Googles site operator its limitations – Google’s site operator, a powerful tool for finding specific content on a website, has limitations. This post delves into those limitations, exploring how they impact search results, and examining alternative strategies for achieving desired search outcomes. Understanding these constraints is key to optimizing your searches and getting the most out of this powerful operator.
We’ll begin by defining the Google site operator and exploring its various applications. Then, we’ll identify the key limitations of this operator, considering factors like website structure, content organization, and the limitations of the operator within the context of search engine algorithms. We’ll also discuss how these limitations can be overcome or circumvented by employing alternative search strategies.
Defining the Google Site Operator
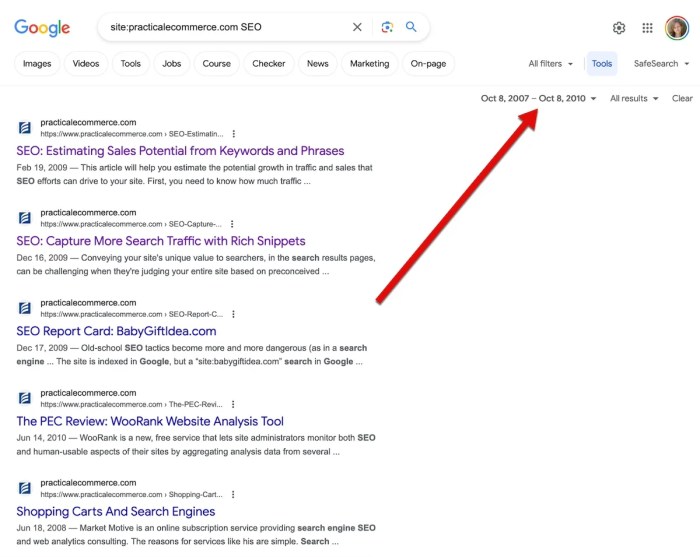
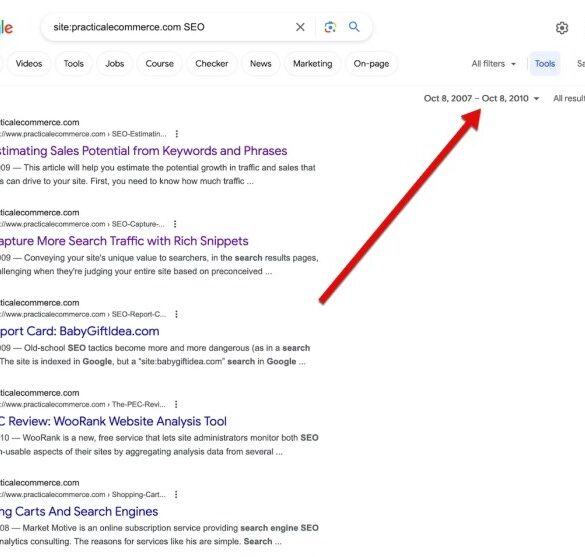
The Google site operator is a powerful search tool that allows you to restrict your search results to a specific website. This is incredibly useful for finding information within a particular domain without wading through irrelevant results from the broader web. It’s a cornerstone of advanced search techniques, offering a streamlined way to target specific content within a website.This operator is fundamental for researchers, students, and anyone needing to quickly find information on a particular site.
It enables precise searches, saving valuable time and effort compared to broader web searches.
Syntax and Forms of the Google Site Operator
The fundamental syntax for the Google site operator is straightforward. You preface your search terms with the phrase “site:” followed by the website’s domain name. For example, to search only on the Google website, you would use “site:google.com”.Various forms and syntaxes exist, enabling more refined searches. You can combine the site operator with other operators, like quotation marks for exact phrases, or the minus sign to exclude specific terms.
Using the Site Operator in Search Queries
The site operator can be integrated into diverse search queries, allowing for a targeted approach. Combining it with other search operators like “intitle:” (to search within page titles) or “inurl:” (to search within URLs) allows for even more precise targeting.You can use the operator to find specific pages or sections within a website. For instance, searching “site:example.com programming language” will find pages on example.com that mention “programming language.”
