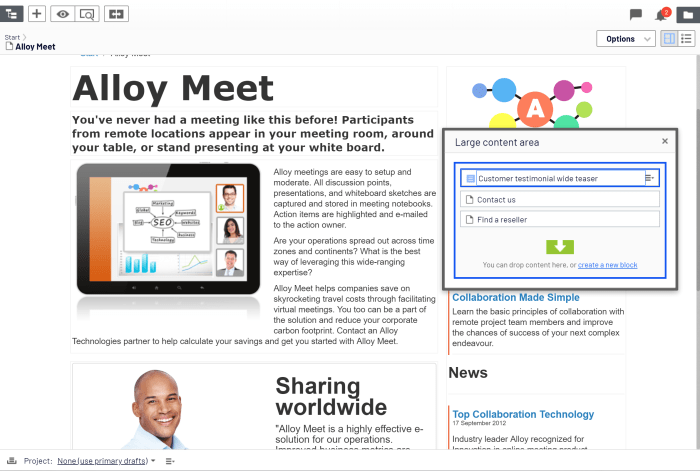
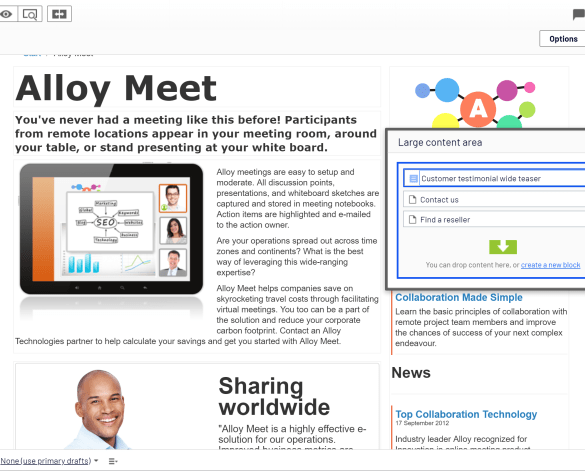
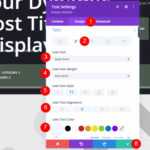
Add editor view top section page – Adding editor view top section page is a key strategy for optimizing user experience in content management systems. This approach puts essential editing tools at the forefront, enhancing workflow efficiency and streamlining content creation. It’s a powerful way to improve the usability of the platform for editors, allowing them quick access to necessary features and tools. The design, functionality, and user experience considerations are crucial for success.
This comprehensive guide delves into the specifics of implementing an editor view at the top of the page. We’ll cover everything from defining the editor view and its typical functionalities to visual design considerations, accessibility, and illustrative examples.
Defining the “Editor View”
An editor view, in the context of a web page, is a specialized interface designed specifically for content creation and modification. It’s a crucial component for users who need to manage and update the website’s content, rather than just browsing it. This interface differs significantly from the standard user view, which is primarily for browsing and interacting with content.Editor views provide tools and functionalities that streamline the content editing process.
They typically include features for formatting text, inserting media, managing images and videos, and controlling the overall presentation of the content. The primary purpose is to facilitate efficient content updates and revisions without requiring extensive technical knowledge.
Typical Functionalities
Editor views offer a wide range of tools to facilitate content modification. These tools enhance the editing experience by allowing users to easily format text, insert media, and manage various aspects of the content’s presentation. They are designed with a user-friendly approach, minimizing the need for complex technical knowledge.
- Text Formatting: Tools for adjusting font styles, sizes, colors, and alignment are essential for creating visually appealing and structured content. Bolding, italicizing, underlining, and bullet points are typical features.
- Media Insertion: Users can seamlessly integrate images, videos, audio clips, and other media types into the content. This functionality ensures that the content is rich and engaging.
- Layout Management: Features for controlling the structure and organization of the content are crucial. These tools allow users to create headings, paragraphs, lists, and other structural elements that enhance the readability and visual appeal of the content.
- Version Control: The ability to track changes and revert to previous versions is important for maintaining a history of edits and allowing users to easily undo mistakes or recover previous versions.
