4 ways to remove indexed content 3 that dont work – 4 ways to remove indexed content 3 that don’t work. Search engines crawl the web, storing and indexing your website’s content. But what if you need to remove specific pages? This guide dives deep into effective and ineffective methods, helping you understand the complexities of content removal from search results.
We’ll explore the fundamentals of indexing, the best strategies for removing unwanted content, and the common pitfalls to avoid. Armed with this knowledge, you can reclaim control over your online presence and ensure only the right content reaches your audience.
Introduction to Indexing and Removal
Search engines like Google, Bing, and DuckDuckGo play a crucial role in connecting users with relevant information online. A fundamental aspect of this process is indexing, the method by which search engines discover, analyze, and store web pages. Understanding how indexing works is essential to comprehending the challenges involved in removing content from search results.The process of indexing involves search engine crawlers systematically exploring the vast expanse of the internet.
These automated programs, often referred to as bots or spiders, follow links from one page to another, gathering information about the content, structure, and other attributes of each page. This information is then processed and stored in massive databases, forming the foundation of search engine results.
Factors Influencing Content Visibility
Search engines employ complex algorithms to determine the relevance and authority of web pages. These algorithms consider various factors, including density, website age, backlink profiles, and user engagement metrics. Content with high relevance to user queries, coupled with strong signals of authority, tends to rank higher in search results.
The Search Engine Indexing Process
Search engines utilize sophisticated crawlers to systematically navigate the internet. These crawlers follow hyperlinks to discover new pages, gather information, and build an index of the web’s content. This process is continuous, with new content being added and existing content being updated or removed from the index.
Ever tried to banish unwanted indexed content? While there are definitely four methods to remove indexed content, three common approaches often fall flat. Understanding the nuances of search engine optimization, like the crucial difference between on-page and off-page SEO, is key to effective content management. A solid grasp of importance of on page vs off page seo comparison helps you understand why those three ineffective removal strategies simply won’t cut it.
Ultimately, focusing on the right techniques is crucial for getting rid of that unwanted digital baggage.
Content Removal Challenges
Removing indexed content from search results is a complex undertaking. Search engines maintain comprehensive indices, meaning removing content is not as simple as deleting a file. The content may remain visible for some time after deletion from the original source. Moreover, there is no guarantee that removal requests will be immediately or fully successful.
Limitations of Content Removal
Search engines do not have real-time access to every website’s content. They periodically crawl and index sites. A change to a page’s content may not be immediately reflected in search results. Likewise, some search results may still show the removed content from cached copies or links.
Implications of Indexed Content Removal
The implications of removing indexed content vary depending on the context and the nature of the content. For businesses, it can impact their online visibility and search engine rankings. For individuals, it can affect their online reputation and the accessibility of information. Removing content from search results may also affect any links pointing to that content, potentially affecting the ranking of the pages linking to it.
Techniques for Removing Indexed Content
Removing unwanted content from search engine indexes is a crucial aspect of online reputation management and content control. This process isn’t always straightforward, and various methods have varying degrees of success. Understanding the different approaches and their limitations is key to effectively managing your online presence.Effective removal strategies require careful consideration of the specific circumstances and the search engine involved.
Not all requests are guaranteed to be successful, and the effectiveness can depend on the nature of the content, the search engine’s policies, and the validity of your removal request.
Methods for Requesting Removal
Several methods exist for requesting the removal of specific content from search engine indexes. These methods typically involve formal communication channels provided by the search engines themselves. A crucial element is adhering to the guidelines and procedures set by each search engine, as deviating from them can negatively impact your chances of success.
