How to migrate to GA4 is a critical question for businesses today. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the process, outlining everything from the fundamentals of GA4 and its differences from Universal Analytics to practical implementation steps and crucial data analysis techniques. We’ll cover planning, data migration strategies, implementing tracking, customization, and reporting, all the way to troubleshooting common issues and providing valuable resources.
Understanding the benefits of migrating to GA4 is key to success. This guide helps you grasp the advantages and empowers you to make an informed decision about your digital analytics strategy. You’ll discover how to effectively transition your data and utilize GA4’s powerful features to gain actionable insights.
Introduction to Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) represents a significant shift in how website and app data is collected and analyzed. It’s a fundamental upgrade from Universal Analytics (UA), designed for a future where data is collected in a more holistic, unified, and versatile manner. GA4 embraces the increasing complexity of digital experiences and the importance of understanding user behavior across various touchpoints.GA4’s core architecture is based on a more flexible and adaptable approach, shifting from a session-based model to a more event-driven model.
This allows for richer insights into user interactions, from initial engagement to conversions. This adaptability is critical in today’s dynamic digital landscape where user journeys are often non-linear and interactions can occur across multiple devices and channels.
Key Differences from Universal Analytics
GA4 differs from Universal Analytics in several fundamental ways. UA focused primarily on session-based data, while GA4 utilizes an event-driven model, providing a more granular and comprehensive view of user interactions. This event-driven approach allows for the tracking of a wider range of user actions, providing a richer understanding of user behavior. GA4 also utilizes machine learning to better understand user behavior and provide more accurate predictions.
Benefits of Migrating to GA4
Migrating to GA4 offers numerous advantages for businesses. It provides a more comprehensive understanding of user behavior, enabling businesses to personalize experiences and optimize campaigns. GA4’s event-driven model allows for a more granular understanding of user journeys, providing insights into the factors that influence conversions. Furthermore, GA4 provides a more streamlined and unified platform for analyzing data from websites and apps, reducing complexity and improving efficiency.
Importance of Data Integrity and Migration Strategies
Data integrity is paramount during the migration process. A meticulous approach to data migration ensures the accuracy and consistency of data from Universal Analytics to GA4. This process requires a careful mapping of existing UA metrics to equivalent GA4 events, ensuring that critical data points are not lost or misinterpreted. Effective migration strategies are crucial to minimize disruption and maximize the value of the data transition.
A phased approach, testing and validation, and a clear plan for data integration are vital elements in ensuring a smooth and successful transition.
Effective Migration Strategies
A well-defined migration strategy is critical for a successful transition. The process should include a thorough audit of existing UA data and a careful analysis of the business objectives. This process should also encompass the establishment of a clear timeline, a detailed mapping of UA metrics to GA4 events, and a rigorous testing and validation plan to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
Implementing a phased approach to the migration, where you gradually transition traffic and data, is essential to minimize disruption to business operations. It’s crucial to regularly review and evaluate the effectiveness of the migration to identify any potential areas for improvement.
Migrating to GA4 can seem daunting, but it’s crucial for tracking website performance. Before diving into the technical aspects, you need to optimize your website’s visibility. Luckily, getting your start in SEO with these 10 free tools get your start in seo with these 10 free tools will set you up for success. This will help you understand user behavior and ultimately refine your GA4 setup for accurate insights.
Then you can effectively analyze the data and adjust your strategies for better results.
Data Mapping
Careful mapping of existing Universal Analytics (UA) metrics to equivalent Google Analytics 4 (GA4) events is essential for data integrity. This mapping should be meticulously performed, taking into account all crucial metrics and their corresponding GA4 event equivalents. It ensures that no significant data points are lost or misinterpreted during the transition. A clear documentation of the mapping process will aid in future reference and troubleshooting.
A dedicated team should be responsible for the accuracy of the mapping to avoid errors. For instance, if a UA “purchase” event corresponds to a GA4 “purchase completion” event, this mapping should be clearly defined and tracked. The accuracy of this mapping is critical to maintaining data integrity and ensuring the insights gained from GA4 are reliable and actionable.
Planning the Migration
Migrating to Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is a crucial step for businesses looking to leverage the latest analytics platform. Careful planning is essential for a smooth transition, minimizing disruption to your existing workflows and maximizing the benefits of the new system. This process involves more than just setting up a new property; it encompasses a comprehensive strategy for data collection, analysis, and reporting.A well-planned GA4 migration ensures that your business retains its historical data while adapting to the new platform’s features and structure.