While Google’s site operator allows for some targeted searches, it has limitations. Knowing those limitations is key, and the recent Google Search Console updates to its merchant opportunities report, like this one , can be incredibly helpful for understanding how your products are performing in search results. Ultimately, though, Google’s site operator remains a powerful but limited tool for comprehensive site analysis.
Targeting Specific Website Sections
The site operator can be used to pinpoint particular sections of a website. If you know the URL structure of a site, you can use the operator to find pages with specific folders or categories.For instance, to find blog posts on a site, you could search “site:example.com/blog”.
Examples and Applications
Here’s a table showcasing various site operator syntaxes and their applications:
| Syntax | Description | Example Search Query | Potential Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| site:example.com | Searches only on example.com | site:example.com programming language | Finding specific content on example.com related to programming languages |
| site:example.com “programming languages” | Searches for pages containing the exact phrase “programming languages” on example.com | site:example.com “best programming languages” | Finding articles or pages discussing the best programming languages on example.com |
| site:example.com -tutorial | Searches on example.com, excluding results containing the word “tutorial” | site:example.com -tutorial java | Finding content on example.com about Java, excluding tutorial-related pages |
| site:example.com/blog | Searches only within the blog section of example.com | site:example.com/blog javascript | Finding blog posts about Javascript on example.com |
Impact on Search Results: Googles Site Operator Its Limitations

The Google site operator, while a powerful tool, isn’t a magic bullet for boosting search rankings. Understanding its limitations is crucial for effective . Its impact on results depends heavily on factors beyond just including the operator in a query.The site operator, in essence, tells Google to prioritize results from a specific domain. However, this prioritization doesn’t guarantee top rankings, as other factors like content quality, authority, and user experience play a significant role.
Impact on Ranking Factors
The Google site operator’s influence on search results is multifaceted. It doesn’t directly elevate a website to the top of the search engine results page (SERP), but rather filters the results, showing content from the specified domain more prominently. Crucially, this prioritization doesn’t guarantee higher rankings for all pages within the site.
Potential Biases and Limitations
Using the site operator can introduce biases into search results. If a website has a large number of low-quality or irrelevant pages, the operator might not always deliver optimal results. Furthermore, the operator’s effectiveness depends on how well the website is indexed by Google. If Google’s index of the website is incomplete or outdated, the results will reflect this.
Google’s site operator is a powerful tool, but it has limitations. You can’t, for example, directly target local searches using site operators. To effectively boost your service area business’s visibility in local searches, consider strategies like optimizing your Google My Business profile and focusing on local SEO. A great place to learn more about boosting your service area business local SEO is here: boost service area business local seo.
Ultimately, while site operators are helpful, understanding and leveraging the broader local SEO landscape is key for better results.
Examples of Less-Than-Ideal Results
Consider a website with numerous thin content pages. Using the site operator might yield a higher volume of results from this site, but the individual pages might not rank highly due to poor content quality. Another example is a site with a poorly structured internal linking system. Even if the site is indexed comprehensively, if the internal links don’t guide users effectively, the operator won’t guarantee relevant results for users.
Website Optimization and the Operator
Effective website optimization can significantly enhance the operator’s effectiveness. High-quality content, well-structured pages, and a robust internal linking strategy contribute to better indexing and, consequently, improved visibility when the site operator is used. A site with well-optimized content and a clear site architecture will perform better when the operator is used, as Google can more easily find and rank relevant pages.
Role of Indexation
The operator’s usefulness is deeply intertwined with how well a site is indexed. A website with frequent content updates, appropriate metadata, and a well-structured sitemap is more likely to be indexed comprehensively, making the site operator more effective. If Google doesn’t have a complete understanding of the website’s content and structure, the site operator’s value diminishes.
Impact of Website Structure on Search Results
This table illustrates how different website structures influence search results when the site operator is used. The impact is contingent on Google’s indexation and how effectively the site is optimized.
| Website Structure | Potential Impact on Search Results |
|---|---|
| Well-organized site with clear hierarchy, high-quality content, and a robust internal linking structure | Improved visibility and potentially higher rankings for relevant pages when the operator is used |
| Website with numerous thin content pages and poor internal linking | Potentially high volume of results but lower individual page rankings |
| Website with frequent content updates, optimized metadata, and a well-structured sitemap | Higher likelihood of comprehensive indexing, leading to more effective use of the site operator |
| Website with outdated content, poor site architecture, and no clear internal linking structure | Lower visibility and less effective use of the operator, as Google might not have a complete understanding of the site |
Alternative Search Strategies
Beyond the Google site operator, a wealth of alternative search strategies can be employed to find specific information on a website. These methods often offer advantages in terms of precision and control, especially when dealing with complex or large websites. Understanding these techniques can significantly enhance your ability to navigate and extract information effectively.Effective search goes beyond just using the site operator; it involves tailoring your search to the specific website’s structure and organization.