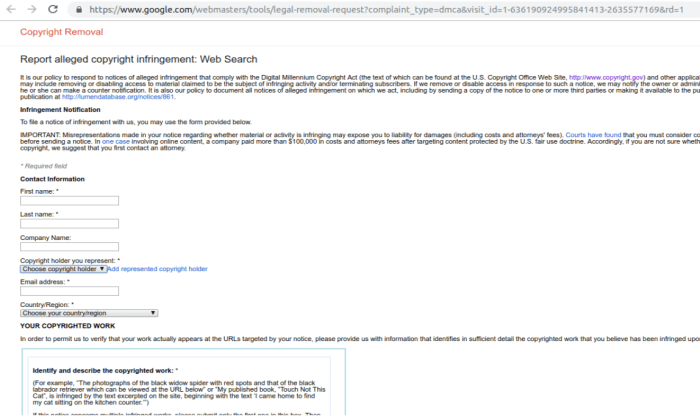
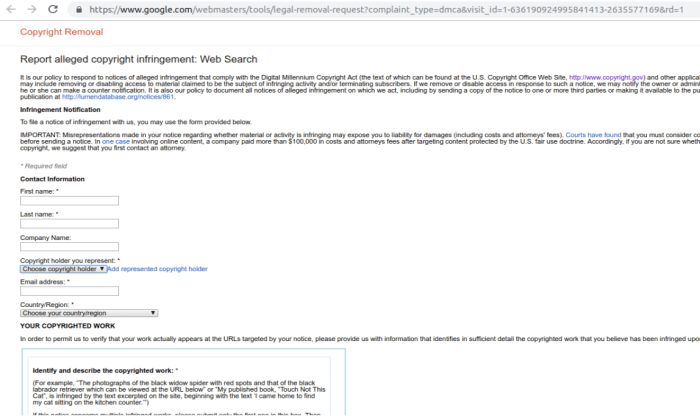
- Using Search Engine Removal Tools: Many search engines offer dedicated tools and forms for submitting removal requests. These tools typically require specific information about the content, including the URL of the page, the reason for removal, and any supporting documentation. Google, for example, has a dedicated URL removal tool within its Search Console. Successfully using these tools requires a thorough understanding of the specific guidelines for each search engine.
Trying to banish unwanted content from Google’s index? Four methods often touted as quick fixes frequently fall short. Sometimes, focusing on building a robust strategy for driving organic traffic, like the definitive strategy for driving organic traffic without ranking in Google’s top 10 , can be more effective than chasing fleeting removal tactics. Ultimately, understanding Google’s indexing mechanisms and focusing on creating valuable, unique content is key to preventing unwanted content from showing up.
These four seemingly simple methods for removing indexed content often fail because they ignore the bigger picture.
- Contacting Search Engine Support: In certain cases, contacting the search engine’s support team directly might be necessary. This route is often recommended for complex or nuanced removal requests, or when the automated tools are not suitable. This approach requires a clear and concise explanation of the reasons for removal and supporting evidence. It also requires adherence to the specific communication channels and procedures defined by the search engine.
- Legal Action: In situations where the content is considered harmful or infringes on copyright, legal action may be necessary. This route is often reserved for serious cases, where the other removal methods have failed or are not appropriate. It’s essential to consult with legal professionals to understand the specifics of the legal process and ensure compliance with all relevant laws and regulations.
Effectiveness Comparison
The effectiveness of different methods for content removal varies. Automated tools often offer a quicker response, but their success rate can be limited. Direct communication with search engine support might be more effective for specific situations, but it can be more time-consuming. Legal action is the most intensive approach but can be the most effective for addressing serious issues.
Trying to banish unwanted content from search results? While some methods for removing indexed content seem promising, a lot of them fall flat. For instance, deleting files won’t magically erase them from the digital ether. It’s like expecting a quick fix from Amazon ads – they’re a powerful tool, but they aren’t a get-rich-quick scheme.
Amazon ads isn’t the instant gratification you’re looking for. Similarly, a lot of supposed “removal” tricks don’t work. Focusing on legitimate strategies like Google’s removal requests is crucial for getting those unwanted results out of the mix. So, be realistic, understand the process, and don’t get caught up in scams. You’re better off with a long-term strategy, not a quick fix.
Pros and Cons of Removal Strategies
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Search Engine Removal Tools | Generally faster, often automated | Limited scope, may not address complex cases, varying success rates |
| Contacting Search Engine Support | Potential for more nuanced cases, direct interaction | More time-consuming, requires detailed justification |
| Legal Action | Potentially most effective for serious issues, legally binding | Most expensive and time-consuming, requires legal expertise |
Effective Removal Strategies (4 Ways): 4 Ways To Remove Indexed Content 3 That Dont Work
Removing indexed content is a complex process. While many methods promise quick solutions, many fail to deliver. This section delves into four effective strategies, each with detailed steps and real-world examples, to help you understand how to achieve successful removal.Effective removal strategies involve a multifaceted approach that considers various factors. Simply submitting a request isn’t enough. Understanding search engine algorithms, the nature of the indexed content, and the specific removal method are crucial.
