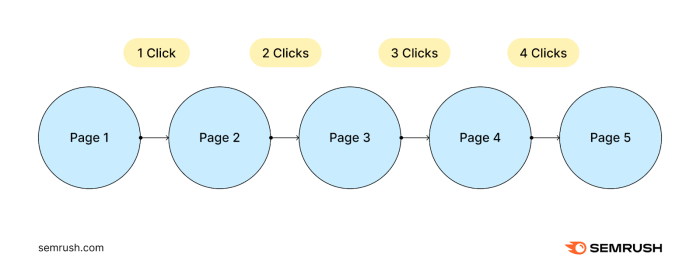
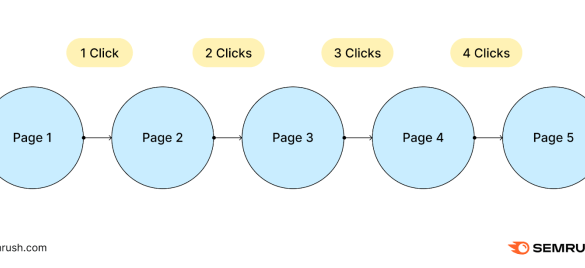
Impact on search traffic due to excessive depth of pagination is a critical issue for website owners. Deep pagination, with its numerous numbered pages or endless scrolling, can severely hinder search engine crawlers, making it difficult for them to discover and index all the content on your site. This can lead to lower rankings and reduced organic traffic.
We’ll explore the problem, the negative impacts on user experience, and the technical solutions to mitigate these issues.
Imagine a vast library with books organized in deeply nested sections. If the librarian can’t easily navigate the stacks, the patrons will have a difficult time finding the information they need. Similarly, search engines struggle with websites using complex pagination. We’ll analyze the different pagination methods, how search engines deal with them, and strategies to make your website more discoverable.
Defining the Problem: Impact On Search Traffic Due To Excessive Depth Of Pagination
Excessive pagination, a common web design practice, involves breaking up content into multiple pages. While seemingly straightforward, its implementation can significantly hinder user experience and negatively impact search engine visibility. This is particularly true when the number of pages becomes substantial, leading to a frustrating user journey and potentially reduced engagement.Pagination, when implemented poorly, can cause several problems.
A user might need to navigate numerous pages to find the desired information, a process that can be time-consuming and tedious. Moreover, a deep pagination structure can negatively affect the overall website architecture and user experience, making the site feel less intuitive and navigable. Understanding the different methods of pagination, their implications, and how to implement them effectively is crucial for optimizing user engagement and search engine visibility.
Pagination Methods
Different methods exist for implementing pagination, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these methods is crucial for optimizing user experience and website performance.
- Numbered Pages: This traditional approach involves displaying numbered page links. Users click on the desired page number to access the relevant content. While simple, it can be problematic when dealing with extensive content. Users often need to navigate through multiple pages to reach their desired information, leading to a potentially negative user experience. For example, a blog post with dozens of pages might discourage users from reading the entire article.
- Infinite Scroll: This method displays content continuously as the user scrolls down the page. New content loads automatically as the user approaches the end of the current page. This can improve the user experience by reducing the need to manually navigate through multiple pages. For instance, news websites often use infinite scroll to display the latest articles, keeping the user engaged and up-to-date.
- Load More Buttons: This approach displays a limited amount of content on a single page. A “Load More” button allows users to progressively load additional content. This method can be a good compromise between numbered pages and infinite scroll. It offers a more controlled loading experience than infinite scroll, while allowing for better organization of content compared to numbered pages, especially for large datasets.
For example, product listings often use load more buttons to display products in batches.
Potential Impacts on User Experience
Deep pagination, characterized by numerous pages, can significantly impact user experience. A user might lose interest if they encounter numerous pages to find the desired information. This, in turn, can lead to reduced time spent on the site and potentially lower conversion rates. Moreover, deep pagination can create a poor user experience by making the site feel overwhelming and less user-friendly.
