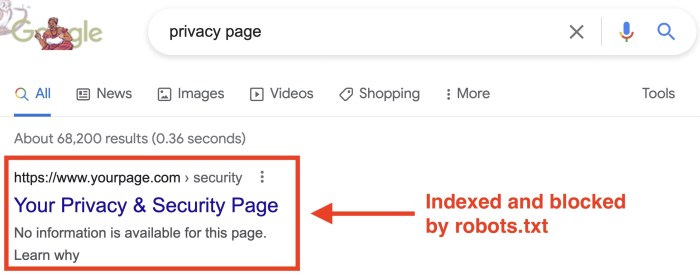
How to block urls robots txt – How to block URLs robots.txt is crucial for website owners seeking to control web crawler access. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of robots.txt, explaining how to effectively block specific URLs, directories, or even entire sections of your website. Understanding the nuances of robots.txt directives is essential for maintaining website integrity and optimizing search engine visibility.
From basic implementation to advanced techniques, this guide walks you through the process of configuring and optimizing your robots.txt file. We’ll cover everything from setting up the file and placing it in the correct directory, to testing its effectiveness and troubleshooting common errors. Learn how to manage specific crawler behavior and understand the impact of robots.txt on sitemaps and .
Introduction to Robots.txt
The Robots.txt file is a crucial part of website management, serving as a guide for web crawlers like Googlebot. It dictates which parts of your website these automated programs are allowed to access and index. This file is fundamental for controlling the crawling process, helping to prevent unwanted indexing of sensitive data or resources. It also plays a role in optimizing website performance by directing crawlers to focus on important content.This file is a simple text file that tells search engine crawlers which parts of your website they are allowed to access and which they should avoid.
This is done through a set of directives that are interpreted by the crawlers. Understanding how to use Robots.txt effectively is vital for website owners to control how search engines index their content.
Robots.txt File Structure
A typical Robots.txt file follows a specific format. It uses directives to communicate with web crawlers. The directives are lines of text, each starting with a , followed by a space, and then the target.
The file is plain text, easily created and modified by any text editor.
Common Uses of Robots.txt
Robots.txt is primarily used to control web crawler access. This includes directing crawlers away from specific directories, files, or even the entire site. This is often used for protecting sensitive data, such as:
- Protecting private content: Such as user accounts, payment information, or internal documents.
- Preventing indexing of dynamically generated content: This can save server resources and prevent the indexing of pages that are not meant for public viewing.
- Controlling the crawling frequency: Some websites want to control how often search engine crawlers visit their pages to avoid overloading their servers.
- Protecting resources: This is vital for preventing unauthorized access to resources like scripts, images, or files that should not be directly accessible.
Importance of a Well-Maintained Robots.txt File
A well-maintained Robots.txt file is crucial for managing a website’s visibility and performance. A properly configured file ensures that search engines index only the relevant and appropriate content. This leads to:
- Improved site performance: By controlling crawler access, you can reduce server load and improve overall website speed.
- Enhanced : Proper usage can help focus indexing on high-value content, improving your website’s search engine rankings.
- Data security: Protecting sensitive data through the file is vital for maintaining privacy and security.
- Reduced crawl budget issues: Following best practices prevents search engines from spending their crawl budget on unwanted content.
Common Robots.txt Directives
The file uses a set of directives to communicate with web crawlers. Here’s a table outlining common directives and their functions:
| Directive | Description |
|---|---|
| User-agent | Specifies the web crawler the directive applies to (e.g., Googlebot, Bingbot). A wildcard (*) applies to all crawlers. |
| Allow | Specifies the URLs or directories that the specified user-agent is allowed to access. |
| Disallow | Specifies the URLs or directories that the specified user-agent is not allowed to access. |
| Sitemap | Provides a link to the sitemap file, helping search engines understand the website’s structure and content. |
Blocking URLs with Robots.txt
Robots.txt is a crucial tool for website owners to control how search engine crawlers interact with their site. By strategically using the “Disallow” directive, you can instruct these crawlers to skip specific pages, directories, or even entire sections of your website. This precise control prevents unwanted indexing and protects sensitive content from being displayed in search results.
