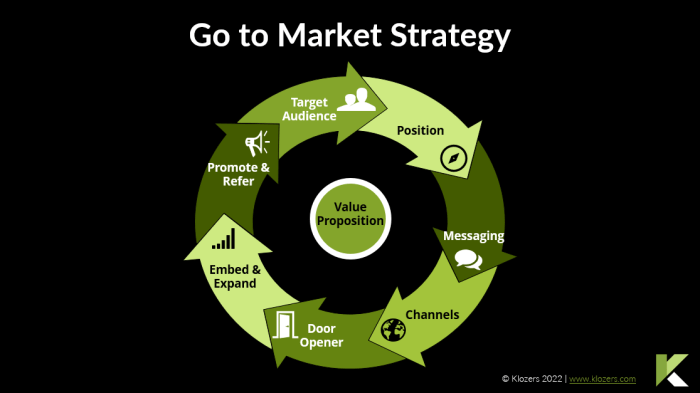
Go to market strategy is the roadmap for launching a product or service successfully. It Artikels how you’ll reach your target customers, position your offering, and ultimately drive sales. This detailed guide breaks down the essential components of a robust GTM strategy, from identifying your target market to measuring performance and adapting to market changes.
We’ll explore key elements like defining your target audience, crafting compelling messaging, choosing the right sales channels, and executing effective marketing campaigns. Understanding these aspects is crucial for maximizing your chances of success in any market.
Defining Go-to-Market Strategy: Go To Market Strategy
A go-to-market (GTM) strategy is a comprehensive plan outlining how a company will introduce and sell its products or services to its target market. It encompasses all the activities, processes, and resources required to achieve specific business objectives. This plan is dynamic, adapting to changing market conditions and customer needs. A well-defined GTM strategy is crucial for achieving sales targets and building a strong market presence.A robust GTM strategy is more than just a marketing plan.
It integrates sales, marketing, product, and operations to ensure a seamless customer journey. It involves meticulous market research, detailed customer segmentation, and a clear understanding of competitive landscapes. This holistic approach maximizes efficiency and effectiveness in penetrating the market.
Key Components of a Robust GTM Strategy
A comprehensive GTM strategy integrates various elements to ensure alignment with business objectives. These elements are crucial for success and include market research, customer segmentation, and a well-defined sales process.
- Market Research: Understanding the target market, its needs, and its preferences is paramount. Thorough market research involves analyzing industry trends, competitive landscapes, and customer behavior. Data-driven insights from this research help inform product development, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns.
- Customer Segmentation: Identifying distinct customer groups with shared characteristics is vital. This allows for tailored marketing messages and targeted sales efforts. Different segments may require unique value propositions and channels to reach them effectively. For instance, a software company targeting small businesses may use online marketing, while targeting large enterprises might involve direct sales.
- Sales Process: A clear and efficient sales process is essential. Defining steps from lead generation to closing deals ensures consistency and maximizes conversion rates. This involves developing sales scripts, qualifying leads, and providing effective customer support.
- Marketing Strategy: Defining the appropriate marketing channels and messaging is critical. Choosing the right channels, such as social media, content marketing, or search engine optimization (), depends on the target audience and budget. A consistent brand message across all channels is important for building brand awareness and customer trust.
- Distribution Channels: Determining how products will reach the customer is critical. Direct sales, online marketplaces, or partnerships with distributors are some of the options. The chosen distribution channel should align with the target market and overall business goals.
Relationship Between GTM Strategy and Business Objectives
A well-defined GTM strategy directly supports the overall business objectives. It ensures that resources and efforts are focused on achieving key performance indicators (KPIs). Alignment between the GTM strategy and the overarching business goals is crucial for maximizing returns on investment.
