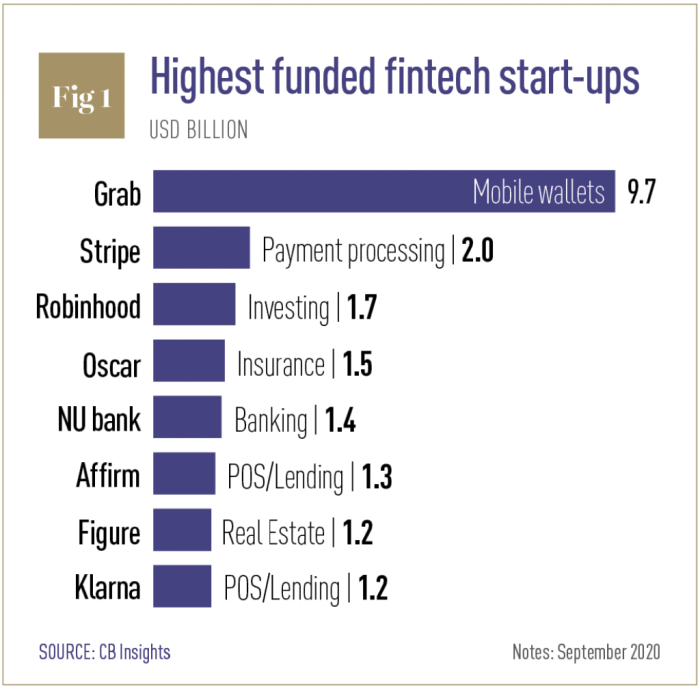
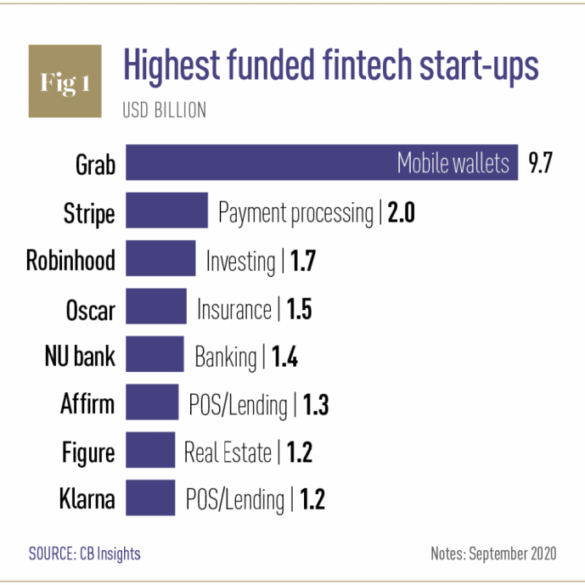
Silicon Valley stumbles and Oracle snaps up the pieces, revealing a fascinating shift in the tech landscape. Recent events paint a picture of a dynamic industry, where established giants like Oracle are positioning themselves to capitalize on the struggles of some prominent players. This analysis explores the underlying factors driving the valley’s current downturn, Oracle’s acquisition strategy, and the potential impact on innovation, the job market, and the future of technology.
We’ll delve into specific examples, examining the successes and failures of key players and the broader implications for the global economy.
The changing dynamics of the tech industry, marked by the rise of new players and the decline of others, are profoundly influencing the competitive landscape. Financial pressures, market shifts, and regulatory actions are all contributing factors to the current state of flux. This analysis compares and contrasts strategies employed by Silicon Valley companies with those of other global tech hubs, providing a comprehensive overview of the situation.
Shifting Tech Landscape
Silicon Valley, once the undisputed epicenter of innovation, is experiencing a period of significant upheaval. The recent wave of layoffs, coupled with the acquisition of struggling startups by established giants like Oracle, paints a picture of a landscape in flux. This shift isn’t just about individual companies; it reflects broader changes in the tech industry, including the emergence of new players and the repositioning of established ones.
The factors driving this transformation range from escalating financial pressures to shifting market demands and a more scrutinizing regulatory environment.The tech industry is no longer a purely American affair. Global competition is intensifying, with hubs like China and India rapidly developing their own tech ecosystems. This global competition necessitates a re-evaluation of strategies and approaches. Companies are adapting to survive and thrive in this increasingly complex environment.
From the traditional venture capital model to the rise of private equity, the dynamics are continuously evolving, shaping the future of innovation and disrupting existing norms.
