Google ads experiments six steps to success – Google Ads Experiments: Six Steps to Success. Unlocking the potential of your Google Ads campaigns requires a strategic approach to experimentation. This guide dives deep into six crucial steps, from understanding the basics of Google Ads experiments to optimizing your campaigns for maximum ROI. Learn how to effectively test, analyze, and implement changes for consistent improvements.
We’ll explore different types of experiments, from A/B testing ad copy to optimizing bidding strategies. The detailed breakdown of each step will equip you with the knowledge to conduct impactful experiments that drive measurable results. This isn’t just about theoretical knowledge; we’ll provide practical examples and actionable steps to put your learnings into practice.
Introduction to Google Ads Experiments
Google Ads Experiments is a powerful feature that allows advertisers to test different versions of their campaigns to see what performs best. It’s a valuable tool for optimizing ad copy, targeting strategies, and bidding strategies, ultimately leading to improved campaign performance and higher return on ad spend (ROAS). By systematically testing variations, advertisers can identify the most effective approach for their specific goals and audience.Using Google Ads Experiments, advertisers can gain insights into what resonates most with their target audience, allowing them to tailor their campaigns for optimal results.
This iterative approach to campaign management is crucial in a dynamic advertising landscape where constantly evolving consumer preferences and market trends demand adaptability. It’s not just about trial and error; it’s about informed experimentation to drive measurable improvements in campaign effectiveness.
Different Types of Google Ads Experiments, Google ads experiments six steps to success
Google Ads Experiments offers a variety of tests to address diverse optimization needs. These tests are designed to evaluate different aspects of a campaign, from ad copy variations to bidding strategies and targeting parameters. Understanding the available options allows advertisers to choose the most appropriate test for their specific objectives.
- Ad Copy Experiments: These experiments focus on testing variations of ad copy, including headlines, descriptions, and calls to action. Testing different ad copy elements allows advertisers to identify which variations generate more clicks, conversions, and ultimately, sales.
- Targeting Experiments: These experiments examine how different targeting parameters impact campaign performance. Advertisers can test various audience segments, demographics, and interests to discover the most effective audience segments for their campaigns.
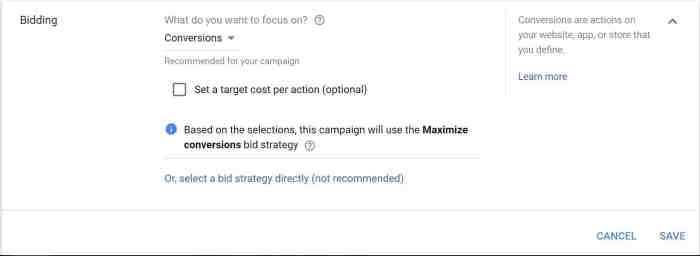
- Bidding Strategy Experiments: These experiments evaluate different bidding strategies to determine which strategy yields the best results. Examples include maximizing clicks, conversions, or conversions value. This optimization is vital for maximizing the return on ad spend (ROAS).
Examples of Optimizing Campaigns with Experiments
A retailer might use an ad copy experiment to test different product descriptions to see which one encourages more purchases. Another advertiser might run a targeting experiment to identify which age groups respond best to their specific product. A business-to-business (B2B) company could use a bidding strategy experiment to determine which bidding strategy maximizes qualified leads. These examples demonstrate the diverse applications of experiments to optimize performance across various campaign types.