This allows for seamless comparison between previous and current data, enabling a more accurate understanding of trends and performance changes.
Step-by-Step Migration Process
A structured approach to migration is key to success. A phased rollout minimizes disruption and allows for testing and adjustments along the way. Start by identifying your goals and key metrics. This involves understanding your business objectives and which GA4 features will best support them. Defining success criteria early allows you to measure the effectiveness of the migration.
- Assessment & Planning: Evaluate your current Google Analytics setup, identify key reporting areas, and determine your desired outcome for the migration. Understand the differences between Universal Analytics and GA4 to anticipate any data discrepancies or potential challenges.
- Data Collection Strategy: Determine the data points you’ll need from GA4. This includes defining the events and dimensions crucial to your reporting needs. Carefully consider which custom dimensions and metrics will be required in GA4.
- GA4 Property Setup: Create a new GA4 property, carefully following Google’s instructions. Verify the correct data stream settings are configured, ensuring all necessary data is captured.
- Tagging Implementation: Implement GA4 tags on your website or app. Testing is crucial to ensure accurate data collection. Thoroughly review tag configurations to avoid data loss or inconsistencies.
- Data Validation & Reporting: Verify the accuracy of the data collected in GA4. Compare reports with your previous Universal Analytics data to identify discrepancies and make necessary adjustments. A side-by-side comparison of reports can quickly highlight areas for improvement.
- Data Migration (Optional): Depending on your needs, a data migration may be required to transfer historical data from Universal Analytics to GA4. This is a complex process, requiring expert guidance and careful planning.
- Training & Documentation: Provide training to your team on using the GA4 platform and the new reporting features. Comprehensive documentation is essential for maintaining consistency and ensuring long-term success.
Required Resources
Effective migration requires careful consideration of personnel, tools, and time.
- Personnel: Dedicated personnel, including data analysts or digital marketing specialists, are essential for overseeing the migration process. The required skillset includes technical expertise in web analytics, a strong understanding of data collection, and an ability to translate data into actionable insights. Consider outsourcing specialized tasks like data migration if your internal resources are limited.
- Tools: Tools like Google Tag Manager (GTM) and other data collection tools are crucial. Consider utilizing external tools for data migration if necessary. This might include specialized software designed to facilitate the transfer of data between platforms.
- Time: Realistic timelines must be set. The migration process can take several weeks or even months, depending on the complexity of your website or app and the scope of your data collection needs. Allow sufficient time for planning, testing, and implementation.
Migration Checklist
A comprehensive checklist ensures no critical steps are overlooked.
| Task | Status |
|---|---|
| Define migration goals | |
| Assess current GA setup | |
| Identify key metrics | |
| Create GA4 property | |
| Configure data streams | |
| Implement GA4 tags | |
| Test data collection | |
| Validate data accuracy | |
| Train team on GA4 | |
| Document procedures |
Setting up GA4 Property and Tag
Properly setting up your GA4 property and tag is essential for accurate data collection. This involves configuring data streams, implementing tags, and ensuring data accuracy.
- Create a GA4 Property: Access the Google Analytics admin panel, and create a new GA4 property. Fill in the necessary information about your website or app, including the appropriate data stream type.
- Implement GA4 Tags: Utilize Google Tag Manager (GTM) to implement the GA4 tag. Configure the tag to capture the desired events and dimensions. Double-check your settings to ensure they align with your data collection goals.
Data Migration Strategies
Navigating the transition from Universal Analytics to Google Analytics 4 (GA4) requires a well-defined migration strategy. A thoughtful approach ensures minimal disruption to your existing analytics workflow and allows for a smooth integration of the new platform’s features. This involves careful planning, execution, and validation to maintain accurate and insightful data.Choosing the right migration strategy, coupled with thorough data validation and cleansing, is crucial for successful GA4 implementation.
This section delves into various migration approaches, highlighting the importance of data quality and the process of mapping Universal Analytics metrics to their GA4 counterparts. This ensures you can effectively utilize GA4 to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and gain valuable insights for future decision-making.
Data Migration Approaches
Different migration strategies offer varying degrees of complexity and impact on your existing analytics setup. Understanding these approaches allows you to select the best fit for your specific needs.