Knowing these alternative strategies allows for a more comprehensive and targeted approach to information retrieval.
Advanced Search Operators
Various search engines, including Google, support advanced search operators beyond the basic site operator. These operators refine searches by focusing on specific elements within the site.Understanding the nuances of these operators allows for a more focused search, leading to more relevant results. For example, using quotation marks around a phrase forces the search to find that exact phrase, improving precision and relevance.
- Site-Specific Search Boxes: Many websites have their own internal search functions. Utilizing these search boxes can be highly effective, especially when dealing with extensive content. These search boxes often understand the site’s structure and can retrieve results quickly. This often results in a quicker and more precise return of relevant data.
- Site Maps: Site maps, often available on a website’s homepage or navigation, provide a hierarchical view of the site’s content. They act as a visual index of the site’s structure, helping users understand the organization and locate relevant sections quickly. This is particularly useful for large, complex websites.
- Categorization and Navigation: Websites often organize their content into categories or sections. Using the website’s navigation menus can be a direct way to pinpoint specific topics or information, often more efficiently than other methods.
Specialized Search Tools and Databases
Specific tools and databases are tailored to specific types of websites or information. These tools can be invaluable for accessing detailed or structured information that might be hard to find otherwise.
- Academic Databases: Academic journals, research papers, and scholarly articles are frequently accessible through specialized databases. These databases use specific search operators and indexing methods, ensuring high-quality, relevant results.
- Government Resources: Government websites often contain vast amounts of data organized in a structured manner. Dedicated government portals and search engines can often facilitate more precise and streamlined searches.
- Industry-Specific Platforms: Certain industries have dedicated platforms, directories, or databases. These resources provide targeted information on specific industries, markets, and businesses. They often have specialized search capabilities tailored to the needs of that specific industry.
Using Specific Website Features
Understanding and leveraging specific features of a website can significantly enhance search effectiveness. This is especially true for websites with unique structural elements.
- Archives and Historical Data: Websites with archives or historical data sections can be efficiently searched for specific time periods or events. Specific search filters and parameters may be available to refine results.
- Filtering and Sorting Options: Many websites offer filters and sorting options, allowing users to refine their results based on specific criteria. These tools can significantly streamline searches and reduce irrelevant results. For instance, date, type, or category filters can help in finding specific data.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Google Site Operator | Advanced Search Operators | Specialized Tools | Website Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Search Scope | Limited to the specified website | Variable, can be website-specific or broader | Often focused on specific data types or domains | Limited to the website’s structure and features |
| Precision | Relatively straightforward but can be less precise | Potentially higher precision with specific operators | High precision due to specialized indexing and retrieval | High precision when combined with site navigation |
| Ease of Use | Simple and readily available | Requires understanding of operators | Requires knowledge of specific tools and platforms | Dependent on website structure and clarity |
| Examples | “site:example.com marketing” | “intitle:marketing site:example.com” | Searching for research papers in JSTOR | Using filtering options on an e-commerce site |
Advanced Usage and Optimization
Mastering the Google site operator goes beyond basic searches. This section delves into advanced techniques, demonstrating how to use it effectively with other operators, refine results, and achieve precise targeting for your information needs. Leveraging Boolean operators and specific search syntax unlocks a deeper level of control over your Google search experience.
Advanced Search Techniques
The Google site operator, while powerful on its own, becomes even more effective when combined with other search operators. This allows for highly targeted searches, reducing irrelevant results and isolating the information you seek.
- Combining with other operators (e.g., quotation marks, Boolean operators): Using quotation marks around phrases ensures precise matches. Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) refine searches by specifying relationships between s. For example, searching for “site:example.com “1” AND 2″ will narrow down results to pages on example.com containing both “1” and “2”.