Experiment Types and Outcomes
| Experiment Type | Goal | Expected Outcome | Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ad Copy | Improve ad click-through rates and conversions. | Higher click-through rates (CTR) and conversion rates for the winning ad variations. | CTR, Conversion Rate, Cost Per Conversion |
| Targeting | Identify the most effective audience segments. | Increased conversions from the targeted audience segments. | Conversion Rate, Cost Per Conversion, Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) |
| Bidding Strategy | Optimize campaign budget allocation. | Lower cost per conversion and higher conversion volume for the winning bidding strategy. | Cost Per Conversion (CPC), Conversion Volume, Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) |
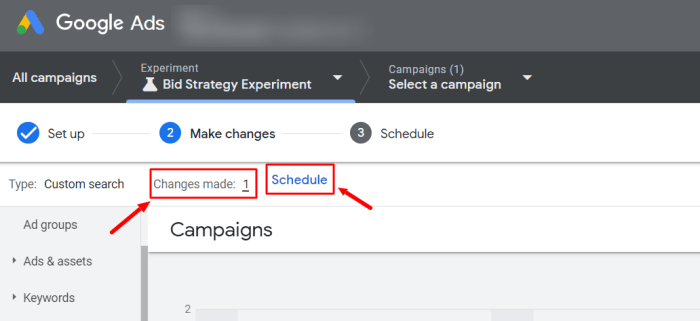
Setting Up Experiments Effectively
Successfully running Google Ads experiments hinges on meticulous setup. A well-structured experiment allows you to gather meaningful data and make informed decisions. This crucial step involves careful consideration of metrics, goals, hypotheses, and the crucial separation of control and experimental groups. Ignoring these aspects can lead to inaccurate results and wasted resources.
Choosing the Right Metrics
Tracking the correct metrics is paramount for evaluating experiment success. Simply monitoring clicks or impressions might not reveal the full impact of changes. Instead, focus on conversions, cost per conversion, or other metrics directly related to your business objectives. For instance, if your goal is to improve lead generation, focus on metrics like form submissions or phone calls.
If your objective is to increase sales, track revenue or order volume. Choosing relevant metrics ensures the experiment accurately measures the impact of the tested changes.
Defining Clear Goals and Hypotheses
Clearly defined goals and hypotheses are essential to guide the experiment. A well-defined goal provides a direction for the experiment and helps in choosing the appropriate metrics. A hypothesis, on the other hand, proposes a specific prediction about how the change will affect the outcome. For example, a goal might be to increase click-through rates, and a hypothesis might be that a redesigned ad copy will result in a 15% increase in click-through rates compared to the current ad copy.
Formulating clear goals and testable hypotheses ensures the experiment aligns with your business objectives.
Control and Experimental Groups
The control and experimental groups are fundamental to a valid experiment. The control group serves as a baseline, and the experimental group receives the tested changes. A crucial aspect of this process is ensuring that the control and experimental groups are as similar as possible in all other aspects, such as demographics, ad targeting, and time of day.
Randomly assigning users to each group minimizes bias and increases the accuracy of results. This helps to isolate the impact of the specific change being tested. A balanced allocation to each group prevents extraneous factors from skewing the results.
Essential Steps for Setting Up an Experiment
A structured approach ensures a smooth experiment setup. The following table Artikels the key steps involved:
| Step | Description | Required Information |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Define Goals and Hypothesis | Clearly articulate the desired outcome and formulate a testable prediction about the impact of the change. | Specific business objectives, proposed changes, predicted impact |
| 2. Select Metrics | Identify the key performance indicators (KPIs) to track and measure the effectiveness of the changes. | Relevant KPIs, data collection methods |
| 3. Establish Control and Experimental Groups | Divide the target audience into two groups: one receiving the existing setup (control), and another receiving the modified setup (experimental). | Target audience, randomization method |
| 4. Set Experiment Duration | Determine the time frame for the experiment to allow sufficient data collection for analysis. | Sufficient data collection time, anticipated impact |
| 5. Monitor and Analyze Results | Track performance metrics and compare results between the control and experimental groups. | Data visualization tools, analysis methods |
| 6. Draw Conclusions and Implement Changes | Evaluate the results based on the defined metrics and decide whether to implement the changes or make further adjustments. | Results, decision-making criteria |
Designing Effective Experiment Strategies
Mastering Google Ads Experiments hinges on meticulously designed strategies. A well-structured approach allows you to effectively test various elements, optimize campaigns, and maximize ROI. This involves understanding A/B testing principles, choosing appropriate variations, segmenting your audience, and structuring the experiment for optimal results. By employing these strategies, you can significantly improve your Google Ads performance.Effective experimentation involves a meticulous understanding of the nuances of A/B testing.