Recent Significant Events in Silicon Valley
Several significant events have marked the recent evolution of the tech landscape in Silicon Valley. These include the substantial layoffs across various tech giants, reflecting a cooling market and a recalibration of priorities. Furthermore, the acquisition spree, with established players like Oracle snapping up smaller, struggling startups, highlights the consolidation and reshuffling occurring within the industry. This signifies a shift from aggressive expansion to a more measured approach in the face of challenging economic conditions.
Changing Dynamics of the Tech Industry
The rise of new players and the decline of others is a defining characteristic of the current tech landscape. Startups with innovative technologies are emerging in various sectors, presenting significant challenges to established companies. This competitive pressure is pushing established players to adapt and innovate to maintain their market share. The traditional model of venture capital funding is also evolving, with private equity firms playing a more prominent role in the financing landscape.
Silicon Valley’s recent hiccups and Oracle swooping in to pick up the pieces are interesting, aren’t they? It’s a bit like deciding whether to update WordPress or its plugins first – both need attention, but one step can affect the other. Just like you need to carefully consider the order of updates for a smooth WordPress experience, Oracle’s acquisition strategy is crucial to their success, should I update WordPress or plugins first.
Ultimately, both the tech world and your website need a well-planned approach to avoid any unforeseen problems.
Factors Contributing to Silicon Valley Stumbles
Several interconnected factors are contributing to the current challenges faced by Silicon Valley companies. The rise of inflationary pressures and interest rate hikes has significantly impacted the valuations of startups and established companies. This financial instability has resulted in increased scrutiny from investors and potential investors, and the market’s cooling effect has made expansion and acquisition less appealing.
Regulatory actions, including heightened scrutiny of data privacy and antitrust enforcement, are also shaping the landscape, demanding greater accountability and compliance from tech companies.
Comparison of Strategies Across Tech Hubs
The strategies employed by companies in Silicon Valley differ from those adopted by other tech hubs. For example, some Asian tech hubs are more focused on specific niche markets and emerging technologies. Silicon Valley, historically, has embraced a broader approach, encompassing a wider range of technologies and applications. This difference in approach reflects the varying strengths and priorities of each region, impacting the pace and direction of innovation.
Analysis of Company Stumbles and Recovery Strategies
| Company | Industry | Stumbling Point | Recovery Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| WeWork | Shared Workspaces | Overvaluation, unsustainable growth | Focused on profitability and operational efficiency; restructuring and cost-cutting |
| Coinbase | Cryptocurrency Exchange | Regulatory hurdles, market volatility | Re-evaluating business model; exploring new opportunities in regulated financial products. |
| Snap | Social Media | Declining user growth, competition from other platforms | Investing in new features and technologies to attract users; focusing on AR and metaverse integrations. |
| Meta Platforms | Social Media and Metaverse | Slowing user growth, fluctuating VR/AR market | Re-evaluating priorities in the metaverse and AR; focusing on more stable revenue streams like advertising. |
Oracle’s Acquisition Strategy
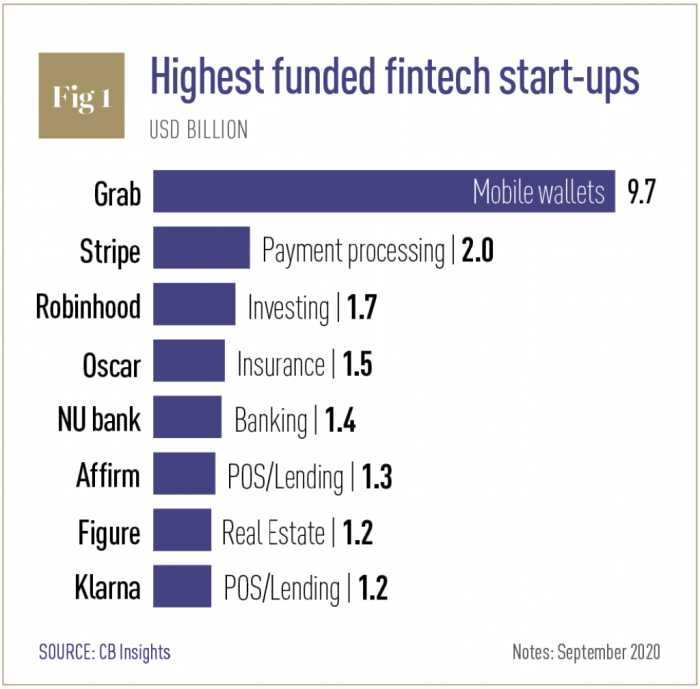
Oracle’s acquisition strategy has consistently focused on bolstering its existing product portfolio and consolidating its market dominance. This approach, often criticized for its potential anti-competitive effects, has yielded a complex and multifaceted technological empire. Oracle views acquisitions as a means to acquire innovative technologies, skilled personnel, and market share, all contributing to its overall strategic objectives.Oracle’s motivations for these acquisitions are multi-faceted.