- Full Migration:
- Incremental Migration:
This approach involves immediately switching all data collection to GA4. While potentially faster, it requires a complete overhaul of your tracking implementation. It is often preferred when a complete overhaul is deemed necessary, and the organization has sufficient resources to manage the transition and potential data discrepancies.
This strategy gradually transitions data collection to GA4. It involves a phased approach, allowing you to monitor the impact of the change and address any issues that arise. This approach minimizes disruptions to existing workflows and allows for a more controlled transition, especially for large organizations with intricate analytics setups.
Data Validation and Cleansing
Maintaining data integrity during the migration process is paramount. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading insights and flawed decision-making. Therefore, validating and cleansing your data is a critical step in the GA4 migration process.
- Data Validation:
- Data Cleansing:
Validating data involves verifying the accuracy and completeness of the data collected. This step checks for missing values, inconsistencies, and outliers. Techniques such as data profiling, data quality checks, and data scrubbing are commonly used.
Cleansing involves correcting or removing inaccurate or incomplete data. This ensures data quality and reliability. It includes addressing inconsistencies, correcting errors, and handling missing values.
Identifying Critical Data Points and KPIs for GA4
A crucial aspect of the migration is identifying the key metrics that are most important for your business. These data points, known as Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), will guide your analysis and decision-making after the migration.
- Defining KPIs:
- Example KPIs:
The identification of crucial data points and KPIs should be tailored to the specific goals of your business. Factors like website traffic, user engagement, conversion rates, and revenue are often crucial. This process should be collaborative, involving stakeholders from various departments.
Some example KPIs include website sessions, bounce rate, conversion rate, average session duration, and revenue per user. The selection of KPIs depends on the objectives of your business.
Mapping Universal Analytics Metrics to GA4 Equivalents, How to migrate to ga4
Successfully migrating data requires a clear understanding of how Universal Analytics metrics translate to GA4. A detailed mapping process ensures seamless data transfer and analysis.
- Metric Mapping:
- Example Mapping:
This process involves identifying the corresponding GA4 metrics for each Universal Analytics metric. A detailed mapping document can be extremely useful. This often requires thorough research and cross-referencing documentation.
For example, “Sessions” in Universal Analytics might correspond to “Sessions” in GA4, but the exact implementation details might differ. Understanding these nuances is critical for accurate reporting.
Implementing GA4 Tracking
Getting your website set up for Google Analytics 4 (GA4) tracking is a crucial step in leveraging its powerful features. This involves integrating the GA4 tracking code into your website’s codebase and configuring various settings to capture the data you need. Proper implementation ensures accurate data collection, enabling you to make informed decisions about your website’s performance.Effective implementation is not just about inserting code; it’s about understanding how to configure tags for different events and conversions, allowing you to gain deep insights into user behavior and website effectiveness.
This detailed guide walks you through the necessary steps, including event tracking examples and using enhanced measurement for a comprehensive data collection strategy.
Migrating to GA4 can seem daunting, but it’s easier than you think. A crucial part of the process involves setting up your Google Tag Manager for video tracking, which is essential for accurate data collection. Understanding how to correctly implement google tag manager for videos will help you get the most out of your GA4 setup.
Ultimately, a well-configured GTM implementation is key to a smooth GA4 migration.
Installing the GA4 Tracking Code
Integrating the GA4 tracking code is the foundation for data collection. This involves placing a snippet of JavaScript code on all pages of your website. This code communicates with the GA4 servers, allowing data to be sent for analysis. The specific code snippet is generated in your GA4 property settings. Copy this snippet and paste it into the `
` section of each page’s HTML code. This ensures that GA4 can collect data from all pages.Configuring GA4 Tags for Website Elements
Once the tracking code is installed, you need to configure GA4 tags to capture data from various website elements. This involves specifying which actions and interactions you want to track. For example, you might want to track button clicks, form submissions, or video plays. Configuring these tags allows for a detailed analysis of user interactions with your website.
Event Tracking Examples
Tracking specific user actions is vital for understanding user behavior. Here are some examples of event tracking for various actions:
- Product Clicks: When a user clicks on a product image or link, an event can be triggered. This allows you to track which products are generating the most interest. Example: The event name could be “product_click,” and the parameters could include the product ID, category, and price.
- Form Submissions: Tracking form submissions is crucial for understanding conversion rates and lead generation. An event can be triggered when a user submits a contact form or newsletter signup. Example: The event name could be “form_submission,” and the parameters could include the form type and any submitted data.
