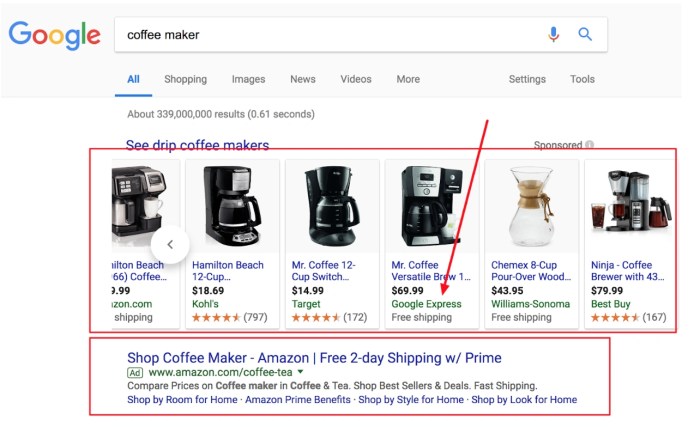
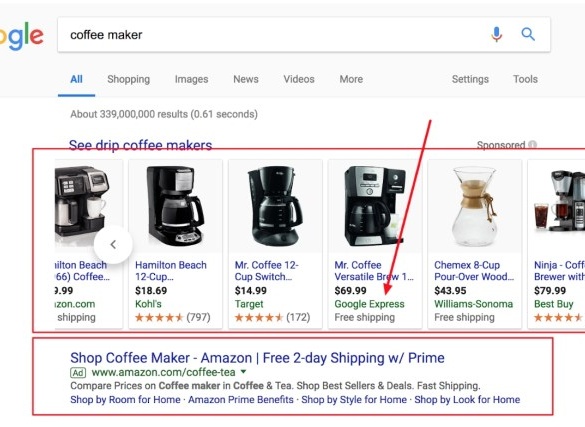
Google express launched pay per sale shopping actions – Google Express launched pay-per-sale shopping actions, offering a novel approach to online purchases. This innovative model allows consumers to try products before committing to a full purchase, while businesses can potentially reduce risk and increase sales. The service’s impact on the e-commerce landscape, customer experience, and business opportunities are all significant factors to consider. This new model presents both exciting possibilities and potential challenges, making it a compelling topic for analysis.
The core concept involves a pay-per-use system for online purchases, giving buyers the chance to sample or try products before fully committing to a purchase. It also provides businesses with an opportunity to reduce risk by offering a trial-based model, which could stimulate growth. This new model offers a dynamic approach to online shopping, potentially disrupting the traditional e-commerce paradigm.
The following sections will delve deeper into the nuances of this new system, examining it from the perspectives of consumers, businesses, and technology.
Introduction to Google Express Pay-Per-Sale Actions
Google Express is rolling out a new shopping model, “pay-per-sale actions,” designed to reshape the way businesses and consumers interact in the e-commerce world. This innovative approach shifts the traditional transaction model, offering a fresh perspective on how goods are purchased and sold. This new model could potentially revolutionize the way businesses manage inventory and marketing, while simultaneously providing consumers with more flexibility and control.This new pay-per-sale system fundamentally changes how businesses and consumers engage in e-commerce.
Instead of upfront payments, businesses receive payment only when a sale is made. This shifts the risk and reward dynamics in a way that can be hugely beneficial for both parties.
Key Features and Functionalities
The pay-per-sale model offers a unique approach to e-commerce transactions. Crucially, this new model allows businesses to test new products or services with minimal upfront investment. It also allows for dynamic pricing and promotion strategies, responding to real-time market demands and competitive pressures. Furthermore, this model allows for a more nuanced approach to inventory management, eliminating the need for excessive stockpiling in anticipation of sales.
Google Express’s system will likely automate much of this process, streamlining the workflow for both sides.
Potential Benefits for Consumers, Google express launched pay per sale shopping actions
Consumers will likely benefit from increased product variety and potentially lower prices. By encouraging more businesses to participate, the pay-per-sale model will potentially bring a wider selection of goods and services to market. The flexibility of this model can result in more competitive pricing, making goods and services more accessible to consumers.