Effective use of Robots.txt can significantly impact your website’s visibility and . By understanding how to utilize the Disallow directive, you can optimize your website’s crawl budget and manage the content that search engines index. This, in turn, can lead to a more focused and efficient crawling process, potentially improving your website’s overall performance in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Specifying URLs to Block
The “Disallow” directive in Robots.txt tells search engine crawlers which parts of your site they should not access. This directive is crucial for managing crawl budget and protecting sensitive content. It is important to be precise when specifying URLs to block to avoid unintended consequences.
Using the Disallow Directive for URL Blocking
The Disallow directive takes a path as input, typically a relative path from the root of your website. For example, if your site’s root is www.example.com, and you want to block access to the /admin/ directory, you would use the directive Disallow: /admin/. A single Disallow directive can block multiple files or directories.
Blocking Specific Directories, Files, or Sections, How to block urls robots txt
You can use wildcards in the “Disallow” directive to block entire directories or groups of files. For instance, to block all files within the /images/ directory, you would use Disallow: /images/*. This would prevent crawlers from accessing all files within the /images/ directory. Similarly, to block specific files, you can use their exact names, like Disallow: /confidential_report.pdf.
Blocking Entire Sections
To block an entire section of your website, use a broader path. For example, if you want to prevent indexing of all pages within a specific sub-domain, use the sub-domain in the Disallow directive. For instance, if you have a sub-domain like staging.example.com, use Disallow: / in the Robots.txt file within the staging.example.com site.
Blocking a URL Entirely vs. Partially
Blocking a URL entirely prevents search engine crawlers from accessing and indexing it. Partial blocking, on the other hand, might allow access to certain parts of a URL but not others. This can be useful for specific elements within a page that you don’t want indexed. For instance, a site might block the entire /products/ directory, but allow access to /products/sitemap.xml for sitemap indexing.
Impact on Search Engine Indexing
Blocking URLs using Robots.txt directly impacts search engine indexing. Search engines will not attempt to index pages or files explicitly disallowed. This can affect search rankings, as search engines may not have the complete picture of your website’s structure and content. Proper use of Robots.txt, therefore, helps maintain control over the content search engines see, contributing to a well-optimized strategy.
Comparison of Blocking Methods
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Blocking a specific file | Disallow a particular file. | Disallow: /important_document.pdf |
| Blocking a directory | Disallow an entire directory. | Disallow: /private/ |
| Blocking with wildcards | Disallow multiple files/directories using wildcards. | Disallow: /images/* |
| Blocking a section of a website | Disallow a specific section of the website. | Disallow: /admin/* |
Robots.txt Directives and Usage
Robots.txt is a crucial file for website owners to control how search engine crawlers and other web robots interact with their site. It’s a simple text file placed in the root directory of a website, providing instructions on which parts of the site should be crawled and which should be excluded. Understanding its directives is vital for optimizing site traffic and maintaining server resources.This section delves into the various directives within Robots.txt, outlining their functions, syntax, and practical applications.
It provides clear examples to demonstrate how to utilize these directives effectively to manage web crawler access to different parts of your site.
Common Robots.txt Directives
Robots.txt directives are commands that tell web crawlers how to behave when visiting your site. Understanding these directives is key to controlling the crawling process.
Knowing how to block URLs in your robots.txt file is crucial for SEO. It’s all about controlling what search engine crawlers like Google see. This is becoming even more important as Google AI overviews expands to more users, helping them better understand your website structure. Understanding these blocks helps ensure your site’s crawlability and prevents unwanted indexing, making your site more efficient and search engine friendly.
- User-agent: Specifies the web crawler or robot for which the directive applies. It’s essential for targeting specific bots, like Googlebot, Bingbot, or others. This directive is crucial to prevent certain bots from accessing sensitive areas or to optimize for specific search engines.
- Disallow: This directive instructs a specified bot to not crawl specific URLs or directories. Its syntax is `Disallow: /path/to/directory/`. By using this, you prevent unwanted indexing of certain content, protecting your site’s privacy or resources.
- Allow: The opposite of Disallow, this directive instructs a bot to crawl specific URLs or directories. It’s often used to override a Disallow directive or to allow access to particular pages while disallowing others. The syntax is `Allow: /path/to/page/`
- Sitemap: This directive points to a sitemap file, providing a structured list of URLs on your website. Search engine crawlers can use this to efficiently crawl your site.