Pagination Use Cases
The optimal pagination method depends heavily on the context of the website and the type of content being displayed. The following table Artikels different pagination methods and their typical use cases:
| Pagination Method | Typical Use Case | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Numbered Pages | Blog posts, articles, long lists of items | Suitable for easily navigable content with a defined structure. |
| Infinite Scroll | News feeds, social media updates, product catalogs | Efficient for displaying frequently updated content. |
| Load More Buttons | Product listings, blog posts with many comments, image galleries | Provides a balance between numbered pages and infinite scroll, allowing for controlled content loading. |
Impact on Crawlability
Deep pagination, with its numerous pages of results, presents a significant hurdle for search engine crawlers. This impacts how effectively search engines can discover and index the content on a website, potentially affecting search visibility. Understanding these challenges is crucial for website owners to optimize their site architecture and improve search engine rankings.Crawlers, the automated agents of search engines, systematically explore websites to collect and index information.
When faced with deep pagination, they encounter a series of links leading to increasingly deeper layers of content. This can significantly impact the crawl budget allocated to a website, leading to missed pages and incomplete indexing. The efficiency of the crawl process is directly affected by the structure of the pagination, with deep pagination often resulting in a less thorough crawl and index.
Crawler Navigation Challenges
Crawlers follow links, and with deep pagination, they face a considerable navigational challenge. Each page’s links often point only to the next page of results, creating a long chain of clicks that can exhaust the crawl budget. This means crawlers may not have enough resources to explore all pages, potentially missing important content, especially on sites with hundreds or thousands of pages.
The crawler’s limited budget forces it to prioritize links, sometimes resulting in pages lower in the pagination sequence being missed entirely. This limitation is further compounded by the dynamic nature of some pagination schemes, which often use JavaScript or AJAX to load pages, adding complexity to the crawl process.
Indexing Impact
Excessive pagination can severely impact indexing. Search engines may not be able to fully index all pages, leading to incomplete or outdated representations of the website’s content. This is particularly true for sites that use intricate pagination methods. The crawler may only have enough resources to crawl a small portion of the content, resulting in a significant amount of valuable content being excluded from the index.
The consequence is that relevant pages may not be returned in search results, which can negatively impact user experience and website traffic.
Optimization Strategies
Implementing efficient pagination strategies can mitigate the indexing issues associated with deep pagination. One crucial strategy is to employ techniques like pagination through the use of sitemaps, which allow search engine crawlers to readily identify and access all pages. Using canonical tags to establish a clear hierarchy can also aid crawlers in understanding the site structure and ensure they don’t crawl duplicate content.
Implementing a well-structured pagination strategy that facilitates easy navigation for crawlers is essential. Using server-side pagination is often a better choice for crawlers.
Comparison of Pagination Approaches
| Pagination Approach | Indexing Effectiveness | Crawler Experience | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Server-Side Pagination | High | Efficient; crawler can easily access all pages | Using database queries to retrieve data and display it on different pages |
| Client-Side Pagination (JavaScript/AJAX) | Moderate | Complex; requires significant effort to follow links | Loading pages dynamically as the user scrolls |
| Infinite Scroll | Low | Very complex; crawlers may not fully understand the content structure | Loading more content as the user scrolls down the page |
The table illustrates the varying effectiveness of different pagination approaches in terms of crawler experience and indexing effectiveness. Server-side pagination often results in higher indexing effectiveness due to crawlers having easy access to all content. Client-side pagination, while potentially more user-friendly, can be more challenging for crawlers to navigate. Infinite scroll is the most complex approach, often making it difficult for crawlers to fully understand the content structure and potentially hindering indexing.
User Experience and Engagement
Deep pagination, with its numerous pages of results, can significantly impact user experience and engagement on a website. Users often perceive a large number of pages as cumbersome and time-consuming, leading to decreased satisfaction and potentially lower conversion rates. Understanding the negative effects of excessive pagination on user engagement metrics is crucial for optimizing website design and user experience.