- Collaboration Tools: Some editor views allow multiple users to work on the same content simultaneously, with features like real-time collaboration, commenting, and version control.
Common Use Cases
Editor views are indispensable for websites requiring frequent content updates. They empower users to efficiently manage and modify the content, without needing extensive technical expertise. These applications are vital for a wide array of online platforms.
- News Websites: News outlets rely on editor views to quickly update articles, headlines, and other content.
- Blogs and Personal Websites: Bloggers use editor views to write and publish posts, manage their website’s content, and maintain an organized layout.
- E-commerce Platforms: Online stores often utilize editor views for updating product descriptions, images, and pricing information.
- Educational Portals: Educational websites can use editor views for managing course materials, assignments, and other educational resources.
Layout and Structure
A well-designed editor view typically employs a clear and intuitive layout. The interface is structured to minimize distractions and maximize the user’s focus on the content being edited. Key elements are organized for ease of use.
Adding an editor view to the top section of a page is crucial for content management. Understanding how Google’s rich results can improve search visibility is key. This is directly relevant to optimizing your page, and you should really check out why Google’s rich results tool to see how this can be achieved. Ultimately, a well-designed editor view top section significantly boosts user engagement and streamlined content updates.
- Visual Editor: A visual editor allows users to see the content as it will appear on the website, providing real-time feedback on the formatting and presentation. This helps maintain a consistent look and feel across the website.
- Formatting Toolbar: A toolbar with various formatting options, such as font styles, sizes, colors, and alignment, is crucial for quick and easy formatting changes.
- Media Uploader: A dedicated section for uploading and managing media files ensures efficient media integration into the content.
- Navigation and Control Panels: Panels that allow for navigating through different sections of the content and controlling the editing process are essential.
Differences from Standard User View
The primary distinction between an editor view and a standard user view lies in the available functionalities. The editor view is explicitly designed for content creation and modification, while the standard user view is focused on browsing and interacting with the content.
| Feature | Editor View | Standard User View |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Content creation and modification | Content browsing and interaction |
| Functionality | Extensive formatting tools, media management, version control | Limited formatting options, basic navigation |
| User Role | Content creators and editors | Website visitors and consumers |
Content Organization Within the View
Organizing the top section of the editor view is crucial for user experience and efficient content creation. A well-structured top section allows users to quickly access important information and make necessary adjustments without getting lost in a sea of options. Clear categorization and intuitive layouts are key to maximizing productivity.Effective content organization ensures users can readily find and manage relevant elements, making the editing process more streamlined and less time-consuming.
This directly impacts the overall user satisfaction and the quality of the final product.
Content Arrangement Options
Different layouts for the editor view’s top section can be implemented to suit various needs and preferences. A structured approach is essential for maintaining a consistent and user-friendly interface. Below is a table outlining potential layouts:
| Layout Type | Description | Use Cases | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Content organized in rows and columns, providing a visually appealing and structured presentation. | Displaying multiple pieces of information simultaneously, like metadata or tags. | A grid displaying image thumbnails, titles, and brief descriptions for articles. |
| List | Content presented sequentially in a list format. | Showing a series of options or actions, such as a list of available templates. | A list of recent edits with timestamps and user names. |
| Accordion | Sections of content are collapsed by default, revealing details when expanded. | Presenting large amounts of information in a compact way, allowing users to focus on specific areas. | A section for advanced options within the editor, hidden until the user chooses to expand it. |
| Tabbed Interface | Content is divided into different tabs, each containing a specific set of information. | Managing various aspects of content, such as metadata, tags, and formatting options. | A tabbed interface to switch between sections like “Basic Settings”, “Advanced Options”, and “Preview”. |
Data Type Display Methods
Implementing diverse data types within the editor view top section requires careful consideration of visual presentation. Consistent display methods ensure a seamless user experience.
- Text: Textual information can be displayed in labels, headings, or paragraphs, utilizing different font styles and sizes to highlight important details. For example, the title of an article or a description of a section can be displayed using a prominent font.