Method 1: Google Search Console Removal Request
This method focuses on utilizing Google’s official tools to request removal. It’s often the first step for many website owners.
- Verification: Ensure your website is verified in Google Search Console. This allows Google to recognize your requests.
- Identifying URLs: Carefully identify the URLs you want removed. Be precise; vague requests may not be processed.
- Submitting Requests: Use the “Remove URLs” tool in Google Search Console. Provide clear explanations for the removal request, citing reasons like outdated content or copyright issues.
- Monitoring Progress: Track the status of your removal requests. Google will inform you of their processing.
- Example: A website owner discovers a page containing outdated product information. They use Google Search Console to identify and submit a removal request for that specific URL, explaining the outdated nature of the content.
Method 2: Contacting Webmasters
This method focuses on human intervention. If a website’s content infringes on another’s rights or is otherwise problematic, contacting the appropriate webmasters can be effective.
- Identifying the Source: Pinpoint the website or page hosting the content you wish to remove.
- Crafting a Polite Request: Write a clear and respectful message to the website’s owner or webmaster, explaining the reason for removal. Include specific URLs and a description of the issue.
- Providing Evidence: Support your request with evidence, such as copyright infringement notices or terms of service violations.
- Following Up: If you don’t receive a response, politely follow up after a reasonable time.
- Example: A company notices its product images are being used on another site without permission. They contact the webmaster of the other site, explaining the copyright infringement and requesting removal of the images.
Method 3: Using a Third-Party Removal Service
This approach leverages specialized tools and expertise. These services often handle complex removal requests.
- Researching Services: Evaluate different third-party removal services based on their reputation and success rates.
- Understanding Their Processes: Carefully review the service’s approach to ensure it aligns with your needs and goals.
- Submitting Your Request: Provide the necessary information to the service, including the URLs and justification for removal.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Track the progress of your request through the service’s dashboard. Ensure timely communication from the service provider.
- Example: A large e-commerce site uses a specialized removal service to handle a significant number of duplicate product listings, which are automatically indexed across various domains. This method is efficient and potentially cost-effective in situations involving large volumes of content.
Method 4: Deleting the Original Content
This strategy focuses on removing the source of the indexed content. This is often the most effective, but requires technical knowledge.
- Identifying the Source Files: Locate the files or directories containing the content you want to remove.
- Implementing Removal: Permanently delete the files. This could involve using file management tools or FTP clients.
- Testing: Verify that the content is no longer accessible through the webserver.
- Recreating Content (if needed): If the removed content is important for your website, consider creating new, updated content to replace it.
- Example: A blogger accidentally publishes a post containing sensitive data. They immediately delete the post from their server. This effectively removes the content from their site and reduces the chances of it being indexed by search engines.
Comparison of Removal Methods
| Method | Description | Effectiveness | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Official Google tool | High if content is valid for removal | Variable, can take days to weeks |
| Contacting Webmasters | Human intervention | High for specific content issues | Variable, can take days to weeks |
| Third-Party Removal Service | Specialized tools | High for large-scale or complex issues | Variable, can take days to weeks |
| Deleting Original Content | Direct removal | High, but requires technical knowledge | Instant, if done correctly |
Ineffective Content Removal Strategies (3 That Don’t Work)
Unfortunately, not every attempt to remove indexed content from search engine results is successful. Many methods, while seemingly logical, fail to address the fundamental mechanisms behind search engine indexing and ranking. Understanding why these strategies don’t work is crucial for developing effective removal procedures.Common misconceptions about content removal often lead to ineffective strategies. Simply deleting content from your website doesn’t guarantee its disappearance from search engine results.
Search engines often maintain cached copies of pages, and indexing occurs based on various factors beyond a simple file deletion. The effectiveness of a removal request relies heavily on the search engine’s policies and the specific circumstances surrounding the content.