Impact on Engagement Metrics
Users encountering deep pagination often exhibit reduced engagement. This manifests in higher bounce rates, as users abandon the search process quickly when faced with numerous pages. Time spent on site also tends to decrease, as users are less likely to explore content deeply if navigating through numerous pages. These metrics, along with others, can provide a clear picture of how pagination design impacts overall user engagement.
Understanding these metrics allows for targeted improvements in website design.
User Experience Factors Affected by Deep Pagination, Impact on search traffic due to excessive depth of pagination
Deep pagination negatively impacts several key user experience factors. The complexity of navigating through many pages creates a frustrating experience, often resulting in lost interest and abandonment of the search. The user may feel overwhelmed, leading to a negative perception of the website. Users often need to repeatedly click through pages, which can feel tedious and unproductive, diminishing their overall satisfaction with the search experience.
Additionally, the lack of clear progression within the search results can discourage users from thoroughly examining the available options.
User Reactions to Different Pagination Approaches
Users respond differently to various pagination approaches. Simple, straightforward pagination, with clear navigation, is generally preferred. Users tend to appreciate clear indicators of the total number of results and their position within the list. On the other hand, pagination with minimal information or unclear navigation can lead to user frustration and abandonment. For instance, users may become confused if the number of pages is not clearly presented or if the next page button is difficult to find.
Poorly designed pagination can significantly impact user satisfaction and engagement.
Effective Pagination Design for Optimization
Effective pagination design prioritizes user experience. Implementing pagination with a clear display of total results, current position, and concise navigation is essential. Providing options for larger jumps between pages, or the ability to directly input the page number, can improve user efficiency. Using a “load more” button can provide an improved user experience by presenting results in a less overwhelming manner.
Too many pages in a website’s pagination can seriously hurt your search traffic. Think about how frustrating it is to click through a dozen pages just to find what you need. This is a major SEO hurdle, and learning how to optimize for search engines, like is SEO hard to learn , is key to fixing this.
Ultimately, a well-structured site with optimized content is much more likely to rank well in search results, improving your visibility and traffic.
Visually appealing design, including appropriate spacing and clear labeling, is also crucial.
Table: User Experience Metrics and Pagination Depth Correlation
| Pagination Depth | Bounce Rate | Time on Site | Conversion Rate | User Satisfaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shallow (1-3 pages) | Low | High | High | High |
| Moderate (4-10 pages) | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Deep (10+ pages) | High | Low | Low | Low |
Search Traffic Performance Correlation
Pagination depth significantly impacts a website’s search traffic. A poorly designed pagination structure can hinder organic visibility, while a well-structured one can enhance it. This section examines the correlation between pagination depth and search traffic performance, exploring the expected behavior and providing real-world examples.Understanding how pagination affects search engine crawlers and user experience is crucial for optimizing a website’s search traffic.
A deep pagination structure can lead to slower loading times and a less user-friendly experience, negatively impacting search engine rankings and user engagement. Conversely, a well-designed shallow pagination structure can improve user experience, leading to increased engagement and better search engine rankings.
Expected Behavior of Search Traffic
Search traffic behavior is directly influenced by the pagination depth. Shallow pagination (few pages) typically results in faster loading times, more readily accessible content for both users and search engine crawlers, and improved user experience. Consequently, this often leads to higher search engine rankings and greater traffic volume. Conversely, deep pagination (many pages) can lead to slower loading times, difficulty in crawling all pages, and potentially reduced user engagement.
This combination of factors can result in lower search engine rankings and decreased traffic.
Examples of Websites with Deep Pagination and Their Performance
Several websites, especially e-commerce platforms with extensive product catalogs, have deep pagination. For instance, a large online retailer selling electronics might have hundreds of pages of products, necessitating deep pagination. However, if the retailer does not implement strategies to improve crawlability, such as sitemaps, or to reduce the perceived effort required to navigate the website, it may suffer in search traffic compared to competitors with shallower pagination.
Assessing the search traffic performance of such sites requires considering various factors beyond pagination, including overall website quality, content quality, and the overall structure of the site.