- Images: Images should be displayed in a visually appealing manner, with appropriate sizing and aspect ratios to avoid distortion. Thumbnail previews are useful for showing images associated with a post or article.
- Links: Links can be embedded within the text or presented as buttons, clearly indicating the destination of the link. Using descriptive text for links improves user understanding.
- Buttons: Buttons are used for actions, such as saving, previewing, or applying formatting changes. Clear labels and visually distinct appearances are important to avoid confusion.
Data Entry Fields
Incorporating data entry fields allows users to customize content within the editor view top section. Using appropriate input fields enhances user experience.
- Text Boxes: Text boxes allow users to enter and edit text-based information, like titles, descriptions, or s.
- Dropdowns: Dropdowns provide a list of predefined options, making it easier for users to select choices. For instance, choosing a category or a template.
- Checkboxes: Checkboxes allow users to select multiple options from a predefined set, such as selecting specific tags or formatting styles.
- Radio Buttons: Radio buttons provide mutually exclusive options, such as selecting a single template or a publication status.
Layout Considerations
The layout of the editor view top section directly impacts user interaction and efficiency. The layout should be chosen to align with the purpose and scope of the editor.
- Grid Layouts: Grid layouts provide a structured and organized view, making it easy to navigate various elements.
- List Layouts: List layouts are well-suited for sequential data or a series of choices. They are intuitive and straightforward.
- Custom Layouts: Custom layouts are designed for specific use cases. These may involve innovative visual arrangements, unique functionality, or integrations with other systems.
Interaction & Functionality
The top section of the editor view is crucial for rapid control and initiation of actions. Effective interaction design directly impacts user experience and workflow efficiency. This section provides a streamlined interface for essential tasks, enabling users to manage their editing process seamlessly.The design of this top section should prioritize intuitive interaction and a clear visual hierarchy. The layout should be well-organized, making it easy for users to locate and engage with the desired controls.
The interaction mechanisms should be consistent with other parts of the application, fostering familiarity and reducing learning time.
Interactive Elements
This section details the common interactive components typically found in an editor view’s top bar. Buttons, toggles, and dropdowns are essential for quick actions and customization. Well-designed visual cues, like hover effects or highlighted states, improve usability and help users understand the effect of their interactions.
- Buttons: Action buttons, like “Save,” “Publish,” “Undo,” “Redo,” “Preview,” and “Cancel,” are fundamental. These buttons should be clearly labeled and visually distinct to avoid confusion.
- Toggles: Toggle switches are useful for controlling settings or options (e.g., “Bold,” “Italic,” “Show Comments”). A clear on/off state for each toggle is vital for immediate understanding.
- Dropdowns: Dropdown menus provide a way to select from a range of options. They are suitable for tasks like choosing font styles, colors, or specific formatting elements.
Typical Workflow and Actions
The editor view should facilitate a smooth and efficient workflow. Users should be able to perform common tasks, like saving their work, previewing their edits, and applying various formatting options. Actions should be well-defined, with clear feedback to users on the successful completion of each task.
- Saving: The “Save” action is critical. Users should be able to save their work at various intervals to prevent data loss. The system should offer automatic saving mechanisms for enhanced safety.
- Previewing: A “Preview” function allows users to see how their edits will appear in the final output. This preview should ideally show the formatted text as it will be displayed.
- Formatting: Users should be able to apply various formatting options, such as font changes, text alignment, and paragraph formatting. The interface should clearly display the current formatting settings.
User Feedback Mechanisms
Incorporating user feedback is crucial for improving the editor view. The system should provide clear and timely feedback to users on the actions they perform. Visual cues, such as success/error messages or loading indicators, are effective ways to notify users of ongoing or completed actions.
I’ve been working on the add editor view top section page, and it’s been a real challenge. Figuring out the best way to present this information is key. Finding the right marketing partner is crucial for success, especially when you’re looking at options like choosing a marketing company st louis. Ultimately, the goal is to make the add editor view top section page as user-friendly as possible for everyone.
