Click rate vs click through rate – Click rate vs click-through rate sets the stage for understanding crucial website metrics. CTR (click-through rate) and CR (click rate) are both vital for measuring user engagement, but they differ significantly in how they’re calculated and what they reveal about user behavior. This in-depth look at these metrics will clarify their distinctions, highlighting how they are used in marketing campaigns and websites.
This discussion delves into the nuances of CTR and CR, exploring how they’re calculated, interpreted, and optimized. We’ll uncover the factors influencing these metrics, from ad copy to user experience, and examine how they vary across different marketing channels and user segments. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how to leverage these metrics for improved website performance and better marketing strategies.
Defining Click-Through Rate (CTR) and Click Rate (CR)
Understanding the metrics that measure user engagement with online content is crucial for optimizing digital marketing strategies. Click-Through Rate (CTR) and Click Rate (CR), while often used interchangeably, represent distinct aspects of user behavior. Distinguishing between these two metrics allows for a more nuanced understanding of campaign performance and user interaction.Click-Through Rate and Click Rate are essential metrics for analyzing user engagement with online advertisements and content.
Knowing the difference between them helps businesses refine their strategies to maximize effectiveness. A clear understanding of these metrics allows for better decision-making and improved return on investment.
Understanding click rate versus click-through rate is crucial for any online business. A high click rate, or how often people click on a specific ad, can be great, but it’s the click-through rate that really matters – the percentage of those who see an ad and actually click. This is particularly important in the wake of Temu’s recent ad changes, where the decision to turn off certain ad campaigns is affecting click-through rates significantly.
Learning more about the situation can be helpful, and a deeper dive into why Temu turned off ads can be found here: temu turned off ads what happened. Ultimately, optimizing for click-through rate is key to ensuring a successful online advertising strategy.
Click-Through Rate (CTR) Definition
Click-Through Rate (CTR) is a crucial metric in digital marketing that measures the percentage of users who click on a specific link or advertisement after viewing it. It provides insights into the effectiveness of a particular ad or call-to-action. CTR is a key indicator of how compelling and engaging your content is to your target audience.
Click Rate (CR) Definition
Click Rate (CR) is a metric that measures the percentage of users who click on a specific element within a website or app. This metric focuses on the proportion of total users who click on a particular button, link, or any other interactive element, regardless of whether it’s an advertisement. CR is used to gauge the effectiveness of a particular call to action or user interaction within the platform itself.
Difference between CTR and CR
CTR and CR, while both related to clicks, differ significantly in their scope and application. CTR is primarily associated with advertising campaigns, measuring the response to ads, while CR measures the click-through rate on any element within a website or app, encompassing user interactions beyond just advertisements. The difference lies in the context of the click: CTR is focused on ad effectiveness, while CR encompasses all clicks within a given platform.
Calculation and Application
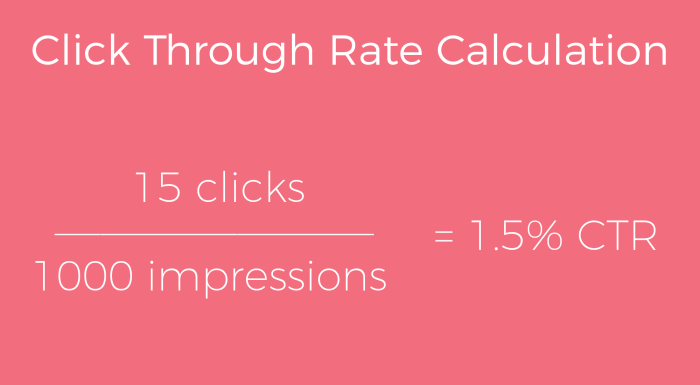
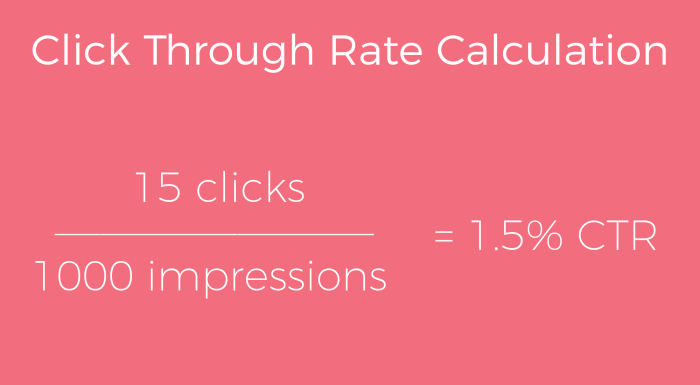
CTR is calculated by dividing the number of clicks by the number of impressions (the total number of times an ad or link was displayed). CR is calculated by dividing the number of clicks by the total number of users who viewed the element.