Different GTM Approaches
The choice of GTM approach depends on several factors, including the product, target market, and budget.
| GTM Approach | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Sales | Selling products or services directly to customers through a sales team. | Strong customer relationships, personalized service, control over messaging, and higher conversion rates with key accounts. | Higher initial investment in sales personnel, limited reach compared to online marketing, and potentially higher costs per lead. |
| Online Marketing | Utilizing online channels like social media, search engine marketing (SEM), and content marketing to reach potential customers. | Wider reach, cost-effective for initial lead generation, and measurable results. | Requires expertise in digital marketing, potential for lower conversion rates, and more complex to nurture leads. |
| Partnerships | Collaborating with other businesses to expand market reach and access new customer segments. | Access to existing customer bases, leveraging expertise of partners, and shared costs. | Potential conflicts of interest with partners, dependency on partners’ performance, and less control over messaging. |
Target Market Identification
Defining your target market is crucial for a successful go-to-market strategy. It’s not just about identifying who might buy your product; it’s about understanding their needs, motivations, and pain points so you can tailor your messaging and offerings to resonate with them. A well-defined target market allows for more effective resource allocation, focused marketing efforts, and ultimately, higher conversion rates.
Factors to Consider When Defining a Target Market
Identifying a target market requires a multifaceted approach. Several key factors must be considered. Understanding the demographics (age, gender, location, income) of potential customers is fundamental, but it’s equally important to consider their psychographics (lifestyle, values, interests, attitudes). Furthermore, analyzing their needs, motivations, and pain points is vital to creating products or services that directly address these issues.
A deep dive into their behavior, including purchase patterns and media consumption habits, will provide valuable insight. Competitor analysis and understanding the existing market landscape are also essential to gain a comprehensive view of the target market’s characteristics and preferences.
Methods for Segmenting and Characterizing Target Audiences
Effective segmentation and characterization of target audiences is crucial for successful marketing. Several methods can be employed to achieve this. Demographic segmentation divides the market based on measurable characteristics like age, gender, income, education, and occupation. Psychographic segmentation categorizes customers based on lifestyle, values, interests, personality traits, and attitudes. Behavioral segmentation focuses on customer purchasing patterns, usage rates, brand loyalty, and responses to marketing campaigns.
Finally, geographic segmentation groups customers based on location, climate, population density, and cultural nuances. Combining these segmentation approaches often provides the most comprehensive view of the target market.
Importance of Market Research in Defining the Target Market
Market research plays a pivotal role in defining the target market. It provides the necessary data and insights to understand customer needs, preferences, and behaviors. Through surveys, focus groups, and observational studies, businesses can gather first-hand information on the target audience. Data analysis reveals trends and patterns, allowing for more accurate predictions about customer behavior and preferences.
This data informs product development, marketing strategies, and sales tactics, ultimately maximizing the return on investment. Furthermore, market research provides a clear understanding of the competitive landscape, helping businesses position their products effectively.
A killer go-to-market strategy hinges on a lot of factors, but understanding your pricing model is crucial. You need to consider not only your costs but also the market value and competitive landscape. Checking out the best pricing pages, like the best pricing pages , can offer some valuable insights. Ultimately, a well-defined go-to-market strategy, supported by a clear pricing structure, is key to success.
Characteristics of a Potential Target Market for a New Fitness Tracker
| Characteristic | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | Age, Gender, Location, Income | Ages 25-45, predominantly female, residing in urban areas, with an annual household income of $60,000+. |
| Psychographics | Lifestyle, Values, Interests | Health-conscious individuals actively seeking fitness solutions, value convenience and technology, interested in data-driven insights for personal improvement. |
| Behavior | Purchase patterns, media consumption | Actively searching online for fitness trackers, engage with fitness-related content on social media platforms, frequently visit fitness communities and forums. |
| Needs | Specific needs or pain points | Desire for accurate activity tracking, personalized workout plans, integration with other fitness apps, and motivation tools. |
| Motivations | Drivers for purchase | Goal-oriented individuals aiming to improve their physical well-being, seeking a comprehensive fitness solution that seamlessly integrates with their lifestyle. |
Product Positioning and Messaging
Crafting a compelling go-to-market strategy hinges significantly on effectively communicating the value proposition of your product to the target market. Product positioning isn’t just about what your product
- is*; it’s about how it
- fits* into the minds of your customers and what problems it solves for them. Clear messaging is crucial for driving adoption and ultimately achieving your sales targets.
Positioning your product strategically in the market allows you to stand out from competitors. This involves identifying your unique selling points and emphasizing the benefits they provide to customers. This positioning directly influences the customer’s perception of your product and drives their decision-making process.