- Visual Feedback: Visual cues, such as highlighting changes, confirming successful saves, and displaying loading indicators, provide immediate feedback to users.
- Error Messages: Clear error messages should be displayed to guide users in fixing errors or correcting mistakes.
- Progress Indicators: Progress indicators are essential during long-running operations, like large file uploads or complex formatting tasks.
Interaction Types and Actions
The following table demonstrates different interaction types and their corresponding actions in the editor view’s top section.
| Interaction Type | Action |
|---|---|
| Clicking a “Save” button | Saves the current document |
| Toggling a “Bold” switch | Applies/removes bold formatting |
| Selecting a font from a dropdown | Changes the font of the selected text |
| Clicking a “Preview” button | Opens a preview window showing the document’s formatted appearance |
Approaches to Handling User Input
Different approaches can be used to handle user input in the top editor view section. A crucial consideration is the speed and efficiency of the response.
- Asynchronous Operations: For tasks that take time, asynchronous operations are preferable to prevent the UI from freezing. Progress indicators are vital in such cases.
- Immediate Feedback: For actions with immediate effects, the interface should provide instant feedback to users (e.g., changes in formatting are reflected instantly).
- Validation: Input fields should validate user input to prevent errors. Clear error messages guide users toward the correct input.
Visual Design Considerations
Crafting a visually appealing and intuitive editor view top section is crucial for user experience. A well-designed top section enhances user engagement and provides a smooth editing process. This section acts as the primary control panel, so visual appeal and ease of use are paramount.The top section of the editor view needs to seamlessly integrate with the overall website design, making it a natural part of the user flow.
Visual consistency is key to ensuring users feel comfortable and confident navigating the editing tools. Implementing a clean and uncluttered design is essential to avoid overwhelming users with too many options or complex layouts.
Color Palettes
Color palettes play a significant role in establishing brand identity and guiding user interactions. Consistent color usage creates a recognizable and trustworthy experience. A well-chosen color scheme can subtly influence user moods and create a specific atmosphere within the editor. For instance, a calming blue palette might be suitable for a collaborative editing environment, while a vibrant orange palette might work better for a creative editing application.
- A primary color, usually associated with the brand, should be used for important elements such as buttons and calls to action.
- Secondary colors should be used for accents and supporting elements, such as highlighting selected text or emphasizing specific actions.
- Neutral colors, like grays or whites, should be used for backgrounds and separators to create visual balance and readability.
Typography Choices
Typography choices significantly impact readability and brand personality. Selecting fonts that are easy to read, particularly in smaller sizes, is essential for ensuring the editor view is user-friendly. Font size and line spacing must be optimized for clarity and reduce eye strain.
- Choose a font family that aligns with the overall brand aesthetic. A clean, sans-serif font like Arial or Helvetica is often a good choice for its readability, while a serif font like Times New Roman might be appropriate for a more traditional feel.
- Ensure that font sizes are scalable across different screen sizes and devices. This guarantees a consistent and user-friendly experience regardless of the device used.
- Use appropriate spacing between lines of text (line height) and between characters (letter spacing) to enhance readability.
Imagery and Visual Elements
Visual elements such as icons, logos, and images should be strategically incorporated to enhance understanding and improve user engagement. Icons, especially, should be clear and instantly recognizable, representing the associated action or function effectively. High-quality imagery can also be used to create a visual hierarchy, guide users’ attention, and enhance the overall aesthetic appeal of the editor.
- Use high-quality, relevant images and graphics to visually represent the available options and functionalities.
- Icons should be easily identifiable and represent their intended function clearly. For instance, an icon of a pencil might represent the editing function, and a save icon should be readily apparent.
- Use images that are consistent with the overall brand aesthetic. Ensure that the images’ resolution and quality are high enough to maintain a professional appearance.