- Host: Specifies the hostname for the Robots.txt file. Often redundant, as it is typically implied by the file location, it can be useful when the website has multiple domains.
User-agent Directive
The `User-agent` directive is fundamental to controlling which bots access your site. Specifying different user agents allows you to tailor crawl behavior for various bots.
- Specificity: You can be specific by naming a particular bot (e.g., `User-agent: Googlebot`). Or you can use a wildcard (e.g., `User-agent:
-`) to apply the rule to all bots. - Practical Example: If you want to block Googlebot from accessing your `/admin` directory, you’d specify `User-agent: Googlebot` and `Disallow: /admin/`.
Allow and Disallow Directives
These directives are crucial for fine-grained control over crawling. They essentially work in conjunction, with Disallow generally having precedence over Allow.
The Disallow directive prevents crawling, while Allow permits crawling, often used in conjunction to selectively control which parts of a site are crawled.
- Impact Comparison: A `Disallow` directive completely blocks access to a given path. An `Allow` directive overrides the `Disallow` directive for a particular URL, path, or directory.
- Example of Overriding: If you have `Disallow: /images/` and `Allow: /images/featured/`, Googlebot will only crawl the `/images/featured/` directory within the `/images/` directory.
Complex Rules and Combinations
A Robots.txt file can contain multiple directives to create complex rules. Combining directives with different user agents, allow, and disallow directives provides precise control over crawling behavior.
- Example of Multiple Directives: A site might have `User-agent:
-` followed by `Disallow: /private/` to prevent all bots from accessing the `/private/` directory, and then a specific `User-agent: Googlebot` and `Allow: /private/news/` rule for the news directory.
Table of Directive Combinations
| User-agent | Disallow | Allow | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Googlebot | /images/ | /images/featured/ | Googlebot can crawl only /images/featured/ |
| * | /admin/ | All bots are disallowed from /admin/ | |
| Bingbot | / | /index.html | Bingbot can only crawl the index.html |
Implementing and Testing Robots.txt
The Robots.txt file is a crucial component for managing how search engines and other web crawlers interact with your website. Proper implementation ensures that bots only access the content you intend them to, protecting your resources and improving website performance. This section details the steps for implementing and testing your Robots.txt file to maximize its effectiveness.Implementing a Robots.txt file is a straightforward process, but precise placement and accurate syntax are essential.
Following these steps will guarantee your file’s proper function.
Implementing the Robots.txt File
A Robots.txt file is a text file that tells web crawlers which parts of your website they are allowed to access. To implement it, you need to create a file named robots.txt in the root directory of your website. The root directory is the top-level folder where all other website files reside.
Placing the Robots.txt File
The Robots.txt file must be located in the root directory of your website. This ensures that search engine crawlers can easily find it. If it’s not in the root directory, crawlers might not be able to access and read the file, making your directives ineffective.
Testing Robots.txt Effectiveness
Testing the effectiveness of your Robots.txt file is crucial to ensure search engines respect its directives. The steps below Artikel a practical approach for this crucial task.
Step-by-Step Testing Procedure
- Verify File Existence: First, ensure the robots.txt file exists in the root directory of your website. Check for any errors in the file’s name or location. If it’s missing, create one.
- Check Syntax: Verify the syntax of the file adheres to the Robots.txt standard. Review each directive to ensure correct formatting, including capitalization and spacing.
- Test with a Web Crawler: Use a web crawler simulator or a dedicated Robots.txt testing tool. These tools simulate the behavior of search engine crawlers and show you what URLs they’ll crawl or skip, based on your rules. These tools often provide a clear report, highlighting any potential issues.
- Check Search Engine Results: Analyze the content visible in search engine results pages (SERPs). Look for pages that should be excluded, based on your directives, to ensure search engines are respecting your rules. If certain pages are still appearing in results despite the Robots.txt directives, there may be an issue with the file’s syntax or the server’s response to the crawler’s requests.
- Analyze Crawl Errors: If you’re using Google Search Console, review the crawl errors section for any issues related to your Robots.txt file. This can reveal problems like server errors or improperly formatted directives.
Tools for Verifying and Analyzing Robots.txt
Several tools aid in verifying and analyzing Robots.txt files. Using these tools can expedite the process of identifying potential issues and ensures optimal crawler behavior.