- Using wildcards (*): Wildcards allow for flexibility in searches. The asterisk (*) can replace any characters in a word, useful when you’re not entirely sure of the exact spelling or phrasing. For instance, searching for “site:example.com *ing” will return pages containing words starting with “”.
- Employing search syntax for refinement: Google search syntax allows for advanced filtering and control. Using operators like `filetype:pdf` or `intitle:` can target specific file types or page titles, providing a more focused search. This ensures that your search results are relevant to your specific needs, whether you’re looking for a particular document type or content within a specific page title.
Boolean Operators with the Site Operator
Boolean operators significantly enhance the precision of your searches when used in conjunction with the site operator. They define the relationships between s, ensuring that results align with your specific needs.
Google’s site operator is a powerful tool, but it has its limitations. Knowing how to use it effectively is key, but sometimes you need more than just keyword searches. That’s where crafting a compelling tagline comes in. For example, if you’re a professional services firm, think about how to develop a tagline that effectively communicates your value proposition to potential clients.
A strong tagline can be a crucial part of your online presence. how to develop a tagline for your professional services firm will help you understand the process. Ultimately, even with refined search strategies, a strong brand identity, like a well-crafted tagline, is invaluable in standing out online.
- Using AND: The AND operator requires both specified s to be present in the search results. For example, searching for “site:example.com 1 AND 2” will yield results containing both “1” and “2”.
- Using OR: The OR operator allows for either to be present in the search results. Searching for “site:example.com 1 OR 2” will show results containing either “1” or “2” or both.
- Using NOT: The NOT operator excludes specific s from the search results. For example, searching for “site:example.com 1 NOT 2” will return results containing “1” but not “2”.
Complex Search Examples
The following table demonstrates the application of the Google site operator with other operators and Boolean logic, showcasing various complex search scenarios.
| Search Query | Description | Expected Results |
|---|---|---|
| site:example.com “advanced search” AND optimization | Find pages on example.com containing both “advanced search” and “optimization”. | Pages on example.com explicitly discussing advanced search optimization techniques. |
| site:wikipedia.org “digital marketing” OR “online advertising” | Find pages on Wikipedia about digital marketing or online advertising. | Pages on Wikipedia related to either digital marketing or online advertising. |
| site:nytimes.com “climate change” NOT “political debate” | Find New York Times articles about climate change, excluding those focusing on political debates. | Articles about climate change that do not include discussions of political debates. |
| site:support.google.com filetype:pdf “account recovery” | Find PDF support documents on Google’s support site related to account recovery. | PDF documents on Google’s support site related to account recovery. |
Site Structure and Content Optimization
The effectiveness of the Google site operator hinges significantly on how well a website is structured and its content is organized. A meticulously planned site architecture, coupled with optimized content, dramatically improves a site’s visibility in search results, making it easier for users to find relevant information. This section delves into the crucial relationship between site structure, content organization, and search engine optimization, using the Google site operator as a tool.Well-structured websites, easily navigable by both users and search engine crawlers, directly benefit from the Google site operator.
Search engines prioritize sites with logical hierarchies, clear navigation, and relevant internal linking, allowing them to quickly understand the site’s content and structure. This facilitates better indexing, enhancing the chances of pages matching user queries.
Relationship Between Website Structure and Google Site Operator
The Google site operator is highly sensitive to website structure. A well-organized site, with clear hierarchies and logical navigation, allows search engines to easily understand the site’s content. Conversely, a poorly structured site, with confusing navigation and disorganized content, negatively impacts the effectiveness of the operator. The operator’s ability to identify and retrieve relevant pages within a website is directly linked to the site’s architecture.
How Well-Structured Websites Benefit from the Operator
Well-structured websites benefit from the Google site operator because they provide search engines with a clear map of the site’s content. This allows the operator to quickly identify pages relevant to a specific search query. Internal linking structures, carefully chosen anchor text, and a clear sitemap contribute to the operator’s effectiveness. These elements provide the operator with crucial context about the relationships between pages.
Content Organization and Search Results
Content organization directly influences search results when using the Google site operator. Search engines analyze content organization, including headings, subheadings, and paragraph structure. By structuring content logically, websites ensure search engines understand the topics covered on each page, making it easier to match user queries. The operator will more effectively find relevant content within the targeted website.