Visual Design Best Practices
Adhering to visual design best practices ensures a user-friendly and aesthetically pleasing editor view. Key best practices include ensuring consistency in style, color scheme, and typography across all platform elements. Employing a responsive design that adapts to different screen sizes and resolutions is also critical.
- Prioritize clear visual hierarchy. Elements that are more important or require immediate attention should be visually prominent.
- Use whitespace effectively to create visual breathing room and avoid clutter.
- Ensure accessibility for users with disabilities. For example, ensure sufficient color contrast and proper font sizes.
Accessibility & User Experience
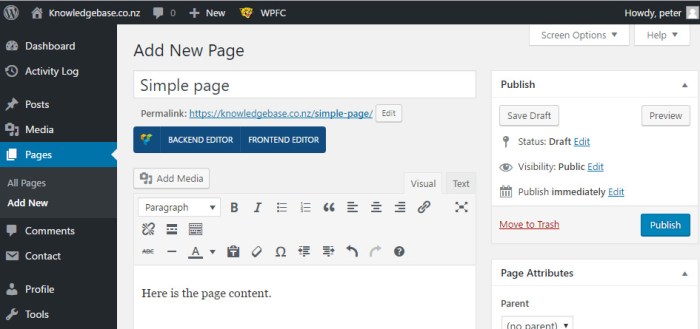
Designing an editor view that’s both powerful and usable requires careful consideration of accessibility and user experience. A well-designed top section caters to a wide range of users, ensuring everyone can effectively utilize the tool, regardless of their abilities or preferences. This section dives into key strategies for creating a truly inclusive and intuitive editor view.A user-friendly editor view fosters positive interactions and a smooth workflow.
I’ve been tinkering with the add editor view top section page lately, and it’s been a bit of a challenge. It’s interesting to see how Google is pushing the boundaries of search on mobile with features like Circle integration on iPhones, as detailed in this recent article about google brings circle to search to iphone. Hopefully, some of these innovative approaches can help streamline the editor view’s top section page layout for a better user experience.
This translates to higher user satisfaction and increased productivity, ultimately leading to a more effective tool for everyone. Prioritizing accessibility from the outset is critical for creating a universally usable product.
Accessibility Considerations for Users with Disabilities
Ensuring accessibility for users with disabilities is not an afterthought but a foundational element of design. A multitude of factors contribute to an accessible design. These include color contrast, keyboard navigation, screen reader compatibility, and alternative text for images. Adhering to WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) standards ensures the editor view is usable for people with visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive impairments.
This proactive approach fosters a more inclusive and equitable user experience.
User-Friendly and Intuitive Design
Creating a user-friendly and intuitive editor view involves anticipating user needs and designing a logical flow. The design should be easily navigable and predictable, with clear visual cues and intuitive controls. Simple and clear labeling for elements, consistent formatting, and well-organized layout enhance user comprehension and reduce frustration. Users should intuitively understand how to perform actions and accomplish tasks.
Usability for All Users
Making the editor view highly usable involves careful consideration of diverse user needs and skill levels. For example, providing multiple ways to perform the same action, such as keyboard shortcuts alongside mouse clicks, enhances usability. Offering comprehensive help documentation and tutorials can further support users who need additional guidance. This inclusive approach empowers all users to effectively utilize the editor view.
Optimizing User Experience, Add editor view top section page
Optimizing the user experience involves a multi-faceted approach. This includes clear and concise instructions, visually appealing and easy-to-understand interface elements, and a responsive design that adapts to various screen sizes and devices. The layout should be clean and uncluttered, with ample white space to improve readability and visual clarity.
Importance of User Testing and Feedback
Incorporating user testing and feedback throughout the design process is crucial for identifying potential usability issues early on. This allows for iterative improvements and ensures the final product aligns with user needs and expectations. Observing users interacting with the editor view provides invaluable insights into areas needing adjustments, thereby refining the experience and enhancing overall satisfaction. Feedback from diverse user groups is especially valuable for ensuring inclusivity and addressing specific needs.
Analyzing user behavior and patterns helps identify usability problems before they become major obstacles.