Beyond immediate market gains, the company often seeks to acquire companies with proprietary technologies or unique expertise that complement its existing offerings. This strategic approach aims to enhance its competitive position and solidify its leadership in the ever-evolving tech landscape. Additionally, acquisitions can provide a shortcut to expanding into new markets or acquiring talent pools that would otherwise be difficult to recruit.
Oracle’s Acquisition Rationale
Oracle’s acquisition strategy is driven by a desire for vertical integration, enhancing its existing cloud offerings, and acquiring cutting-edge technologies. By integrating acquired companies’ technologies into its own product lines, Oracle aims to create a more comprehensive and robust suite of solutions for its clients. This strategy often includes acquiring companies with a strong focus on specific areas within the tech industry, allowing Oracle to add those specialized capabilities to its portfolio.
This strategy also allows Oracle to expand its customer base and reach new markets.
Past Acquisitions and Their Impact
Oracle’s acquisition history is extensive, encompassing numerous companies across various sectors. Some acquisitions have been highly successful, significantly impacting the technology industry. Others have faced challenges in integration, highlighting the complexities of merging different corporate cultures and technological platforms. The long-term impact of these acquisitions often depends on how effectively Oracle can integrate the acquired company into its existing structure.
Table of Oracle’s Acquisitions
| Acquired Company | Industry | Oracle’s Justification | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sun Microsystems | Server technology, Java | To strengthen its hardware and software capabilities, particularly in the Java ecosystem. | Strengthened Oracle’s position in the server market and Java development. However, integration challenges were reported. |
| BEA Systems | Enterprise application integration | To expand its middleware portfolio and enhance its cloud offerings. | Added key enterprise integration capabilities to Oracle’s suite, improving its appeal to larger enterprises. |
| Siebel Systems | Customer relationship management (CRM) | To gain a strong foothold in the CRM market and improve its customer-facing solutions. | Enhanced Oracle’s CRM offerings, but integration issues and significant restructuring efforts were reported. |
| Hyperion Solutions | Business intelligence and analytics | To add robust business intelligence and analytics tools to its suite. | Expanded Oracle’s offerings in the analytics space, further consolidating its position in enterprise software. |
Impact on Innovation and Job Market
The recent stumbles in Silicon Valley, coupled with Oracle’s aggressive acquisition strategy, are reshaping the tech landscape. This shift presents both challenges and opportunities, particularly regarding innovation and the job market. The acquisitions and resulting changes in the competitive environment are creating uncertainty for startups and established companies alike, potentially altering the trajectory of innovation in the region.The impact on the job market is complex, with potential job losses in some areas alongside the creation of new positions in others.
The overall effect on entrepreneurship and venture capital funding remains to be seen, but the shift in power dynamics is undeniable. Oracle’s actions are influencing the entire ecosystem, altering the playing field for smaller companies and individual innovators.
Potential Impact on Innovation in Silicon Valley
Oracle’s acquisitions, while potentially bolstering its own technological capabilities, could stifle innovation in the region. The competitive landscape is being altered, possibly leading to a consolidation of power and fewer opportunities for smaller, more innovative companies. The loss of independent companies and their innovative cultures could have a negative effect on the overall pace of technological advancement in Silicon Valley.
The region’s dynamism and its role as a hub for disruptive technologies might diminish if the acquisitions create an environment less conducive to experimentation and risk-taking.
Silicon Valley’s recent stumbles are interesting, and Oracle seems poised to pick up the pieces. This tech landscape shift is also making room for new social media platforms, like the newly launched Instagram competitor, introducing threads an instagram app. While Threads is certainly a new player, it’s worth watching how this new app evolves, and how it might affect the overall Silicon Valley narrative as Oracle continues its strategic acquisitions.
Impact on the Job Market
The job market will undoubtedly be affected by these changes. Potential job losses will occur in companies targeted for acquisition or those that struggle to compete in the new, consolidated market. Conversely, Oracle’s expansion may create new positions, but the specific nature and scale of these new opportunities remain uncertain. A careful analysis of current and projected job market trends, both before and after the acquisitions, is needed to understand the full extent of the impact.
