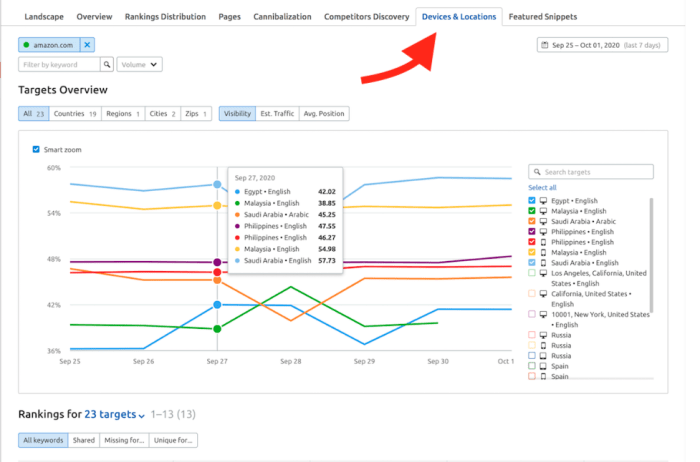
How to understand the Semrush competitive positioning map? This guide dives deep into deciphering these powerful visual tools, revealing how they unlock crucial insights for your marketing strategies. We’ll explore the map’s components, interpreting competitor positions, and identifying market trends to inform your business decisions. Get ready to master the art of competitive analysis!
Semrush competitive positioning maps offer a bird’s-eye view of your industry, showcasing where your competitors stand and how they’re positioned in relation to each other. By understanding these maps, you can gain a strategic advantage, spot opportunities, and refine your marketing tactics. This comprehensive guide will break down the process, from understanding the axes to developing actionable strategies.
Introduction to Competitive Positioning Maps (Semrush): How To Understand The Semrush Competitive Positioning Map
A Semrush competitive positioning map is a visual representation of how different websites rank for specific s. It provides a comprehensive overview of your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses in the search engine results pages (SERPs). This allows you to identify opportunities for improvement and tailor your strategy to better compete in your niche. Understanding these maps is crucial for effective campaigns and strategic market analysis.This map helps you see how competitors are positioned against each other, their strengths in specific s, and the opportunities to surpass them in your niche.
By understanding the competitive landscape, you can adjust your strategies to target high-value s, gain market share, and drive more organic traffic to your website.
Definition of a Competitive Positioning Map
A Semrush competitive positioning map is a dynamic visual tool that displays the competitive landscape for specific s. It graphically represents the relative positions of competing websites based on their rankings. This allows users to quickly grasp the strengths and weaknesses of each competitor in relation to their own website.
Key Elements and Components of a Positioning Map
The map typically shows websites plotted along two axes. The horizontal axis often represents the difficulty or search volume. The vertical axis commonly displays the website’s position in search results for those s. This graphical representation helps quickly identify the s where competitors excel and where your site has potential to gain an advantage. Other important elements include website names, ranking positions, and sometimes even website traffic data.
Visual Representation of a Positioning Map
Imagine a two-dimensional coordinate plane. The x-axis represents the difficulty of ranking for specific s, potentially showing search volume, competitiveness, and other relevant factors. The y-axis represents the ranking positions of the websites for those s. Each website is represented by a marker (circle, square, or other symbol) placed at a point on the map corresponding to its average ranking for a given set of s.
Websites with high rankings and lower difficulty would be clustered in the top-left quadrant, while those with lower rankings and high difficulty would be in the bottom-right quadrant. The closer two markers are to each other, the more similar their rankings and positioning are.
Types of Data Presented on the Map
The map displays crucial data points, including the websites’ domain names or brand names, their average rankings, and their organic search performance. It also might display data about website traffic, estimated monthly search volume, and difficulty. These details offer a holistic view of the competitive landscape and allow for deeper strategic insights.
Format and Layout of a Semrush Competitive Positioning Map
The layout is usually intuitive and straightforward. It typically includes a legend clarifying the different data points, such as ranking positions (1-10, 11-20, and so on), difficulty levels (low, medium, high), or even traffic estimations. The map’s structure enables quick and easy identification of competitor strengths and weaknesses. The map is color-coded to highlight key data points, making it easier to spot patterns and trends.
Understanding the Axes and Dimensions
Competitive positioning maps, like those provided by Semrush, offer a visual representation of the competitive landscape. Understanding the axes and dimensions underlying these maps is crucial for interpreting the data and deriving actionable insights. These maps aren’t just pretty pictures; they reveal the strategic positions of your competitors and provide a framework for analyzing your own position.The axes of a positioning map are not arbitrary; they represent key factors that drive competition within a particular market.
