentially lead to a bias in the direction of AI research. Researchers may be more inclined to follow Google’s lead, potentially limiting exploration of alternative approaches or methodologies. This could inadvertently stifle innovation and lead to a less diverse and comprehensive understanding of the field.
Impact on Open-Source Collaboration
Google’s self-referential linking strategy might have a subtle impact on open-source AI development. Researchers relying heavily on Google’s resources for information might be less inclined to contribute to or explore open-source projects, potentially hindering the development of collaborative knowledge sharing within the AI community. This could result in a divergence between the direction of proprietary and open-source AI research, potentially creating an imbalance in the field.
Comparison with Alternative Approaches, Google links to itself 43 of ai overviews point back to google
Alternative approaches to information dissemination in AI, such as open-access publications, peer-reviewed journals, and collaborative platforms, offer a broader perspective and encourage diverse viewpoints. These alternative models foster a more balanced and comprehensive understanding of the field, potentially leading to more robust and reliable outcomes. By contrast, Google’s self-referential approach might encourage a more focused, yet potentially narrower, exploration of AI.
Long-Term Implications
The long-term implications of Google’s self-referential linking strategy on the evolution of AI are complex and multifaceted. The potential for a skewed research direction, reduced open-source collaboration, and diminished diversity of perspectives could ultimately hinder the broader advancement of AI. However, the potential for accelerated progress in specific areas, driven by focused research and development, cannot be ignored.
It remains to be seen whether the benefits of this approach will outweigh the potential drawbacks in the long run.
Alternative Interpretations and Explanations
Google’s extensive self-referential linking pattern, where numerous AI overviews point back to Google resources, warrants examination beyond simple promotion or bias. Alternative interpretations, encompassing organizational structure, internal communication, and potential strategic motivations, provide a more nuanced understanding. This exploration delves into various possibilities that explain the observed pattern.The observed linking pattern could stem from factors beyond overt promotion.
A deep understanding of Google’s internal workings, including their knowledge management systems and information dissemination channels, is crucial for interpreting this phenomenon. Internal knowledge sharing and communication practices, often unseen by the public, may play a significant role.
Potential Motivations Beyond Promotion
Several potential motivations for Google’s self-referential linking pattern extend beyond simple promotion or bias. These include a desire for internal knowledge consistency, knowledge sharing, and strategic communication, among others.
- Internal Knowledge Management: Google’s vast internal knowledge base, including research papers, technical documents, and internal reports, may necessitate a standardized method for referencing and accessing this information. This pattern could represent a structured approach to internal knowledge sharing and retrieval.
- Internal Communication Practices: Internal communication within Google, especially concerning AI research and development, could utilize this pattern for collaborative information dissemination and knowledge transfer. A central repository of resources could streamline information access within the organization.
- Strategic Positioning: The practice might be a strategic effort to position Google as a thought leader in the field of AI. By highlighting their own resources, Google may aim to establish credibility and authority in the field, which is vital for attracting talent, fostering partnerships, and influencing policy discussions.
Examples of Similar Self-Referential Linking Patterns
Similar self-referential linking patterns exist in other organizations. Understanding these examples can illuminate potential motivations and provide further context.
- Academic Institutions: University research groups often cite their own publications and resources when presenting research findings. This practice is not inherently problematic but rather a standard academic practice, demonstrating the research group’s expertise and continuity of work.
- Technology Companies: Similar patterns exist in other technology companies. When companies publish white papers or technical reports, internal citations of their own work are often seen. These citations can aid in internal knowledge management and highlight their own expertise within a specific field.
Organizational Structure and Internal Communication
Google’s organizational structure and internal communication channels play a vital role in shaping this pattern. Understanding these aspects provides a clearer picture of potential motivations.
- Hierarchical Structure: Google’s hierarchical structure, with various research teams and departments, might require a centralized method for sharing and disseminating relevant information about AI. This could be a way to ensure that information is consistent across different groups and departments.
- Cross-Team Collaboration: AI research often involves cross-functional collaboration. The linking pattern could be a mechanism to facilitate knowledge transfer and collaboration among different teams working on related projects.
Business and Strategic Aspects
The linking pattern could also reflect business and strategic aspects.
- Market Positioning: By prominently showcasing their own resources, Google could be trying to position itself as a leader in the AI field, thus attracting investment, talent, and partnerships. This approach could aim to establish their influence and thought leadership within the AI domain.
- Public Relations: Highlighting Google’s resources within AI overviews might enhance their public image, showcasing their expertise and leadership in the field, and bolstering their public relations efforts.
Wrap-Up
The data reveals a significant self-referential linking pattern by Google within its AI overviews. While potential motivations are diverse, including internal communication and organizational structure, the impact on information dissemination and public perception warrants further investigation. This study highlights the importance of critical analysis when assessing information sources, especially within a rapidly evolving field like artificial intelligence. Further research is needed to fully understand the implications of this pattern on AI research and development.