- Video Plays: Monitoring video plays helps understand user engagement with video content. An event can be triggered when a user starts watching a video. Example: The event name could be “video_play,” and the parameters could include the video title and duration.
These examples demonstrate how you can tailor event tracking to your specific needs, allowing you to collect relevant data about user interactions.
Using Enhanced Measurement Settings
Enhanced measurement settings automatically collect data about various interactions without requiring explicit event tracking. This includes automatic tracking of page views, scrolling depth, and outbound clicks. This feature significantly simplifies implementation and provides additional insights into user behavior. The enhanced measurement settings can improve data collection by automatically detecting and tracking various events without explicit configuration, saving time and effort.
Customizing GA4 for Your Needs
Beyond the basic tracking, GA4 offers powerful customization options to tailor the platform to your specific business needs. This allows you to delve deeper into user behavior and gain insights directly relevant to your objectives. By configuring custom dimensions and metrics, you can collect data uniquely relevant to your business processes, and create custom events to capture specific user interactions.
Furthermore, sophisticated segmentation enables the extraction of targeted insights, ultimately driving data-driven decisions.Customizing GA4 isn’t just about adding bells and whistles; it’s about unlocking the true potential of your data. By tracking the right metrics and segmenting your audience effectively, you can pinpoint the most valuable customer segments, understand their behaviors, and ultimately optimize your marketing strategies.
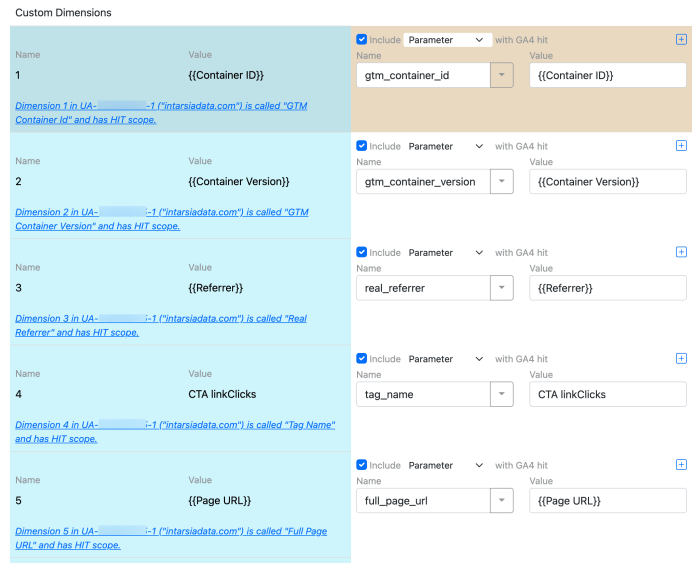
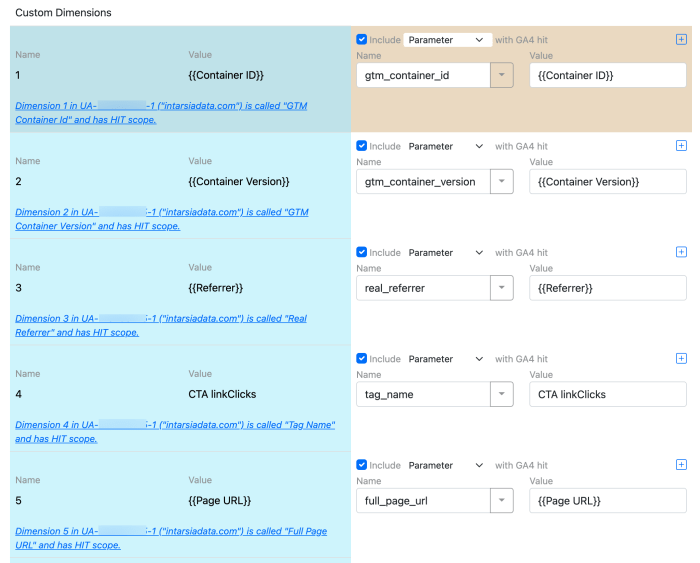
Custom Dimensions and Metrics
Custom dimensions and metrics provide a way to categorize and measure aspects of your data that aren’t covered by the standard GA4 properties. This is crucial for building a richer understanding of user interactions.
- Defining Custom Dimensions: These allow you to categorize data points. For instance, you might track the source of a lead (e.g., social media, email, referral). This extra layer of detail allows you to segment users by source and analyze which channels are most effective.