Potential Benefits for Businesses
Businesses will find the pay-per-sale model to be a more agile way to manage inventory. The system is expected to reduce the risk associated with upfront investment in inventory, allowing businesses to focus on selling and marketing. The ability to adjust pricing and promotions in real time will also be beneficial, responding to changing market conditions and consumer preferences.
Impact on the E-commerce Landscape
The pay-per-sale model has the potential to reshape the e-commerce landscape. It is likely to encourage greater innovation and experimentation in the online marketplace. The model’s potential for increased efficiency and reduced risk could attract new players and invigorate existing businesses. It is a radical shift, which might see a rise in niche businesses and products as smaller ventures can test their wares without substantial initial investments.
Comparison to Existing Models
| Feature | Pay-Per-Sale | Traditional Upfront Payment | Subscription Models |
|---|---|---|---|
| Payment Timing | Payment upon sale | Payment upfront | Recurring payment |
| Inventory Risk | Lower risk for businesses | Higher risk for businesses | Moderate risk for businesses |
| Pricing Flexibility | High flexibility | Lower flexibility | Moderate flexibility |
| Market Entry Barriers | Potentially lower | Potentially higher | Potentially moderate |
This table highlights the key differences between the pay-per-sale model and its existing counterparts. The pay-per-sale model’s potential for reduced risk and greater flexibility stands out compared to other models. This will likely attract new entrants to the online market.
Customer Perspective on Pay-Per-Sale: Google Express Launched Pay Per Sale Shopping Actions
The Google Express Pay-Per-Sale model presents a fascinating new approach to online shopping. It shifts the traditional transaction paradigm, potentially impacting both customer expectations and purchasing behavior. Understanding the customer’s perspective is crucial for evaluating the model’s success and how businesses can best leverage it.The core of the pay-per-sale model hinges on the idea of purchasing actions rather than the product itself.
This paradigm shift could create new opportunities for customers to experiment with products or services, offering a more flexible and potentially more economical shopping experience.
Ease of Use and Perceived Value
Customers will likely appreciate the ease of trying new products without the commitment of a full purchase. This could lead to a higher trial rate for items they might not otherwise consider. The perceived value is tied to the flexibility of purchasing only what’s needed, potentially reducing buyer’s remorse and encouraging more informed purchasing decisions. Customers could view this model as a way to “test-drive” products or services before committing to a larger purchase, thus increasing perceived value by eliminating the risk associated with buying something they might not need or use.
Potential Advantages for the Customer
- Reduced risk: Customers can try before they buy, potentially avoiding impulse purchases and costly mistakes. This is especially valuable for higher-priced or complex products.
- Increased flexibility: This approach enables customers to buy only what they need, which can be particularly useful for subscription services, consumables, or products with varying quantities. A customer might only purchase a portion of a bulk product instead of the whole package.
- Improved budgeting: The pay-per-sale model enables customers to manage their expenses more effectively, especially for products they need only occasionally.
Potential Disadvantages for the Customer
- Transaction complexity: The process of purchasing actions rather than whole products might be more intricate than traditional online payment methods. The learning curve for understanding the model could deter some customers.
- Pricing transparency: The pay-per-sale model needs clear pricing structures for individual actions. Customers may struggle to assess the total cost of their desired outcome upfront.
- Limited product availability: The pay-per-sale model might restrict the availability of certain products or services to specific actions, thus limiting customer choices.
Impact on Customer Expectations and Purchasing Behaviors
The pay-per-sale model will likely alter customer expectations. Customers might expect more flexibility and control over their purchases, expecting businesses to offer this model for a wider range of products. This could also affect purchasing behaviors by encouraging more calculated and targeted buying decisions. Customers may be more inclined to explore products or services with a pay-per-use or pay-per-action structure, even if they’re not aware of the model’s existence at present.