Significance of Product Positioning
Effective product positioning isn’t just a marketing tactic; it’s a fundamental aspect of your go-to-market strategy. A well-defined position helps clarify your product’s value proposition and target the right customer segments. It ensures your marketing efforts resonate with the specific needs and desires of your ideal customers. It also aids in differentiating your product from competitors, creating a strong brand identity, and fostering customer loyalty.
Crafting a Compelling Value Proposition
A compelling value proposition highlights the unique benefits your product offers to customers and how it solves their problems. It’s about articulating the specific value your product brings to the table. This involves clearly outlining the pain points your product addresses and the corresponding solutions it provides. For instance, if your product streamlines a complex process, highlight the time and cost savings it offers.
If your product enhances user experience, showcase how it improves efficiency and productivity.
Examples of Effective Product Messaging
Different customer segments often require different messaging approaches. A message tailored to a tech-savvy startup might emphasize innovation and cutting-edge technology, while a message aimed at a large enterprise might focus on scalability and reliability. Here are some examples:
- For the budget-conscious consumer: “Get the quality you deserve at an affordable price.” This emphasizes value for money and addresses the need for cost-effective solutions.
- For the environmentally conscious customer: “Reduce your environmental footprint with our sustainable product.” This highlights the product’s eco-friendly attributes and appeals to a specific market segment.
- For a high-end customer: “Experience unparalleled performance and luxury with our premium product.” This emphasizes the high quality and exclusivity of the product.
Product Positioning Strategies
Choosing the right positioning strategy is vital for effectively communicating your product’s value to your target market. Various approaches exist, each tailored to specific needs and market conditions.
| Positioning Strategy | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Price Leadership | Focuses on offering the lowest possible price for a product or service. | Discount stores, budget airlines. |
| Differentiation | Focuses on highlighting unique product features and benefits that distinguish it from competitors. | Luxury brands, niche software solutions. |
| Niche Marketing | Targeting a specific, well-defined market segment with a specialized product or service. | Specialized medical equipment, artisan crafts. |
| Value-Based | Highlighting the total value delivered by the product or service, including benefits beyond the core features. | Subscription services offering curated content, fitness programs that offer a holistic approach to health and wellness. |
Sales and Distribution Channels

Choosing the right sales and distribution channels is critical for a successful go-to-market strategy. It directly impacts reach, cost, and ultimately, revenue. Different products and markets demand different approaches. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each channel is essential for optimizing your strategy and maximizing ROI.Effective go-to-market strategies consider the entire customer journey. This includes not just the initial purchase but also the ongoing relationship with the customer, from product use to support.
Selecting appropriate sales and distribution channels plays a vital role in ensuring a positive and sustainable customer experience.
Sales Channel Options
Understanding the diverse options available for reaching customers is key. Various sales channels offer unique advantages and disadvantages depending on factors like product complexity, target market characteristics, and budget. Direct sales, online marketplaces, and partnerships are just a few examples.
- Direct Sales: This approach involves employing sales representatives to directly interact with potential customers. This is particularly suitable for complex products or high-value transactions, allowing for personalized service and strong relationship building. However, it can be costly due to the need for a dedicated sales team and infrastructure.
- Indirect Sales (Distributors/Resellers): Utilizing intermediaries like distributors or resellers can expand market reach, particularly for products with a broad target market. This model often involves lower upfront investment but can lead to less control over the customer experience and potentially diluted brand messaging.
- Online Marketplaces: Platforms like Amazon or specialized online marketplaces offer significant reach and exposure to a large customer base. This can be highly effective for products with a broad appeal and a clear online presence. However, it may require substantial marketing efforts to stand out amidst competition and often involves a commission structure.
- Partnerships: Collaborating with complementary businesses can leverage existing customer bases and expertise. This approach is effective for reaching niche markets or expanding into new territories. It can be challenging to manage relationships and ensure consistent messaging across multiple partners.
- Subscription Services: This channel is well-suited for recurring revenue models, enabling consistent income streams and cultivating customer loyalty through ongoing product engagement. However, it demands meticulous customer onboarding and retention strategies.
Comparing Sales Channels
A crucial aspect of choosing the right sales channel is understanding its specific advantages and disadvantages.