Potential Consequences for Entrepreneurship and Venture Capital
Venture capital funding could shift towards larger, established companies that are more likely to survive the changing landscape. This could potentially decrease funding availability for smaller startups and early-stage ventures, hindering innovation and entrepreneurship. Furthermore, the competitive environment created by the acquisitions might make it harder for new entrepreneurs to secure funding and establish themselves. This is especially true for companies focusing on areas of technology already occupied by Oracle.
Silicon Valley’s recent struggles are interesting, with Oracle seemingly poised to pick up the pieces. This isn’t just about big tech; it’s also a fascinating time to examine how businesses leverage online presence. Understanding a strong Google My Business strategy, for instance, is crucial for local businesses trying to thrive in this evolving landscape. google my business strategy Ultimately, Oracle’s potential moves highlight the changing dynamics in the tech world and the opportunities for companies to adapt and succeed.
In the past, the influx of venture capital into Silicon Valley has been crucial in supporting startups, fueling innovation, and creating jobs.
Influence of Oracle’s Actions on the Overall Ecosystem of Silicon Valley
Oracle’s acquisitions have significant implications for the entire ecosystem of Silicon Valley. The consolidation of power within the tech sector could lead to a decrease in competition, impacting innovation and potentially increasing prices for consumers. The overall effect on the region’s reputation as a global center of technological innovation remains to be seen. However, the potential consequences for the local economy are significant and will need careful consideration and analysis.
Comparison of Job Market Trends Before and After Acquisitions
| Metric | Before Acquisitions | After Acquisitions |
|---|---|---|
| Job Growth Rate | High, driven by numerous startups and rapid innovation | Uncertain, potential for slower growth in some sectors, possible increases in others |
| Job Loss Rate | Low, associated with the high rate of startups and innovation | Potential for increase, particularly in acquired companies or competitors |
| Average Salary | Generally high, reflective of the highly skilled workforce | Potential for fluctuation depending on specific job roles and companies |
| Industry Concentration | High degree of competition and diversity | Potential for higher concentration in key areas, with established players holding more sway |
Future Implications
The recent acquisition of tech startups by Oracle signals a significant shift in the tech landscape, potentially reshaping the future of innovation and competition. Oracle’s strategy, focusing on consolidating its position and acquiring key technologies, suggests a broader trend towards corporate consolidation in the industry. This development raises questions about the long-term impact on innovation, job markets, and the overall global economy.The actions of Oracle, a large, established player, could lead to reduced competition in certain areas.
This, in turn, could potentially affect the speed and direction of innovation, as smaller, more nimble startups may find it harder to compete. However, Oracle’s acquisition strategy might also introduce new resources and capital to promising technologies, potentially accelerating development in specific sectors. The resulting impact on the global economy is likely to be multifaceted, with implications for both job creation and job displacement.
Potential Long-Term Effects on the Tech Industry
The acquisition trend may encourage more large corporations to adopt similar strategies, potentially leading to a less fragmented and more centralized tech industry. This centralization could stifle innovation by limiting the number of independent players and potentially leading to less diversity in approaches. However, it could also lead to economies of scale and the development of more sophisticated technologies.
Possible Ripple Effects and Wider Implications for the Global Economy
The ripple effects of these acquisitions extend beyond the tech sector. The impact on job markets is a significant concern. Job displacement due to consolidation could be substantial, requiring proactive measures for workforce retraining and reskilling. Simultaneously, the acquisition of innovative technologies by large companies could lead to the creation of new jobs in areas like software development and support.
Potential Future Strategies and Innovations in Response to the Changes in Silicon Valley
Startups may adopt more strategic alliances and partnerships to compete with large corporations. Open-source software could become even more critical, allowing startups to leverage existing technologies and avoid direct competition with large companies. The focus on niche markets and specialized technologies could become more prominent, allowing startups to carve out distinct positions in the industry.
Potential Shifts in the Competitive Landscape and the Emergence of New Leaders
The competitive landscape is expected to shift dramatically. Smaller companies will need to focus on innovation and differentiation to maintain their relevance. The rise of new leaders could come from outside Silicon Valley, as companies in other regions leverage opportunities presented by the evolving landscape. Strategic partnerships between startups and established corporations will become increasingly important.