Verifying Robots.txt Directives
- Online Robots.txt Testers: Numerous online tools allow you to input your Robots.txt file and simulate how search engines would interpret it. These tools offer immediate feedback on the validity of your directives.
- Google Search Console: Google Search Console provides valuable insights into how Googlebot interacts with your website, including crawl errors potentially related to your Robots.txt file.
Checking Search Engine Respect for Robots.txt
A crucial aspect of ensuring effectiveness is verifying search engines’ adherence to the Robots.txt rules. Tools like Google Search Console offer data to confirm that search engine crawlers are properly respecting your directives.
Step-by-Step Guide for Robots.txt Implementation
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Create a file named robots.txt in the root directory of your website. |
| 2 | Open the robots.txt file in a text editor. |
| 3 | Add directives like User-agent:
, Disallow /private/ |
| 4 | Save the robots.txt file. |
| 5 | Test the robots.txt file using an online validator or simulator. |
| 6 | Review the results and make necessary corrections. |
Advanced Robots.txt Techniques
Robots.txt, while seemingly simple, offers powerful tools for controlling web crawler behavior beyond basic blocking. This section dives into advanced strategies for optimizing crawling, managing specific crawler interactions, and fine-tuning the relationship between Robots.txt and sitemaps for improved website performance. Mastering these techniques can significantly impact how search engines index and present your site to users.Understanding how different crawlers behave and adjusting your Robots.txt accordingly is crucial.
A blanket approach may not always be the most effective strategy. Advanced techniques allow you to tailor your site’s visibility to specific crawlers or to control the depth and frequency of their crawls.
Controlling Crawling Frequency and Depth
Controlling crawling frequency is essential to prevent overloading your server. Overzealous crawling can strain resources and negatively impact website performance. Robots.txt allows you to specify how often a crawler should revisit a page. Using directives like `Crawl-delay` you can introduce pauses between crawls. This prevents overloading and helps maintain a healthy server environment.
For example, setting a `Crawl-delay` of 5 seconds allows the server to recover before the next crawl. This approach is especially helpful for dynamically generated content.
Managing Specific Crawler Behavior
Certain crawlers may exhibit unique behaviors. Robots.txt offers ways to tailor responses to individual bots. For example, you might want to allow a specific crawler to access only certain types of content, while blocking others. This can be useful for managing content intended for specific audiences or preventing crawling of sensitive data. Careful consideration of the crawler’s behavior and your site’s needs is crucial for successful implementation.
Robots.txt and Sitemaps: A Synergistic Relationship
Robots.txt and sitemaps work together to optimize website crawling. Sitemaps provide a list of all pages on your website, while Robots.txt controls access. Using both tools effectively can lead to improved indexing. By directing crawlers to your sitemap, you inform them about the overall structure of your site, aiding them in understanding its hierarchy and content. This can improve the efficiency of crawling.
Best Practices for Robots.txt Optimization
Careful consideration of best practices is essential for optimizing Robots.txt. A well-structured Robots.txt file improves search engine visibility and avoids issues. Always ensure your Robots.txt file is accessible at the root of your domain (e.g., `example.com/robots.txt`). Use clear and concise directives, avoiding ambiguity. Regularly review and update your Robots.txt to adapt to changes in your website and crawler behavior.
Thorough testing is also crucial to ensure that the file is correctly implemented and functioning as intended.