Crafting a solid go-to-market strategy is crucial for any business, especially in today’s digital landscape. Recent changes to YouTube Shorts view counts, with no adjustments to monetization, as detailed in this article ( youtube changes shorts view counts no change to monetization ), highlight the need for marketers to adapt quickly. This necessitates careful analysis of the evolving digital ecosystem and a re-evaluation of existing go-to-market plans.
| Sales Channel | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Sales | Strong customer relationships, greater control over messaging, high potential for customization | High upfront costs, limited market reach initially, dependence on sales team effectiveness |
| Indirect Sales (Distributors/Resellers) | Wider market reach, lower initial investment, leverage existing infrastructure | Less control over customer experience, potential for inconsistent messaging, lower profit margins |
| Online Marketplaces | Large customer base, high visibility, potential for global reach | Competition from other sellers, commission structures, potential for negative reviews impacting brand reputation |
| Partnerships | Access to niche markets, shared resources and expertise, leverage established customer bases | Coordination challenges, potential for conflicts in messaging, dependence on partner performance |
| Subscription Services | Recurring revenue, customer loyalty, predictable income stream | High customer acquisition costs initially, demanding retention strategies, need for robust support structure |
Optimizing Sales and Distribution Networks
Effective optimization strategies are essential to maximize sales and minimize costs. A key strategy is to tailor your approach to each channel. Consider aspects like training, incentive programs, and performance metrics to enhance sales effectiveness. Leveraging data analytics to track performance and adjust strategies is critical.
“A well-structured sales and distribution network is not static. Regular review and adaptation are essential to maintain its effectiveness in a dynamic market.”
Marketing and Promotion Strategies
Crafting a compelling marketing and promotion strategy is crucial for effectively reaching your target market and driving sales. This involves a deep understanding of your target audience’s needs, preferences, and pain points, as well as a well-defined understanding of your product’s unique value proposition. A successful GTM strategy necessitates a cohesive approach to marketing communications, ensuring consistency across all channels and touchpoints.A comprehensive marketing plan acts as a roadmap, guiding the execution of promotional activities and ensuring alignment with the overall go-to-market strategy.
It details the specific actions, timelines, and budget allocated to each marketing initiative. This ensures focused efforts and measurable results.
Effective Marketing Strategies
Effective marketing strategies leverage various channels to reach and engage the target market. These channels need to be carefully selected based on the target audience’s preferences and the product’s characteristics. Understanding the potential reach of each channel is critical for allocating resources efficiently.
- Content Marketing: Creating valuable, informative, and engaging content like blog posts, articles, videos, and infographics is a powerful way to attract and educate potential customers. This strategy builds trust and establishes your brand as an authority in the industry. For example, a software company could create tutorials and case studies showcasing the benefits of their product, or a B2B SaaS provider could publish thought leadership articles on industry trends.
- Social Media Marketing: Utilizing platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn to connect with potential customers, share updates, and engage in conversations. This can include running targeted ads, engaging with influencers, and fostering a community around your brand. A clothing brand, for instance, could use Instagram to showcase its latest collections with visually appealing posts and stories.
- Search Engine Optimization (): Optimizing your website and content to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). This involves research, on-page optimization, and link building to improve organic visibility. A website selling gardening tools could optimize its product pages for relevant s like “best gardening shears” or “high-quality trowel.”
Promotional Activities
Effective promotional activities are essential to generate interest and drive sales. Promotional activities need to be tailored to specific products and target audiences.
- Product Launches: Generate excitement and anticipation around new product launches through pre-launch campaigns, media outreach, and exclusive previews. A tech startup could host a webinar or online event to unveil its new software platform.
- Sales Promotions: Offer discounts, coupons, bundles, or contests to incentivize purchases. A retail store could offer a limited-time discount on a specific product category to attract customers.
- Events and Trade Shows: Participate in industry events and trade shows to showcase your product, network with potential customers, and generate leads. A manufacturing company could exhibit its machinery at a trade show, allowing potential clients to see demonstrations and interact with representatives.
Comprehensive Marketing Plan
A comprehensive marketing plan is critical for achieving alignment with the GTM strategy. It should Artikel specific objectives, target audiences, marketing channels, budget, and timelines.