Comparison with Other Online Payment Methods
The pay-per-sale model differs significantly from traditional online payment methods, such as one-time purchases or subscriptions. It introduces a new dimension of flexibility and control over the purchase process. While subscriptions offer recurring payments for ongoing access, pay-per-sale offers targeted payments for specific actions within a product or service.
How Businesses Can Leverage the Model
- Enhanced product exploration: Businesses can use pay-per-sale to encourage customers to try different features or aspects of their products or services. For example, a software company could offer a pay-per-use model for certain functions within its software.
- Increased customer engagement: Pay-per-sale could foster more engagement with the product or service. Customers who pay for specific actions might interact with the product more frequently and actively.
- Flexible pricing models: Businesses can design pricing models that are tailored to specific customer needs. This flexibility is not always possible with traditional pricing models.
Business Perspective on Pay-Per-Sale
Google Express’s introduction of a pay-per-sale model for shopping actions presents a compelling, yet complex, landscape for businesses. This model, while offering potential advantages, also introduces unique challenges. Understanding these intricacies is crucial for businesses considering adopting this new approach. Businesses need to carefully evaluate the potential benefits and drawbacks before integrating it into their strategies.This model shifts the traditional transaction paradigm, offering a potentially lucrative avenue for increased sales, but also requiring a strategic approach to pricing, risk management, and customer acquisition.
The pay-per-sale mechanism necessitates a calculated and data-driven strategy to maximize returns while mitigating potential risks.
Potential Business Opportunities
This model presents businesses with the chance to expand their reach and potentially increase their sales without the commitment of traditional wholesale or retail arrangements. Businesses can leverage this opportunity to access new customer segments and market niches, potentially broadening their market share.
- Access to new markets: Pay-per-sale actions can allow businesses to participate in markets they might not otherwise have access to, such as those dominated by established online retailers or requiring significant upfront investment.
- Reduced upfront costs: The pay-per-sale model eliminates the need for significant upfront inventory investment. This is particularly valuable for businesses with fluctuating demand or those in rapidly evolving markets.
- Increased flexibility: Businesses can adapt their offerings more quickly, responding to changing customer demand or trends in real time. This adaptability is essential in the dynamic e-commerce landscape.
Challenges of the Pay-Per-Sale Model
Despite the opportunities, businesses must be prepared for potential challenges. A critical aspect is the need to carefully evaluate potential revenue generation and cost structures. There is a high degree of dependence on successful customer conversion, which necessitates effective marketing and sales strategies.
Google Express’s new pay-per-sale shopping actions are intriguing, but how do you manage your website’s visibility and prevent unwanted indexing? Knowing how to block URLs using a robots.txt file is crucial for optimizing your online presence. This ensures your site isn’t cluttered with irrelevant content, and is vital for success with programs like Google Express’s pay-per-sale model, allowing you to focus on relevant items for sale.
Check out how to block URLs robots txt for a detailed guide on this essential SEO practice, which is important to remember when launching new shopping features.
- Competition and market saturation: The pay-per-sale model can attract competitors, increasing competition and potentially diluting the value proposition for the participating businesses. Existing e-commerce giants may leverage this model to expand their offerings, increasing the competition for smaller businesses.
- Profitability considerations: The pay-per-sale model’s success hinges on carefully calculated pricing models that balance revenue generation and risk mitigation. Businesses need to account for potential fluctuations in customer demand and ensure their margins are sufficient to cover their costs.
- Customer acquisition and retention: Attracting and retaining customers in a pay-per-sale model requires a robust marketing strategy to highlight the value proposition and foster customer trust. Maintaining customer satisfaction and driving repeat sales will be critical to long-term success.
Impact on Profitability and Revenue Streams
The impact on profitability will significantly depend on the pricing model implemented and the overall performance of the business within the Google Express platform. Successful implementation can generate substantial revenue, while poor execution can result in decreased profitability.
- Pricing strategies: Businesses need to develop pricing strategies that consider their costs, market conditions, and the value proposition for consumers. Factors such as the complexity of the product, the level of service offered, and the overall demand for the product will influence the optimal pricing strategy.