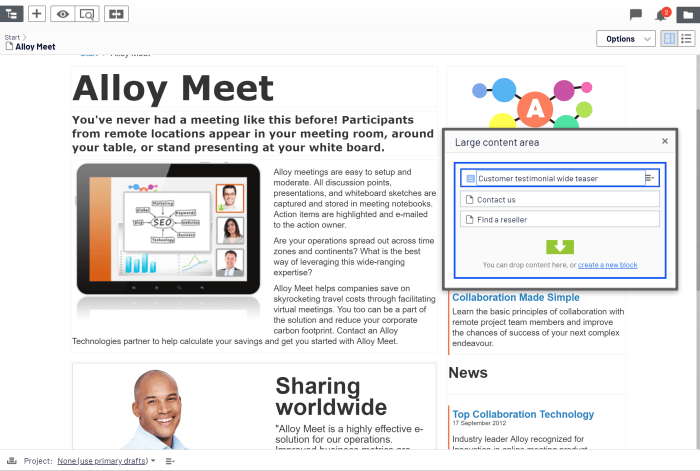
Illustrative Examples of Editor View Top Sections: Add Editor View Top Section Page
The editor view top section, often the first thing a user interacts with, sets the tone for the entire editing experience. Its design and functionality directly impact the efficiency and user satisfaction of content creation. Understanding how different platforms implement this crucial section reveals best practices and common pain points.This section explores real-world examples of editor view top sections, ranging from content management systems (CMS) to e-commerce platforms.
Each example demonstrates how the layout and functionality of the editor view integrate with the overall website architecture, addressing different aspects of content creation and management.
Content Management Systems (CMS)
Content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla utilize editor views to allow users to create, edit, and manage website content. These views typically feature a toolbar with formatting options, image insertion, and links. The integration with other sections of the webpage is seamless, allowing users to easily preview changes in real-time. For instance, a WordPress editor view allows users to add images, change text formatting, and add links within the content body.
This integration ensures the user experience remains consistent throughout the platform, making it easy to create and maintain web content.
E-commerce Platforms
E-commerce platforms like Shopify and WooCommerce have editor views specifically tailored to product listings and descriptions. These views often include features for managing product images, descriptions, pricing, and inventory. The layout of these editor views emphasizes visual appeal, allowing users to easily create compelling product pages. The integration with the product catalog is key; editing a product description in the editor view immediately updates the product page.
The editor view often includes functionalities to update stock levels and manage different product variations.
Social Media Platforms
Platforms like Facebook and Instagram utilize editor views to allow users to create posts, stories, and other content. The layout of these editor views is typically simple and intuitive, focusing on the content itself. The integration with the social media platform’s feed is crucial, ensuring that the newly created content is visible to the intended audience. The views often prioritize visual elements, such as images, videos, and links, and their ability to be embedded within the platform’s content stream.
Specific CMS Implementations
- WordPress: The WordPress editor view typically features a visual editor (WYSIWYG) with formatting options, media upload, and link insertion. The view’s integration with the site’s structure is seamless, allowing users to quickly create and manage content.
- Drupal: Drupal’s editor view often provides a more flexible and customizable approach. Users have options to select different display formats and styles, offering greater control over the presentation of their content.
- Joomla: Joomla editor views usually offer a balance between visual editing and code-based customization. The layout is often adaptable to different content types, allowing users to create varied web pages.
Key Considerations in Editor View Design
The effectiveness of an editor view is directly tied to its design and functionality. Clear and intuitive navigation, along with well-organized toolbars, contribute significantly to user experience. The ability to preview changes before publishing is crucial, allowing users to ensure their content is formatted correctly and meets design requirements. Real-time feedback mechanisms, such as visual previews, help users identify issues promptly.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, strategically placing the editor view in the top section can dramatically improve the editor’s workflow. By considering factors like user experience, accessibility, and visual design, you can create a streamlined and intuitive experience. This approach, when implemented effectively, boosts productivity and satisfaction among content creators.