- Defining Custom Metrics: These provide numerical values for your data. For example, if you want to measure the average time a user spends on a specific page, you can define a custom metric. This gives you a more comprehensive view of user engagement.
Custom Events
Custom events are fundamental to tracking specific user interactions within your website or app. They extend GA4’s tracking capabilities by enabling the capture of actions that are not standard.
Migrating to GA4 can seem daunting, but it’s actually quite manageable. A key part of understanding your website traffic is recognizing referral paths in Google Analytics. Knowing where your visitors are coming from, especially through channels like social media or other websites, is crucial for optimizing your marketing strategies. Understanding these referral paths in Google Analytics referral paths in google analytics will help you tailor your GA4 setup to get the most meaningful data.
This ultimately helps you refine your migration process and gain a more accurate view of your website’s performance.
- Defining Event Categories, Actions, and Labels: By categorizing events, you can group similar actions together for analysis. Action names describe the specific event, and labels offer additional context. For example, you could categorize “product interactions” as an event category, “view” as the action, and “shoes” as the label for tracking when a user views a pair of shoes. This detailed tracking lets you see how users interact with specific products.
- Triggering Events: Events are triggered when specific user actions occur. This could be anything from a button click to a form submission. Properly implemented events give a detailed account of the user journey.
Audience Segmentation
Segmentation is a powerful tool for extracting actionable insights from your data. By segmenting your audience, you can isolate specific groups of users for targeted analysis.
- Defining Segments: GA4 allows you to define segments based on various criteria, such as user demographics, behavior, and interactions. You can create segments based on factors like the channel through which a user came, their purchase history, or the pages they visited. For example, you can segment users who viewed a specific product page but didn’t make a purchase.
Analyzing this segment reveals why users might be abandoning the purchase process.
- Analyzing Segments: Analyzing segmented data enables you to understand the behaviors of specific user groups. You can compare their engagement metrics, identify patterns, and determine what aspects of your website or app are performing well for these specific segments. For instance, you can analyze segments of users who converted vs. those who didn’t to pinpoint areas needing improvement in your conversion funnel.
Data Analysis and Reporting in GA4
Unlocking the power of your website data is crucial for informed decision-making. Google Analytics 4 (GA4) offers a robust framework for analyzing user behavior and website performance, moving beyond simple page views to a more comprehensive understanding of user journeys. This section dives into interpreting GA4 reports, creating custom reports, and understanding key performance indicators (KPIs) for actionable insights.
Interpreting GA4 Reports
GA4 reports provide a wealth of data, but understanding its structure is key to deriving actionable insights. The reports are designed around user journeys and engagement metrics. Focus on the key metrics within each report, such as engagement, acquisition, and conversion rates. Identify trends and patterns in user behavior. For example, a significant drop in session duration might indicate a need to improve content quality or site navigation.
By examining user flows and engagement rates, you can understand which parts of your website are effective and where improvements are needed.
Creating Custom Reports for Specific Insights
GA4’s custom reports allow for tailoring the data presentation to your specific needs. You can select dimensions and metrics relevant to your business goals. For example, if you want to track conversions based on specific marketing campaigns, you can create a custom report focusing on the campaign source, medium, and the associated conversion rates. By filtering and segmenting data, you can drill down to specific user segments and their behavior.
This will give you a much deeper understanding of your user base and what motivates them to engage with your content.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in GA4
Identifying the right KPIs is vital for measuring the success of your website. In GA4, important KPIs include user engagement metrics (session duration, bounce rate, pages per session), acquisition metrics (traffic sources, channels), and conversion rates. Understanding how these metrics correlate with your business goals is essential. For example, a high bounce rate might indicate that your website’s landing pages are not effectively capturing user interest.
Tracking these metrics across different timeframes helps you identify trends and patterns that drive your business objectives.
Comparison of Universal Analytics and GA4 Reports
| Metric | Universal Analytics | GA4 | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sessions | Counts of user sessions | Counts of user interactions | GA4 moves beyond sessions to a more comprehensive view of user interactions. |
| Pageviews | Counts of page views | Engagement events (e.g., page views, video plays, button clicks) | GA4 tracks more detailed user interactions beyond just page views. |
| Conversion Tracking | Based on goals | Based on events | GA4’s event-based approach offers more granular control over conversion tracking. |
| User Acquisition | Focus on channels | Focus on user journeys and engagement across touchpoints | GA4 provides a more holistic view of user acquisition and engagement. |
This table highlights the fundamental shifts in data reporting between the two platforms. Understanding these differences is critical for effectively utilizing GA4’s capabilities.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues

Migrating to GA4 can be challenging, but anticipating and addressing potential issues is crucial for a smooth transition. Understanding common problems and their solutions will empower you to navigate the migration process effectively and avoid costly delays. This section focuses on troubleshooting common pitfalls, emphasizing data validation and the importance of handling tracking discrepancies.