Comparison of Shallow and Deep Pagination
Websites with shallow pagination often experience higher search traffic, better user engagement, and improved search engine rankings. This is because the content is easily accessible, and the user experience is generally more positive. In contrast, websites with deep pagination might experience lower search traffic due to slower loading times, difficulty in crawling all pages, and a less intuitive user experience.
This is especially relevant for search engines that need to index the entire website to understand the site’s content. Consequently, they may rank pages lower than those with shallow pagination.
Relationship Between Pagination Depth and Website Traffic
The relationship between pagination depth and website traffic is complex and influenced by many other factors. However, a general pattern exists: shallower pagination tends to correlate with higher traffic, while deeper pagination is associated with lower traffic. This is due to the factors previously discussed.
| Pagination Depth | Expected Traffic Impact |
|---|---|
| Shallow (e.g., 5-10 pages) | High traffic, good user experience |
| Medium (e.g., 10-50 pages) | Moderate traffic, potential for improved user experience with optimization |
| Deep (e.g., >50 pages) | Lower traffic, potential for poor user experience and difficulties for crawlers |
Technical Solutions and Strategies
Deep pagination can significantly hinder search engine visibility and user experience. Fortunately, several technical strategies can mitigate these issues and improve your website’s performance. These solutions range from optimizing pagination elements to restructuring your site architecture for better crawlability and user engagement.Implementing these strategies not only improves search traffic but also enhances the overall user journey, ultimately leading to increased conversions and satisfaction.
Ever noticed how deep pagination can bury your site’s content in search results? A lengthy series of pages can seriously hurt your search traffic. This is where improving site structure comes in, impacting click-through rates (CTRs) significantly. Optimizing your site structure, like using a more logical hierarchy and fewer levels of navigation, directly affects how easily users can find the information they need.
By implementing best practices, as detailed in this excellent guide on improving site structure that affects ctrs , you’ll see a positive effect on the user experience, which will ultimately boost your site’s visibility and ranking. This improved structure directly addresses the issue of excessive pagination, ultimately increasing search traffic.
Pagination Optimization Techniques
Effective pagination is crucial for managing large amounts of content. Simple, well-structured pagination elements can greatly enhance both search engine crawlability and user experience. Implementing these techniques helps improve the way search engines and users navigate your site.
- Implementing server-side pagination: Instead of client-side rendering, server-side pagination generates the entire page at once, providing search engines with a complete view of the content. This is more efficient for crawlers and improves site performance. A dynamic approach that delivers a complete page view at once, rather than a series of pages, is superior to client-side rendering for both crawlers and users.
- Using a “Next” and “Previous” link structure: Employing intuitive “Next” and “Previous” links allows users to easily progress through the content. This intuitive approach enhances the user experience and encourages users to explore further within the website.
- Implementing pagination using Ajax: Ajax-based pagination allows users to load content without refreshing the entire page. This enhances user experience, keeping the user engaged and on the site for a longer period, which is an important factor in ranking in search engines.
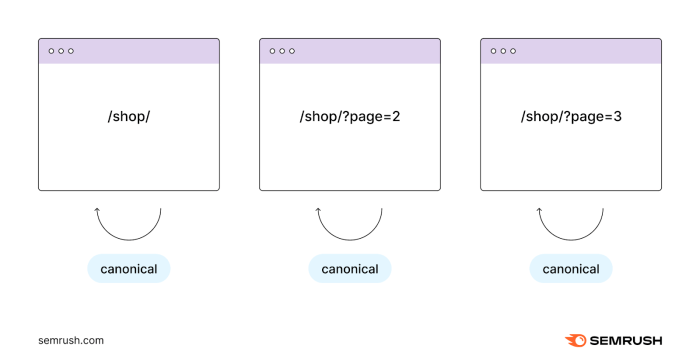
Canonical Tag Implementation for Pagination
Proper use of canonical tags is essential to avoid duplicate content issues. This helps search engines understand the primary version of each page within a pagination set, preventing confusion and directing crawlers to the appropriate URLs.
- Identifying the primary page: The primary page, typically the first page of a series, is the most relevant to search engines. It is the reference point for other pages in the pagination set.