- Revenue streams: The pay-per-sale model potentially diversifies revenue streams by allowing businesses to participate in multiple sales channels and expand their market reach. This diversification can reduce reliance on single revenue streams and enhance resilience.
- Risk mitigation: Strategies to mitigate risks should focus on careful selection of products or services that have demonstrable demand and customer interest. Thorough market analysis and cost analysis are critical to assess risk factors and develop strategies for minimizing losses.
Strategies for Attracting Customers
Attracting customers to the pay-per-sale model requires a strong marketing strategy that clearly communicates the benefits and value proposition to potential customers. Transparency and clear communication are key.
- Highlighting the value proposition: Focus on the benefits of the pay-per-sale model, such as convenience, lower upfront costs, and potentially lower prices. Clear communication of the terms and conditions of the model will be crucial for customer trust.
- Building brand awareness: Creating a positive brand image and reputation is essential for attracting customers to the pay-per-sale model. This can be achieved through effective marketing campaigns, engaging content, and customer testimonials.
- Leveraging Google Express features: The use of Google Express’s platform features, such as search optimization and targeted advertising, will be crucial for visibility and driving sales.
Potential Pricing Models
Various pricing models are possible, ranging from simple per-sale fees to tiered models based on sales volume or product category. The ideal pricing model will depend on the specific business and its goals.
- Fixed pricing per sale: A straightforward model where a fixed fee is charged for each successful sale.
- Tiered pricing: A model that offers different pricing tiers based on the volume of sales or the product category.
- Commission-based pricing: A model where businesses receive a percentage of each sale.
Technical Implementation and Integration
The pay-per-sale model, while conceptually straightforward, requires robust technical infrastructure and meticulous integration with existing systems. This section delves into the critical technical considerations, highlighting the necessary tools and architectures for a successful implementation. A well-structured approach ensures smooth operations, reduced errors, and scalability for future growth.Implementing a pay-per-sale system demands careful planning and execution. It’s not just about connecting systems; it’s about building a flexible and reliable mechanism that handles transactions, tracks sales, and ensures accurate payouts to sellers.
Technical Aspects of Implementation
The technical architecture for a pay-per-sale system needs to handle a high volume of transactions, ensure secure payment processing, and track sales attribution accurately. Key components include a robust transaction processing engine, a reliable data storage system, and a secure payment gateway. Data integrity and security are paramount.
Necessary Infrastructure and Tools
The infrastructure needed for a pay-per-sale system hinges on several key elements. A reliable database is crucial for storing product information, seller details, transaction history, and payout information. A robust payment gateway is essential for processing transactions securely and efficiently. Furthermore, a real-time analytics dashboard is vital for monitoring performance, identifying trends, and facilitating decision-making.
Integration with Existing E-commerce Platforms
Seamless integration with existing e-commerce platforms is vital for a smooth transition. The integration process involves careful API design, data mapping, and a robust error-handling mechanism. Existing e-commerce platforms often have their unique data structures and APIs. Careful consideration is needed to map these to the pay-per-sale system’s data model, ensuring accurate data flow and avoiding data loss.
Google Express’s new pay-per-sale shopping actions are interesting, especially considering the ongoing debate around paywalls and their impact on SEO. How can businesses strike a balance between monetization and organic reach? For example, exploring innovative models like pay-per-sale shopping actions might offer a unique way to monetize content while still maintaining a strong SEO presence. This is where exploring topics like paywalls and SEO can they work together becomes crucial for companies looking to navigate this new landscape.
Ultimately, Google Express’s new pay-per-sale actions might be a sign of a shift in e-commerce strategies, promising new opportunities for both buyers and sellers.
Testing and validation of the integration process are crucial to prevent disruptions to the existing platform.
Examples of Technical Architectures
Various architectures can support a pay-per-sale system. One approach utilizes a microservices architecture, allowing independent scaling of different components. Another approach might leverage a serverless architecture, minimizing infrastructure management and optimizing costs. A hybrid architecture combining elements of both microservices and serverless can also be employed, offering a balance of flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
Steps in Setting Up a Pay-Per-Sale Model
A structured approach to setting up a pay-per-sale model is essential for success. This process ensures a well-defined framework for development, testing, and deployment. A comprehensive plan will include steps to design the system, implement the necessary tools, and ensure the system’s functionality.