Analyzing these factors reveals the competitive landscape and helps businesses identify opportunities and threats. By understanding the dimensions that define a competitor’s position, you gain insights into their target audience, pricing strategies, and marketing approaches. This knowledge is vital for developing effective strategies and gaining a competitive edge.
Horizontal and Vertical Axes
The horizontal and vertical axes of a positioning map typically represent different competitive dimensions. These dimensions can vary depending on the industry and the specific analysis being conducted. A common example is comparing price and quality. One axis might represent price, and the other axis could represent features, or brand reputation.
Defining Competitive Dimensions
Competitive dimensions are the key factors that differentiate competitors. They are the specific characteristics that customers value and use to make purchasing decisions. These dimensions can include product features, price points, target audience, marketing strategies, brand image, and customer service.
Decoding the Semrush competitive positioning map can seem daunting, but it’s easier than you think. Essentially, you’re looking at how your competitors stack up against you across different keywords and metrics. Understanding this requires a good grasp of your own website’s performance, which often hinges on data from analytics tools like Google Analytics. Switching to Google’s new GA4 platform from Universal Analytics is a significant change, impacting how you interpret data.
To effectively use the Semrush map, you need to ensure your data is accurate and reliable. By comparing your GA4 (or Universal Analytics, if that’s still your current platform) data with the Semrush map, you can fine-tune your strategy for greater visibility and competitive advantage. ga4 vs universal analytics This helps you tailor your SEO and marketing efforts to capture the most relevant traffic and outrank competitors.
Measuring and Interpreting Dimensions
Semrush, and other similar tools, measure these dimensions using various metrics. These metrics are often numerical or qualitative. Numerical metrics can include price, customer satisfaction ratings, or website traffic. Qualitative metrics might include brand perception, product quality, or customer service levels. These metrics are crucial for accurately positioning competitors on the map.
Interpretation depends on the specific context. For example, a high score on customer satisfaction might be associated with a premium price point, indicating a high-quality brand.
Positioning Competitors
Competitors are positioned on the map based on their scores on the chosen dimensions. For example, a competitor known for high-quality products and premium pricing would likely be positioned in the upper-right quadrant of the map. Conversely, a competitor focused on affordability and basic features would likely be positioned in the lower-left quadrant. These positions give a quick overview of each competitor’s approach and how they compare to each other.
Common Metrics for Positioning Map Axes
- Price: Typically measured in monetary units (e.g., USD, EUR). A lower price point is positioned on the left side of the map, while a higher price point is positioned on the right.
- Product Features: Measured by the number and sophistication of features offered. More features are positioned on the right side of the map.
- Customer Service: Assessed through customer satisfaction ratings, reviews, or response times. Higher ratings are typically positioned on the upper side of the map.
- Brand Reputation: Measured by brand awareness, customer loyalty, and positive reviews. Higher reputation is usually placed towards the upper part of the map.
- Market Share: Often presented as a percentage of the total market. A higher market share suggests a stronger position in the market.
By understanding these metrics and their interpretation, businesses can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
Interpreting Competitor Positions
Understanding where your competitors sit on a Semrush Competitive Positioning Map is crucial for crafting effective strategies. It’s not just about identifying their general area; it’s about deciphering the nuances of their position to uncover their strengths and weaknesses. By analyzing their relative placement, you can pinpoint opportunities to capitalize on their vulnerabilities and solidify your own market position.
Analyzing Competitor Positioning, How to understand the semrush competitive positioning map
Competitor positioning on the map reveals valuable insights into their target audience, marketing strategies, and overall business approach. A competitor positioned close to you likely shares similar strengths and weaknesses. Conversely, a competitor far removed might utilize different tactics, offering unique avenues for differentiation.
Evaluating Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses
A competitor’s position on the map offers a glimpse into their core competencies and areas needing improvement. Consider the dimensions represented on the map. If a competitor excels in a specific dimension, it suggests a targeted strategy. Conversely, a weaker position in a certain area signifies a potential vulnerability. For instance, if a competitor scores highly in the “Brand Awareness” dimension but struggles in “Search Visibility,” their marketing might be heavily focused on brand building but potentially lacking in optimization.
Understanding these strengths and weaknesses allows you to develop targeted counter-strategies.