- Marketing Objectives: Clearly define the measurable goals of the marketing plan, such as increasing brand awareness, generating leads, or driving sales. These objectives should directly support the overall business goals.
- Target Audience Segmentation: Divide the target market into distinct segments based on their needs, preferences, and behaviors. This enables targeted messaging and promotional campaigns.
- Marketing Budget Allocation: Allocate resources across various marketing channels based on their potential reach and effectiveness. This ensures efficient use of the allocated budget.
Marketing Channels and Reach
This table illustrates the potential reach of various marketing channels.
| Marketing Channel | Potential Reach | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Social Media | High | Reaching a large audience through targeted ads and organic posts |
| Search Engine Optimization () | High | Driving organic traffic to a website based on search engine rankings |
| Email Marketing | Medium | Reaching a segmented audience through targeted email campaigns |
| Content Marketing | Medium to High | Attracting and educating potential customers through blog posts and articles |
| Paid Advertising | High | Reaching a wide audience through targeted ads on various platforms |
Customer Acquisition and Onboarding
Attracting new customers is a critical component of any successful go-to-market strategy. Effective customer acquisition goes beyond simply generating leads; it’s about attracting the right customers who are most likely to become loyal advocates for your product or service. A robust onboarding process, equally important, ensures a positive initial experience that fosters long-term customer satisfaction and retention. This section will explore strategies for efficiently acquiring new customers and the importance of a seamless onboarding experience.
Strategies for Efficient Customer Acquisition, Go to market strategy
Customer acquisition is a multifaceted process requiring a blend of targeted marketing efforts and strategic partnerships. To ensure efficiency, focus on channels that resonate with your target audience and align with your budget. This approach leads to a higher return on investment and allows you to optimize your marketing spend.
- Targeted Advertising Campaigns: Leveraging platforms like Google Ads, social media ads, and search engine marketing (SEM) allows for highly targeted campaigns reaching potential customers based on demographics, interests, and online behavior. This precision reduces wasted ad spend and increases conversion rates.
- Content Marketing: Creating valuable content, such as blog posts, articles, videos, and infographics, positions your company as an industry expert. This attracts organic traffic and builds brand awareness, ultimately leading to more qualified leads.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Collaborating with complementary businesses or influencers can expose your product to a wider audience. Joint ventures and co-marketing initiatives can amplify your reach and generate high-quality leads.
- Referral Programs: Encourage existing customers to refer new business by offering incentives. Referral programs are a cost-effective method of customer acquisition that leverages the power of word-of-mouth marketing.
Importance of a Seamless Customer Onboarding Process
A smooth onboarding experience is crucial for turning new customers into loyal advocates. It sets the tone for their relationship with your company and influences their long-term satisfaction. By streamlining the process, you reduce friction points and increase the likelihood of customer retention.
- Clear and Concise Onboarding Materials: Provide easily digestible guides, tutorials, and FAQs to assist new users in navigating your product or service. A well-structured onboarding process empowers customers to get started quickly and efficiently.
- Personalized Onboarding Experiences: Tailor the onboarding process to each customer’s specific needs and goals. This personalized approach demonstrates that you value each customer and their unique situation.
- Proactive Customer Support: Offer readily available support channels, such as email, phone, or chat, to address any questions or concerns promptly. A proactive approach to customer support ensures that new users receive the assistance they need when they need it.
- Continuous Engagement: After initial onboarding, maintain consistent engagement through regular updates, helpful tips, and exclusive content. This ongoing interaction reinforces the value you provide to your customers.
Examples of Effective Customer Acquisition Tactics
Successful customer acquisition tactics often combine various marketing strategies. For instance, a SaaS company might use targeted advertising campaigns to generate leads and follow up with a comprehensive onboarding process including personalized tutorials and dedicated support channels.
- Case Study: A software company targeting small businesses successfully implemented a multi-channel strategy. They used targeted social media ads to reach potential customers, followed by email marketing campaigns that educated potential clients about the benefits of their product. Then, they offered a free trial and implemented a comprehensive onboarding process to support new users.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) by Marketing Channel
Understanding the cost of acquiring each customer across various channels is vital for optimizing marketing spend. This data helps determine which channels yield the highest return on investment.
| Marketing Channel | CAC (Estimated) |
|---|---|
| Social Media Ads | $50-$150 |
| Search Engine Marketing (SEM) | $75-$200 |
| Content Marketing | $25-$75 |
| Partnerships | $100-$300 |
| Referral Programs | $25-$50 |
Note: CAC figures are estimates and can vary significantly based on industry, target audience, and campaign specifics.