| Metric | Definition | Calculation | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Percentage of users who click on an ad or link after viewing it. | (Clicks / Impressions)
|
Evaluating ad campaign performance, assessing the effectiveness of call-to-actions in online ads, determining the success of email marketing campaigns. |
| Click Rate (CR) | Percentage of users who click on a specific element within a website or app. | (Clicks / Total Users)
|
Measuring user engagement with website buttons, assessing the effectiveness of calls-to-action on websites or applications, tracking the success of user interactions within an application. |
Importance of Understanding the Difference
A crucial aspect of online marketing is understanding the distinction between CTR and CR. This difference allows for a more comprehensive analysis of user behavior. By evaluating both metrics, businesses can gain a better understanding of their marketing campaigns’ effectiveness and the overall user experience on their platforms. This knowledge enables the development of more targeted and effective strategies.
In essence, understanding the difference between CTR and CR allows for a more nuanced and comprehensive view of user interaction.
Calculating and Interpreting CTR and CR
Click-Through Rate (CTR) and Click Rate (CR) are crucial metrics for evaluating the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and website design. Understanding how to calculate and interpret these values can provide valuable insights into user engagement and campaign performance. This section will delve into the formulas, interpretations, and practical applications of CTR and CR.Calculating and interpreting these metrics correctly is vital for optimizing online campaigns.
A deeper understanding of these metrics will allow you to identify areas of improvement on your website and campaigns, leading to better user engagement and increased conversions.
Calculating Click-Through Rate (CTR)
CTR measures the percentage of users who click on a specific link or advertisement after seeing it. It’s a fundamental metric for assessing the effectiveness of online advertising and website design.
CTR = (Clicks / Impressions) – 100
Where:* Clicks: The total number of times users clicked on a specific link or advertisement.
Impressions
Understanding click rate versus click-through rate is crucial for online success. A poorly designed website, however, can drastically impact your SEO efforts. For instance, redesigns, while seemingly positive, can often lead to significant drops in organic traffic and negatively impact your click-through rate, making it difficult to achieve positive click rates. This is explored in more detail in this insightful article on why redesigns sabotage your SEO.
Ultimately, focusing on a seamless user experience is key to maximizing both click-through rates and overall click rates.
The total number of times the link or advertisement was displayed to users.
Calculating Click Rate (CR)
Click Rate (CR) is a metric used to evaluate the percentage of users who click on a particular element (e.g., a call-to-action button) on a webpage. It’s often used to assess user engagement and the effectiveness of webpage design.
CR = (Clicks / Total Visits) – 100
Where:* Clicks: The total number of times users clicked on a specific element.
Total Visits
The total number of visits to the webpage.
Interpreting CTR and CR Values
Understanding the context of the campaign or website section is critical to interpreting CTR and CR values. A high CTR or CR in one context might be low in another.
- Different marketing campaigns have varying goals and target audiences. A campaign targeting a niche audience might have a lower CTR than a campaign targeting a broader audience. A high CTR on a banner ad might not necessarily translate to high conversions if the landing page is not optimized.
- Website sections with higher CTR or CR often indicate successful design elements. Well-placed call-to-actions, compelling content, and intuitive navigation are examples of elements that contribute to higher click rates. A high click rate on a “contact us” form might indicate high user interest but does not necessarily mean successful conversions.
Examples of High and Low CTR/CR Values and Implications
High CTR/CR values suggest strong user engagement and successful campaign execution. Low values, on the other hand, highlight potential areas for improvement.