Exploiting Competitor Weaknesses
Recognizing a competitor’s weaknesses based on their positioning allows you to identify opportunities for growth. If a competitor is underperforming in a specific dimension, you can leverage that gap to cater to the unmet needs of the market segment. For example, if a competitor lacks robust content marketing strategies, you can leverage high-quality content to capture their audience.
Remember to be data-driven in your approach, rather than relying on assumptions.
Comparative Analysis of Competitor Positions
This table illustrates a hypothetical comparison of competitor positions on a Semrush Competitive Positioning Map, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
| Competitor | Brand Awareness | Search Visibility | Customer Acquisition Cost | Customer Lifetime Value | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | High | Medium | Low | High | Strong brand presence, cost-effective acquisition. | Needs improvement in search visibility for better organic traffic. |
| Company B | Medium | High | Medium | Medium | Excellent performance. | Potentially higher customer acquisition costs, average customer lifetime value. |
| Company C | Low | Low | High | Low | None. | Poor brand awareness and low visibility in search. High CAC, low CLV. |
This table provides a snapshot of potential competitor positions. Real-world scenarios will involve more detailed data and specific metrics. The data presented is hypothetical and for illustrative purposes only.
Analyzing Market Trends and Shifts
Competitive positioning maps aren’t just static snapshots; they’re dynamic tools reflecting evolving market landscapes. Understanding how the competitive landscape shifts over time is crucial for strategic decision-making. By analyzing trends and shifts revealed within Semrush’s competitive positioning maps, businesses can proactively adjust their strategies to maintain or gain a competitive edge.Analyzing these maps allows for the identification of emerging opportunities and threats.
It provides insights into how competitors are reacting to market changes, enabling businesses to anticipate and adapt to the ever-shifting dynamics of the market. This dynamic understanding of the competitive landscape is vital for long-term success.
Identifying Market Trends
Market trends manifest as patterns in competitor positions, reflected in the positioning map. Identifying these patterns requires careful observation of how competitors shift their positions over time. The movement of competitors along the axes of the map indicates changes in their offerings, target audience, and market positioning strategies. A clustering of competitors in a particular area signifies a growing market segment or a burgeoning trend.
Conversely, the absence of competitors in a certain area suggests an unmet need or a niche that might be ripe for exploitation.
Decoding the Semrush competitive positioning map can feel overwhelming, but it’s crucial for strategic planning. Essentially, you’re looking at how your competitors are positioned in the market and identifying gaps and opportunities. This understanding is vital for crafting a winning strategy, and, as you’ll see from this insightful article on how the 7 habits of highly effective people is a blueprint for the positionless marketer , adapting your approach to become a positionless marketer is key.
Ultimately, mastering the map allows you to craft a more impactful and focused approach in your digital marketing strategy.
Detecting Patterns and Changes
To detect patterns and changes, analyze the map’s data points over time. This includes observing the frequency of movement, direction of shifts, and any clustering or dispersion of competitors. Tracking competitor positions over a period, such as quarterly or annually, provides valuable data. Tools like Semrush allow for the comparison of different time frames, revealing how competitors react to market fluctuations.
Analyzing these movements allows you to identify market trends and shifts with increased accuracy.
Significance of Understanding Market Trends
Understanding market trends is vital for strategic decision-making. Recognizing shifts in the competitive landscape enables companies to adapt their marketing strategies and product development efforts to maintain relevance. This adaptability is crucial for remaining competitive in a dynamic market. Recognizing emerging trends and opportunities allows businesses to proactively adjust their strategies, taking advantage of potential gains and mitigating potential risks.
Adapting Strategies to Changing Conditions
Adapting strategies is a direct outcome of understanding market trends. Semrush’s competitive positioning maps provide a framework for businesses to analyze how their competitors are adjusting their strategies. Identifying areas where competitors are gaining traction or losing ground is key. Businesses can then allocate resources to capitalize on emerging opportunities or mitigate threats to their position. By adapting to changing market conditions, companies can strengthen their competitive advantage.
Evolution of Competitor Positions
The following table illustrates the evolution of competitor positions over a period of two years. The data, derived from Semrush, displays the movement of key competitors along the axes of the positioning map.
| Competitor | Year 1 Position (x-axis, y-axis) | Year 2 Position (x-axis, y-axis) | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | (High Value, High Service) | (High Value, Medium Service) | Shifting focus towards a more cost-effective service model |
| Company B | (Medium Value, Low Service) | (High Value, High Service) | Significant repositioning to a premium value and service provider |
| Company C | (Low Value, High Service) | (Low Value, Low Service) | Maintaining a basic value proposition, possibly facing market pressures |
Note: This is a sample table. Actual data would be specific to the industry and competitors being analyzed. Real-world data would incorporate quantitative metrics to support the trends observed.