Measuring and Evaluating GTM Performance
A successful go-to-market (GTM) strategy isn’t just about planning; it’s about continuous monitoring and adaptation. Measuring the effectiveness of your GTM efforts is crucial for identifying what’s working, what’s not, and ultimately, maximizing your return on investment. Regular evaluation allows you to fine-tune your approach and ensure alignment with your overall business objectives.Thorough performance measurement helps to understand the impact of your GTM strategy on key business metrics.
By analyzing data from various touchpoints, you can identify areas for improvement and proactively address potential challenges. This ongoing analysis ensures that your GTM strategy remains agile and responsive to evolving market conditions.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for GTM Effectiveness
Tracking the right metrics is paramount for assessing GTM success. A well-defined set of KPIs allows you to measure progress towards objectives, identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions. These indicators should align with your overall business goals, such as revenue targets, market share, and customer acquisition costs.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This metric represents the average cost incurred to acquire a new customer. A lower CAC signifies greater efficiency in your GTM strategy. High CAC often signals areas needing optimization in marketing and sales processes.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): CLTV estimates the total revenue a customer is expected to generate throughout their relationship with your company. A high CLTV indicates that your product or service is valuable to customers and that your GTM strategy is effective in attracting high-value clients.
- Conversion Rate: This measures the percentage of leads that convert into paying customers. A higher conversion rate indicates an effective sales process and compelling messaging. Low conversion rates might suggest improvements are needed in lead qualification or sales outreach.
- Sales Cycle Length: This measures the time it takes for a lead to progress through the sales funnel to become a customer. A shorter sales cycle often indicates efficiency in your sales process. A longer sales cycle may suggest improvements in lead nurturing or sales team efficiency.
- Website Traffic and Engagement: Monitoring website traffic, bounce rate, and time spent on pages provides insights into the effectiveness of your marketing efforts. High traffic but low engagement might indicate a need for improvements in content or website design.
Analyzing GTM Performance Data
Data analysis is essential for extracting actionable insights from GTM performance metrics. Utilizing various analytical tools and techniques allows for a deeper understanding of the data, leading to strategic decisions and informed adjustments to your GTM strategy.
A killer go-to-market strategy hinges on understanding your target audience. For international expansion, this means diving deep into local SEO best practices. Knowing how to optimize your website for different languages and cultures is crucial, and a good starting point is this guide on how to international SEO. Ultimately, a successful go-to-market strategy relies on tailoring your approach to each market, and mastering international SEO is a key component of that.
- Data Visualization: Employing charts and graphs to present GTM data allows for easier comprehension of trends and patterns. This visual representation can highlight key insights and areas for improvement, such as declining conversion rates or rising customer acquisition costs.
- Segmentation Analysis: Analyzing performance data by customer segment, geographic region, or product line allows for a granular understanding of variations in effectiveness. This granular view provides insights into specific strengths and weaknesses of different parts of your GTM strategy.
- A/B Testing: Experimentation with different marketing messages, sales approaches, or website designs allows you to identify the most effective elements. A/B testing helps in optimization of various aspects of the GTM strategy.
- Attribution Modeling: This technique traces the source of customer acquisition to different marketing campaigns. It helps in understanding which channels are most effective in driving conversions and optimizing your marketing spend.
Adapting the GTM Strategy Based on Performance Metrics
Understanding GTM performance metrics is not enough; adapting the strategy based on the insights gained is critical. Regular review and adjustments based on the data are key to staying ahead of the curve and optimizing performance.
- Adjusting Marketing Spend: If certain marketing channels are underperforming, redirecting resources to more effective ones is necessary. This adaptation ensures that marketing budgets are allocated to the most efficient channels.
- Refining Sales Processes: Identifying bottlenecks in the sales process, such as long sales cycles or low conversion rates, enables you to refine your approach. This could include training sales teams, implementing new sales tools, or improving lead qualification processes.