Google Express just launched pay-per-sale shopping actions, which is pretty cool for online shopping. It’s a neat way to try new things without committing to a full purchase. Thinking about alternative ways to shop if you’re looking for ways to get creative with your online shopping experience, exploring options like alternatives for users if tiktok banned could be beneficial.
This new Google Express feature is definitely something to keep an eye on; it’s a refreshing approach to e-commerce.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Define Requirements | Clearly Artikel the functionalities and specifications of the pay-per-sale system, including payment processing, data tracking, and reporting. |
| 2. Design the System Architecture | Choose an appropriate technical architecture, considering factors like scalability, security, and integration with existing systems. |
| 3. Develop and Test the System | Implement the system using the chosen tools and technologies, ensuring thorough testing to identify and resolve potential issues. |
| 4. Integrate with E-commerce Platforms | Integrate the pay-per-sale system with existing e-commerce platforms, ensuring smooth data flow and seamless user experience. |
| 5. Deploy and Monitor | Deploy the system and establish monitoring mechanisms to track performance, identify issues, and make necessary adjustments. |
Market Analysis and Competition
Google Express’s foray into pay-per-sale shopping actions presents a compelling opportunity, but navigating the competitive landscape is crucial for success. Understanding existing offerings and potential threats is essential for crafting a winning strategy. This section delves into the competitive landscape, highlighting key players, their strategies, and potential market positioning for Google Express.The pay-per-sale model, while innovative, isn’t entirely new.
Analyzing competitors’ approaches and identifying potential gaps in the market will help Google Express differentiate itself and capture market share. Ultimately, a robust understanding of the competitive landscape is critical for Google Express to not only survive but thrive in this dynamic market.
Key Competitors and Their Strategies
Several companies offer services similar to Google Express’s pay-per-sale actions, though their approaches and target markets vary. Amazon’s extensive marketplace and logistics network provide a formidable presence, while smaller players often focus on niche markets.
- Amazon: Amazon’s vast marketplace and logistics infrastructure position them as a dominant player. Their Prime Now service and flexible delivery options offer significant competition. They utilize a combination of volume discounts, extensive logistics partnerships, and aggressive pricing to maintain their market leadership.
- Instacart: Instacart excels in grocery delivery, using a network of independent shoppers. Their focus on convenience and rapid delivery is a strong competitive advantage. The pay-per-sale model could be implemented within their current platform to better address delivery costs and service quality.
- DoorDash: DoorDash’s extensive restaurant delivery network presents a different competitive angle. Their pay-per-delivery model, while not directly comparable to pay-per-sale, is highly relevant in terms of understanding customer expectations and delivery logistics.
Potential Market Positioning for Google Express
Google Express needs a clear market positioning strategy to effectively compete. Positioning it as a premium, tech-driven solution for time-sensitive and high-value purchases could differentiate it.
- Focus on high-value, time-sensitive purchases: Differentiating Express from general e-commerce platforms through emphasizing expedited delivery for essential goods and services could be a crucial strategy.
- Leverage Google’s ecosystem: Seamless integration with Google Search, Maps, and other products could enhance user experience and drive discovery. The integration of Express into Google Assistant could offer another compelling avenue for growth.
Strategies for Gaining Competitive Advantage
Several strategies can help Google Express establish a competitive advantage:
- Competitive Pricing: Strategic pricing strategies need to be developed, factoring in the pay-per-sale model, delivery costs, and potential for volume discounts to maintain profitability while remaining competitive.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Offering personalized recommendations, real-time delivery updates, and flexible order management options can improve customer satisfaction and encourage repeat business.
- Partnerships and Strategic Alliances: Collaborating with local businesses and optimizing delivery routes could streamline the process and enhance the service.
Potential Threats and Opportunities
The competitive landscape presents both threats and opportunities for Google Express. Understanding these is critical to developing successful strategies.