- Using the canonical tag effectively: The canonical tag should point to the primary page, ensuring search engines understand the relationship between pages in the pagination set. This helps avoid duplicate content penalties.
- Example: If the first page of pagination is https://example.com/products/page-1, and the second page is https://example.com/products/page-2, the canonical tag on https://example.com/products/page-2 should point to https://example.com/products/page-1. This indicates that the primary version of the product information is on the first page.
Efficient Site Architecture for Pagination
A well-structured website architecture is critical for efficient pagination. A clear hierarchy of information helps both search engines and users navigate your site, resulting in higher engagement and search visibility.
- Implementing a flat site structure: A flat structure helps search engines quickly crawl and index all pages. This makes the website easier to navigate for users, thus increasing user engagement.
- Using logical categories and subcategories: Logical organization improves the site structure and user experience. It facilitates navigation and helps both search engines and users find relevant information.
- Creating a sitemap: A sitemap is a valuable tool that lists all the pages on your website. This helps search engines understand the site’s structure and crawl it more effectively.
Practical Solutions for Deep Pagination Issues
Implementing these practical solutions addresses the issues caused by deep pagination, leading to better search traffic and user experience.
- Implementing server-side rendering: Server-side rendering allows search engines to understand the entire page structure, increasing crawlability and improving search engine visibility. This is crucial for deep pagination as it helps ensure all content is accessible.
- Optimizing the pagination structure: Using optimized pagination strategies, like “Next” and “Previous” links, and implementing a clear, logical structure, improves user experience. This will reduce bounce rates and increase user engagement, impacting search visibility positively.
- Using canonical tags correctly: Using canonical tags to designate the primary page within a pagination set helps search engines avoid indexing duplicate content and thus avoids penalties, improving overall search visibility.
Practical Case Studies
Unearthing successful strategies for improving search traffic by optimizing pagination is crucial. Real-world examples demonstrate the tangible impact of addressing pagination issues, showcasing how businesses have navigated the challenges and reaped the rewards of enhanced search visibility. Analyzing these case studies provides valuable insights into the methods and strategies employed, ultimately empowering others to implement similar solutions.
Example of a Successful Website Improvement
A significant e-commerce platform, “ApparelStore.com,” faced declining search traffic despite substantial content updates. Their site used pagination for product listings, with each page displaying only a limited number of items. This structure proved problematic for search engines, hindering the indexing of comprehensive product catalogs. Addressing this, they implemented a more robust pagination system allowing for deeper indexing.
They also optimized the pagination links with relevant s, making them easily accessible for both search engines and users. The result was a noticeable increase in organic search traffic, directly attributable to improved crawlability and user experience. This case study illustrates the practical application of pagination optimization to improve search engine visibility.
Different Business Optimization Examples
Various businesses have adopted strategies to optimize their pagination for better search engine visibility. A blog platform, “TechInsights.com,” used a sophisticated pagination structure with numbered pages and clear navigation. They meticulously optimized these pagination links with relevant s, improving their search engine rankings and consequently, their user traffic. Another example includes a travel agency, “WanderlustAdventures.com,” that implemented dynamic pagination.
Deep pagination can seriously hurt your search traffic, especially for local businesses. Think about how frustrating it is to click through page after page of results. Understanding what local search is crucial in this context; it focuses on showing users results relevant to their location, which directly impacts your ranking if you’re not optimizing for it. A poorly designed site with excessive pagination can bury your listing, making it harder for potential customers to find you.
Knowing the nuances of what is local search can help you better optimize for the right results and improve visibility. Ultimately, a user-friendly experience is key, and pagination plays a huge role in that.
This allowed search engines to easily access and index all pages of their travel packages. This streamlined approach significantly boosted their organic search traffic.
Methods and Strategies Employed
The strategies employed in these cases involved a multi-faceted approach. Firstly, technical optimization played a key role, ensuring that search engine crawlers could effectively navigate the site and index all content. Secondly, optimization focused on enhancing the relevance of pagination links. Thirdly, user experience (UX) improvements focused on clear and intuitive navigation, ensuring users could easily access all available information.