- Product Positioning Adjustments: Based on customer feedback and sales data, your product positioning might need adjustments. Understanding what resonates with your target market allows for better positioning of your product.
- Improving Customer Onboarding: Analyzing customer onboarding experiences can identify areas needing improvement. A smooth onboarding process is crucial for customer satisfaction and retention.
Example Metrics Calculation Table
This table illustrates the calculation of key metrics for evaluating GTM success.
| Metric | Formula | Example Values | Calculation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | Total Marketing & Sales Costs / Number of Customers Acquired | $50,000 / 100 Customers | $500 per customer |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) | Average Revenue Per Customer
|
$1,000 – 3 Years | $3,000 per customer |
| Conversion Rate | (Number of Leads Converted / Total Number of Leads) – 100% | 50 Leads Converted / 100 Leads | 50% |
Adapting to Market Changes
A successful go-to-market (GTM) strategy isn’t a static document; it’s a living entity that needs constant adjustment to thrive in dynamic markets. Ignoring market shifts and competitor actions can lead to lost opportunities and diminished market share. Adaptability is key to maintaining momentum and achieving long-term success.Adapting a GTM strategy is not just about reacting to change; it’s about proactively anticipating and incorporating new trends into your approach.
This requires a keen eye for market trends, competitor moves, and evolving customer needs. Continuous monitoring and strategic adjustments ensure that your product or service remains relevant and appealing to the target audience.
Monitoring Market Trends and Competitor Activities
Staying informed about market trends and competitor actions is crucial for a successful GTM strategy. This involves analyzing various data sources to identify emerging patterns and anticipate future developments. Competitor analysis should focus on their strategies, product offerings, pricing models, and marketing campaigns.Market research is a critical component in this process. This can include tracking industry reports, news articles, social media sentiment, and customer feedback.
By meticulously collecting and analyzing this information, you gain a deeper understanding of evolving customer preferences, emerging technologies, and potential threats.
Responding to Evolving Customer Needs
Understanding and anticipating evolving customer needs is fundamental to adapting your GTM strategy. Direct engagement with customers is vital to gauge changing preferences and pain points. Conducting regular surveys, focus groups, and customer interviews can provide invaluable insights.Analyzing customer feedback and reviews is crucial for identifying unmet needs and areas for improvement. This feedback helps tailor your product messaging, pricing strategies, and sales approaches to better resonate with the target audience.
Strategies for Responding to Market Shifts
Adapting to market shifts necessitates a proactive approach, encompassing several key strategies. These include modifying marketing campaigns to reflect evolving trends, adjusting product features to address customer needs, and altering sales approaches to accommodate changing buyer behaviors.The adaptability of your GTM strategy must align with the dynamic nature of the market. Continuous evaluation and refinement of your strategies, including product development, sales processes, and marketing materials, will be crucial to maintain relevance and success.
Potential Market Shifts and Corresponding Adjustments
| Potential Market Shift | Corresponding Adjustment to GTM Strategy |
|---|---|
| Increasing consumer demand for sustainable products | Highlighting eco-friendly aspects of the product in marketing materials, exploring partnerships with environmentally conscious retailers, and incorporating sustainability into product development |
| Rise of e-commerce and digital marketing | Investing in digital marketing channels, optimizing the website for conversions, implementing robust online customer service, and ensuring seamless online ordering and fulfillment processes |
| Shift in customer demographics and preferences | Conducting surveys to identify evolving customer segments and preferences, updating marketing materials to reflect new demographics, and adjusting sales pitches to align with the evolving values of the target audience |
| Economic downturn impacting purchasing power | Adjusting pricing strategies to reflect reduced purchasing power, highlighting value propositions, and focusing on products and services with high cost-effectiveness |
| Emergence of new competitors | Analyzing competitor strategies, refining your product differentiation, emphasizing unique value propositions, and enhancing marketing efforts to reinforce brand identity and create a stronger brand perception |
End of Discussion
In conclusion, a well-defined go to market strategy is vital for any business aiming to succeed. From meticulously identifying your target market to meticulously crafting a compelling value proposition, every step contributes to a comprehensive plan. This guide highlights the crucial elements of a successful GTM strategy, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of the market and achieve your business objectives.