Common GA4 Migration Issues
The GA4 migration process presents various potential problems. These include issues with data collection, tracking implementation, and reporting discrepancies. Addressing these issues proactively is key to a successful transition.
Tracking Implementation Errors
Correct implementation of the GA4 tracking code is paramount. Incorrectly configured tags, missing or outdated scripts, or issues with container integration can lead to incomplete data collection. Careful review of the implementation steps and thorough testing are essential to avoid such errors.
- Missing or Incorrect Tracking Code: Ensure the GA4 tracking code is correctly integrated into all relevant pages and that the code is up-to-date. Use the GA4 debugging tools to identify any missing or incorrect code snippets.
- Incorrect Tag Configuration: Double-check that the GA4 tags are correctly configured to capture the necessary data points. Review the documentation and ensure that event parameters and dimensions are correctly set up.
- Container Integration Problems: Issues with the GA4 container, such as conflicts with other scripts or incorrect placement, can affect data collection. Verify that the container is properly integrated and doesn’t interfere with other elements on the page.
Data Validation and Error Handling
Robust data validation procedures are essential during and after the GA4 migration. This ensures data accuracy and facilitates timely identification of discrepancies. Implementing error handling mechanisms can prevent data loss and ensure that issues are addressed promptly.
- Data Validation Processes: Establish a systematic approach to validate the data collected by GA4. This involves comparing data from the previous analytics platform with the GA4 data to identify any discrepancies or inconsistencies.
- Error Handling Mechanisms: Implement error handling routines to identify and address potential issues. These mechanisms can help to prevent data loss and provide insights into problems that may arise during the migration process.
Handling Tracking Issues and Data Discrepancies
Data discrepancies between the previous analytics platform and GA4 may arise. A structured approach to handling these issues is crucial.
- Identifying Discrepancies: Establish a clear process to identify discrepancies between the previous analytics platform and GA4 data. Utilize data comparison tools and reports to pinpoint any significant variations.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Develop a systematic approach to troubleshoot tracking issues and data discrepancies. This involves checking the tracking code implementation, reviewing data collection settings, and examining the configuration of reports.
- Resolution Strategies: Implement specific strategies to resolve the identified discrepancies. These strategies may involve updating the tracking code, adjusting configuration settings, or implementing additional validation steps.
Example of a Data Validation Issue
Imagine a significant drop in website traffic after migrating to GA4. A detailed comparison of data from the previous platform and GA4 reveals that specific event categories are missing in the GA4 data. Investigating the implementation reveals a configuration error in the tracking tags, causing the loss of crucial data points. Correcting the tag configuration restores the data flow, demonstrating the importance of meticulous validation and error handling.
Tools and Resources
Navigating the GA4 migration journey can be smoother with the right tools and resources. This section provides a comprehensive overview of essential aids, official documentation, and support channels to ensure a successful transition. Understanding these resources will streamline your process and help you maximize the benefits of GA4.The migration to GA4 requires careful planning and execution. Access to reliable resources is crucial for successful implementation and optimization.
The correct tools and documentation will enable you to make informed decisions throughout the process.
Essential Tools and Resources
The GA4 migration process is facilitated by a range of tools and resources. These resources provide comprehensive guidance, support, and best practices to ensure a smooth transition. They include:
- Google Analytics 4 Documentation: The official Google Analytics 4 documentation serves as the primary resource for understanding the platform. It provides detailed explanations of features, functionalities, and implementation strategies.
- Google Analytics 4 Training Courses: Numerous online training courses offered by Google cover various aspects of GA4, including setup, configuration, and data analysis. These courses are invaluable for gaining a practical understanding of the platform and its features.
- Community Forums and Q&A Platforms: Engaging with online communities and forums dedicated to Google Analytics 4 provides opportunities to learn from others’ experiences and ask questions. Sharing experiences and seeking support from peers can accelerate your migration.
Official Google Analytics Documentation
The official documentation is a cornerstone of the GA4 migration. It offers in-depth details and instructions for every aspect of the platform. Accessing and understanding this resource is essential for a successful migration.