Common Ineffective Strategies, 4 ways to remove indexed content 3 that dont work
These strategies, while tempting, often fail to remove indexed content due to the complex nature of search engine indexing. Their ineffectiveness stems from a misunderstanding of how search engines operate and the various factors involved in their indexing process.
Deleting Content from the Website
Deleting content from a website is a common first response, but it is often insufficient. Search engines maintain cached copies of web pages. These cached versions, which may contain the content, persist in the search engine’s index, even after the content is removed from the live website.
Using Robots.txt
While robots.txt directives can prevent search engine crawlers from accessing specific files or directories, they do not guarantee removal from the index. Search engines may already have indexed the content before the robots.txt file was updated. The robots.txt file acts as a guideline, not a command.
Requesting Manual Review
Submitting a manual removal request to a search engine is often a necessary step, but it doesn’t guarantee success. Search engines prioritize content quality and accuracy, which may affect the handling of removal requests. The request may be rejected if the content does not violate the search engine’s policies or if the reasons for removal are not compelling.
Reasons for Rejection of Content Removal Requests
Search engines don’t automatically remove content upon request. Several factors influence whether a removal request is approved or denied.
- Content not violating policies: Search engines index a vast amount of content. A request to remove content that doesn’t violate any policies is likely to be rejected. This is particularly true for content that is factually correct, legally permissible, and does not infringe on copyright or intellectual property.
- Insufficient justification: Providing vague or insufficient reasons for removal can lead to rejection. A compelling explanation is required, detailing why the content should be removed and what harm it causes.
- Content already archived: If the content has already been archived or cached by the search engine, removal might be unsuccessful, or partial at best. The search engine may still display the content from its cached copy.
- Duplicate content: If the content is duplicated elsewhere, removal might not have a significant impact. The search engine may consider the content as part of a larger body of information.
- User generated content: If the content was user-generated, the search engine may not be able to remove it. They are often more inclined to leave it to the user to resolve, or if they consider it part of a community forum.
Content Removal Request Considerations
Navigating the digital landscape often involves encountering unwanted content. Understanding the nuances of content removal requests is crucial for both preserving online reputation and ensuring compliance with legal and ethical standards. A well-structured and considered approach can significantly improve the chances of successful removal. Conversely, a poorly conceived request can lead to frustration and potentially exacerbate the issue.Thorough consideration of the specific circumstances surrounding the content and the platform where it resides is paramount.
This encompasses a wide range of factors, including the nature of the content, the platform’s policies, and the legal ramifications of the request. A proactive and well-informed approach is key to minimizing risks and maximizing the chances of a successful outcome.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Content removal requests are not always straightforward. Understanding the legal and ethical implications is critical. For example, removal requests related to potentially defamatory statements must be carefully considered, as they can have significant legal consequences. Similarly, requests for removal of copyrighted material must adhere to copyright law and potentially involve negotiations with the copyright holder. The legal landscape varies significantly across jurisdictions, and a detailed understanding of the applicable laws is vital.
Factors Influencing Removal Success
Several factors influence the success rate of content removal requests. Accuracy and precision in the request are paramount. Vague or ambiguous requests can lead to delays or rejection. The platform’s policies and guidelines play a critical role. Understanding and adhering to these policies is essential for a successful outcome.
Additionally, the nature of the content itself impacts the likelihood of removal. For instance, content that violates platform terms of service is more likely to be removed than content that does not.
Accuracy and Precision in Requests
Crafting a precise and well-argued request is essential. A detailed explanation of the reasons for the removal request, supported by evidence, significantly increases the chances of success. This includes referencing specific terms of service violations, citing legal precedents (if applicable), and providing accurate and verifiable information. The request should clearly and concisely state the desired action and provide sufficient information to support the claim.
This detailed explanation helps to establish the legitimacy of the request.
Potential Risks of Improper Removal Attempts
Improper removal attempts can lead to unintended consequences. For example, attempting to remove content that is protected by free speech principles can result in legal repercussions. Misinterpreting platform policies or legal frameworks can also have adverse effects. Similarly, submitting incomplete or inaccurate information can undermine the credibility of the request and potentially lead to a denial. Understanding the potential risks is critical in developing a strategic approach to content removal.