Developing Strategies Based on Insights
Understanding competitor positioning isn’t just about observation; it’s about action. A Semrush competitive positioning map reveals not only where competitors stand but also the opportunities for your brand to carve out a unique space in the market. By analyzing these insights, you can develop targeted strategies that strengthen your market presence and propel your business forward.Leveraging the insights from the map requires a strategic approach, going beyond simply identifying competitors’ strengths and weaknesses.
It involves a deep dive into market trends, understanding customer needs, and identifying gaps in the existing landscape. This allows you to craft effective marketing campaigns and fine-tune your product offerings to better meet the needs of your target audience.
Strategies for Leveraging Insights
Understanding competitor positioning is crucial for developing effective marketing strategies. Analyzing the data reveals potential opportunities for differentiation and market positioning. This includes identifying niche markets or underserved customer segments that your competitors are overlooking. Identifying these untapped opportunities allows you to carve out a distinct space in the market.
- Competitive Differentiation: Identify unique selling propositions (USPs) that set your brand apart from the competition. Consider factors like pricing strategies, product features, customer service, and brand identity. If your competitors are focusing on high-end products, a strategy focused on mid-range value could attract a broader audience. Conversely, if your competitors are primarily focused on cost leadership, emphasizing superior quality or customer service could be a differentiator.
- Market Segmentation: Segment your target market based on the positioning map. Identify customer groups that your competitors are not effectively serving. This can be a specific demographic, a particular need, or a particular pain point. By focusing your marketing efforts on these underserved segments, you can capture a significant share of the market.
- Refining Marketing Campaigns: Use the positioning map to identify areas where your marketing campaigns need adjustment. For example, if your campaigns are not effectively reaching your target audience, the map might highlight a need to adjust messaging or channels. The positioning map might reveal that your current campaign messaging is too broad, prompting you to tailor it to a more specific customer segment.
- Identifying Opportunities for Market Positioning: Look for unfilled spaces or gaps in the market. The map can highlight areas where no competitors are present, or where they are under-represented. This could be a specific product feature, a price point, or a particular customer segment. This could mean exploring new product lines or services or even repositioning your existing offerings to fill this gap.
Examples of Positioning Analysis in Marketing Strategies
The insights gained from competitor positioning analysis can inform various aspects of your marketing strategy.
- Product Development: A positioning map might reveal a need for a new product line or a specific feature that is currently missing in the market. For instance, a competitor may be dominating the premium segment, while the budget-conscious segment remains underserved. This analysis could suggest developing a product with a comparable level of quality but at a lower price point.
- Pricing Strategies: By analyzing competitor pricing, the map can provide insights into optimal pricing strategies for your products. If competitors are offering similar products at a premium price, a strategy focused on value pricing or a lower entry price could be more attractive to customers. Likewise, if competitors are significantly undercutting you, your strategy might need to focus on emphasizing superior quality or value-added services.
- Marketing Channel Optimization: The positioning map can highlight which marketing channels are most effective for reaching your target audience. If your competitors are heavily focused on social media advertising, you might need to explore alternative channels like email marketing or content marketing to stand out.
Improving Business Position on the Map
A detailed action plan is essential for improving your business’s position on the competitive positioning map.
- Establish Clear Objectives: Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives for your business. This could include increasing market share, gaining more customers, or entering new segments.
- Develop a Detailed Action Plan: Artikel the specific actions required to achieve your objectives. This could include product development, marketing campaigns, or strategic partnerships. For example, if the analysis shows a gap in the market for a specific product feature, the action plan might involve developing that feature and launching a targeted marketing campaign highlighting it.
- Monitor and Adapt: Continuously monitor your progress and adapt your strategies based on the results. The competitive landscape is constantly evolving, so it’s essential to stay updated and adjust your approach accordingly.
Practical Application Examples
Putting the principles of competitive positioning map analysis into practice can unlock valuable insights for businesses. By visualizing the competitive landscape, companies can identify opportunities for differentiation, pinpoint areas of vulnerability, and develop more effective strategies. Understanding where your competitors stand relative to your own position is crucial for success in today’s dynamic market.