- High CTR (e.g., 5%): A high CTR often indicates that the ad or link is relevant and compelling to the target audience. The ad content likely resonates with the user, leading to higher click-through rates.
- Low CTR (e.g., 0.1%): A low CTR suggests that the ad or link might not be relevant to the target audience or is poorly designed. It could indicate a need for refining the ad copy, targeting, or visual appeal.
- High CR (e.g., 10%): A high CR suggests that the webpage’s design elements are effective at capturing user attention and encouraging clicks on specific calls to action. This might be due to compelling design, clear messaging, or well-placed elements.
- Low CR (e.g., 1%): A low CR might indicate that the webpage’s design elements are not engaging enough, or that the calls to action are not clearly defined or attractive enough to the target audience. It could also mean the webpage content is not persuasive enough to encourage clicks on the target elements.
Identifying Areas for Improvement
CTR and CR metrics can help pinpoint areas where a website or marketing campaign can be improved. Comparing CTRs across different ad groups or website sections can reveal which elements are performing well and which need attention.
Table: CTR/CR Values and Interpretations
| Value Range | Interpretation | Actions to Take |
|---|---|---|
| CTR > 5% | High engagement | Maintain and optimize current strategies |
| CTR 1-5% | Moderate engagement | Refine ad copy, targeting, and visuals |
| CTR < 1% | Low engagement | Re-evaluate ad targeting, design, and content |
| CR > 10% | High conversion rate | Maintain and optimize existing design elements |
| CR 1-10% | Moderate conversion rate | Enhance clarity and attractiveness of calls to action |
| CR < 1% | Low conversion rate | Re-evaluate design elements, clarity of calls to action |
Factors Influencing CTR and CR
Understanding click-through rate (CTR) and click rate (CR) is crucial for optimizing online marketing campaigns. These metrics directly reflect user engagement and the effectiveness of your strategies. This section delves into the key factors influencing both CTR and CR, providing actionable insights to improve your campaign performance.CTR and CR are interconnected but measure different aspects of user interaction.
CTR focuses on the initial attraction of an ad or a link, while CR measures the action taken by the user after clicking. A high CTR indicates that your ad or link is enticing and relevant to the target audience, whereas a high CR demonstrates a seamless and compelling user experience following the click.
Ad Copy and Landing Page Design
Effective ad copy and a well-designed landing page are essential for attracting clicks and driving conversions. Compelling ad copy that highlights the unique value proposition of the offer is key to driving interest. The ad copy should clearly communicate the benefit to the user and entice them to click. Similarly, a landing page should align with the ad copy, providing a relevant and user-friendly experience.
A visually appealing and easy-to-navigate landing page with clear calls to action increases the likelihood of conversions.
Targeting and User Experience
Precise targeting ensures that your ad or link reaches the right audience. Tailoring your messaging and visuals to the specific interests and demographics of your target audience is paramount. A good user experience (UX) after clicking is crucial. A seamless and intuitive navigation on the landing page minimizes user frustration and maximizes the chance of a conversion.
Website Design and Call-to-Actions
The design of your website plays a critical role in driving conversions. A clean, uncluttered, and user-friendly website with easy navigation encourages users to explore and engage with your content. Clear and compelling call-to-actions (CTAs) are essential to guide users towards desired actions. Well-placed CTAs, with clear language, will increase the likelihood of conversion.
User Behavior and Engagement
User behavior significantly influences CTR and CR. Understanding how users interact with your ads and website is key to optimizing both metrics. Analyzing user behavior data can reveal patterns and trends, helping to refine your strategies for better engagement. High engagement on your website, through features like interactive content or personalized recommendations, can increase the likelihood of users clicking through and completing desired actions.
Marketing Channels
Different marketing channels have varying impacts on CTR and CR. For instance, social media ads often have higher CTRs due to their visual nature and broad reach, while search engine ads typically have higher CRs because users are actively searching for products or services. The choice of channel should align with your target audience and campaign objectives.