Advanced Robots.txt Scenarios
| Scenario | Robots.txt Configuration | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Blocking specific crawlers | User-agent: MyCrawler Disallow: / |
Blocks the “MyCrawler” bot from accessing any part of the site. |
| Controlling crawl frequency for a specific crawler | User-agent: Googlebot Crawl-delay: 5 |
Instructs Googlebot to wait 5 seconds between crawls. |
| Allowing access to specific directories | User-agent:
Figuring out how to block URLs in your robots.txt file is crucial for website security and SEO. Once you’ve got your site up and running, understanding how to host a website how to host a website is equally important. This knowledge helps you control which search engine crawlers see what content. Properly blocking URLs in robots.txt prevents unwanted indexing and ensures only the right pages get discovered. /private/ |
Allows access to the “/public/” directory while blocking the “/private/” directory. |
| Prioritizing important content for a crawler | User-agent: Bingbot Allow: /important-content/ Disallow: /other-content/ |
Directs Bingbot to prioritize crawling of the “/important-content/” directory. |
Common Errors and Troubleshooting
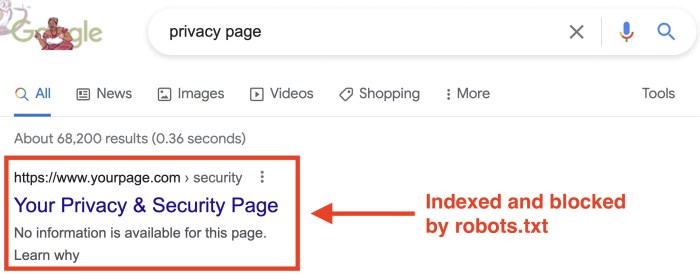
Robots.txt, while a simple file, can trip you up if not configured correctly. Mistakes in syntax, improper implementation, or misunderstanding of directives can lead to unwanted blocking or, conversely, allow access to areas you want to restrict. Thorough troubleshooting is key to ensuring your robots.txt file effectively manages web crawler access and optimizes your site’s .Troubleshooting Robots.txt issues involves identifying the specific error, understanding its impact, and applying the correct solution.
Knowing how to block URLs in your robots.txt file is crucial for SEO. But, to really maximize your website’s visibility and engagement, understanding how to leverage behavioral marketing is key. Check out 7 ways to put behavioral marketing to work starting now for some actionable strategies. This will help you understand how to best target your audience and personalize your content for better results.
Ultimately, combining these strategies with a well-structured robots.txt file will give you a competitive edge online.
Careful examination of the file’s contents, combined with analysis of crawler behavior, is crucial to pinpointing the root cause.
Common Syntax Errors
Incorrect syntax is a frequent cause of Robots.txt problems. These errors can be subtle, but they significantly impact how search engines interpret your file. Errors like missing directives, improper capitalization, or incorrect use of special characters can lead to confusion.
- Missing or Incorrect Directives: A missing “User-agent:” line or an incorrect “Allow” directive will prevent the directive from working as intended. Always ensure every directive begins with the correct , and that values are specified correctly.
- Incorrect Use of Special Characters: Special characters like quotation marks or backslashes, if not properly escaped, can cause errors. Double-check all special characters and ensure they are used correctly.
- Incorrect URL Formatting: URLs within “Disallow” directives must be accurately formatted to prevent crawl errors. Incorrect or incomplete URLs can cause the directive to not work or to be applied to the wrong resource.
Implementation Issues
Implementation issues can arise from incorrect placement or structure of the Robots.txt file. These problems are often related to the server’s configuration and can hinder the effectiveness of the file.
- Incorrect File Location: Ensure the Robots.txt file is placed in the root directory of your website. Incorrect placement can cause search engine crawlers to fail to find it.
- File Permissions: The Robots.txt file must have the correct permissions to be accessible to crawlers. If the file has incorrect permissions, search engines might not be able to read it.
- Server Configuration: Some web servers might have settings that interfere with the Robots.txt file’s operation. Verify your server configuration does not impede the Robots.txt file from working as intended.
Troubleshooting Error Messages
Understanding error messages is critical for effective troubleshooting. These messages, while often cryptic, contain valuable information about the source of the problem. Analyzing the message’s content helps pinpoint the specific error.
- Error Messages from Search Engines: Search engines provide logs or reports that can pinpoint issues. These reports often indicate which directives caused the error.
- Analyzing Server Logs: Your server logs can provide insights into the behavior of crawlers and potential problems with your Robots.txt file. Look for error messages related to file access or processing.
Impact of Incorrect Robots.txt
Issues with Robots.txt can have a significant impact on . Incorrect configurations can lead to either unwanted blocking of crucial content or failure to properly direct crawlers, ultimately affecting indexation and ranking.
- Incorrect Blocking: If essential pages are blocked from crawlers, search engines may not index them. This directly affects your site’s visibility.
- Crawling Inefficiency: If your robots.txt file is poorly structured, it can cause crawlers to waste time on unnecessary URLs. This can lead to decreased crawl budget and reduced indexation.
- Crawl Errors: Incorrectly structured or formatted robots.txt files can trigger crawl errors, preventing search engines from properly accessing and understanding your site.