Retail Industry Example
Retailers often use positioning maps to analyze the competitive landscape and understand customer preferences. For example, consider a map plotting price against product quality for electronics retailers. A map might show a cluster of competitors, like Best Buy, focused on a higher price point with a premium quality positioning. Meanwhile, budget-focused retailers like Walmart might occupy a different area of the map, emphasizing lower prices but with slightly lower quality products.
Smaller, specialty retailers might occupy a niche position, offering a specific type of product at a competitive price point. Analyzing these positions helps identify gaps in the market, areas where retailers can differentiate themselves, and target specific customer segments.
Software as a Service (SaaS) Example
In the SaaS industry, positioning maps can be used to identify competitors based on features and pricing models. A map might plot the number of features against the price tier. Some companies might focus on a comprehensive suite of features at a higher price point, while others may offer a more limited feature set at a lower price.
The map can reveal where your company fits into the landscape and identify areas where you can differentiate your product by offering a specific set of features at a competitive price point. Companies can target specific customer segments by focusing on a niche in the market.
Table: Competitive Positioning of Online Grocery Retailers
| Company | Price | Selection | Convenience | Customer Service |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon Fresh | Mid-range | Extensive | High | Good |
| Instacart | Mid-range | Limited (dependent on local availability) | High | Average |
| Walmart Grocery | Low | Extensive | Medium | Average |
| Kroger | Low | Extensive | Medium | Good |
This table illustrates how different online grocery retailers position themselves based on four key dimensions. This allows companies to quickly identify their strengths and weaknesses relative to competitors and adapt their strategies accordingly. Note that these are illustrative positions and specific data would vary based on market research.
Analyzing Market Trends and Shifts
Competitive positioning maps can be instrumental in analyzing market trends. For instance, if a trend toward subscription-based services emerges in a specific market, the positioning map will likely show a shift in competitor positioning. By monitoring these shifts, companies can adjust their strategies to capitalize on emerging opportunities or mitigate potential threats.
Visualizing Competitor Data
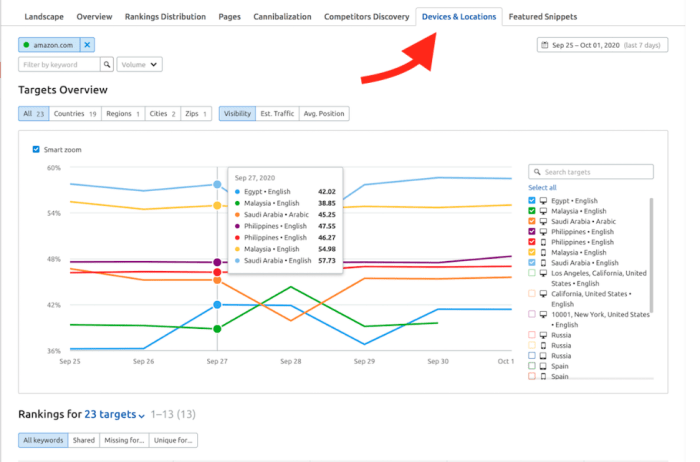
Bringing competitor data to life is crucial for effective strategy development. Visual representations of competitive positioning maps allow for quick comprehension of market dynamics, competitor strengths and weaknesses, and emerging trends. By visualizing this information, businesses can swiftly identify opportunities and adapt to changing market conditions.
Creating a Visually Appealing Competitive Positioning Map
A well-designed map is key to understanding the data. Use colors to differentiate competitors and segments. Clearly label axes with relevant metrics like price, quality, or features. Employ icons or symbols to represent specific aspects of each competitor’s offering, such as product type, target audience, or key differentiators. A legend should be included to quickly clarify the meaning of symbols and colors.
Illustrating Competitor Positioning Relative to Others
A scatter plot representation is ideal. Each competitor is plotted as a point on the map, with its coordinates representing its position on the chosen axes. For example, a competitor focusing on high quality and high price would be positioned in the upper-right quadrant. The proximity of competitors on the map visually illustrates their relative similarity or difference in terms of the selected parameters.
The visual distance between points directly correlates with the difference in their positioning.
Illustrating Market Trends and Shifts
The map can highlight shifts in the market. For example, if a cluster of competitors moves towards a higher-quality quadrant over time, it suggests a growing demand for higher-quality products in that segment. The map can also reveal emerging niches or unoccupied spaces, where new entrants or existing competitors could potentially capitalize. Visualize these shifts using different colors or markers to indicate time periods.