Google Ads Experiments, in essence, allow you to systematically compare different versions of your campaigns, identifying what resonates best with your target audience. This iterative approach leads to enhanced campaign performance, higher conversion rates, and better return on investment.
A/B Testing Principles in Google Ads Experiments
A/B testing in Google Ads Experiments is about comparing two versions of a specific element (e.g., ad copy, landing page, bidding strategy) to determine which performs better. The core principle is to isolate the variable you’re testing and measure its impact on key metrics. This ensures that observed improvements are directly attributable to the specific change you’ve implemented, rather than external factors.
This method is crucial for data-driven optimization and avoids relying on intuition alone.
Strategies for Testing Variations
Testing different variations of ads, landing pages, and bidding strategies is essential for optimizing campaign performance. You can test various ad copy variations, headlines, images, and call-to-actions. A/B testing landing page elements, like layout, content, and call-to-action placement, can also significantly impact conversions. For bidding strategies, consider testing different automated bidding strategies, such as target CPA or target ROAS, to see which delivers the best results.
Segmenting Your Audience for Experiments
Segmenting your audience for experiments is crucial for obtaining accurate and meaningful results. By segmenting your audience based on demographics, interests, or previous interactions, you can tailor your experiments to specific groups. This ensures that you’re testing the effectiveness of your variations on the most relevant audiences. For instance, you might segment users by location or device type.
Best Practices for Experiment Structure
To ensure optimal results, experiments should be structured in a way that allows for clear interpretation of data. Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for each experiment. Choose appropriate metrics to track and analyze, like click-through rate (CTR), conversion rate, cost-per-acquisition (CPA), or return on ad spend (ROAS). Establish a clear timeframe for the experiment and ensure sufficient data collection for accurate results.
Thorough documentation is essential for tracking the experiment’s progress and analyzing results.
Mastering Google Ads experiments involves six crucial steps, but a robust security operations center (SOC) is equally vital. A highly trained SOC team, like the one discussed in the importance of training on a high functioning security operations center soc , is critical for safeguarding your campaigns from fraud and ensuring the success of those experiments. Ultimately, understanding the intricacies of your ads, and the security measures behind them, are key to maximizing your Google Ads experiment outcomes.
Experiment Variations Table
| Variation | Description | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Ad Copy A | Short, concise copy focusing on urgency. | Potentially increased CTR and conversions due to urgency. |
| Ad Copy B | Detailed copy highlighting benefits and features. | Potentially increased conversions, but lower CTR due to length. |
| Headline A | Direct and benefit-driven headline. | Potentially increased CTR, but may need to be tested further to ensure high conversion rates. |
| Headline B | Intriguing and curiosity-driven headline. | Potential for increased CTR and click-through rate, but the conversion rate needs to be verified. |
| Image A | High-quality image with clear product presentation. | Increased CTR and engagement due to visual appeal. |
| Image B | Image with a strong call to action. | Potentially increased conversions due to strong call to action. |
Implementing and Monitoring Experiments
Putting your Google Ads experiment to work requires careful implementation and vigilant monitoring. This stage involves more than just setting up the parameters; it demands active engagement to ensure the experiment runs smoothly and provides valuable insights. Success hinges on correctly executing the setup, consistently tracking progress, and effectively analyzing the results.Experiment implementation and monitoring isn’t a passive process.
It’s a dynamic interplay of action and observation, ensuring you’re gathering the right data to inform crucial decisions. A well-structured approach will provide a clear picture of the experiment’s performance, enabling you to make data-driven adjustments and ultimately improve campaign effectiveness.
Implementing the Experiment Setup in Google Ads
The implementation process involves a series of steps within the Google Ads platform. First, ensure the experiment is correctly configured with the specified variations and control group. Secondly, carefully review the metrics and attribution models to ensure they align with the objectives of the experiment. Finally, set up the desired duration for the experiment, remembering that longer durations generally yield more statistically significant results.