- Comprehensive GA4 Guides: The official GA4 documentation provides comprehensive guides covering installation, setup, and various implementation strategies.
- Detailed Implementation Tutorials: Step-by-step tutorials are available to walk users through various aspects of implementing GA4 tracking on their websites and applications.
- API Reference: The API reference provides detailed information about the GA4 API, enabling developers to integrate GA4 with other systems and applications.
Helpful Guides, Tutorials, and Best Practices
Numerous helpful guides, tutorials, and best practices provide valuable insights into the GA4 migration process. These resources are essential for effective implementation and optimization.
- Best Practices for Data Collection: Understanding and applying best practices for data collection ensures accurate and reliable data for analysis.
- Advanced Reporting and Analysis Techniques: Learning advanced reporting and analysis techniques helps maximize the insights gained from GA4 data.
- Troubleshooting Common Issues: Comprehensive guides and tutorials address common issues and troubleshooting steps to resolve potential problems encountered during the migration.
Support Resources for GA4 Migration
Access to various support resources can accelerate the GA4 migration process and resolve potential challenges. These resources can offer guidance and support at different stages of the migration.
- Google Analytics Support Forums: Engage with the Google Analytics support forums to seek answers to your questions and discuss specific challenges encountered during the migration.
- Google Analytics Experts and Consultants: Consider seeking assistance from GA4 experts and consultants for personalized support and guidance, particularly for complex migrations.
- Third-Party Migration Tools: Explore third-party tools specifically designed to assist with the GA4 migration process, which can offer automated solutions and streamline the transition.
Case Studies and Examples
GA4 migration isn’t a one-size-fits-all process. Understanding how other businesses have successfully transitioned provides valuable insights and helps tailor your own strategy. This section presents case studies across various industries, highlighting key strategies and outcomes to aid in your own GA4 journey.
Retail Sector Example
A major online retailer, specializing in fashion, migrated to GA4. Their previous analytics platform offered limited insights into customer behavior on mobile devices. Post-migration, they observed a significant increase in the conversion rate for mobile users, revealing a previously hidden mobile-first trend. This improvement allowed them to optimize their mobile app and website design to better cater to the needs of their mobile-centric customers.
By analyzing user journeys, the retailer identified specific touchpoints where customers dropped off. This allowed them to refine their marketing strategies and improve user experience, leading to increased engagement and sales.
E-commerce Case Study: Improved Customer Segmentation
An e-commerce company, focusing on beauty products, successfully migrated to GA4. The platform’s enhanced capabilities allowed for a more granular understanding of customer behavior. Previously, the company struggled to segment customers based on purchase history and product preferences. Post-migration, they created detailed customer segments based on factors such as product category interest, purchase frequency, and engagement with specific marketing campaigns.
This resulted in more targeted marketing campaigns, leading to a noticeable improvement in conversion rates and customer lifetime value. They observed significant increases in sales and reduced marketing costs by focusing their efforts on the most profitable customer segments.
Hospitality Industry Migration Strategy
A hotel chain with multiple properties across the country implemented a GA4 migration strategy tailored to their specific needs. They focused on measuring guest satisfaction and optimizing their online booking process. Their strategy emphasized data collection from all online channels, including their website, social media, and travel aggregators. By analyzing user journeys and interactions across different booking stages, the chain identified pain points in the booking process and implemented improvements to reduce friction.
This strategy resulted in a substantial increase in online bookings and a positive impact on guest satisfaction scores.
Table: Examples of Business Implementations
| Industry | Use Case | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Retail | Analyzing mobile user behavior | Improved mobile conversion rates |
| E-commerce | Enhanced customer segmentation | Targeted marketing campaigns, improved conversion rates, increased customer lifetime value |
| Hospitality | Optimizing online booking process | Increased online bookings, improved guest satisfaction |
| Media | Measuring engagement with different content formats | Increased content consumption, improved audience segmentation |
Final Wrap-Up: How To Migrate To Ga4
Migrating to GA4 isn’t a daunting task when approached methodically. This guide has provided a clear roadmap, covering essential steps from planning to implementation, analysis, and troubleshooting. By following the strategies and utilizing the resources presented, you can successfully navigate the migration process and unlock the full potential of GA4. Remember, meticulous planning and a data-driven approach are crucial for maximizing your ROI and achieving your business objectives.