Table of Factors Influencing CTR and CR
| Factor | Impact | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Ad Copy | Attracts clicks by highlighting value proposition | Clear, concise language; strong benefits; compelling visuals |
| Landing Page Design | Drives conversions with clear CTAs and intuitive navigation | Visually appealing; easy-to-find information; clear calls to action |
| Targeting | Increases relevance and reach to the right audience | Demographic targeting; interest-based targeting; retargeting |
| User Experience | Minimizes user frustration, maximizing conversions | Intuitive navigation; fast loading times; mobile-friendliness |
| Website Design | Encourages exploration and engagement | Clean layout; easy navigation; clear hierarchy; visually appealing |
| Call-to-Actions | Guides users towards desired actions | Strong verbs; clear instructions; compelling visuals |
| User Behavior | Provides insights for optimizing campaigns | Heatmaps; clickstream data; session durations |
| Marketing Channels | Affects CTR and CR depending on audience and objective | Social media; search engines; email marketing; display ads |
Optimizing CTR and CR
Click-through rate (CTR) and click rate (CR) are crucial metrics for evaluating the effectiveness of online advertising and website design. Optimizing these metrics leads to better user engagement, increased conversions, and ultimately, a more profitable online presence. Understanding how to optimize these metrics requires a multifaceted approach that considers ad copy, landing page design, user experience, and the utilization of data analytics.Improving CTR and CR goes beyond simply increasing traffic.
It’s about attracting the right audience and guiding them seamlessly through the desired action, whether it’s clicking an ad, making a purchase, or filling out a form. By strategically optimizing both metrics, businesses can achieve higher conversion rates and more impactful campaigns.
Optimizing Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Effective ad copy is the cornerstone of a high CTR. Compelling headlines, clear calls to action, and relevant s are essential components. The ad copy should resonate with the target audience, highlighting the unique value proposition of the product or service. A well-written ad copy captures attention and encourages clicks. For example, instead of a generic “Shop Now,” a more specific call to action like “Get 20% Off Your First Order” can significantly improve CTR.
Optimizing Click Rate (CR)
A high click rate (CR) indicates that visitors who land on the landing page are taking the desired action. A crucial element in optimizing CR is enhancing the user experience (UX). A user-friendly website design, intuitive navigation, and easily accessible information contribute to a positive experience, encouraging users to complete the desired action. A well-designed landing page with a clear and concise message that speaks directly to the user’s needs and expectations can significantly improve the click rate.
A/B Testing Strategies
A/B testing is a powerful method to optimize both CTR and CR. It involves creating variations of ad copy, landing page layouts, and website elements. These variations are then presented to different segments of the target audience, allowing marketers to analyze which version performs better. For instance, testing different headlines for an ad can reveal which one captures more attention and leads to a higher CTR.
Similarly, A/B testing different calls to action on a landing page can identify the most effective option for driving conversions.
User Feedback and Analytics
User feedback provides invaluable insights into the user experience and areas for improvement. Gathering feedback through surveys, feedback forms, and user reviews can reveal pain points and areas where the website or ad copy could be more effective. Furthermore, analytics tools like Google Analytics provide detailed information on user behavior, click paths, and conversion rates. Analyzing this data allows for informed decisions about refining the website and ad copy for maximum impact.
Actionable Steps for Optimizing CTR/CR
- Conduct thorough research to identify relevant s that resonate with the target audience. This research should inform the content of both the ad copy and the landing page.
- Craft compelling ad copy with clear and concise language, highlighting the unique value proposition of the product or service.
- Design user-friendly landing pages with intuitive navigation, clear calls to action, and easily accessible information.
- Implement A/B testing to compare different variations of ad copy and landing page elements to identify the most effective versions.
- Gather user feedback through surveys, reviews, and other feedback mechanisms to understand user experience and identify areas for improvement.
- Utilize analytics tools to track and monitor CTR, CR, and other key metrics to measure campaign performance and make data-driven decisions.
- Continuously refine and optimize ad copy, landing pages, and website elements based on performance data and user feedback.
CTR and CR in Different Contexts
Click-Through Rate (CTR) and Click Rate (CR) are crucial metrics for evaluating the effectiveness of digital marketing campaigns. Understanding how these metrics behave across various channels, demographics, and business objectives provides valuable insights for optimizing campaigns and achieving desired outcomes. This section delves into the nuances of CTR and CR performance in different contexts.Analyzing CTR and CR across various digital marketing platforms, user segments, and business goals allows for a more refined understanding of campaign performance.