Monitoring Experiment Progress in Real-Time
Real-time monitoring is crucial for identifying potential issues early. Use Google Ads’ built-in reporting tools to track key metrics such as click-through rate (CTR), conversion rate, cost per conversion, and impressions. Regularly review these metrics to spot any unusual trends or deviations from expected performance. This proactive approach allows for timely adjustments if the experiment isn’t performing as anticipated.
Analyzing Data Gathered During the Experiment
Data analysis is a critical step in understanding the experiment’s outcome. Thorough examination of the collected data is vital for extracting meaningful insights. This involves identifying trends, patterns, and correlations between variations and performance metrics.
Mastering Google Ads experiments involves six key steps, but solid setup in Google Tag Manager is crucial for accurate tracking. Understanding the top 10 must-have tags for business in Google Tag Manager, like those covered in this detailed guide, top 10 must have tags for business in google tag manager , will give you the insights needed for your experiments to truly succeed.
This will ultimately boost the effectiveness of your Google Ads strategies.
Interpreting Experiment Results
Interpreting the results requires careful consideration of the collected data and the defined hypotheses. A key aspect is understanding the statistical significance of the observed differences between variations. Don’t rely solely on raw data; instead, focus on identifying the statistically significant differences and their implications for campaign optimization. Avoid drawing conclusions based on minor variations, and look for consistent patterns across multiple metrics.
Analyzing Experiment Data to Draw Conclusions and Insights
A structured approach to analyzing experiment data is essential. Start by creating a table to summarize the key performance indicators (KPIs) for each variation. Then, calculate the statistical significance of the differences between the variations. Look for trends and patterns in the data to identify the most promising variations. Consider the overall business context and the specific goals of the experiment to draw meaningful conclusions and insights.
Use this information to inform future campaigns and strategies. For instance, if one variation significantly outperforms others in conversion rate, that variation should be prioritized in future campaigns.
Interpreting and Analyzing Experiment Results
Decoding your Google Ads experiment data is crucial for maximizing ROI. Understanding the patterns, trends, and statistical significance of your results empowers you to make informed decisions, optimize campaigns, and achieve your marketing goals. This phase goes beyond simply observing numbers; it’s about extracting actionable insights to drive future success.
Google Ads experiments offer six key steps to success, focusing on targeted campaigns and optimized results. However, exploring AI-powered solutions like salesforce einstein ai smarter business solutions can further elevate your strategies, providing insights that refine your ad targeting and ultimately improve ROI. By understanding these intricate steps, you’ll be well-equipped to master the complexities of Google Ads.
Identifying Patterns and Trends
Analyzing experiment data requires a keen eye for patterns and trends. Look for consistent differences between the control group and the experimental group across various metrics. Visualizations like charts and graphs are invaluable for spotting trends, such as a gradual increase in conversions or a sudden drop in click-through rate. Regularly reviewing the data, ideally daily or weekly, allows for early identification of anomalies or unexpected shifts.
By focusing on both short-term and long-term performance, you can better understand the impact of your changes.
Interpreting Statistically Significant Results
Statistical significance indicates that the observed difference between the control and experimental groups is unlikely due to random chance. A statistically significant result provides strong evidence that the experimental changes had a real impact on the metric being measured. This doesn’t necessarily mean the change ispositive*. A statistically significant result could indicate a negative impact, such as a decrease in conversions, which still requires investigation and analysis.
Tools within Google Ads can help determine statistical significance, often represented by a p-value. A p-value below a certain threshold (often 0.05) suggests statistical significance.
Drawing Conclusions from Experiment Outcomes
After identifying patterns and interpreting statistical significance, you can draw concrete conclusions. Document the observed effects, including both positive and negative changes. Focus on the practical implications of the results. For example, if a particular ad variation resulted in a statistically significant increase in click-through rate, this suggests that the variation is likely more effective in attracting users.
Correlation doesn’t equal causation, so consider other potential factors that might have influenced the outcome. Thorough documentation of the experiment and its results is critical for future reference and reporting.