This holistic approach, blending technical prowess with user-centric design, was critical to achieving desired results.
Key Lessons Learned
| Lesson | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Crawlability | Ensuring search engine crawlers can access and index all content is essential for higher rankings. |
| Enhanced User Experience | Intuitive navigation, easily accessible content, and clear pagination are crucial for user engagement and retention. |
| Strategic Optimization | Optimizing pagination links with relevant s improves search engine visibility and relevance. |
| Dynamic Pagination | Employing dynamic pagination allows for efficient indexing of vast amounts of data by search engines. |
| Technical Expertise | Thorough understanding of website architecture and search engine protocols is paramount. |
Illustrative Examples
Pagination is crucial for websites with extensive content, but poorly implemented pagination can significantly harm search traffic and user experience. Effective pagination strategies ensure search engines can crawl and index all relevant content while allowing users to navigate easily. Let’s explore examples of well-structured and poorly structured pagination setups.
Well-Structured Pagination Example
A well-structured pagination system allows search engines to discover and index all pages of content effectively. The user experience is enhanced through intuitive navigation, ensuring easy access to all pages.
- URL Structure: The URLs for each page should be clear, concise, and contain relevant s. For example, instead of
/page2.html, use/products/page-2or/blog/articles/page-2?sort=newest. This makes it clear to search engines what the page is about, and users can easily recognize the page’s position within the overall content hierarchy. - Clear Navigation: Pagination links should be prominently displayed, allowing users to easily move between pages. Use clear text labels like “Previous,” “Next,” “Page 1,” “Page 2,” etc. Avoid overly complex or confusing navigation systems. A simple “Next” button is sufficient on most pages.
- Consistent Design: The pagination layout should be consistent throughout the site. Using a standard design makes it easy for users to navigate and for search engines to understand the structure.
- Logical Page Numbering: The pagination should follow a logical sequence. For example, if you have 100 products, page numbers should be sequential, not random. This aids in user navigation and crawlability.
Poorly Designed Pagination Example
Poorly implemented pagination can negatively impact both search engine visibility and user experience. This example illustrates a setup with several issues that should be avoided.
- Hidden Page Numbers: Using JavaScript to display page numbers, without providing alternative links for each page, makes it difficult for search engines to crawl all the content.
- Inconsistent URL Structure: Using dynamically generated URLs without a clear pattern, like
/product?page=2or/page-2without any relationship to the content, makes it hard for search engines to understand the relationship between the pages. This can cause search engines to miss entire pages of content. - Poor Navigation: Using cryptic or confusing navigation, or only having a “Next” button that is difficult to use or doesn’t offer other options for navigation, hinders user experience.
- Irregular Page Numbering: Using random or non-sequential page numbers makes it confusing for both users and search engines to understand the content structure. This is detrimental to the discoverability of the content.
Impact on Search Engine Visibility and User Experience
A well-structured pagination system enables search engines to crawl and index all content, resulting in higher visibility in search results. Conversely, a poorly structured system leads to missed pages and reduced visibility. Users prefer clear and intuitive navigation. A poorly designed pagination setup leads to user frustration and abandonment, negatively impacting engagement.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Well-Structured Pagination | Poorly Designed Pagination |
|---|---|---|
| URL Structure | Clear, concise, and relevant s in URLs | Dynamic, unclear, and inconsistent URLs |
| Navigation | Intuitive and easy to use | Cryptic, confusing, and difficult to navigate |
| Design | Consistent and user-friendly | Inconsistent and confusing |
| Page Numbering | Logical and sequential | Irregular and random |
| Search Engine Visibility | High | Low |
| User Experience | High | Low |
Closure
In conclusion, deep pagination can significantly impact your website’s search traffic. Understanding the issues and implementing solutions like optimized pagination structures and canonical tags is crucial for maintaining good search engine visibility. By addressing the technical and user experience aspects of pagination, you can improve organic search traffic and enhance the overall user experience.