- Increased Competition: New entrants or existing players aggressively expanding their services into the pay-per-sale market could pose a significant threat.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: Consumer demands and preferences are dynamic. Google Express needs to adapt to these changes to remain relevant.
- Regulatory Landscape: Changes in regulations related to e-commerce and delivery services could impact the business model.
Future Implications and Predictions
The launch of Google Express Pay-Per-Sale actions signals a significant shift in e-commerce, potentially reshaping the industry’s dynamics. This model, where sellers pay for customer actions rather than upfront purchases, introduces a new paradigm for both buyers and businesses. The implications for the future are multifaceted, affecting everything from pricing strategies to customer engagement.
Potential Developments and Innovations
This new model encourages innovative approaches to online shopping experiences. Expect to see more dynamic pricing strategies, personalized offers, and interactive shopping features designed around the pay-per-sale structure. For instance, businesses might offer tiered pay-per-sale models, incentivizing specific actions like product reviews or social media sharing. Furthermore, integration with existing loyalty programs and reward systems will likely become more common, offering customers even greater incentives for engaging with products.
A key area for innovation will be the development of novel ways to measure and reward desired customer actions, moving beyond simple clicks and purchases.
Long-Term Implications for E-Commerce
The pay-per-sale model will fundamentally alter the e-commerce landscape. Businesses will need to re-evaluate their pricing models, focusing on the value of individual customer actions rather than complete sales. This shift may lead to a more performance-based approach to online advertising, where advertisers pay only for demonstrable results like leads or conversions. Moreover, the focus on specific customer actions will likely lead to a more nuanced understanding of consumer behavior, enabling businesses to tailor their offerings and strategies with greater precision.
The emphasis on actions rather than immediate purchases may also foster a more engaged and interactive online shopping environment.
Impact on the Broader Retail Landscape
Pay-per-sale actions will affect traditional retail as well. The model presents a unique opportunity for brick-and-mortar stores to integrate online shopping elements, possibly partnering with e-commerce platforms to offer incentives for in-store visits. Additionally, the dynamic pricing model may lead to a more fluid pricing structure for physical goods, potentially adjusting to market demand and competitor offerings in real-time.
The ability to test and measure different strategies for product engagement will be critical, potentially leading to more agile and responsive retail strategies.
Potential Disruptions in the Industry
The pay-per-sale model could disrupt established industry practices in several ways. Traditional advertising models, reliant on upfront payments, may face pressure to adapt. Also, existing business models built around high-volume, low-margin sales may need to re-evaluate their strategies. The shift toward a more performance-based system could lead to greater competition, particularly for businesses less adept at measuring and incentivizing specific customer actions.
Furthermore, the need for new metrics and data analysis tools will be paramount, requiring a new skillset for businesses.
Possible Future Scenarios for E-Commerce
| Scenario | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Rapid Adoption | Businesses quickly embrace pay-per-sale, leading to a more dynamic and interactive e-commerce environment. | Increased competition, potentially disrupting established models. |
| Scenario 2: Gradual Integration | Businesses adopt pay-per-sale incrementally, focusing on specific product categories or customer segments. | A period of experimentation and adaptation, potentially slower disruption. |
| Scenario 3: Limited Uptake | Limited adoption by businesses due to complexities in implementation or concerns about measurement accuracy. | Existing e-commerce models remain largely unchanged. |
| Scenario 4: Disruptive Innovation | Pay-per-sale actions transform the entire retail landscape, impacting both online and offline channels. | Significant shift in pricing, advertising, and customer engagement strategies. |
Wrap-Up
Google Express’s pay-per-sale initiative marks a significant shift in the e-commerce landscape. It presents both compelling opportunities and challenges for both consumers and businesses. The potential for increased customer engagement, reduced risk for businesses, and a more dynamic online shopping experience is significant. However, the success of this model hinges on factors such as user adoption, business strategies, and technical implementation.
Further analysis will reveal how this model evolves and potentially impacts future e-commerce trends.