Representing Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses
A visual representation of strengths and weaknesses can be overlaid on the map. For example, a competitor positioned in the lower-left quadrant might be highlighted with a weakness symbol in the “price” category, while having a strength in the “ease of use” category. Visual cues like arrows, symbols, or different shades of color can be used to indicate strengths and weaknesses, thereby providing a clear snapshot of the competitor’s position in the market.
Figuring out the Semrush competitive positioning map is all about spotting the gaps and overlaps in your competitors’ strategies. Understanding their strengths and weaknesses helps you pinpoint areas where you can gain a competitive edge. This, in turn, directly connects to the difficulty of technical SEO, a critical component in any successful digital marketing strategy. For instance, are your competitors struggling with site speed or mobile-friendliness?
Knowing this, you can adjust your technical SEO approach accordingly, as outlined in a great article on is technical seo hard. Ultimately, a deep dive into the competitive positioning map is key to building a solid SEO strategy that will withstand the challenges of the online landscape.
Representing Competitor Positions on the Map
A crucial step is selecting appropriate axes and data points. For example, if analyzing e-commerce businesses, the axes could represent “average order value” and “customer acquisition cost.” Competitor data points should be accurately plotted, considering the relevant parameters, and ideally, updated regularly. By visually depicting each competitor’s position, the map allows for a quick comparison of strengths and weaknesses, leading to a deeper understanding of the competitive landscape.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
Delving deeper into Semrush’s competitive positioning maps requires understanding nuances beyond the initial visualization. This section explores advanced techniques for a more robust analysis, including identifying potential pitfalls and incorporating external factors for a more complete picture. Accurate interpretation hinges on recognizing limitations and acknowledging external influences that shape the competitive landscape.Advanced analysis of competitive positioning maps isn’t just about identifying where competitors sit; it’s about understandingwhy* they’re there and how their strategies might evolve.
This includes considering the potential impact of market trends, economic shifts, and even unforeseen events.
Refining Accuracy and Reliability
Understanding the factors that influence the accuracy of a competitive positioning map is crucial for a sound analysis. Data sources, the timeframe of the data, and the methodology used to collect and analyze competitor data all play a role. For example, relying solely on organic search data may not fully capture the competitive landscape if competitors heavily invest in paid advertising.
Evaluating Data Sources and Methodology
The quality of data used directly impacts the reliability of the map. Positioning maps are often based on various data points, including website traffic, rankings, and social media engagement. Using multiple sources and diverse metrics helps ensure a more comprehensive and balanced view. For instance, combining website traffic data with social media engagement metrics provides a more holistic understanding of a competitor’s overall online presence.
A competitor might rank high for certain s but have minimal social media engagement, indicating a focus on different aspects of their strategy.
Potential Limitations and Caveats
Competitive positioning maps offer valuable insights, but they aren’t without limitations. The static nature of the map can mask dynamic market shifts and competitor adaptations. For example, a competitor might rapidly shift their strategy in response to a market trend or new technological development. The map might not reflect these changes immediately, potentially leading to an inaccurate assessment of their current positioning.
Moreover, the map might not capture nuanced aspects of competitor strategies, like their brand reputation or customer loyalty programs.
Considering External Factors
The competitive landscape isn’t confined to the parameters of a positioning map. External factors, such as economic conditions, technological advancements, and regulatory changes, can significantly impact competitor strategies and market dynamics. For instance, a rise in inflation could affect consumer spending patterns, potentially impacting the demand for certain products or services, and influencing competitor positioning in the market.
Robustness Framework
Developing a framework for evaluating the robustness of the analysis is essential. This framework should incorporate checks on data accuracy, consideration of external factors, and an assessment of the map’s limitations. A robust framework should involve a multi-faceted approach, including cross-referencing data from various sources, assessing the historical trends, and evaluating the potential for future shifts.
Example: Evaluating a Competitor’s Shift
Imagine a competitor that suddenly jumps to a higher position in the positioning map. A thorough analysis should delve beyond the map itself. Factors like new product launches, successful marketing campaigns, or even industry-specific events could explain this shift. The robustness of the analysis hinges on the researcher’s ability to connect the dots and consider external factors to paint a more complete picture.
A thorough analysis could reveal that the competitor recently launched a new product that resonated with a specific demographic, causing a significant increase in demand.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, mastering Semrush competitive positioning maps empowers you to make data-driven decisions and gain a competitive edge. By understanding competitor positioning, market trends, and leveraging the insights gained, you can refine your marketing strategies, identify opportunities for differentiation, and ultimately, improve your business’s market position. This guide has provided the tools you need to navigate these powerful visuals and gain a competitive advantage.