Platform-Specific Policies
Each platform has its own unique set of policies and procedures regarding content removal. Understanding these policies is crucial to avoid misunderstandings or violations. Platform policies often specify the types of content that are subject to removal, the required procedures for submitting a request, and the timeframe for review. Familiarizing oneself with these specific guidelines is vital for a successful outcome.
Furthermore, engaging with the platform’s support channels is often necessary to understand their specific requirements and guidelines.
Examples of Successful Removal Requests
Successful removal requests often involve a clear and concise explanation of the violation, along with supporting evidence. Examples can include providing a link to the offending content, referencing specific terms of service violations, and demonstrating how the content infringes on copyright or other intellectual property rights. Accurate and complete information is key to a successful outcome.
Long-Term Strategies for Preventing Indexing
Preventing unwanted content from appearing in search results requires proactive measures beyond simply removing existing indexed pages. A long-term strategy focuses on building websites that are less likely to be crawled and indexed in the first place. This approach prioritizes website design, content creation, and maintenance practices that reduce the risk of undesirable material surfacing in search engine results.Implementing these strategies ensures that future issues with unwanted content are less likely to occur.
Proactive measures are far more effective than reactive ones, minimizing the need for removal attempts and saving time and resources.
Website Design and Maintenance Practices
A well-structured website, designed with search engine best practices in mind, can significantly reduce the chances of unwanted content being indexed. These practices build a strong foundation for long-term and content management.
- Employing robots.txt: A crucial aspect of website management is using the robots.txt file. This file instructs search engine crawlers which parts of your website to crawl and which to ignore. Properly configured, it can prevent unwanted pages or directories from being indexed.
- Implementing strong URL structures: Clear and concise URL structures are vital. Avoid overly long, complex, or dynamically generated URLs that might contain sensitive or unwanted information. Use descriptive and meaningful s in URLs to improve user experience and , but be mindful of avoiding potentially problematic s.
- Utilizing server-side includes (SSI): SSI can be a useful tool to include dynamically generated content, but proper implementation is crucial. Carefully evaluate and monitor SSI usage to ensure that unwanted content isn’t inadvertently included in the output that is crawled and indexed.
Content Optimization Strategies
Content optimization plays a crucial role in preventing unwanted content from being indexed. Creating content that is less likely to be misconstrued or associated with unwanted information is key.
- Creating comprehensive content: Well-researched and comprehensive content is less likely to be flagged as spam or low-quality. Detailed and thorough articles, accompanied by proper formatting and clear headings, tend to be favored by search engines. This strategy ensures that the content is valuable and informative.
- Implementing robust content management systems (CMS): A robust CMS with features to manage content efficiently and effectively is important. It should provide mechanisms to control access and visibility to different sections of the website. A CMS can aid in preventing unauthorized content from being published and indexed.
- Implementing content filters: Content filters can be implemented to prevent the publication of inappropriate or unwanted material. These filters can be automated or involve human review processes, and should be adapted to specific content needs.
Proactive Steps to Minimize Risk
Proactive steps are essential to prevent issues with unwanted content appearing in search results. These steps focus on preventative measures rather than reactive ones.
- Regularly reviewing and auditing content: Routine reviews of website content can uncover and prevent issues before they become significant problems. This involves scrutinizing the content for accuracy, completeness, and potential indexing issues. Auditing should include checking for unwanted content or links.
- Monitoring search engine results pages (SERPs): Regularly monitoring your website’s presence on SERPs is crucial. This allows you to identify any unexpected or unwanted results promptly and take action. Tracking how your content is presented in search results is important to identify potential issues early.
- Utilizing advanced security measures: Implementing robust security measures is vital to prevent malicious activity that could compromise your website and lead to the inclusion of unwanted content in search results. This includes measures like regular security audits and implementing strong passwords.
Closure
In conclusion, successfully removing indexed content requires a nuanced approach. While some methods may seem straightforward, they often fall short of achieving the desired outcome. Understanding the nuances of search engine indexing, the intricacies of removal requests, and the common pitfalls is crucial for effective and lasting results. By understanding these concepts and utilizing the recommended strategies, you can navigate the complexities of content removal and maintain a clean, focused online presence.