This deeper understanding allows for more targeted optimization strategies and ultimately, better results.
CTR and CR Performance Across Digital Marketing Channels
Different channels have inherent characteristics that influence CTR and CR. The nature of the audience and the format of the advertisement impact the metrics significantly.
| Channel | Average CTR/CR | Factors Influencing Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Search Ads | Generally higher CTR (around 2-4%) and variable CR (depends on the conversion goal) | Relevance of s, ad copy quality, landing page experience, competition level |
| Social Media Ads | Lower CTR than search ads (around 0.5-2%) but can have higher CR for specific campaigns | Target audience alignment, ad creative quality, platform-specific ad formats, engagement with the post |
| Email Marketing | Relatively low CTR (around 0.2-1%) but potentially high CR for nurtured leads | Email list quality, subject line, email content relevance, timing of sending |
| Display Ads | Lowest CTR among the channels (around 0.1-0.5%) but can achieve high CR if targeting is precise | Relevance of ad to user interests, ad format, ad placement |
The table above provides a general overview. Actual CTR and CR will vary based on specific campaign elements and target audience.
Click rate and click-through rate are often used interchangeably, but they’re subtly different. Ultimately, high click rates, and even high click-through rates, don’t automatically translate into real value if they aren’t driving genuine engagement. Think about how a focus on value creation, rather than simply revenue extraction, might influence those metrics. For example, if you’re optimizing for true user value, you might see a lower click-through rate but a higher conversion rate and increased customer lifetime value.
Ultimately, a deeper understanding of value creation vs revenue extraction is key to interpreting your click rate vs click-through rate data accurately. This leads to more strategic decisions regarding your campaigns and products.
CTR and CR Variation Across Demographics, Click rate vs click through rate
CTR and CR can fluctuate based on the demographic characteristics of the target audience.Different age groups, genders, locations, and interests may react differently to the same ad or content. For example, a younger demographic might respond better to visually engaging ads on social media, while an older demographic might be more receptive to detailed information in email campaigns. Therefore, segmenting audiences and tailoring ads to specific demographics is essential for maximizing CTR and CR.
Significance of CTR and CR for Business Objectives
The significance of CTR and CR varies depending on the business objective. A high CTR is not necessarily indicative of a successful campaign.For lead generation campaigns, a high CTR combined with a high CR on the landing page is a positive indicator. Conversely, for brand awareness campaigns, a high CTR might not be the primary goal. Instead, focus should be on driving traffic and engagement with the brand.
Examples of Successful CTR/CR Optimization Campaigns
Several successful campaigns showcase the importance of optimizing CTR and CR.A clothing retailer that increased its social media ad CTR by 25% through A/B testing different ad visuals. Another example involves an e-commerce company that improved email open rates and click-through rates by segmenting its email list and personalizing email content.
Tools and Techniques for Measurement and Analysis
Understanding click-through rates (CTR) and click rates (CR) is crucial for optimizing online campaigns. Accurate measurement and analysis of this data allow marketers to identify trends, pinpoint areas for improvement, and ultimately drive better results. This section delves into the tools and techniques used to effectively track and analyze CTR and CR data.
Popular Tools for Tracking CTR and CR
Several powerful tools are available for monitoring CTR and CR. These tools offer detailed insights into campaign performance, allowing for data-driven decisions. Choosing the right tool depends on factors like budget, desired level of detail, and the specific needs of your campaign.
- Google Analytics: A comprehensive analytics platform, Google Analytics provides extensive data on website traffic, including click-through rates and click rates for various elements like ads, links, and pages. It offers robust reporting features and integrates seamlessly with other Google products.
- Hotjar: This tool provides heatmaps and recordings of user behavior on websites. These visual representations can reveal where users are clicking and scrolling, giving valuable insight into user interaction with your website’s design. This data is invaluable for optimizing website layout and navigation.
- Clicky: Another popular web analytics tool, Clicky offers detailed reports on website traffic, including CTR and CR data. It’s known for its user-friendly interface and ability to provide real-time insights.