Using Data to Inform Future Optimizations
Experiment results provide invaluable data for future optimization. If an experimental change yielded positive results, consider implementing it into your broader campaigns. Conversely, if a change had a negative impact, use this knowledge to avoid repeating similar errors in future experiments. This iterative approach is crucial for continuous improvement. Regular A/B testing allows you to continually refine your campaigns based on the data you gather.
The key is to use the insights to tailor future experiments to address areas needing improvement.
Example Data Analysis Table
| Metric | Baseline Value | Experiment Value | Statistical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conversion Rate | 2.5% | 3.2% | Yes (p<0.05) |
| Cost Per Click (CPC) | $2.00 | $1.80 | Yes (p<0.01) |
| Click-Through Rate (CTR) | 4.0% | 3.5% | No (p>0.05) |
Optimizing Campaigns Based on Experiment Results: Google Ads Experiments Six Steps To Success
Putting the insights gained from Google Ads Experiments to work is crucial for maximizing campaign effectiveness. This stage involves translating experimental data into actionable strategies for campaign improvement, ensuring that your efforts yield the best possible return on investment. It’s not just about identifying what worked; it’s about understanding
why* it worked and how to replicate that success across other campaigns.
The core principle is to move beyond simple observation and delve into the data to identify patterns and trends. This data-driven approach allows for the implementation of changes that optimize campaign performance in a targeted and sustainable manner. By analyzing the results of experiments, you can make informed decisions about which changes to implement and how to best measure their impact.
Implementing Changes Based on Experiment Results
Understanding the results of an experiment is only the first step. Implementing the changes identified as successful requires a structured approach. First, clearly define the specific changes to be implemented. This includes defining which elements of the campaign will be altered, the precise adjustments to be made, and the timeline for implementation. Documenting these decisions will ensure consistency and accountability throughout the process.
Secondly, prioritize the changes according to their potential impact and ease of implementation. This prioritization will allow for a phased approach to optimizing the campaign. Finally, carefully test the changes in a controlled environment before fully deploying them across the entire campaign. This allows for iterative improvement, adjusting the strategy based on real-time performance data.
Applying Learnings to Other Campaigns
Identifying transferable insights from successful experiments across different campaigns is key to maximizing overall ROI. This involves carefully examining the variables that drove positive results in one campaign and identifying how these variables might apply to others. Consider the audience segments, campaign objectives, and target s for each campaign. If similar patterns emerge across experiments, consider implementing the winning strategies in related campaigns.
For example, if a particular ad copy performed well in a campaign targeting millennials, similar copy variations can be tested in campaigns targeting Gen Z. This approach requires careful consideration of the specific context and variables within each campaign, but can significantly accelerate the optimization process.
Measuring the Impact of Changes
Measuring the impact of changes made based on experiment results is essential for demonstrating the effectiveness of the optimization strategy. Establish clear metrics to track the performance of the campaign before and after the changes are implemented. Crucially, these metrics should be aligned with the campaign’s overall goals, such as increased conversions, higher click-through rates, or improved return on ad spend.
Monitor these metrics closely after implementing the changes to evaluate their effectiveness. Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as click-through rate (CTR), conversion rate, and cost per acquisition (CPA) to quantify the impact of the changes. Regular monitoring and analysis will provide insights into how the changes are affecting the campaign’s performance.
Improvement Table
| Area Optimized | Change Implemented | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Ad copy | Replaced existing ad copy with a more compelling and persuasive version | Increased click-through rate by 15% and conversion rate by 10%. |
| Landing page | Redesigned the landing page to improve user experience and streamline the conversion process. | Reduced bounce rate by 8% and increased conversion rate by 5%. |
| Bidding strategy | Switched from manual bidding to automated bidding, targeting higher conversion value | Reduced cost per acquisition (CPA) by 12% while maintaining conversion volume. |
Closure
In conclusion, Google Ads Experiments are a powerful tool for optimizing your campaigns. By following these six steps, you’ll gain the insights you need to consistently improve performance. From setting up effective experiments to analyzing results and implementing changes, this guide provides a comprehensive roadmap. Don’t just manage your campaigns, master them with the power of experimentation.