Best Practices for Website Design
Implementing these best practices significantly enhances a website’s searchability:
- Use descriptive URLs: URLs should clearly reflect the page’s content, making it easier for both users and search engines to understand the page’s purpose. Avoid using generic or cryptic URLs.
- Implement a logical sitemap: A sitemap clearly displays the hierarchy of pages on a website, allowing users and search engines to navigate the site easily. This contributes significantly to indexing and crawlability.
- Employ descriptive page titles and meta descriptions: These elements are crucial for search engine optimization. Using relevant s and clear descriptions accurately reflect the page’s content, enhancing its visibility in search results.
- Use semantic HTML: Semantic HTML (HTML5) helps search engines understand the structure and meaning of web pages. This improves the accuracy and efficiency of the Google site operator in finding relevant content.
Creating Easily Searchable Websites
Creating websites easily searchable using the Google site operator involves careful attention to both content and structure. Implementing the following practices ensures the operator effectively locates and retrieves relevant content:
- Employ clear headings and subheadings: Using headings (H1, H2, etc.) helps structure content and improve readability, aiding search engine understanding.
- Use internal linking strategically: Connecting related pages through internal links helps search engines discover and understand the relationships between content pieces, increasing the site’s overall searchability.
- Prioritize user experience: Easy navigation, fast loading times, and mobile-friendliness enhance the user experience and indirectly support search engine optimization, thus facilitating the use of the operator.
Effective website structure and content optimization are essential for improving search visibility. By creating clear hierarchies, implementing semantic HTML, and using descriptive elements, websites can enhance the effectiveness of the Google site operator, ensuring relevant content is retrieved in search results.
Operator Limitations in Different Search Engines
The Google site operator, a powerful tool for targeting specific websites in search results, isn’t universally applicable. Other search engines employ different approaches and have varying degrees of support for site-specific searches. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective strategies that transcend a single platform.Beyond Google, site-specific searches vary considerably. The functionalities and limitations of site operators are not always consistent.
Some search engines might offer similar operators but with different parameters, impacting the precision and effectiveness of your search.
Comparison of Site Operators Across Search Engines
Different search engines have their own approaches to site-specific searches. This divergence affects the precision and comprehensiveness of results. Understanding these variations is key to refining search strategies for optimal results.
| Search Engine | Site Operator | Functionality | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| site:example.com | Returns results from example.com. Highly effective for broad searches. | Limited by Google’s algorithm; might not capture all relevant pages if the site is large or has dynamic content. | |
| Bing | site:example.com | Similar to Google’s, returning results from example.com. | Bing’s algorithm might prioritize different factors than Google’s, impacting the results. |
| DuckDuckGo | site:example.com | Provides results from example.com, generally mirroring Google’s functionality. | DuckDuckGo’s emphasis on privacy may affect indexing and the visibility of results. |
| Yandex | site:example.com | Provides site-specific results, but may differ in terms of indexing and algorithm prioritization. | The specific implementation of the site operator and its limitations are influenced by Yandex’s unique search engine architecture. |
Impact of Algorithm Updates
Search engine algorithms are constantly evolving. These updates can significantly affect the effectiveness of site operators. For instance, a site’s ranking can fluctuate based on factors such as content quality, backlink profile, and user engagement, influencing the operator’s ability to return relevant results.
Search Engine-Specific Features and Limitations, Googles site operator its limitations
Search engines employ various features beyond basic site operators. For example, Bing’s “search within a website” feature allows users to search within a specific website without using the site operator, while Google prioritizes its “site:” operator. This difference impacts how a user might approach finding relevant content.
Examples of Other Search Engines Handling Site-Specific Searches
Bing often prioritizes results based on freshness and relevance. DuckDuckGo focuses on privacy and may exclude certain results from its indexing. Yandex emphasizes local search results in certain regions. These factors contribute to the distinct outcomes when utilizing site-specific operators across different platforms.
Last Recap
In conclusion, while the Google site operator is a valuable tool, understanding its limitations is crucial for effective use. We’ve explored how website structure and content organization impact search results, and how algorithm updates can influence the operator’s effectiveness. By understanding these factors and employing alternative strategies, you can optimize your search results and gain a deeper understanding of the nuances of online information retrieval.