- Adobe Analytics: A powerful solution for large enterprises and complex websites, Adobe Analytics offers advanced features for analyzing website traffic and user behavior, including detailed tracking of CTR and CR. Its robust reporting capabilities make it ideal for comprehensive performance analysis.
- VWO (Visual Website Optimizer): This tool is specifically designed for A/B testing and multivariate testing, allowing you to experiment with different versions of your website or marketing materials. By testing various elements, you can discover what resonates best with your audience, directly impacting CTR and CR.
Methods for Analyzing CTR and CR Data
Analyzing CTR and CR data requires more than just gathering numbers. It involves identifying trends, patterns, and correlations to gain meaningful insights. Effective analysis involves considering the context surrounding the data, like recent changes in marketing campaigns or website updates.
- Trend Identification: Tracking CTR and CR over time reveals patterns and trends in user behavior. Monitoring seasonal variations, daily fluctuations, and overall performance improvements or declines provides valuable insights.
- Pattern Recognition: Analyzing CTR and CR data across different segments (e.g., demographics, geographic locations, or device types) reveals patterns in user behavior. These insights can be used to tailor marketing strategies to specific segments for increased effectiveness.
- Correlation Analysis: Identifying correlations between CTR/CR and other variables (e.g., ad copy, landing page design, or specific s) helps understand which factors significantly impact user engagement.
Using Data Visualization Tools
Data visualization tools are crucial for transforming raw CTR and CR data into easily digestible insights. These tools make it easier to spot trends and patterns.
- Charts and Graphs: Representing CTR and CR data using charts (e.g., line graphs, bar graphs, or pie charts) allows for a clear visual representation of trends over time or across different segments. This helps identify significant fluctuations and patterns easily.
- Dashboards: Dashboards consolidate key metrics, including CTR and CR, into a single view. This centralized view provides an overview of overall performance and helps track progress toward goals. Dashboards facilitate quick identification of potential issues or opportunities.
- Heatmaps: Heatmaps are useful for understanding user engagement on websites by highlighting areas with higher or lower click rates. This data provides insights into website design effectiveness and helps optimize user experience.
Segmenting Data for Deeper Understanding
Segmenting data allows for a more nuanced understanding of CTR and CR performance. Dividing data by different criteria helps pinpoint specific factors driving engagement or disengagement.
- Demographic Segmentation: Analyzing CTR and CR data based on age, gender, location, or other demographic factors reveals how these factors influence user engagement. This allows marketers to tailor campaigns to specific demographics, increasing their effectiveness.
- Behavioral Segmentation: Dividing data by user behavior, such as browsing history or previous interactions, helps understand how specific actions impact engagement. This approach enables targeted optimization for user-specific actions.
- Device Segmentation: Analyzing CTR and CR based on the device users are using (desktop, mobile, tablet) allows for tailored experiences and optimization of content for each device.
Tools for CTR/CR Tracking and Analysis
| Tool | Key Features | Data Visualization Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Google Analytics | Comprehensive website analytics, detailed tracking of various interactions, integration with other Google products. | Various chart types (line, bar, pie), customizable dashboards. |
| Hotjar | Heatmaps, recordings of user behavior, scroll maps, and other interaction data. | Interactive heatmaps, user recordings, visual representations of user engagement. |
| Clicky | Detailed reports on website traffic, including real-time data. | Charts, graphs, and other visualizations to represent website traffic and user behavior. |
| Adobe Analytics | Advanced analytics for large enterprises, detailed tracking of user behavior and website interactions. | Advanced dashboards and reporting features, various chart types and customization options. |
| VWO | A/B testing and multivariate testing, focused on optimizing website elements to improve conversions. | Visual representations of test results, graphs to compare different variations. |
Wrap-Up: Click Rate Vs Click Through Rate
In conclusion, understanding the difference between click-through rate (CTR) and click rate (CR) is paramount for effective digital marketing. CTR focuses on ad visibility, while CR emphasizes the user journey and actions on a website. By meticulously tracking and analyzing both, businesses can gain valuable insights into user behavior, optimize campaigns, and ultimately boost conversion rates. The key takeaway is that a comprehensive approach, considering both metrics, leads to more informed decisions and stronger results.