Evolution of Technology and the Role of Silicon Valley
| Year | Technology Focus | Silicon Valley Role |
|---|---|---|
| 2024-2028 | AI-driven automation, cloud computing advancements, and the continued rise of the Internet of Things (IoT). | Silicon Valley’s dominance is challenged by other global tech hubs, though it remains a significant player in the development and adoption of new technologies. |
| 2029-2033 | Continued refinement of AI, personalized medicine, and advanced materials science. | Silicon Valley’s influence may shift towards fostering interdisciplinary collaborations and supporting emerging tech ecosystems globally. |
| 2034-2038 | Emergence of more sophisticated and integrated technologies like quantum computing and advanced robotics. | Silicon Valley could transition into a center for advanced research and development, attracting talent from across the globe. |
Illustrative Examples: Silicon Valley Stumbles And Oracle Snaps Up The Pieces
Silicon Valley’s dynamism often fuels spectacular successes, but also painful stumbles. The tech landscape is a constant battleground of innovation, adaptation, and sometimes, inevitable failure. Understanding these examples illuminates the forces at play, providing valuable insights into the cyclical nature of industry disruption and the strategic choices made by companies like Oracle.The rise and fall, or more accurately, the evolution, of companies often reflects the shifting sands of technology.
Analyzing specific examples of both struggles and triumphs, coupled with Oracle’s acquisition strategies, provides a comprehensive picture of the tech industry’s intricate interplay. The consequences of these decisions ripple through the job market and reshape the very definition of innovation.
Specific Examples of Tech Stumbles
The tech industry is replete with examples of companies that once held significant market share but faltered. Understanding the reasons behind their struggles provides valuable lessons for aspiring entrepreneurs and established firms alike. Sometimes, the culprit is poor execution, an inability to adapt to evolving consumer needs, or the emergence of more disruptive technologies.
- Kodak: A once-ubiquitous photographic giant, Kodak failed to adapt to the digital revolution. Their core competency, film photography, became obsolete as digital cameras gained popularity. Their failure to recognize and invest in the burgeoning digital market ultimately led to their decline.
- Blockbuster: The king of video rentals, Blockbuster was unable to respond to the rising popularity of streaming services like Netflix. Their resistance to adopting new technologies and their reliance on a traditional business model proved fatal.
- MySpace: A social media pioneer, MySpace lost ground to Facebook due to a combination of factors, including a less user-friendly interface, an inability to effectively monetize user data, and poor strategic decisions regarding the development of the platform.
Oracle’s Acquisitions and Their Impact
Oracle’s acquisition strategy has been a significant factor in shaping the tech landscape. Their acquisitions often involve integrating acquired companies’ technologies and talent into Oracle’s existing infrastructure. The outcomes, however, can vary depending on how effectively Oracle integrates these acquisitions.
- Sun Microsystems: Oracle’s acquisition of Sun Microsystems, a key player in the Java ecosystem, provided Oracle with critical intellectual property and a vast network of engineers. The integration was complex, but the acquisition significantly strengthened Oracle’s position in the server and software markets. However, some argued that the acquisition resulted in a diluted product offering and less emphasis on innovation in areas not directly related to their core offerings.
- Talend: Oracle’s acquisition of Talend, a leader in data integration software, showcased their focus on bolstering their data-centric offerings. This acquisition brought a specialized skill set and technology to Oracle’s arsenal, enhancing their position in big data management and analytics.
Evolution of the Tech Landscape, Silicon valley stumbles and oracle snaps up the pieces
The tech landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies emerging and disrupting existing industries. This dynamism necessitates adaptability and foresight. Historical context reveals how past innovations paved the way for current advancements.
- The rise of the internet: The emergence of the internet and the subsequent development of the World Wide Web fundamentally altered the way businesses operate and how consumers interact with information. This period saw the emergence of e-commerce, online advertising, and social media platforms.
- Mobile revolution: The proliferation of smartphones and mobile apps transformed communication, commerce, and entertainment. The shift from desktop-based computing to mobile devices dramatically changed user expectations and the competitive landscape.
Historical Context of the Tech Industry
Understanding the historical context provides insight into the forces shaping the present and future of the industry. The industry’s trajectory is often punctuated by periods of rapid growth, innovation, and significant disruptions.
- Early computing: The initial development of computers and their applications laid the foundation for future advancements. The focus was on computational power and storage, with early applications in scientific and governmental sectors.
“The future belongs to those who believe in the beauty of their dreams.”Eleanor Roosevelt
Closing Summary
In conclusion, the recent stumbles in Silicon Valley and Oracle’s strategic acquisitions present a complex and multifaceted picture. The interplay of financial challenges, evolving market demands, and Oracle’s calculated moves is reshaping the tech industry. This analysis has explored the potential impacts on innovation, the job market, and the future trajectory of technology. The long-term effects on the global economy and the emergence of new leaders in the competitive landscape remain to be seen.
But one thing is certain: the future of technology is undoubtedly in flux, and Oracle’s actions are a significant factor in this evolution.