Resolving Issues with Robots.txt Directives
Troubleshooting involves systematically addressing each directive to identify the source of the problem. A methodical approach to checking directives ensures that every aspect is correctly configured.
- Reviewing Directives: Carefully review each directive in your Robots.txt file to identify potential issues. Look for incorrect syntax, missing directives, or misconfigured URLs.
- Testing with a Web Crawler Simulator: Use a web crawler simulator to test your Robots.txt file and see how crawlers react. This helps pinpoint problems with the file’s implementation.
- Implementing Changes and Retesting: Implement any necessary changes and retest your Robots.txt file. Regularly check search engine logs to ensure changes are effective.
Common Robots.txt Errors and Solutions
| Error | Solution |
|---|---|
| Incorrect syntax in “User-agent” directive | Ensure “User-agent” is followed by a colon and the user-agent string. |
| Missing “Disallow” or “Allow” directive | Add the missing directive with the correct syntax. |
| Incorrect URL format in “Disallow” directive | Double-check the URL format for accuracy. Ensure the URL is complete and correctly formatted. |
| Incorrect file location | Move the Robots.txt file to the root directory of your website. |
Robots.txt and
Robots.txt, while seemingly a simple file, plays a crucial role in how search engines interact with your website. Understanding its impact on is vital for optimizing your site’s visibility and performance. A well-configured Robots.txt file can enhance your search engine ranking and user experience. Conversely, improper use can negatively affect your website’s visibility and ranking.A carefully crafted Robots.txt file can act as a communication channel between your website and search engine crawlers, guiding them to the most important and relevant parts of your site.
This precise guidance can significantly impact your search engine ranking by ensuring that search engines focus their efforts on high-value content.
Relationship Between Robots.txt and Search Engine Optimization
Robots.txt is a crucial component of website . It directly impacts how search engines crawl and index your site’s content, ultimately influencing its ranking. By strategically directing search engine crawlers, you can improve the website’s ranking on search results.
Impact on Search Engine Indexing and Ranking
Proper Robots.txt implementation can lead to improved search engine indexing and ranking. By allowing search engines to focus on essential content, you can achieve a higher ranking in search results. Conversely, a poorly implemented Robots.txt file can hinder search engine crawling, potentially leading to a lower ranking. For instance, if you block crucial content from crawlers, search engines may not index it, impacting your site’s overall visibility.
Examples of How Robots.txt Affects Content Visibility
A Robots.txt file can control the visibility of specific content types or pages on your website. For example, if you want to prevent search engines from indexing a specific product page, you can include a directive to block it. This allows you to fine-tune your content visibility and control which pages are indexed and shown in search results.
Another example involves dynamically generated pages; you can instruct search engines to not index them.
Avoiding Pitfalls When Using Robots.txt
Carefully avoid common pitfalls when using Robots.txt. Blocking essential content, like product pages or blog posts, is a frequent error. Ensure that your Robots.txt file doesn’t inadvertently block pages that should be indexed. Incorrect implementation of directives can also lead to problems. Understanding the syntax and rules of Robots.txt is paramount for preventing unintended consequences.
Improving Website Performance and User Experience
A well-structured Robots.txt file can positively influence both website performance and user experience. By directing crawlers to prioritize important pages, you can improve loading times, leading to a better user experience. This focused crawling also helps your website perform more efficiently. Blocking unnecessary content can also reduce server load, thereby improving website performance.
Correlation Between Robots.txt Configurations and Metrics
| Robots.txt Configuration | Potential Impact | Metrics Affected |
|---|---|---|
| Allowing crawlers access to important content | Improved indexing and higher ranking | Higher visibility, increased organic traffic |
| Blocking irrelevant or duplicate content | Reduced indexing clutter, improved site quality | Better search result quality, lower bounce rate |
| Blocking sensitive or unoptimized content | Protection of sensitive data, better user experience | Positive user experience, enhanced trust |
| Using proper syntax and avoiding errors | Effective crawling and indexing | Improved website performance, higher search ranking |
Last Point: How To Block Urls Robots Txt
In conclusion, mastering how to block URLs using robots.txt is a vital skill for any website owner. By strategically utilizing the various directives and techniques Artikeld in this guide, you can effectively control web crawler access, optimize search engine visibility, and enhance your website’s overall performance. Remember, a well-maintained robots.txt file is key to a successful online presence.